News & Views |
Featured
-
-
Article |
 Actively tunable laser action in GeSn nanomechanical oscillators
Actively tunable laser action in GeSn nanomechanical oscillators
An on-chip tunable laser operates by harnessing nanomechanical resonances at the radio frequency, achieving ultralow tuning power consumption.
- Hyo-Jun Joo
- , Jiawen Liu
- & Donguk Nam
-
Article |
 Phase-separated porous nanocomposite with ultralow percolation threshold for wireless bioelectronics
Phase-separated porous nanocomposite with ultralow percolation threshold for wireless bioelectronics
An in situ phase-separation method at microscale level creates stretchable superelastic porous nanocomposite conductors, reduces conductive filler usage and enables strain-resilient wireless wearable and implantable bioelectronics.
- Yadong Xu
- , Zhilu Ye
- & Zheng Yan
-
Article |
 Functionalized nanowires for miRNA-mediated therapeutic programming of naïve T cells
Functionalized nanowires for miRNA-mediated therapeutic programming of naïve T cells
Ex vivo engineering of T cells for adoptive T-cell therapy without pre-activation is challenging and hinders therapeutic efficacy. Here, using nanowires, the delivery of microRNAs to primary naïve mouse and human CD8+ T cells without pre-activation for immune protection against pathogens is demonstrated.
- Kristel J. Yee Mon
- , Sungwoong Kim
- & Ankur Singh
-
Article |
 Toroidic phase transitions in a direct-kagome artificial spin ice
Toroidic phase transitions in a direct-kagome artificial spin ice
Toroidic phases and their phase transitions are notoriously hard to study in natural materials. Now, a direct-kagome spin ice provides access to two low-temperature toroidal phases, ferrotoroidicity and paratoroidicity, as well as to toroidic phase transitions.
- Wen-Cheng Yue
- , Zixiong Yuan
- & Yong-Lei Wang
-
Article |
 Self-assembly of peptide nanocapsules by a solvent concentration gradient
Self-assembly of peptide nanocapsules by a solvent concentration gradient
Biobased materials are of interest for many applications. Here the authors report insect-derived peptides that self-assemble into hollow nanocapsules through a gradient-driven, single-step, solvent exchange process, enabling the encapsulation of diverse cargoes with potential for drug delivery applications.
- Haopeng Li
- , Xuliang Qian
- & Jing Yu
-
Article |
 Nanoscale doping of polymeric semiconductors with confined electrochemical ion implantation
Nanoscale doping of polymeric semiconductors with confined electrochemical ion implantation
A simple manipulation of an electrolyte’s glass transition enables nanoresolved electrochemical ion implantation doping in a variety of polymeric semiconductors.
- Lanyi Xiang
- , Zihan He
- & Daoben Zhu
-
Article |
 Nanosurface-reconstructed perovskite for highly efficient and stable active-matrix light-emitting diode display
Nanosurface-reconstructed perovskite for highly efficient and stable active-matrix light-emitting diode display
Acid-etching-driven nanosurface reconstruction of perovskite quantum-dot pure-red LEDs facilitates a peak external quantum efficiency of 28.5% and a half-lifetime of 30 h at 100 cd m−2 luminance, enabling highly efficient solution-processed active-matrix perovskite displays.
- Hongjin Li
- , Yifeng Feng
- & Zhizhen Ye
-
Article |
 Upconversion electroluminescence in 2D semiconductors integrated with plasmonic tunnel junctions
Upconversion electroluminescence in 2D semiconductors integrated with plasmonic tunnel junctions
Plasmonic tunnel junctions integrated with a monolayer semiconductor are found to emit photons with energies exceeding the input electrical potential. This peculiar phenomenon is ascribed to being triggered by inelastic electron tunnelling dipoles inducing optically forbidden transitions in the carrier injection electrode.
- Zhe Wang
- , Vijith Kalathingal
- & Goki Eda
-
News & Views |
 Nanoparticles subdue antibiotic-resistant bacteria’s defences while enhancing innate immunity
Nanoparticles subdue antibiotic-resistant bacteria’s defences while enhancing innate immunity
A method for overcoming antibiotic resistance uses multimodal nanoparticles that target bacterial defence mechanisms while enhancing the innate immune response.
- Julia C. Lang
- & Keira Melican
-
Article
| Open Access Giant nanomechanical energy storage capacity in twisted single-walled carbon nanotube ropes
Giant nanomechanical energy storage capacity in twisted single-walled carbon nanotube ropes
A single-walled carbon nanotube spring stores three times more mechanical energy than a lithium-ion battery, while offering wide temperature stability and posing no explosion risk.
