Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access In-section Click-iT detection and super-resolution CLEM analysis of nucleolar ultrastructure and replication in plants
In-section Click-iT detection and super-resolution CLEM analysis of nucleolar ultrastructure and replication in plants
Application of correlative light and electron microscopy (CLEM) in plants remains challenging. Here, the authors use Click-iT chemistry as a tool for CLEM, due to its unique properties in resin permeability and super-resolution microscopy. They use this approach to study cellular physiology in Arabidopsis.
- Michal Franek
- , Lenka Koptašíková
- & Jíří Fajkus
-
Article
| Open Access Rejuvenation as the origin of planar defects in the CrCoNi medium entropy alloy
Rejuvenation as the origin of planar defects in the CrCoNi medium entropy alloy
High and medium-entropy alloys have shown excellent mechanical performance, yet the role of short-range order (SRO) on these properties has been unclear. Here, the authors demonstrate that the reduction of SRO by deformation leads to rejuvenation, explaining their remarkable damage tolerance.
- Yang Yang
- , Sheng Yin
- & Andrew M. Minor
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrasmall single-layered NbSe2 nanotubes flattened within a chemical-driven self-pressurized carbon nanotube
Ultrasmall single-layered NbSe2 nanotubes flattened within a chemical-driven self-pressurized carbon nanotube
The chemical-driven large pressure arising inside carbon nanotubes creates energetically stable, flattened, single-layered NbSe2 nanotubes with enhanced intermolecular electronic interactions, suggesting a chemical approach to produce materials with tailored structural and electronic properties.
- Yaxin Jiang
- , Hao Xiong
- & Fei Wei
-
Article
| Open Access Exact inversion of partially coherent dynamical electron scattering for picometric structure retrieval
Exact inversion of partially coherent dynamical electron scattering for picometric structure retrieval
By combining real and diffraction space data recorded in electron microscopes, ptychography retrieves specimen details with super-resolution. Here, the inverse problem is solved in the presence of thermal diffuse scattering and applied to measure ferroelectric displacements with picometer precision.
- Benedikt Diederichs
- , Ziria Herdegen
- & Knut Müller-Caspary
-
Article
| Open Access In-plane charged antiphase boundary and 180° domain wall in a ferroelectric film
In-plane charged antiphase boundary and 180° domain wall in a ferroelectric film
The correlation between charged and antiphase states in BiFeO3 remain elusive. Here, the authors report a fabrication of in-plane charged antiphase boundaries in BiFeO3 thin films, revealing the atomic bonding configurations and atomically sharp 180° polarization reversal of such boundaries.
- Xiangbin Cai
- , Chao Chen
- & Deyang Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Incommensurate grain-boundary atomic structure
Incommensurate grain-boundary atomic structure
Grain boundary atomic structures of crystalline materials have long been believed to be commensurate with the crystal periodicity of the adjacent crystals. Here, the authors discover an incommensurate grain boundary structure based on direct observations and theoretical calculations.
- Takehito Seki
- , Toshihiro Futazuka
- & Naoya Shibata
-
Article
| Open Access Operando analysis of a solid oxide fuel cell by environmental transmission electron microscopy
Operando analysis of a solid oxide fuel cell by environmental transmission electron microscopy
By contacting a solid oxide fuel cell to a microelectromechanical system inside an environmental electron microscope, the authors establish links between environmental conditions (gas atmosphere, temperature), cell voltage and atomic-scale structure.
- Q. Jeangros
- , M. Bugnet
- & M. Duchamp
-
Article
| Open Access Solving complex nanostructures with ptychographic atomic electron tomography
Solving complex nanostructures with ptychographic atomic electron tomography
Transmission electron microscopy is essential for three-dimensional atomic structure determination, but solving complex heterogeneous structures containing light elements remains challenging. Here, authors solve a complex nanostructure using atomic resolution ptychographic electron tomography.
- Philipp M. Pelz
- , Sinéad M. Griffin
- & Colin Ophus
-
Article
| Open Access Atomic-level polarization in electric fields of defects for electrocatalysis
Atomic-level polarization in electric fields of defects for electrocatalysis
The visible evidence bridging atomic defects with catalytic properties has been scarcely explored. Using differential phase contrast technology, this work discloses the existence of a polarized electric field surrounding the antisite defects of a monolayer MoS2 material and its correlation to its electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution property.
