News & Views |
Featured
-
-
Article |
 Deprotonated 2-thiolimidazole serves as a metal-free electrocatalyst for selective acetylene hydrogenation
Deprotonated 2-thiolimidazole serves as a metal-free electrocatalyst for selective acetylene hydrogenation
Although metal-free catalysts, featuring defined active sites, represent alternatives to scarce or problematic metals, metal-free compounds rarely show activities as promising as metal-based materials. Now deprotonated 2-thiolimidazole is shown to serve as a metal-free electrocatalyst for selective acetylene hydrogenation and achieves competitive performances with metal-based catalysts.
- Lei Zhang
- , Rui Bai
- & Jian Zhang
-
Article |
 Catalyst self-assembly accelerates bimetallic light-driven electrocatalytic H2 evolution in water
Catalyst self-assembly accelerates bimetallic light-driven electrocatalytic H2 evolution in water
Although the light-driven generation of hydrogen from water is a promising approach to renewable fuels, the H–H bond formation step represents a persistent mechanistic question. Now light-harvesting molecular catalysts have been shown to self-assemble into nanoscale aggregates that feature improved efficiency for photoelectrochemical H2 evolution.
- Isaac N. Cloward
- , Tianfei Liu
- & Alexander J. M. Miller
-
Article |
 Visualization of CO2 electrolysis using optical coherence tomography
Visualization of CO2 electrolysis using optical coherence tomography
Electrolysers can upgrade CO2 into high-value chemicals, but there are few tools capable of tracking the reactions that occur within these devices during operation. Now an electrolysis optical coherence tomography platform has been developed to visualize the electrochemical conversion of CO2 to CO, plus the movement of components, within the device.
- Xin Lu
- , Chris Zhou
- & Curtis P. Berlinguette
-
Article
| Open Access Operando film-electrochemical EPR spectroscopy tracks radical intermediates in surface-immobilized catalysts
Operando film-electrochemical EPR spectroscopy tracks radical intermediates in surface-immobilized catalysts
Although surface-bound molecular catalysts offer well-defined active sites on heterogeneous supports, it is challenging to identify key radical intermediates in the reaction mechanism. Now, a characterization method has been developed that combines film electrochemistry and EPR spectroscopy to track radical intermediates in real time, exemplified by alcohol oxidation with a surface-immobilized nitroxide.
- Maryam Seif-Eddine
- , Samuel J. Cobb
- & Maxie M. Roessler
-
-
News & Views |
 Electrolyte type affects electrochemical bubble formation
Electrolyte type affects electrochemical bubble formation
Gas bubble accumulation at interfaces is a barrier to achieving more efficient electrochemical devices. A clever model system to understand bubble formation during electrochemical hydrogen evolution now reveals similarities between the forces at play during their detachment from the catalyst surface and those involved in wine climbing up a glass.
- Gaurav Ashish Kamat
- & Michaela Burke Stevens
-
Article |
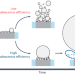 Solutal Marangoni effect determines bubble dynamics during electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution
Solutal Marangoni effect determines bubble dynamics during electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution
Although gas bubble dynamics during electrochemical processes dramatically affect performance, the fundamental understanding and manipulation of such dynamics have been limited. Now, electrolyte composition is found to be a key factor in inducing a solutal Marangoni instability that impacts both H2 gas detachment and coalescence between H2 microbubbles.
- Sunghak Park
- , Luhao Liu
- & Marc T. M. Koper
-
Article |
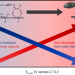 Triarylmethyl cation redox mediators enhance Li–O2 battery discharge capacities
Triarylmethyl cation redox mediators enhance Li–O2 battery discharge capacities
Although Li–O2 batteries offer high theoretical capacities, redox mediators are necessary to control intermediate reaction kinetics and to limit electrode passivation. Now it has been shown that a family of triarylmethyl cations can rival top-performing quinone-based redox mediators. Cations with sluggish catalytic rates were found to suppress surface-mediated O2 reduction and achieve higher capacitances.
- Erik J. Askins
- , Marija R. Zoric
- & Ksenija D. Glusac
-
Article
| Open Access Electrochemical synthesis of propylene from carbon dioxide on copper nanocrystals
Electrochemical synthesis of propylene from carbon dioxide on copper nanocrystals
The electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide to propylene requires multiple C–C coupling steps and the transfer of 18 electrons, posing kinetic and thermodynamic barriers. Now the electrosynthesis of propylene from carbon dioxide using copper nanocrystals has been demonstrated, with analysis revealing that the key step for its formation is probably the coupling between carbon dioxide or carboxyl with intermediates involved in the ethylene pathway.
