Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access An optofluidic platform for interrogating chemosensory behavior and brainwide neural representation in larval zebrafish
An optofluidic platform for interrogating chemosensory behavior and brainwide neural representation in larval zebrafish
Studying chemosensory processing desires precise chemical cue presentation, behavioral response monitoring, and large-scale neuronal activity recording. Here, the authors report a fluidics-based toolkit for studying chemosensation in larval zebrafish, and used it to reveal the brainwide neural representations of cadaverine sensing and its binasal input-dependent behavioral avoidance.
- Samuel K. H. Sy
- , Danny C. W. Chan
- & Ho Ko
-
Article
| Open Access A quantitative analysis of various patterns applied in lattice light sheet microscopy
A quantitative analysis of various patterns applied in lattice light sheet microscopy
Light sheet microscopes reduce phototoxicity and background while improving imaging speed compared to widefield and confocal microscopes. Here the authors quantify the differences between Gaussian and lattice light sheets using simulations and experimental data in fixed and live cells.
- Yu Shi
- , Timothy A. Daugird
- & Wesley R. Legant
-
Article
| Open Access Nuclear speed and cycle length co-vary with local density during syncytial blastoderm formation in a cricket
Nuclear speed and cycle length co-vary with local density during syncytial blastoderm formation in a cricket
Early in insect embryo development, many nuclei share one large cell, travel varied paths and self-organize into a single layer. Donoughe et al. illuminate this process with live-imaging, modeling, and experimental changes to the embryo’s shape.
- Seth Donoughe
- , Jordan Hoffmann
- & Cassandra G. Extavour
-
Article
| Open Access Embryo-scale epithelial buckling forms a propagating furrow that initiates gastrulation
Embryo-scale epithelial buckling forms a propagating furrow that initiates gastrulation
Drosophila mesoderm invagination begins with the formation of a furrow. Here they show that a long-range mechanism, powered by actomyosin contraction between the embryo polar caps, works like a ‘cheese-cutter wire’ indenting the tissue surface and folding it into a propagating furrow.
- Julien Fierling
- , Alphy John
- & Matteo Rauzi
-
Article
| Open Access Deep learning enables reference-free isotropic super-resolution for volumetric fluorescence microscopy
Deep learning enables reference-free isotropic super-resolution for volumetric fluorescence microscopy
Volumetric fluorescence microscopy is often limited by anisotropic spatial resolution. Here, the authors present an unsupervised deep-learning approach that enhances axial resolution by learning from high-resolution lateral images, and demonstrate isotropic resolution and restoration of suppressed visual details.
- Hyoungjun Park
- , Myeongsu Na
- & Jong Chul Ye
-
Article
| Open Access Wide field light-sheet microscopy with lens-axicon controlled two-photon Bessel beam illumination
Wide field light-sheet microscopy with lens-axicon controlled two-photon Bessel beam illumination
Here, the authors present a two-photon light-sheet microscopy with an extended Bessel beam for a tunable field of view and reduced photodamage. They demonstrate long-term imaging of cellular dynamics over the whole body of medaka fish.
- Sota Takanezawa
- , Takashi Saitou
- & Takeshi Imamura
-
Article
| Open Access Minutes-timescale 3D isotropic imaging of entire organs at subcellular resolution by content-aware compressed-sensing light-sheet microscopy
Minutes-timescale 3D isotropic imaging of entire organs at subcellular resolution by content-aware compressed-sensing light-sheet microscopy
High resolution imaging of large biological volumes typically takes a long time from hours to days. Here the authors use a Bessel light-sheet approach combined with a content-aware compressed sensing computational pipeline to image whole mouse organs at subcellular resolution in a few minutes.
- Chunyu Fang
- , Tingting Yu
- & Peng Fei
-
Article
| Open Access Non-invasive single-cell morphometry in living bacterial biofilms
Non-invasive single-cell morphometry in living bacterial biofilms
Accurate cell detection in dense bacterial biofilms is challenging. Here, the authors report an image analysis pipeline that is able to accurately segment and classify single bacterial cells in 3D fluorescence images: Bacterial Cell Morphometry 3D (BCM3D).