- Jie Xu
- , Xiong-Xiong Xue
- & Jun Lu
-
Article
| Open Access Atomic scale volume and grain boundary diffusion elucidated by in situ STEM
Atomic scale volume and grain boundary diffusion elucidated by in situ STEM
Here authors explore volume diffusion within crystalline solids at the atomic scale. They use high resolution microscopy techniques to provide insights into the movement of individual atoms within a crystal lattice, revealing the intricate dynamics of volume diffusion processes.
- Peter Schweizer
- , Amit Sharma
- & Xavier Maeder
-
Article
| Open Access Topotactically transformable antiphase boundaries with enhanced ionic conductivity
Topotactically transformable antiphase boundaries with enhanced ionic conductivity
Antiphase boundaries (APBs) have been considered major obstacles to optimizing the ionic conductivity of conductors. Here authors reveal that ionic conductivity can be enhanced through engineering APBs by topotactical transformation at the atomic scale.
- Kun Xu
- , Shih-Wei Hung
- & Jing Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access In situ imaging of the atomic phase transition dynamics in metal halide perovskites
In situ imaging of the atomic phase transition dynamics in metal halide perovskites
Phase transition dynamics are an important concern in the wide applications of metal halide perovskites. Here authors apply low-dose imaging technique to reveal the phase transition dynamics of CsPbI3 during in-situ heating process with atomic resolution.
- Mengmeng Ma
- , Xuliang Zhang
- & Boyuan Shen
-
Article
| Open Access Lorentz microscopy of optical fields
Lorentz microscopy of optical fields
Electron holography and microscopy have long been used to map static electric and magnetic fields. Here, authors establish Lorentz Microscopy of Optical Fields, a new technique that uses the deflection and interference of an electron beam to obtain phase-resolved images of nanoscale optical fields.
- John H. Gaida
- , Hugo Lourenço-Martins
- & Claus Ropers
-
Article
| Open Access Mending cracks atom-by-atom in rutile TiO2 with electron beam radiolysis
Mending cracks atom-by-atom in rutile TiO2 with electron beam radiolysis
Radiolysis is known for damaging crystals. Here, using STEM, researchers observed radiolysis-driven bond-breakage, atomic movements, & crystal restructuring in rutile TiO2, and proposed a “2-step rolling” model of building blocks. These results open possibilities for constructive use of radiolysis.
- Silu Guo
- , Hwanhui Yun
- & K. Andre Mkhoyan
-
Article
| Open Access Reassessing chain tilt in the lamellar crystals of polyethylene
Reassessing chain tilt in the lamellar crystals of polyethylene
The mechanical and thermal properties of semicrystalline polymers are governed by the hierarchical structure comprising lamellar crystals, but the tilt angles of the molecular chains in the lamellae and their origin remains controversial. Here, the authors report a direct determination of molecular chain orientation in the lamellar crystals of high-density polyethylene using electron-diffraction based imaging with nanometre-scale positional resolution.
- Shusuke Kanomi
- , Hironori Marubayashi
- & Hiroshi Jinnai
-
Article
| Open Access Electron counting detectors in scanning transmission electron microscopy via hardware signal processing
Electron counting detectors in scanning transmission electron microscopy via hardware signal processing
Electron detectors used in electron microscope are often unable to provide quantified information without calibration. Here, by combining existing detectors with hardware signal processing, the authors demonstrated that the detectors can be run in an electron counting mode enabling imaging at faster speeds, at lower electron doses, and reduces the barrier to quantitative measurements.
- Jonathan J. P. Peters
- , Tiarnan Mullarkey
- & Lewys Jones
-
Article
| Open Access Imaging the dynamic influence of functional groups on metal-organic frameworks
Imaging the dynamic influence of functional groups on metal-organic frameworks
Here authors use iDPC-STEM to directly image the rotation of linkers in MOFs, demonstrating an approach to study the local flexibility. They show that the dynamic properties of UiO-66-X are likely correlated to their macroscopic properties of CO2 uptake.
