Featured
-
-
Article |
 An alkyl-substituted aluminium anion with strong basicity and nucleophilicity
An alkyl-substituted aluminium anion with strong basicity and nucleophilicity
Owing to the electropositive character of aluminium it is difficult to prepare Al anions; the few that exist are supported by nitrogen ligands. Now, a dialkyl-alumanyl anion has been synthesized that features a polar Al–K bond. This anion reacts as a very strong base that deprotonates benzene, and undergoes nucleophilic substitution reactions.
- Satoshi Kurumada
- , Shuhei Takamori
- & Makoto Yamashita
-
Article |
 Efficient and tunable one-dimensional charge transport in layered lanthanide metal–organic frameworks
Efficient and tunable one-dimensional charge transport in layered lanthanide metal–organic frameworks
High electrical conductivities in metal–organic frameworks—attractive for applications in sensing and energy storage—typically arise in layered MOFs from metal–ligand bonds with strong covalent character. Now, lanthanide-based MOFs have shown high out-of-plane conductivities originating instead from the π-stacking of organic ligands.
- Grigorii Skorupskii
- , Benjamin A. Trump
- & Mircea Dincă
-
Article |
 Isolation, characterization and reactivity of three-coordinate phosphorus dications isoelectronic to alanes and silylium cations
Isolation, characterization and reactivity of three-coordinate phosphorus dications isoelectronic to alanes and silylium cations
The isoelectronic series of alanes [R3Al] and silylium cations [R3Si]+ has now been extended with the synthesis and characterization of two phosphorandiylium dications ([R3P]2+), which are trigonal planar Lewis superacids. The electrophilicity at the phosphorus atom is governed by the π-electron-donating ability of the attached N-heterocyclic imine substituents.
- Paul Mehlmann
- , Tim Witteler
- & Fabian Dielmann
-
Article |
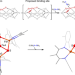 Planar three-coordinate iron sulfide in a synthetic [4Fe-3S] cluster with biomimetic reactivity
Planar three-coordinate iron sulfide in a synthetic [4Fe-3S] cluster with biomimetic reactivity
The four-coordinate iron sites of typical iron–sulfur clusters rarely react with small molecules, implicating three-coordinate iron in many catalytic cycles. Now, a [4Fe-3S] cluster featuring three-coordinate iron sulfide that resembles the proposed substrate binding site has been synthesized. This cluster shows biomimetic reactivity with a low-spin electronic configuration.
- Daniel E. DeRosha
- , Vijay G. Chilkuri
- & Patrick L. Holland
-
Article |
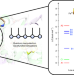 Electronic landscape of the P-cluster of nitrogenase as revealed through many-electron quantum wavefunction simulations
Electronic landscape of the P-cluster of nitrogenase as revealed through many-electron quantum wavefunction simulations
The electronic structures of the metal cofactors of nitrogenase are key to biological nitrogen fixation; however, the [Fe8S7] P-cluster and FeMo cofactor have eluded detailed electronic characterization. Now, the electronic structure of the P-cluster of nitrogenase has been revealed at the many-electron level through exhaustive quantum wavefunction simulations.
- Zhendong Li
- , Sheng Guo
- & Garnet Kin-Lic Chan
-
News & Views |
 Interphase identity crisis
Interphase identity crisis
Interphases that form on the anode surface of lithium-ion batteries are critical for performance and lifetime, but are poorly understood. Now, a decade-old misconception regarding a main component of the interphase has been revealed, which could potentially lead to improved devices.
- Stefan A. Freunberger
-
Article |
 Back-bonding between an electron-poor, high-oxidation-state metal and poor π-acceptor ligand in a uranium(v)–dinitrogen complex
Back-bonding between an electron-poor, high-oxidation-state metal and poor π-acceptor ligand in a uranium(v)–dinitrogen complex
In coordination and organometallic chemistry, back-bonding between an electron-rich, typically mid- or low-oxidation-state d-block metal centre and a ligand with accepting π* orbitals is widespread. Now, such an interaction has been observed between unlikely partners—high-oxidation-state uranium(v) 5f1 ion and the poor π-acceptor ligand dinitrogen—in a U(v)–bis(imido)–N2 complex stabilized by a lithium counterion.