- Shigenori Utsumi
- , Sanjeev Kumar Ujjain
- & Katsumi Kaneko
-
News & Views |
 Acute, controlled inhalation of thin graphene oxide nanosheets in humans with null cardiorespiratory effects
Acute, controlled inhalation of thin graphene oxide nanosheets in humans with null cardiorespiratory effects
A double-blind, randomized, controlled human exposure trial of highly purified and thin nanometre-sized graphene oxide nanosheets shows that acute inhalation of aerosolized nanoparticles is not associated with harmful effects in healthy humans.
- Ulla Vogel
-
Article
| Open Access De novo design of pH-responsive self-assembling helical protein filaments
De novo design of pH-responsive self-assembling helical protein filaments
Engineering the tunability of protein assembly in response to pH changes within a narrow range is challenging. Here the authors report the de novo computational design of pH-responsive protein filaments that exhibit rapid, precise, tunable and reversible assembly and disassembly triggered by small pH changes.
- Hao Shen
- , Eric M. Lynch
- & David Baker
-
-
Research Briefing |
 Light manipulation with sub-pixel wavefront control using gap phases
Light manipulation with sub-pixel wavefront control using gap phases
How can light be efficiently manipulated below the single-pixel level? An answer is now provided using near-field interactions for nanopillars in a metasurface — phase gradients in the gaps between the nanopillars constitute a new degree of freedom that enables efficient wavefront control at the nanoscale.
-
Article |
 Highly efficient vortex generation at the nanoscale
Highly efficient vortex generation at the nanoscale
A metasurface consisting of merely four nanopillars at the wavelength scale is sufficient to generate a high-quality vortex beam.
- Qinmiao Chen
- , Geyang Qu
- & Shumin Xiao
-
News & Views |
 Artificial intelligence assists the synthesis of all-natural plastic substitutes
Artificial intelligence assists the synthesis of all-natural plastic substitutes
Robotics and machine learning are combined to predict and prepare a variety of nanocomposite materials with properties mimicking those of various types of plastics, starting from natural building blocks.
- Zhaoming Liu
-
News & Views |
 Controlling the STING pathway to improve immunotherapy
Controlling the STING pathway to improve immunotherapy
A genetically engineered variant of the stimulator of interferon genes (STING) protein is delivered to cancer cells, showing potential for clinical impact.
- John T. Wilson
-
News & Views |
 Topographic fingerprinting of single proteins and proteoforms
Topographic fingerprinting of single proteins and proteoforms
A distance-based mapping strategy using single-molecule fluorescence resonance energy transfer via DNA eXchange (FRET X) enables full-length fingerprinting of intact protein sequences.
- J. Carlos Penedo
-
News & Views |
 Graphene edge interference improves single-molecule transistors
Graphene edge interference improves single-molecule transistors
The performance of three-terminal molecular transistors is enhanced through the harnessing of quantum interference in the edges of graphene electrodes.
- Héctor Vázquez
-
Article
| Open Access Quantum interference enhances the performance of single-molecule transistors
Quantum interference enhances the performance of single-molecule transistors
An experimental demonstration of how destructive quantum interference effects can increase the performance of single-molecule field-effect transistors to reach levels similar to those of nanoelectronic transistors.
- Zhixin Chen
- , Iain M. Grace
- & James O. Thomas
-
Review Article |
 Engineering colloidal semiconductor nanocrystals for quantum information processing
Engineering colloidal semiconductor nanocrystals for quantum information processing
This Review highlights the current potential for colloidal quantum dots for applications in quantum sensing and quantum circuits.
- Jawaher Almutlaq
- , Yuan Liu
- & Edward H. Sargent
-
Article |
 Engineering interfacial polarization switching in van der Waals multilayers
Engineering interfacial polarization switching in van der Waals multilayers
Operando transmission electron microscopy imaging reveals that modifying interlayer rotations alters both the spatial arrangement and switching dynamics of polar domains in artificially stacked trilayers of WSe2.
- Madeline Van Winkle
- , Nikita Dowlatshahi
- & D. Kwabena Bediako
-
Article |
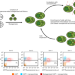 Genome-wide forward genetic screening to identify receptors and proteins mediating nanoparticle uptake and intracellular processing
Genome-wide forward genetic screening to identify receptors and proteins mediating nanoparticle uptake and intracellular processing
Understanding how cells process nanoparticles is crucial to improve nanomedicine efficacy. Here a genome-wide screening is used to discover proteins that are involved in silica nanoparticle accumulation by cells and shows that different apolipoprotein receptors and proteoglycans mediate their internalization.