- Boyang Liu
- , Xiao Chen
- & Tiefeng Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Spatial and functional arrangement of Ebola virus polymerase inside phase-separated viral factories
Spatial and functional arrangement of Ebola virus polymerase inside phase-separated viral factories
Here, the authors characterized the phase separation properties and internal structures of intracellular viral factories induced by Ebola virus and correlated these properties to important steps of viral biogenesis.
- Jingru Fang
- , Guillaume Castillon
- & Erica Ollmann Saphire
-
Article
| Open Access Cryogenic electron ptychographic single particle analysis with wide bandwidth information transfer
Cryogenic electron ptychographic single particle analysis with wide bandwidth information transfer
Cryogenic electron ptychography (Cryo-EPty) is an emerging method for imaging the structure of biomacromolecules. Here, authors develop single particle analysis based on cryo-EPty phase for high contrast, wide spatial frequency-band 3D imaging.
- Xudong Pei
- , Liqi Zhou
- & Peng Wang
-
Article
| Open Access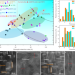 Synergy of multiple precipitate/matrix interface structures for a heat resistant high-strength Al alloy
Synergy of multiple precipitate/matrix interface structures for a heat resistant high-strength Al alloy
Coarsening of precipitates in medium and high temperatures causes reduction in strength of Al alloys. Here, the authors design an Al-Cu-Mg-Ag-Si-Sc alloy with multiple interface structures, showing an excellent combination of strength and heat resistance compared to conventional Al alloys.
- Qiang Lu
- , Jianchuan Wang
- & Yong Du
-
Article
| Open Access Interfacial interaction and intense interfacial ultraviolet light emission at an incoherent interface
Interfacial interaction and intense interfacial ultraviolet light emission at an incoherent interface
Incoherent interfaces usually have weak interfacial interactions and lack of unique properties. Here, Yan et al. demonstrate unexpected strong interfacial interactions and intense ultraviolet light emission at an incoherent AlN/Al2O3 interface.
- Xuexi Yan
- , Yixiao Jiang
- & Xiu-Liang Ma
-
Article
| Open Access Phonon transition across an isotopic interface
Phonon transition across an isotopic interface
Here, the authors probe the phonon changes across an atomically sharp h-10BN/h-11BN isotope interface with sub-unit-cell spatial resolution and momentum resolution. The observed phonon delocalization suggests strong electron-phonon coupling at isotopic interface.
- Ning Li
- , Ruochen Shi
- & Peng Gao
-
Article
| Open Access Emergent chirality in a polar meron to skyrmion phase transition
Emergent chirality in a polar meron to skyrmion phase transition
Polar skyrmions are particle-like objects consisted of swirling electric dipoles that hold promise for next generation nanodevices. Here, the authors explore the strain-induced transition from skyrmions to merons using electron imaging methods.
- Yu-Tsun Shao
- , Sujit Das
- & David A. Muller
-
Article
| Open Access Direct observation of cation diffusion driven surface reconstruction at van der Waals gaps
Direct observation of cation diffusion driven surface reconstruction at van der Waals gaps
Weak interlayer van der Waals (vdW) bonding has significant impact on the structure and properties of vdW layered materials. Here authors use in-situ aberration-corrected ADF-STEM for an atomistic insight into the cation diffusion in the vdW gaps and the etching of vdW surfaces at high temperatures.
- Wenjun Cui
- , Weixiao Lin
- & Xiahan Sang
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamics of the fcc-to-bcc phase transition in single-crystalline PdCu alloy nanoparticles
Dynamics of the fcc-to-bcc phase transition in single-crystalline PdCu alloy nanoparticles
Phase transitions in crystals are challenging to study with atomic resolution. Here, the authors reveal that the transition from fcc to bcc occurs across a few-atoms-wide coherent interface, which serves as a precursor phase for the nucleation of the bcc phase.
- Yingying Jiang
- , Martial Duchamp
- & Utkur Mirsaidov
-
Article
| Open Access Data-driven electron-diffraction approach reveals local short-range ordering in CrCoNi with ordering effects
Data-driven electron-diffraction approach reveals local short-range ordering in CrCoNi with ordering effects
Non-random chemical mixings that are intrinsic to medium- and high-entropy alloys are difficult to detect and quantify. Here the authors perform a diffraction data-mining analysis, revealing nanoclusters of short-range orders in a CrCoNi alloy, and their impacts on chemical homogeneity and dislocations slip.