- Jing Gao
- , Alimohammad Bahmanpour
- & Michael Grätzel
-
Review Article |
 Merging molecular catalysts and metal–organic frameworks for photocatalytic fuel production
Merging molecular catalysts and metal–organic frameworks for photocatalytic fuel production
The light-driven conversion of abundant resources such as CO2 and H2O into chemical fuels for energy storage is crucial to end our dependence on fossil fuels. This Review highlights how molecular catalysts and photosensitizers can be grafted onto metal–organic frameworks to combine the advantages of both classes of compounds. Different synthetic strategies are discussed, along with their advantages and limitations.
- P. M. Stanley
- , J. Haimerl
- & J. Warnan
-
Article |
 Using waste poly(vinyl chloride) to synthesize chloroarenes by plasticizer-mediated electro(de)chlorination
Using waste poly(vinyl chloride) to synthesize chloroarenes by plasticizer-mediated electro(de)chlorination
The facile release of corrosive HCl gas and plasticizers from poly(vinyl chloride) (PVC) makes it a challenging material to recycle. Now, it has been shown that PVC waste can be directly used as a halogen source to synthesize chloroarenes. This paired electro(de)chlorination is mediated by a phthalate plasticizer already contained in PVC waste.
- Danielle E. Fagnani
- , Dukhan Kim
- & Anne J. McNeil
-
Article |
 Inverse kinetic isotope effects in the oxygen reduction reaction at platinum single crystals
Inverse kinetic isotope effects in the oxygen reduction reaction at platinum single crystals
Kinetic isotope effect studies can provide valuable insights into the complex mechanisms of the oxygen reduction reaction; however, inaccessibility to ultra-high-purity D2O has made this difficult. Now, a methodology to prepare ultra-pure D2O has been developed and inverse kinetic isotope effects have subsequently been measured for the oxygen reduction reaction on platinum single-crystal surfaces, providing mechanistic insights.
- Yao Yang
- , Rishi G. Agarwal
- & Héctor D. Abruña
-
News & Views |
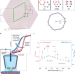 Let’s twist electrochem
Let’s twist electrochem
The electronic structure of an electrode can affect the electron transfer rate of electrochemical processes at its surface. Now, it has been shown that varying the ‘twist’ angle between two stacked layers of graphene modifies the bilayer electronic structure and provides a new dimension to control interfacial redox activity.
- Oluwasegun J. Wahab
- & Patrick R. Unwin
-
Article |
 Fast CO2 hydration kinetics impair heterogeneous but improve enzymatic CO2 reduction catalysis
Fast CO2 hydration kinetics impair heterogeneous but improve enzymatic CO2 reduction catalysis
Carbonic anhydrase enzymatically catalyses CO2 hydration, and its effect on enzymatic and heterogeneous CO2 reduction has now been studied. Through the co-immobilization of carbonic anhydrase, it has been shown that faster CO2 hydration kinetics are beneficial for enzymatic catalysis (using formate dehydrogenase) but detrimental for heterogeneous catalysts, such as gold.
- Samuel J. Cobb
- , Vivek M. Badiani
- & Erwin Reisner
-
Article |
 Spontaneous N2 formation by a diruthenium complex enables electrocatalytic and aerobic oxidation of ammonia
Spontaneous N2 formation by a diruthenium complex enables electrocatalytic and aerobic oxidation of ammonia
The use of ammonia as an alternative fuel relies on its electrochemical conversion to dinitrogen in a fuel cell. Now a stable metal–metal bonded diruthenium complex is shown to spontaneously produce dinitrogen from ammonia under ambient conditions and is also able to electrocatalyse the oxidation of ammonia to dinitrogen at low potentials.
- Michael J. Trenerry
- , Christian M. Wallen
- & John F. Berry
-
Article |
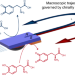 Direct dynamic read-out of molecular chirality with autonomous enzyme-driven swimmers
Direct dynamic read-out of molecular chirality with autonomous enzyme-driven swimmers
Self-propelled artificial chemical swimmers have previously been developed for chemical sensing. Now, hybrid bioelectrochemical swimmers, capable of translating chiral molecular information into macroscopic motion, have been developed. Diastereomeric interactions between enantiopure oligomers immobilized on the swimmer and a chiral molecule present in solution control the trajectory of the device.