- Erli Lu
- , Benjamin E. Atkinson
- & Stephen T. Liddle
-
Article |
 Identifying the components of the solid–electrolyte interphase in Li-ion batteries
Identifying the components of the solid–electrolyte interphase in Li-ion batteries
The solid–electrolyte-interphase layer is extremely important for reversible electrochemical cycling of Li-ion batteries. Now it has been observed that lithium ethylene mono-carbonate, instead of the previously reported lithium ethylene di-carbonate, is the major initial organic species in this layer and it has a high Li-ion conductivity.
- Luning Wang
- , Anjali Menakath
- & Bryan W. Eichhorn
-
Article |
 Incorporation of clusters within inorganic materials through their addition during nucleation steps
Incorporation of clusters within inorganic materials through their addition during nucleation steps
During the synthesis of inorganic materials nickel oxysulfide and nickel–cobalt hydroxide, clusters with well-defined structures—such as polyoxometalates—can co-assemble with nuclei to produce uniform binary assemblies. The resulting materials can, in turn, incorporate a third, and fourth, type of nanocluster deposited on their surface to form ternary and quaternary assemblies, respectively.
- Junli Liu
- , Wenxiong Shi
- & Xun Wang
-
News & Views |
 Precipitates shape up
Precipitates shape up
Precipitation processes enable the fast preparation of a variety of inorganic materials, although typically with little control over their morphology. Now, their one-, two- or three-dimensional growth has been promoted simply by tuning the electrolytic dissociation of the reactants and the supersaturation of the solution.
- Mihui Park
- , Gi-Hyeok Lee
- & Yong-Mook Kang
-
Article |
 Morphology tuning of inorganic nanomaterials grown by precipitation through control of electrolytic dissociation and supersaturation
Morphology tuning of inorganic nanomaterials grown by precipitation through control of electrolytic dissociation and supersaturation
Precipitation enables the straightforward production of a variety of inorganic materials, but the rapid reaction rates involved typically make controlling their morphologies difficult. Now, the growth of either one-, two- or three-dimensional materials has been promoted by tuning of the reactants’ electrolytic dissociation and solution supersaturation, without the need for capping agents and templates.
- Wei-Hong Lai
- , Yun-Xiao Wang
- & Shi-Xue Dou
-
Article |
 Ruthenium-catalysed oxidative conversion of ammonia into dinitrogen
Ruthenium-catalysed oxidative conversion of ammonia into dinitrogen
The production of ammonia from dinitrogen is a well-studied process; however, the catalytic conversion of ammonia into dinitrogen is underdeveloped. Now, ammonia oxidation has been achieved using ruthenium complexes as catalysts. The production of dinitrogen is observed when ammonium salts are treated with a single-electron oxidant, base and ruthenium catalyst.
- Kazunari Nakajima
- , Hiroki Toda
- & Yoshiaki Nishibayashi
-
Article |
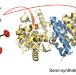 A catalytically active [Mn]-hydrogenase incorporating a non-native metal cofactor
A catalytically active [Mn]-hydrogenase incorporating a non-native metal cofactor
Natural hydrogenases exclusively utilize Ni and/or Fe to activate or produce hydrogen. Now, a catalytically active [Mn]-hydrogenase has been prepared by incorporating a synthetic Mn complex into the apoenzyme of [Fe]-Hydrogenase. The semi-synthetic [Mn]-hydrogenase shows higher activity than the corresponding Fe analogue.
- Hui-Jie Pan
- , Gangfeng Huang
- & Xile Hu
-
Article |
 Isotherms of individual pores by gas adsorption crystallography
Isotherms of individual pores by gas adsorption crystallography
Gas sorption studies in porous materials typically reflect their overall gas uptake. Now, using a ‘gas adsorption crystallography’ method, the gas adsorption isotherms of two metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) have been quantitatively decomposed into sub-isotherms that reflect the pore-filling behaviour of various guests in the different types of pores present in the MOFs.
- Hae Sung Cho
- , Jingjing Yang
- & Osamu Terasaki
-
Article |
 Imaging defects and their evolution in a metal–organic framework at sub-unit-cell resolution
Imaging defects and their evolution in a metal–organic framework at sub-unit-cell resolution
Structural defects are known to exist in metal–organic frameworks (MOFs), and to affect the materials’ properties, but their exact structures have remained difficult to determine. Now, missing-linker and missing-cluster defects have been observed in a MOF using low-dose transmission electron microscopy, enabling their distributions, evolutions during crystallization and effects on the material’s catalytic activity to be explored.