- Daphne Montizaan
- , Roberta Bartucci
- & Anna Salvati
-
Article
| Open Access Machine intelligence-accelerated discovery of all-natural plastic substitutes
Machine intelligence-accelerated discovery of all-natural plastic substitutes
An integrated workflow that uses robotics and machine learning to discover all-natural plastic substitutes with programmable properties is presented.
- Tianle Chen
- , Zhenqian Pang
- & Po-Yen Chen
-
Article |
 Regulation of quantum spin conversions in a single molecular radical
Regulation of quantum spin conversions in a single molecular radical
The characterization and tuning of free radicals at the single molecule level is a challenging endeavour. Here electrical conductance measurements of a single molecule sandwiched between nanogapped graphene electrodes via covalent amide bonds reveal the conversion between closed-shell and open-shell form with temperature, electric and magnetic field in real time.
- Caiyao Yang
- , Zhongxin Chen
- & Xuefeng Guo
-
Review Article |
 Ultrahigh-quality-factor micro- and nanomechanical resonators using dissipation dilution
Ultrahigh-quality-factor micro- and nanomechanical resonators using dissipation dilution
This Review discusses advances in engineering high-quality-factor strained nanomechanical resonators with applications in precision measurements.
- Nils Johan Engelsen
- , Alberto Beccari
- & Tobias Jan Kippenberg
-
Article |
 Van der Waals quaternary oxides for tunable low-loss anisotropic polaritonics
Van der Waals quaternary oxides for tunable low-loss anisotropic polaritonics
Tellurite molybdenum quaternary oxides, a family of van der Waals materials, show slow group velocity and long lifetimes with promising implications for tunable low-loss anisotropic polaritonics.
- Tian Sun
- , Runkun Chen
- & Peining Li
-
Article |
 Complete miscibility of immiscible elements at the nanometre scale
Complete miscibility of immiscible elements at the nanometre scale
Nanoparticles containing immiscible elements can be synthesized under certain experimental conditions.
- Peng-Cheng Chen
- , Mengyu Gao
- & Peidong Yang
-
Article
| Open Access A charge-dependent long-ranged force drives tailored assembly of matter in solution
A charge-dependent long-ranged force drives tailored assembly of matter in solution
In contrast to textbook expectations, experimental findings show that, in certain situations, like-charged particles may either repel or attract each other depending on the sign of their charge and on the solvent.
- Sida Wang
- , Rowan Walker-Gibbons
- & Madhavi Krishnan
-
Research Briefing |
 Fabrication of mechanochromic gallium nanostructures by capillary interactions
Fabrication of mechanochromic gallium nanostructures by capillary interactions
A process that leverages capillary interactions between oligomers in an elastomeric polydimethylsiloxane substrate and deposited Ga enables the formation of Ga nanodroplets with nanoscale gaps in a single step. Gap-plasmon resonances excited within the nanogaps give rise to structural colours that can be tuned by changing the oligomer content in the substrate or by mechanical stretching.
-
Research Briefing |
 Photo-induced chemistry with sub-molecular resolution
Photo-induced chemistry with sub-molecular resolution
By confining and concentrating light in a nanometric volume at the apex of a metallic tip, sub-molecule-scale control of a basic photochemical reaction — phototautomerization — is now shown to be possible. Applicable to other photo-induced reactions, this technique signals a new strategy for the synthesis of complex molecules on surfaces.
-
Article |
 Submolecular-scale control of phototautomerization
Submolecular-scale control of phototautomerization
Weak laser light confined at the apex of a scanning tunnelling microscope tip can drive the tautomerization of a free-base phthalocyanine with atomic-scale precision. The combination of tip-enhanced photoluminescence spectroscopy and hyperspectral mapping paired with theoretical modelling then unravel an excited-state mediated reaction.
- Anna Rosławska
- , Katharina Kaiser
- & Guillaume Schull
-
Article |
 Functional analysis of single enzymes combining programmable molecular circuits with droplet-based microfluidics
Functional analysis of single enzymes combining programmable molecular circuits with droplet-based microfluidics
Integrating droplet-based microfluidics with a modular DNA circuit, here the authors report on monitoring the amplification reaction from single enzyme molecules in real time, revealing the distribution of activity among the catalyst population and alternative inactivation pathways under various stresses.