- Serena Arnaboldi
- , Gerardo Salinas
- & Alexander Kuhn
-
-
Article |
 Immobilization of molecular catalysts on electrode surfaces using host–guest interactions
Immobilization of molecular catalysts on electrode surfaces using host–guest interactions
Molecular catalysts can be made more practical by anchoring them onto electrode surfaces, but such systems are less stable than standard heterogeneous electrocatalysts. Now, supramolecular hosts bound to electrode surfaces have enabled the immobilization of molecular electrocatalysts through host–guest interactions. Desorbed or degraded guest molecules can be replaced with fresh guest molecules, extending their lifetimes.
- Laurent Sévery
- , Jacek Szczerbiński
- & S. David Tilley
-
Article |
 Electrochemically driven desaturation of carbonyl compounds
Electrochemically driven desaturation of carbonyl compounds
Excising hydrogen adjacent to a carbonyl group—one of the most basic and widely employed transformations in organic synthesis—is traditionally achieved using metals and/or stoichiometric oxidants. Now, it has been shown that an electrochemically driven approach removes such requirements, resulting in a more sustainable and easily scalable method with wide substrate scope.
- Samer Gnaim
- , Yusuke Takahira
- & Phil S. Baran
-
Matters Arising |
 Reply to: Questioning the rate law in the analysis of water oxidation catalysis on haematite photoanodes
Reply to: Questioning the rate law in the analysis of water oxidation catalysis on haematite photoanodes
- Camilo A. Mesa
- , Reshma R. Rao
- & James R. Durrant
-
Article |
 Water oxidation electrocatalysis using ruthenium coordination oligomers adsorbed on multiwalled carbon nanotubes
Water oxidation electrocatalysis using ruthenium coordination oligomers adsorbed on multiwalled carbon nanotubes
Efficient and stable water oxidation catalysts are important if photoelectrochemical cells are to be used to provide clean and sustainable solar fuels. A water oxidation catalyst that operates at neutral pH has now been developed that features ruthenium coordination oligomers anchored onto the surfaces of graphitic materials through CH–π interactions.
- Md Asmaul Hoque
- , Marcos Gil-Sepulcre
- & Antoni Llobet
-
Article |
 Dual electrocatalysis enables enantioselective hydrocyanation of conjugated alkenes
Dual electrocatalysis enables enantioselective hydrocyanation of conjugated alkenes
A general method for the enantioselective hydrocyanation of alkenes has been a long-standing synthetic challenge. Now, using a dual electrocatalytic approach that combines two synergistic redox catalytic cycles, a wide variety of chiral nitriles can be synthesized from conjugated alkenes in high enantioselectivity.
- Lu Song
- , Niankai Fu
- & Song Lin
-
Article |
 Iridium single-atom catalyst on nitrogen-doped carbon for formic acid oxidation synthesized using a general host–guest strategy
Iridium single-atom catalyst on nitrogen-doped carbon for formic acid oxidation synthesized using a general host–guest strategy
Single-atom catalysts maximize metal atom efficiency and exhibit properties that can be considerably different to their nanoparticle equivalent. Now a general host–guest strategy to make various single-atom catalysts on nitrogen-doped carbon has been developed; the iridium variant electrocatalyses the formic acid oxidation reaction with high mass activity and displays high tolerance to CO poisoning.
- Zhi Li
- , Yuanjun Chen
- & Yadong Li
-
Article |
 Rechargeable-battery chemistry based on lithium oxide growth through nitrate anion redox
Rechargeable-battery chemistry based on lithium oxide growth through nitrate anion redox
Phase-forming conversion chemistry, like that observed in Li–S and Li–O2 batteries, shows great promise, but these systems suffer some drawbacks, such as practically low cathode areal capacities and electrolyte decomposition. Now, high-energy conversion battery chemistry—based on nitrate/nitrite redox where one of the products is soluble—has been enabled by using nanoparticulate Ni/NiO electrocatalysts.
- Vincent Giordani
- , Dylan Tozier
- & Dan Addison
-
Article |
 Formation of carbon–nitrogen bonds in carbon monoxide electrolysis
Formation of carbon–nitrogen bonds in carbon monoxide electrolysis
The electroreduction of CO2-derived CO is a promising technology for the sustainable production of value-added chemicals. Now, it is shown how C–N bonds can be formed electrochemically through CO electroreduction on a Cu surface in the presence of amines. The formation of acetamides is observed through nucleophilic addition to a ketene intermediate.