- Lingmei Liu
- , Zhijie Chen
- & Yu Han
-
Article |
 N-heterocyclic carbene-functionalized magic-number gold nanoclusters
N-heterocyclic carbene-functionalized magic-number gold nanoclusters
Magic-number Au11 clusters containing N-heterocyclic carbene (NHC) ligands are prepared by ligand exchange on known phosphine clusters and the introduction of even a single NHC results in improved cluster stability. The use of NHC-containing clusters in the electrocatalytic reduction of CO2 to CO is described and correlates with cluster stability.
- Mina R. Narouz
- , Kimberly M. Osten
- & Cathleen M. Crudden
-
Article |
 E- and Z-, di- and tri-substituted alkenyl nitriles through catalytic cross-metathesis
E- and Z-, di- and tri-substituted alkenyl nitriles through catalytic cross-metathesis
Nitriles are widely used in chemistry and are found in many bioactive compounds but, despite recent advances, there are no broadly applicable approaches for the synthesis of di- or tri-substituted alkenyl nitriles. New catalytic cross-metathesis strategies now allow direct access to a wide range of Z- or E-di-substituted cyano-substituted alkenes and their tri-substituted variants.
- Yucheng Mu
- , Thach T. Nguyen
- & Amir H. Hoveyda
-
News & Views |
 Changing the gold standard
Changing the gold standard
Gold — long presumed to be an inert metal — has been increasingly shaking this image over the past couple of decades, mostly through electrophilic behaviour. Now, a two-coordinate gold complex has been shown to exhibit nucleophilic reactivity, with the insertion of CO2 into its polarized Auδ−–Alδ+ bond.
- Didier Bourissou
-
Article |
 An efficient, step-economical strategy for the design of functional metalloproteins
An efficient, step-economical strategy for the design of functional metalloproteins
A concise strategy for engineering functional, supramolecular protein complexes has now been developed based on single-mutation-mediated covalent tethering. Metalloproteins designed with this method can sustain large alterations to the metal coordination environment, bind small molecules, exhibit reversible redox activity and sustain large alterations to the protein structure.
- Jonathan Rittle
- , Mackenzie J. Field
- & F. Akif Tezcan
-
Article |
 Transition-metal-bridged bimetallic clusters with multiple uranium–metal bonds
Transition-metal-bridged bimetallic clusters with multiple uranium–metal bonds
Heterometallic clusters have shown promise in catalysis and small-molecule activation, but species comprising uranium–metal bonds have remained difficult to synthesize. Now, facile reactions between uranium and nickel precursors have led to nickel-bridged diuranium clusters supported by a heptadentate N4P3 scaffold. Computational analysis points to an unusual electronic configuration for uranium, U(iii)-5f26d1.
- Genfeng Feng
- , Mingxing Zhang
- & Congqing Zhu
-
Article |
 A nucleophilic gold complex
A nucleophilic gold complex
A two-coordinate monovalent gold complex that features a highly polarized aluminium–gold covalent bond, Alδ+–Auδ−, has been synthesized using a very strongly electron-donating aluminyl ligand. In solution, the complex reacts as a nucleophilic source of gold towards heteroallenes such as carbodiimides and CO2.
- Jamie Hicks
- , Akseli Mansikkamäki
- & Simon Aldridge
-
News & Views |
 Redox activity goes organic
Redox activity goes organic
Superoxide dismutase mimics can help regulate the levels of O2•− in the body, but typically rely on redox-active metals that are toxic in their free form. Now, a complex featuring a redox-active quinol moiety complexed to a redox-inactive zinc centre has been shown to catalyse O2•− dismutation.
- Diane E. Cabelli
-
Article |
 The role of bridging ligands in dinitrogen reduction and functionalization by uranium multimetallic complexes
The role of bridging ligands in dinitrogen reduction and functionalization by uranium multimetallic complexes
Nitrogen fixation—the direct conversion of dinitrogen into ammonia or other nitrogen-containing products—is notoriously difficult to promote under mild conditions. Now, the reactivity of a multimetallic diuranium(iii) complex recently found capable of reducing and functionalizing N2 has been explored, replacing its nitride bridge with an oxo bridge, which resulted in a markedly different reactivity.