- Haw-Wen Hsiao
- , Rui Feng
- & Jian-Min Zuo
-
Article
| Open Access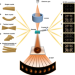 Synchronous quantitative analysis of chiral mesostructured inorganic crystals by 3D electron diffraction tomography
Synchronous quantitative analysis of chiral mesostructured inorganic crystals by 3D electron diffraction tomography
Chiral mesostructured inorganic crystals exhibit distinctive twisting and helical hierarchical stacking. Here, the authors report a general approach for the synchronous quantitative analysis of rotation axis, torsion angle, pitch length, and arrangement modes.
- Jing Ai
- , Xueliang Zhang
- & Lu Han
-
Article
| Open Access Grain boundary structural transformation induced by co-segregation of aliovalent dopants
Grain boundary structural transformation induced by co-segregation of aliovalent dopants
The effect of aliovalent doping on grain boundary is not yet fully understood at the atomic level. Here, the authors report grain boundary structural transformation in α-Al2O3 is induced by co-segregation of multiple dopants using atomic-resolution electron microscopy and theoretical calculations.
- Toshihiro Futazuka
- , Ryo Ishikawa
- & Yuichi Ikuhara
-
Article
| Open Access Observation of formation and local structures of metal-organic layers via complementary electron microscopy techniques
Observation of formation and local structures of metal-organic layers via complementary electron microscopy techniques
Obtaining information about the structure of metal-organic layers (MOLs) using standard electron microscopy methods is challenging due to damage under electron beam irradiation. Here, the authors reveal a multistep formation process of MOLs and identify missing clusters, dislocations, loop and flat surface terminations and ligand connector of MOLs via complementary electron microscopy techniques.
- Xinxing Peng
- , Philipp M. Pelz
- & Mary C. Scott
-
Article
| Open Access Three-dimensional electron ptychography of organic–inorganic hybrid nanostructures
Three-dimensional electron ptychography of organic–inorganic hybrid nanostructures
The authors demonstrate electron ptychographic computed tomography by simultaneously recording high contrast data from both the organic- and inorganic components in a 3D DNA-origami framework hybrid nanostructure.
- Zhiyuan Ding
- , Si Gao
- & Peng Wang
-
Article
| Open Access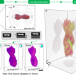 Real-time 3D analysis during electron tomography using tomviz
Real-time 3D analysis during electron tomography using tomviz
High-throughput electron tomography has been challenging due to time-consuming alignment and reconstruction. Here, the authors demonstrate real-time tomography with dynamic 3D tomographic visualization integrated in tomviz, an open-source 3D data analysis tool.
- Jonathan Schwartz
- , Chris Harris
- & Robert Hovden
-
Article
| Open Access Sub-nanometer mapping of strain-induced band structure variations in planar nanowire core-shell heterostructures
Sub-nanometer mapping of strain-induced band structure variations in planar nanowire core-shell heterostructures
Planar growth of nanowire arrays involves interactions between materials that affect the electronic behavior of the effective heterojunction. Here, authors show how core curvature and cross-section morphology affect shell growth, demonstrating how strain at the core-shell interface induces electronic band modulations in ZnSe@ZnTe nanowires.
- Sara Martí-Sánchez
- , Marc Botifoll
- & Jordi Arbiol
-
Article
| Open Access Optimal acceleration voltage for near-atomic resolution imaging of layer-stacked 2D polymer thin films
Optimal acceleration voltage for near-atomic resolution imaging of layer-stacked 2D polymer thin films
High-resolution imaging of organic 2D materials using transmission electron microscopes is challenging. Here, the authors find the optimal electron acceleration voltage, and demonstrate 1.9 Å resolution, enabling detection of interstitial defects and functional groups in 2D polymer thin films.
- Baokun Liang
- , Yingying Zhang
- & Haoyuan Qi
-
Article
| Open Access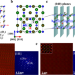 Direct investigation of the atomic structure and decreased magnetism of antiphase boundaries in garnet
Direct investigation of the atomic structure and decreased magnetism of antiphase boundaries in garnet
Iron garnets are widely used in magneto-optical devices, but knowledge of the effects of common defects on performance is limited. Here, using high-resolution microscopy and spectroscopy, the authors find that magnetism is weakened near these defects causing reduced performance, but can be avoided by tuning the growth rate.