- Matthew Jouny
- , Jing-Jing Lv
- & Feng Jiao
-
Article |
 Ruthenium-catalysed oxidative conversion of ammonia into dinitrogen
Ruthenium-catalysed oxidative conversion of ammonia into dinitrogen
The production of ammonia from dinitrogen is a well-studied process; however, the catalytic conversion of ammonia into dinitrogen is underdeveloped. Now, ammonia oxidation has been achieved using ruthenium complexes as catalysts. The production of dinitrogen is observed when ammonium salts are treated with a single-electron oxidant, base and ruthenium catalyst.
- Kazunari Nakajima
- , Hiroki Toda
- & Yoshiaki Nishibayashi
-
News & Views |
 Two are better than one
Two are better than one
Finely tuned interactions in the second coordination sphere of enzymes or homogeneous catalysts can be essential for their function. Now, this concept has been applied to the surface of a catalytic material, utilizing pairs of Cu atoms for the selective electrochemical fixation of CO2.
- Benjamin S. Natinsky
- & Chong Liu
-
Article |
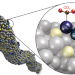 Copper atom-pair catalyst anchored on alloy nanowires for selective and efficient electrochemical reduction of CO2
Copper atom-pair catalyst anchored on alloy nanowires for selective and efficient electrochemical reduction of CO2
Anchored single-atom catalysts have recently been shown to be very active for various processes, however, a catalyst that features two adjacent copper atoms—which we call an atom-pair catalyst—is now reported. The Cu10–Cu1x+ pair structures work together to carry out the critical bimolecular step in CO2 reduction.
- Jiqing Jiao
- , Rui Lin
- & Yadong Li
-
Article |
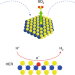 Spontaneous doping of the basal plane of MoS2 single layers through oxygen substitution under ambient conditions
Spontaneous doping of the basal plane of MoS2 single layers through oxygen substitution under ambient conditions
MoS2 single layers spontaneously undergo a slow oxygen substitution reaction under ambient conditions giving rise to solid-solution-type 2D molybdenum oxy-sulfide crystals. The oxygen substitution sites of the 2D MoS2−xOx crystals act as efficient single-atom catalytic centres for the hydrogen evolution reaction.
- János Pető
- , Tamás Ollár
- & Levente Tapasztó
-
News & Views |
 N-doping goes sp-hybridized
N-doping goes sp-hybridized
Specific forms of nitrogen doping can endow carbon-based metal-free materials with electrocatalytic activity. Now, introducing sp-hybridized nitrogen atoms into some acetylenic sites of ultra-thin graphdiyne — a highly π-conjugated lamellar carbon allotrope — has led to excellent oxygen reduction reaction activity.
- Yao Zheng
- & Shi-Zhang Qiao
-
Article |
 Few-layer graphdiyne doped with sp-hybridized nitrogen atoms at acetylenic sites for oxygen reduction electrocatalysis
Few-layer graphdiyne doped with sp-hybridized nitrogen atoms at acetylenic sites for oxygen reduction electrocatalysis
Heteroatom doping is a widely used modification method for carbon-based catalysts. Now, chemically defined sp-hybridized nitrogen atoms have been selectively introduced to the acetylene groups in ultrathin graphdiynes, resulting in good catalytic activity for the oxygen reduction reaction in both alkaline and acidic media.
- Yasong Zhao
- , Jiawei Wan
- & Dan Wang
-
Article |
 Dopant-induced electron localization drives CO2 reduction to C2 hydrocarbons
Dopant-induced electron localization drives CO2 reduction to C2 hydrocarbons
On copper catalysts, Cuδ+ sites play a key role in the electrochemical reduction of CO2 to C2 hydrocarbons, however, they are prone to being reduced (to Cu0) themselves. Now, a Cuδ+-based catalyst is reported that is stable for in excess of ~40 hours while electrochemically reducing CO2 to multi-carbon hydrocarbons and that exhibits a Faradaic efficiency for C2 of ~80%.
- Yansong Zhou
- , Fanglin Che
- & Edward H. Sargent
-
Article |
 High phase-purity 1T′-MoS2- and 1T′-MoSe2-layered crystals
High phase-purity 1T′-MoS2- and 1T′-MoSe2-layered crystals
The phase in which a crystal exists can have a direct influence over its properties; however, it is usually difficult to control during synthesis. Now it has been shown that micrometre-sized metallic 1T′-MoS2- and 1T′-MoSe2-layered crystals can be prepared in high phase purity on a large scale, and that they display promising electrocatalytic activity towards the hydrogen evolution reaction.