- Mingxing Zhang
- , Ji Zhang
- & Andreas Gahlmann
-
Article
| Open Access Image quality guided smart rotation improves coverage in microscopy
Image quality guided smart rotation improves coverage in microscopy
Multi-view SPIM imaging can improve coverage of large samples such as whole embryos, but the procedure increases phototoxicity and involves manual steps that can introduce inconsistencies. Here the authors develop a smart rotation workflow that performs on-the-fly image analysis and identifies optimal set of views to maximize sample coverage.
- Jiaye He
- & Jan Huisken
-
Article
| Open Access Quantitative live cell imaging reveals influenza virus manipulation of Rab11A transport through reduced dynein association
Quantitative live cell imaging reveals influenza virus manipulation of Rab11A transport through reduced dynein association
Here, using high spatiotemporal resolution light-sheet and fluorescence microscopy, the authors investigate the role of cytoskeletal components on the intracellular transport of Rab11A and influenza virus (IAV) vRNP), and show a preference for Rab11A movement along microtubules that is not essential for IAV vRNP transport.
- Amar R. Bhagwat
- , Valerie Le Sage
- & Seema S. Lakdawala
-
Article
| Open Access Multi-scale imaging and analysis identify pan-embryo cell dynamics of germlayer formation in zebrafish
Multi-scale imaging and analysis identify pan-embryo cell dynamics of germlayer formation in zebrafish
The precise cell dynamics of early development have not yet been visualized. Here, the authors use custom 4-lens light sheet microscopy to image and analyze the dynamics of all three fluorescently labeled germlayers, yielding a comprehensive, pan-embryo description of early zebrafish gastrulation.
- Gopi Shah
- , Konstantin Thierbach
- & Jan Huisken
-
Article
| Open Access Adaptive prospective optical gating enables day-long 3D time-lapse imaging of the beating embryonic zebrafish heart
Adaptive prospective optical gating enables day-long 3D time-lapse imaging of the beating embryonic zebrafish heart
Imaging heart development is challenging due to constant tissue movement and changing physical landmarks. Here the authors present an algorithm capable of maintaining phase-locked imaging throughout a 24 hour timespan, enabling long term timelapse imaging studies of zebrafish heart development, repair and regeneration.
- Jonathan M. Taylor
- , Carl J. Nelson
- & Martin A. Denvir
-
Article
| Open Access Rapid single-wavelength lightsheet localization microscopy for clarified tissue
Rapid single-wavelength lightsheet localization microscopy for clarified tissue
It has been challenging to perform super-resolution imaging in large volumes due to aberrations encountered. Here, the authors combine single-wavelength Bessel lightsheet localization microscopy with tissue clearing techniques and image neurons across the whole brain of adult fruit flies.
- Li-An Chu
- , Chieh-Han Lu
- & Bi-Chang Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Fast objective coupled planar illumination microscopy
Fast objective coupled planar illumination microscopy
Light sheet microscopy holds potential for imaging dynamics in 3D biological specimens, but is limited by scan speed and camera acquisition rate. Here the authors address both issues by developing speed-optimized Objective Coupled Planar Illumination and parallelizing image acquisition across cameras to achieve 40 Hz imaging over thick samples.
- Cody J. Greer
- & Timothy E. Holy
-
Article
| Open Access Multi-immersion open-top light-sheet microscope for high-throughput imaging of cleared tissues
Multi-immersion open-top light-sheet microscope for high-throughput imaging of cleared tissues
Light-sheet microscopes are increasingly used for imaging cleared tissues, but have imposed constraints on sample geometries and protocols. Here the authors present a multi-immersion open-top light-sheet microscope to overcome these limitations and enable high-throughput imaging of samples processed with various clearing protocols.
- Adam K. Glaser
- , Nicholas P. Reder
- & Jonathan T. C. Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic and non-contact 3D sample rotation for microscopy
Dynamic and non-contact 3D sample rotation for microscopy
Sample orientation is crucial to ensure optimal image quality in light microscopy. Here the authors enable multi-axis orientation of fixed mouse embryos and shrimp, and live zebrafish embryos and larvae by introducing magnetic beads and rotating the sample with a magnetic field in a microscope.