- Kun Xu
- , Ting Lin
- & Jing Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access Tailoring electron beams with high-frequency self-assembled magnetic charged particle micro optics
Tailoring electron beams with high-frequency self-assembled magnetic charged particle micro optics
Electron beam manipulation is important for their application in microscopes, lithography instruments, and colliders. Here the authors report a wafer scale, self-assembled, microcoil electrically-driven magnetic charge particle optic device that can be implemented into different configurations for controlling of electron beams.
- R. Huber
- , F. Kern
- & A. Lubk
-
Article
| Open Access Measuring and directing charge transfer in heterogenous catalysts
Measuring and directing charge transfer in heterogenous catalysts
Precise control of charge transfer between catalyst nanoparticles and supports presents a unique opportunity to enhance catalytic performance. Here the authors demonstrate a scanning transmission electron microscopy method to visualize atomic-scale structure and sub-nanometer-scale charge distribution in heterogeneous catalysts, shedding light on the atomic-scale mechanisms behind their highly active perimeter sites.
- Michael J. Zachman
- , Victor Fung
- & Miaofang Chi
-
Article
| Open Access Modulating inherent lewis acidity at the intergrowth interface of mortise-tenon zeolite catalyst
Modulating inherent lewis acidity at the intergrowth interface of mortise-tenon zeolite catalyst
The acid sites are important local structures to determine catalytic performances of zeolites. Here, the authors expand the interface engineering to the field of porous zeolites through the lattice mismatch of the intergrown zeolite to enrich the inherent Lewis acid sites at the interface of a mortise-tenon ZSM-5 catalyst.
- Huiqiu Wang
- , Boyuan Shen
- & Weizhong Qian
-
Article
| Open Access Seeing structural evolution of organic molecular nano-crystallites using 4D scanning confocal electron diffraction (4D-SCED)
Seeing structural evolution of organic molecular nano-crystallites using 4D scanning confocal electron diffraction (4D-SCED)
Studying organic molecular nanocrystals with electron microscopy has been challenging due to complex structures and radiation sensitivity. Here, the authors present 4D-scanning confocal electron diffraction, and demonstrate direct in situ observation of structural evolution of bulk heterojunction thin films.
- Mingjian Wu
- , Christina Harreiß
- & Erdmann Spiecker
-
Article
| Open Access Gasdermin-A3 pore formation propagates along variable pathways
Gasdermin-A3 pore formation propagates along variable pathways
Gasdermin-A3 pore formation propagates along diverse pathways. It begins with membrane attachment and oligomeric pre-assembly. Once inserted in the membrane, the oligomers re-assemble into various shapes and sizes, which open their lytic pores.
- Stefania A. Mari
- , Kristyna Pluhackova
- & Daniel J. Müller
-
Article
| Open Access Mre11-Rad50 oligomerization promotes DNA double-strand break repair
Mre11-Rad50 oligomerization promotes DNA double-strand break repair
The Mre11-Rad50 (MR) complex has key functions in the detection, signaling and repair of DNA breaks. Here the authors use transmission electron microscopy to show MR oligomerization is governed by a small beta-sheet protruding from the head domain of Rad50 at the base of the MR structure, and reveal MR head domain oligomerization is required for efficient DNA end resection.
- Vera M. Kissling
- , Giordano Reginato
- & Matthias Peter
-
Article
| Open Access Enabling high energy lithium metal batteries via single-crystal Ni-rich cathode material co-doping strategy
Enabling high energy lithium metal batteries via single-crystal Ni-rich cathode material co-doping strategy
Li-ion cathode active materials are transitioning from poly- to single-crystal structures. However, the performance of high Ni-content single-crystal cathodes remains below expectations. Here, via Al/Zr co-doping, the authors propose a strategy to mitigate structural degradation in this class of materials.