- Yifu Yu
- , Gwang-Hyeon Nam
- & Hua Zhang
-
Article |
 Crystal phase-based epitaxial growth of hybrid noble metal nanostructures on 4H/fcc Au nanowires
Crystal phase-based epitaxial growth of hybrid noble metal nanostructures on 4H/fcc Au nanowires
Heterometallic nanomaterials in unusual crystal phases that are impossible to form in the bulk state can show interesting physical and chemical properties. Here, crystal-phase heterostructured 4H/fcc Au nanowires are used as seeds to epitaxially grow a variety of binary and ternary hybrid noble metal nanostructures on the phase boundary.
- Qipeng Lu
- , An-Liang Wang
- & Hua Zhang
-
Article |
 Theory-driven design of high-valence metal sites for water oxidation confirmed using in situ soft X-ray absorption
Theory-driven design of high-valence metal sites for water oxidation confirmed using in situ soft X-ray absorption
Water oxidation is key to the production of chemical fuels from electricity. Now, guided by theory, NiCoFeP oxyhydroxide catalysts have been developed that require an overpotential lower than that required by IrO2. In situ soft X-ray absorption studies of neutral-pH NiCoFeP catalysts indicate formation of Ni4+, which is favourable for water oxidation.
- Xueli Zheng
- , Bo Zhang
- & Edward H. Sargent
-
Article |
 Activating lattice oxygen redox reactions in metal oxides to catalyse oxygen evolution
Activating lattice oxygen redox reactions in metal oxides to catalyse oxygen evolution
Understanding how oxygen-evolution reaction (OER) catalysts work is important for the development of efficient energy storage technologies. It has now been shown that lattice oxygen participates in O2 generation during the OER on some highly active metal oxides and that this behaviour becomes more prevalent with greater metal–oxygen covalency.
- Alexis Grimaud
- , Oscar Diaz-Morales
- & Yang Shao-Horn
-
Article |
 Mechanism of O2 diffusion and reduction in FeFe hydrogenases
Mechanism of O2 diffusion and reduction in FeFe hydrogenases
FeFe hydrogenases are highly efficient H2 producing enzymes; however, they can be inactivated by O2. Now, a mechanism for O2 diffusion within FeFe hydrogenases and its reactions at the active site of the enzyme has been proposed. These findings could help with the design of hydrogenase mutants with increased resistance to oxidative damage.
- Adam Kubas
- , Christophe Orain
- & Christophe Léger
-
Article |
 High-performance Ag–Co alloy catalysts for electrochemical oxygen reduction
High-performance Ag–Co alloy catalysts for electrochemical oxygen reduction
The oxygen reduction reaction limits fuel cell performance and currently requires costly electrocatalysts with high platinum content to achieve adequate power densities. Now a silver–cobalt surface alloy electrocatalyst has been developed for the oxygen reduction reaction that is stable in alkaline electrolytes and is more economical than traditional platinum-based materials.
- Adam Holewinski
- , Juan-Carlos Idrobo
- & Suljo Linic
-
Article |
 Mass-selected nanoparticles of PtxY as model catalysts for oxygen electroreduction
Mass-selected nanoparticles of PtxY as model catalysts for oxygen electroreduction
The widespread use of fuel cells requires improved catalysts to reduce oxygen efficiently at the cathode. It is shown that model, well-characterized size-selected PtxY nanoparticles can be synthesized by the gas aggregation technique, and that they are highly active for this reaction.
- Patricia Hernandez-Fernandez
- , Federico Masini
- & Ib Chorkendorff
-
Article |
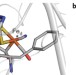 The oxidative inactivation of FeFe hydrogenase reveals the flexibility of the H-cluster
The oxidative inactivation of FeFe hydrogenase reveals the flexibility of the H-cluster
FeFe hydrogenases, the enzymes that oxidize or produce H2, are inactivated under oxidizing conditions. Here, it is shown that this inactivation results from H2 binding to coordination positions that are normally blocked by intrinsic CO ligands. This flexibility of the active site prevents irreversible oxidative damage.
- Vincent Fourmond
- , Claudio Greco
- & Christophe Léger
-
Article |
 Building an appropriate active-site motif into a hydrogen-evolution catalyst with thiomolybdate [Mo3S13]2− clusters
Building an appropriate active-site motif into a hydrogen-evolution catalyst with thiomolybdate [Mo3S13]2− clusters
Non-noble-metal-based MoS2 nanostructures are hydrogen evolution catalysts whose active sites are known to be located at the edges. Supported thiomolybdate [Mo3S13]2− nanoclusters have now been prepared that exhibit a structural motif similar to that of MoS2 edges. The nanoclusters, synthesized by a scalable route, demonstrate a high turnover frequency.