- Marta Falcone
- , Luciano Barluzzi
- & Marinella Mazzanti
-
Article |
 Relativistic quantum chemical calculations show that the uranium molecule U2 has a quadruple bond
Relativistic quantum chemical calculations show that the uranium molecule U2 has a quadruple bond
Establishing a fundamental understanding of the electronic structure of actinides remains a challenging task for both experiment and theory. Now, it is shown that for the uranium dimer, relativity and electron correlation affects not only the nature of the electronic ground state, but also lowers the bond multiplicity in comparison to previous studies.
- Stefan Knecht
- , Hans Jørgen Aa. Jensen
- & Trond Saue
-
News & Views |
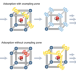 Crumple zones in MOFs
Crumple zones in MOFs
The applicability of metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) — in spite of their obvious potential — is hindered by stability issues, in particular towards water. Now, a ‘crumple zone’ concept has been proposed in which the presence of sacrificial bonds protects a MOF without significantly altering its structure or functionality.
- Jürgen Senker
-
Article |
 A crystalline monosubstituted carbene
A crystalline monosubstituted carbene
So far, monosubstituted carbenes have only been spectroscopically characterized at very low temperatures. Now, it has been shown that a bulky, chemically inert, amino substituent is enough to tame the intrinsic tendency of carbenes towards dimerization, enabling their isolation at room temperature.
- Ryo Nakano
- , Rodolphe Jazzar
- & Guy Bertrand
-
Article |
 Superoxide dismutase activity enabled by a redox-active ligand rather than metal
Superoxide dismutase activity enabled by a redox-active ligand rather than metal
Catalytic superoxide dismutase mimics typically involve manganese centres. Now, a complex based on redox-inactive zinc(ii) and a redox-active quinol ligand is found to catalytically degrade superoxide. The reaction, proposed to occur through oxidation of the ligand to a quinoxyl radical, is hastened rather than inhibited by the presence of phosphate.
- Meghan B. Ward
- , Andreas Scheitler
- & Christian R. Goldsmith
-
Article |
 Formation of the layered conductive magnet CrCl2(pyrazine)2 through redox-active coordination chemistry
Formation of the layered conductive magnet CrCl2(pyrazine)2 through redox-active coordination chemistry
Layered coordination polymers are attractive for the preparation of advanced 2D materials but they are typically non-magnetic insulators. Now such a layered network, CrCl2(pyrazine)2, has been prepared that comprises a paramagnetic metal ion and a redox-active ligand. The material exhibits both magnetism — with a ferrimagnetic ground state — and high electrical conductivity.
- Kasper S. Pedersen
- , Panagiota Perlepe
- & Rodolphe Clérac
-
Article |
 Highly reduced and protonated aqueous solutions of [P2W18O62]6− for on-demand hydrogen generation and energy storage
Highly reduced and protonated aqueous solutions of [P2W18O62]6− for on-demand hydrogen generation and energy storage
The polyoxoanion [P2W18O62]6− has been shown to reversibly accept up to 18 electrons upon reduction in aqueous solution. The resulting highly reduced solution can then be used either for the on-demand generation of hydrogen over a catalyst bed, or as a high-energy-density electrolyte in a redox flow battery.
- Jia-Jia Chen
- , Mark D. Symes
- & Leroy Cronin
-
Article |
 Hydrolytic stability in hemilabile metal–organic frameworks
Hydrolytic stability in hemilabile metal–organic frameworks
The promise shown by metal–organic frameworks for various applications is somewhat dampened by their instability towards water. Now, an activated MOF has shown good hydrolytic stability owing to the presence of weak, sacrificial coordination bonds that act as a ‘crumple zone’. On hydration, these weak bonds are cleaved preferentially to stronger coordination bonds that hold the MOF together.
- Lauren N. McHugh
- , Matthew J. McPherson
- & Russell E. Morris
-
News & Views |
 Scissoring genes with light
Scissoring genes with light
Enzymes can perform various biological functions because of their delicately and precisely organized structures. Now, simple inorganic nanoparticles with a rationally designed recognition capability can mimic restriction enzymes and selectively cut specific DNA sequences.
- Aleksandar P. Ivanov
- & Joshua B. Edel
-
News & Views |
 2D materials worth their salt
2D materials worth their salt
Sodium chloride phases with unconventional non-1:1 stoichiometries are known to exist under high-pressure conditions. Now, Na2Cl and Na3Cl two-dimensional crystals have been obtained under ambient conditions, on graphene surfaces, from dilute solutions.
