Advertisement
-
-

Pouchitis: pathophysiology and management
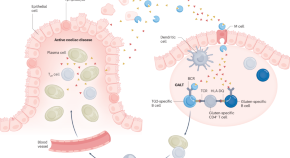
Pouchitis is a common condition that can occur after intestinal surgery. In this Review, Shen discusses our current understanding of the multifactorial pathophysiology, diagnosis and management of pouchitis, primarily in patients with underlying ulcerative colitis.
-
-
MASLD/NAFLD
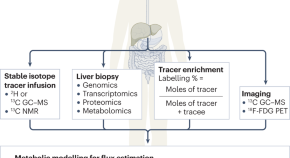
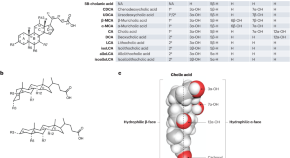
Fuelled by increasing obesity rates, metabolic dysfunction associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD, formerly known as NAFLD) has emerged as a leading global cause of chronic liver disease in the past few decades. Despite growing prevalence, the factors influencing MASLD development and subsequent progression to metabolic dysfunction associated steatohepatitis (MASH), liver fibrosis, cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma are poorly understood. In this article series, Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology explores the epidemiology of MASLD, disease mechanisms and therapeutics, and clinical approaches to diagnosis and management.