- Jakob Kibsgaard
- , Thomas F. Jaramillo
- & Flemming Besenbacher
-
Article |
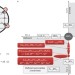 In situ growth of nanoparticles through control of non-stoichiometry
In situ growth of nanoparticles through control of non-stoichiometry
Surfaces decorated with nanoparticles are typically prepared by depositing particles on the substrate. Instead, particles have now been grown in situ directly from perovskites, by exsolution through judicious tuning of the materials’ compositions, particularly their nonstoichiometry. This approach enables control over particle composition, size, surface coverage and anchorage.
- Dragos Neagu
- , George Tsekouras
- & John T. S. Irvine
-
News & Views |
 A basic solution
A basic solution
Hydrogen–oxygen alkaline fuel cells are promising devices for the 'hydrogen economy' but their oxidation of hydrogen fuel is slow compared with that of acidic fuel cells. More efficient electrocatalysts have now been prepared in which the adsorption of hydroxyl groups onto the electrode surface is controlled through suitable promoters.
- Marc T. M. Koper
-
Article |
 An iron complex with pendent amines as a molecular electrocatalyst for oxidation of hydrogen
An iron complex with pendent amines as a molecular electrocatalyst for oxidation of hydrogen
Electricity can be produced by the oxidation of hydrogen in fuel cells, but the best catalyst for this is platinum, a precious metal of low abundance. Now a molecular complex of iron, a very abundant, inexpensive metal, has been rationally designed for the oxidation of H2 at room temperature.
- Tianbiao Liu
- , Daniel L. DuBois
- & R. Morris Bullock
-
Article |
 Molecular engineering of a cobalt-based electrocatalytic nanomaterial for H2 evolution under fully aqueous conditions
Molecular engineering of a cobalt-based electrocatalytic nanomaterial for H2 evolution under fully aqueous conditions
Efficient hydrogen-evolving catalysts comprising readily available elements are needed if hydrogen is to be adopted as a clean alternative to fossil fuels. Now, a diimine–dioxime cobalt complex has been covalently attached to a carbon nanotube electrode to yield an active and robust electrocatalyst for hydrogen generation (55,000 turnovers in seven hours) from aqueous solutions.
- Eugen S. Andreiadis
- , Pierre-André Jacques
- & Vincent Artero
-
Article |
 Ammonia synthesis using a stable electride as an electron donor and reversible hydrogen store
Ammonia synthesis using a stable electride as an electron donor and reversible hydrogen store
Methods that fix atmospheric nitrogen to ammonia under mild conditions could offer a more environmentally benign alternative to the Haber–Bosch process. Now, a Ru-loaded electride, [Ca24Al28O64]4+(e−)4, is reported that acts as an efficient electron donor and reversible hydrogen store, and is demonstrated to function as an efficient catalyst for ammonia synthesis.
- Masaaki Kitano
- , Yasunori Inoue
- & Hideo Hosono
-
-
Article |
 A soluble copper–bipyridine water-oxidation electrocatalyst
A soluble copper–bipyridine water-oxidation electrocatalyst
Copper and bipyridine (bpy) self-assemble in aqueous solutions at high pH into an active electrocatalyst for the oxidation of water to O2, one of the great challenges in energy catalysis. These solutions contain primarily (bpy)Cu(OH)2, and are robust and active catalysts, albeit at high overpotentials.
- Shoshanna M. Barnett
- , Karen I. Goldberg
- & James M. Mayer
-
Article |
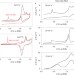 The promoting effect of adsorbed carbon monoxide on the oxidation of alcohols on a gold catalyst
The promoting effect of adsorbed carbon monoxide on the oxidation of alcohols on a gold catalyst
Adsorbed carbon monoxide typically acts to poison the oxidation of alcohols on heterogeneous catalysts and electrocatalysts. Here, it is shown that carbon monoxide that has been adsorbed irreversibly on a Au(111) surface can act as a promoter for this process by enhancing the scission of C–H bonds in the alcohol to yield the corresponding aldehyde.
- Paramaconi Rodriguez
- , Youngkook Kwon
- & Marc T. M. Koper

 Assembling the pieces to improve catalysis
Assembling the pieces to improve catalysis Taking copper’s pulse with Raman
Taking copper’s pulse with Raman Deconvoluting double layers
Deconvoluting double layers