- Artem R. Oganov
-
News & Views |
 The secret is in the ring
The secret is in the ring
An arene-anchored uranium complex has recently been shown to serve as efficient electrocatalyst for the conversion of water into dihydrogen. Now, the crucial role of the arene moiety in enabling catalytic activity — unusual for uranium — has been explored, providing important insight for the design of improved electrocatalysts.
- Marinella Mazzanti
-
Article |
 Transferring the entatic-state principle to copper photochemistry
Transferring the entatic-state principle to copper photochemistry
According to the entatic-state principle, distortions of the coordination geometry of a reacting compound can optimize the energies of starting and final states to improve reaction rates. Here, the entatic-state principle is observed to apply to photoactive copper complexes that have a constrained ligand geometry, resulting in very short charge-transfer state lifetimes.
- B. Dicke
- , A. Hoffmann
- & S. Herres-Pawlis
-
Article |
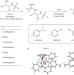 Asymmetric transfer hydrogenation by synthetic catalysts in cancer cells
Asymmetric transfer hydrogenation by synthetic catalysts in cancer cells
Intracellular asymmetric transfer hydrogenation catalysis using Os(II) complexes has now been demonstrated and offers a new approach for selectively killing cancer cells. Enantiomers of Os(II) arene catalysts can penetrate cell membranes enabling the reduction of pyruvate to D- or L-lactate using formate as a hydride source, with high enantioselectivity.
- James P. C. Coverdale
- , Isolda Romero-Canelón
- & Peter J. Sadler
-
News & Views |
 Passing the acid test
Passing the acid test
Water-oxidation catalysts that are fast and efficient in strong acid are rare even though there are several benefits for systems working at low pH. Such catalysts usually feature expensive noble metals such as ruthenium and iridum; however, an electrocatalytic system that is exceptionally efficient and based on cobalt has now been developed.
- Qiushi Yin
- & Craig L. Hill
-
News & Views |
 Measuring up with the early metals
Measuring up with the early metals
Mathematically modelling metal–ligand bonding in late transition-metal complexes has been an important tool in catalyst development — although lacking for early transition metals such as Cr and Ti. Now, a simple method for measuring ligand donor properties promises to elevate high-valent early transition metal catalysis to the same level.
- Ian A. Tonks
-
Editorial |
The bottom line
Our understanding of actinide chemistry lags behind that of the rest of the periodic table. A collection of articles in this issue highlights recent progress featuring uranium(VI) dianions bearing four U–N multiple bonds, berkelium(IV) stabilized in solution and delocalization of 5f electrons in a plutonium material.
-
News & Views |
 Popping up to the surface
Popping up to the surface
Merging the advantages of homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysts is a useful strategy for creating improved catalytic systems. Now, a concept has been developed that uses single Pd atoms — supported within liquid alloy droplets — that emerge from the droplet subsurface and interior to react with molecules approaching from the gas phase.
- Günther Rupprechter
-
Article |
 De novo design of a hyperstable non-natural protein–ligand complex with sub-Å accuracy
De novo design of a hyperstable non-natural protein–ligand complex with sub-Å accuracy
The first demonstration of a protein designed entirely from first principles that binds a small-molecule cofactor in a precisely predetermined orientation has now been described. The design method utilizes a remote protein core that both anchors and predisposes a flexible binding site for the desired cofactor-binding geometry.
- Nicholas F. Polizzi
- , Yibing Wu
- & William F. DeGrado
-
Article |
 Cooperative carbon-atom abstraction from alkenes in the core of a pentanuclear nickel cluster
Cooperative carbon-atom abstraction from alkenes in the core of a pentanuclear nickel cluster
Interest in surface-mediated chemistry has led to the design of small molecule models for surfaces, which provide mechanistic insight and have practical applications. Now, the cooperative behaviour of five nickel centres has been shown to provide reactivity reminiscent of highly active metal surface sites, leading to carbon-atom abstraction from alkenes under ambient conditions.
- Manar M. Shoshani
- & Samuel A. Johnson
-
Article |
 Quantifying ligand effects in high-oxidation-state metal catalysis
Quantifying ligand effects in high-oxidation-state metal catalysis
Catalysis involving high-valent metals is an important facet of modern chemistry, but tools for catalyst development in this field have lagged behind those for low-valent systems. Now, an experimental system that can accurately model and predict reactivity has been developed to aid high-valent catalyst design.