- Frederic Berndt
- , Gopi Shah
- & Jan Huisken
-
Article
| Open Access 3D single-molecule super-resolution microscopy with a tilted light sheet
3D single-molecule super-resolution microscopy with a tilted light sheet
Light-sheet single-molecule 3D super-resolution microscopes can’t image close to a coverslip or may require complex apparatus. Here the authors overcome such limitations using a tilted light sheet strategy with long axial range point spread functions on a standard inverted microscope.
- Anna-Karin Gustavsson
- , Petar N. Petrov
- & W. E. Moerner
-
Article
| Open Access Reflective imaging improves spatiotemporal resolution and collection efficiency in light sheet microscopy
Reflective imaging improves spatiotemporal resolution and collection efficiency in light sheet microscopy
Light-sheet fluorescence microscopy enables high resolution imaging of biological samples. Here the authors use reflective coverslips to obtain multiple sample views simultaneously, improving the speed of acquisition and resolution compared to dual-view selective plane illumination microscopy.
- Yicong Wu
- , Abhishek Kumar
- & Hari Shroff
-
Article
| Open Access Automatic and adaptive heterogeneous refractive index compensation for light-sheet microscopy
Automatic and adaptive heterogeneous refractive index compensation for light-sheet microscopy
Optical clearing of tissue has enabled optical imaging deeper into tissue due to significantly reduced light scattering. Here, Ryan et al. tackle first-order defocus, an artefact of a non-uniform refractive index, extending light-sheet microscopy to partially cleared samples.
- Duncan P. Ryan
- , Elizabeth A. Gould
- & Douglas P. Shepherd
-
Article
| Open Access Volumetric chemical imaging by stimulated Raman projection microscopy and tomography
Volumetric chemical imaging by stimulated Raman projection microscopy and tomography
Recent advances have enabled high-speed three-dimensional optical imaging through the use of fluorescent markers. Here, Chenet al. integrate stimulated Raman imaging into those methods, enabling the label-free and chemically specific volumetric imaging of complex samples.
- Xueli Chen
- , Chi Zhang
- & Ji-Xin Cheng
-
Article
| Open Access Confocal multiview light-sheet microscopy
Confocal multiview light-sheet microscopy
Multiview light-sheet microscopy is a powerful tool for imaging relatively large biological samples over long periods of time, but scattering can limit image quality. Here, the authors combine multiview light-sheet imaging with electronic confocal slit detection to improve image quality, double acquisition speed and streamline data fusion.
- Gustavo de Medeiros
- , Nils Norlin
- & Lars Hufnagel
-
Article
| Open Access Whole-central nervous system functional imaging in larval Drosophila
Whole-central nervous system functional imaging in larval Drosophila
To understand how neuronal networks function, it is important to measure neuronal network activity at the systems level. Here Lemon et al. develop a framework that combines a high-speed multi-view light-sheet microscope, a whole-CNS imaging assay and computational tools to demonstrate simultaneous functional imaging across the entire isolated Drosophilalarval CNS.
- William C. Lemon
- , Stefan R. Pulver
- & Philipp J. Keller
-
Article
| Open Access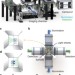 High-speed panoramic light-sheet microscopy reveals global endodermal cell dynamics
High-speed panoramic light-sheet microscopy reveals global endodermal cell dynamics
Systematic large-scale analysis of embryonic development requires the processing of large amounts of microscopy data. Here Schmid et al.solve this problem by developing a high-speed imaging system that projects zebrafish embryos onto a ‘world map’ in real time, revealing characteristic migration patterns in the early endoderm.
- Benjamin Schmid
- , Gopi Shah
- & Jan Huisken

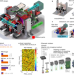 Benchtop mesoSPIM: a next-generation open-source light-sheet microscope for cleared samples
Benchtop mesoSPIM: a next-generation open-source light-sheet microscope for cleared samples