- Xing Ou
- , Tongchao Liu
- & Jun Lu
-
Article
| Open Access Direct imaging of the disconnection climb mediated point defects absorption by a grain boundary
Direct imaging of the disconnection climb mediated point defects absorption by a grain boundary
Grain boundaries can improve the radiation resistance of a material by annihilating point defects formed under irradiation, however the atomistic mechanism is still unclear. Here the authors demonstrate grain boundaries absorb point defects through the climb motion of disconnections.
- Jiake Wei
- , Bin Feng
- & Yuichi Ikuhara
-
Article
| Open Access Twinning-assisted dynamic adjustment of grain boundary mobility
Twinning-assisted dynamic adjustment of grain boundary mobility
Grain boundary can change its structure upon deformation. Here, the authors show that during this process, grain boundary mobility can be tuned dynamically via a self-stimulated twinning process.
- Qishan Huang
- , Qi Zhu
- & Jiangwei Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Thermoresponsive polymer assemblies via variable temperature liquid-phase transmission electron microscopy and small angle X-ray scattering
Thermoresponsive polymer assemblies via variable temperature liquid-phase transmission electron microscopy and small angle X-ray scattering
Thermoresponsive polymers are used in numerous technological applications but well established, direct techniques for elucidating their elevated temperature, solution-phase, nanoscale morphologies and dynamics are lacking. Here, the authors examine thermoresponsive polymeric materials by liquid-cell transmission electron microscopy and gain insight into their thermal-responsive behaviour.
- Joanna Korpanty
- , Lucas R. Parent
- & Nathan C. Gianneschi
-
Article
| Open Access Probing atom dynamics of excited Co-Mo-S nanocrystals in 3D
Probing atom dynamics of excited Co-Mo-S nanocrystals in 3D
The authors introduce an analytical approach for quantitative analysis of 3D atom dynamics during electron microscopy. They image a Co-Mo-S nanocrystal with 1.5 Å resolution, and observe chemical transformations caused by beam-stimulated vibrations.
- Fu-Rong Chen
- , Dirk Van Dyck
- & Stig Helveg
-
Article
| Open Access Mixed alkali-ion transport and storage in atomic-disordered honeycomb layered NaKNi2TeO6
Mixed alkali-ion transport and storage in atomic-disordered honeycomb layered NaKNi2TeO6
Honeycomb layered oxides are an emerging class of materials with peculiar physicochemical properties. Here, the authors report the synthesis and electrochemical energy storage characterisations of a mixed-alkali honeycomb layered oxide material capable of storing Na and K ions simultaneously.
- Titus Masese
- , Yoshinobu Miyazaki
- & Tomohiro Saito
-
Article
| Open Access The nanoscale molecular morphology of docked exocytic dense-core vesicles in neuroendocrine cells
The nanoscale molecular morphology of docked exocytic dense-core vesicles in neuroendocrine cells
The molecular organization of exocytic vesicles regulates their transport and fusion. Prasai, Taraska, and colleagues use correlative light and electron microscopy, along with 3D tomography and gold labeling, to directly map proteins on single exocytic organelles at the plasma membrane.
- Bijeta Prasai
- , Gideon J. Haber
- & Justin W. Taraska
-
Article
| Open Access Quantitative 3D real-space analysis of Laves phase supraparticles
Quantitative 3D real-space analysis of Laves phase supraparticles
3D real-space analysis of thick nanoparticle crystals is non-trivial. Here, the authors demonstrate the structural analysis of a bulk-like Laves phase by imaging an off-stoichiometric binary mixture of hard-sphere-like nanoparticles in spherical confinement by electron tomography, enabling defect analysis on the single-particle level.
- Da Wang
- , Ernest B. van der Wee
- & Alfons van Blaaderen
-
Article
| Open Access Direct observation of nanoscale dynamics of ferroelectric degradation
Direct observation of nanoscale dynamics of ferroelectric degradation
Space charges or injected charges dominate the ferroelectric degradation, however, its physics insight remains unclear. Here, the authors reveal the nature of ferroelectric degradation in nanodevices and the role of the injected charges in polarization reversal.
- Qianwei Huang
- , Zibin Chen
- & Xiaozhou Liao

 Atomic-scale observation of localized phonons at FeSe/SrTiO3 interface
Atomic-scale observation of localized phonons at FeSe/SrTiO3 interface