- Brennan S. Billow
- , Tanner J. McDaniel
- & Aaron L. Odom
-
Article |
 Structure and reactivity of a mononuclear gold(II) complex
Structure and reactivity of a mononuclear gold(II) complex
Mononuclear gold(II) complexes are very labile (and thus very rare) species. Now, a gold(II) porphyrin complex has been isolated and characterized, and its reactivity towards dioxygen, nitrosobenzene and acids investigated. Owing to a second-order Jahn–Teller distortion, the gold atoms were found to adopt a 2+2 coordination mode in a planar N4 environment.
- Sebastian Preiß
- , Christoph Förster
- & Katja Heinze
-
Article |
 A new and selective cycle for dehydrogenation of linear and cyclic alkanes under mild conditions using a base metal
A new and selective cycle for dehydrogenation of linear and cyclic alkanes under mild conditions using a base metal
The direct, selective conversion of linear alkanes to α-olefins — without isomerization — is an important reaction in the field of catalysis from both a fundamental and industrial perspective. Now, a detailed pathway has been described for how a base metal can promote such a reaction with several turnovers, in a non-oxidative set of C–H activation reactions, thus preventing olefin isomerization.
- Douglas P. Solowey
- , Manoj V. Mane
- & Daniel J. Mindiola
-
News & Views |
 Synthesis successes
Synthesis successes
Disentangling the chemistry and physics behind reported unconventional superconductivity and exotic magnetism in alkali-intercalated PAHs has remained problematic due to the lack of phase-pure samples. Two synthetic pathways have now remedied this issue, facilitating studies of cooperative electronic properties based on carbon π-electrons.
- Roser Valentí
- & Stephen M. Winter
-
Article |
 Structural snapshots of concerted double E–H bond activation at a transition metal centre
Structural snapshots of concerted double E–H bond activation at a transition metal centre
X-ray and neutron diffraction studies, in conjunction with quantum chemical techniques, have been used to define a new oxidative bond activation pathway that involves simultaneous activation of both bonds of a β-diketiminate-stabilized GaH2 unit at a single metal centre.
- Joseph A. B. Abdalla
- , Alexa Caise
- & Simon Aldridge
-
Article |
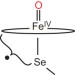 Characterization of a selenocysteine-ligated P450 compound I reveals direct link between electron donation and reactivity
Characterization of a selenocysteine-ligated P450 compound I reveals direct link between electron donation and reactivity
The oxidative prowess of cytochrome P450s has been suggested to stem from the electron-donating axial ligand. Now, a selenocysteine-ligated P450 compound I has been trapped and characterized providing an avenue to examine this hypothesis. Measurements reveal that the selenolate-ligated compound I cleaves C–H bonds more rapidly than the wild-type equivalent.
- Elizabeth L. Onderko
- , Alexey Silakov
- & Michael T. Green
-
Article |
 Incipient class II mixed valency in a plutonium solid-state compound
Incipient class II mixed valency in a plutonium solid-state compound
Unlike in the d block, intervalence charge transfer is rare in the 5f block owing to localized valence electrons and poor overlap between metal and ligand orbitals. Delocalization of 5f electrons has now been observed in a Pu(III)/Pu(IV)–pyridinedicarboxylate solid-state compound. It occurs through metal-to-ligand charge transfer with both plutonium centres.
- Samantha K. Cary
- , Shane S. Galley
- & Thomas E. Albrecht-Schmitt
-
Article |
 Redox-controlled potassium intercalation into two polyaromatic hydrocarbon solids
Redox-controlled potassium intercalation into two polyaromatic hydrocarbon solids
Reports of superconductivity in KxPicene spurred interest in alkali-intercalated polyaromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) compounds, but their compositions and structures have remained unclear. Now crystalline K2Pentacene and K2Picene — neither of which are superconducting — have been prepared by mild synthesis. Structural analysis shows that the cation sites arise within the molecular layers from reorientation of the PAHs within a herringbone packing.
- F. Denis Romero
- , M. J. Pitcher
- & M. J. Rosseinsky

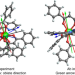 Observation of the asphericity of 4f-electron density and its relation to the magnetic anisotropy axis in single-molecule magnets
Observation of the asphericity of 4f-electron density and its relation to the magnetic anisotropy axis in single-molecule magnets