- Guillaume Gines
- , Rocίo Espada
- & Yannick Rondelez
-
Article
| Open Access Single-step fabrication of liquid gallium nanoparticles via capillary interaction for dynamic structural colours
Single-step fabrication of liquid gallium nanoparticles via capillary interaction for dynamic structural colours
Exploiting capillary interactions of oligomers in polydimethylsiloxane and Ga allows single-step formation of closely spaced Ga nanodroplets in which gap plasmon resonances lead to mechanoresponsive structural colours, bypassing multiple chemical or lithographic steps.
- Renu Raman Sahu
- , Alwar Samy Ramasamy
- & Tapajyoti Das Gupta
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanical stimulation and electrophysiological monitoring at subcellular resolution reveals differential mechanosensation of neurons within networks
Mechanical stimulation and electrophysiological monitoring at subcellular resolution reveals differential mechanosensation of neurons within networks
Here, the authors combined and synchronized single-cell nanoindentation, electrophysiology and functional fluorescence imaging to evaluate the responses of neuronal networks to mechanical stimuli with piconewton force sensitivity and nanometre precision, enabling the exploration of nanomechanobiology and manipulation of neuronal systems.
- Krishna Chaitanya Kasuba
- , Alessio Paolo Buccino
- & Daniel J. Müller
-
Article |
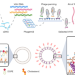 Chimeric nanobody-decorated liposomes by self-assembly
Chimeric nanobody-decorated liposomes by self-assembly
Manufacturing complexities, low yield and stability issues have hampered the clinical translation and scaling-up of immunoliposomes to meet the needs of pharmaceutical-grade products. The authors propose a one-step method of incorporating chimeric nanobodies tagged to hydrophobic linkers into liposomes, allowing targeted delivery of small-molecule anti-cancer drugs to tumours.
- Md. Mofizur Rahman
- , Jing Wang
- & Yuan Wan
-
Article |
 Developing high-power Li||S batteries via transition metal/carbon nanocomposite electrocatalyst engineering
Developing high-power Li||S batteries via transition metal/carbon nanocomposite electrocatalyst engineering
A transition metal/carbon nanocomposite material has been designed for positive electrodes in Li||S batteries. It enables Li||S batteries to be fast charged–discharged in <5 min, which represents a breakthrough in the development of high-power Li||S batteries.
- Huan Li
- , Rongwei Meng
- & Shi-Zhang Qiao
-
Article
| Open Access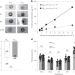 Cellular uptake and in vivo distribution of mesenchymal-stem-cell-derived extracellular vesicles are protein corona dependent
Cellular uptake and in vivo distribution of mesenchymal-stem-cell-derived extracellular vesicles are protein corona dependent
In regenerative medicine, stem-cell-derived extracellular vesicles are emerging as cell-free nanotherapeutics. Here, the authors show that coating these nanovesicles with blood proteins such as albumin improves their uptake by liver cells, offering a better treatment strategy for liver diseases.
- Revadee Liam-Or
- , Farid N. Faruqu
- & Khuloud T. Al-Jamal
-
Article |
 A non-FRET DNA reporter that changes fluorescence colour upon nuclease digestion
A non-FRET DNA reporter that changes fluorescence colour upon nuclease digestion
Here the authors present a non-FRET DNA-templated silver nanocluster probe that exhibits a distinct colour switch from green to red upon nuclease digestion, visible under UV excitation, offering a low-cost, effective alternative to fluorescent reporters for detecting nuclease activities.
- Soonwoo Hong
- , Jada N. Walker
- & Hsin-Chih Yeh
-
Article |
 Full-length single-molecule protein fingerprinting
Full-length single-molecule protein fingerprinting
Distinguishing proteoforms and post-translational modifications has remained a challenge. Here the authors explore single-molecule fluorescence resonance energy transfer to probe amino acids via DNA exchange and map the location of individual amino acids and post-translational modifications within single full-length protein molecules.
- Mike Filius
- , Raman van Wee
- & Chirlmin Joo
-
Comment |
 My cell is better than yours
My cell is better than yours
Scientists encounter pressure to validate their research work, leading to varied benchmarks and methods for performance assessment in the broad energy research field. Interlaboratory studies help highlight discrepancies in reported figures of merit, underscoring the need for standardized protocols, transparent reporting, and detailed analysis for fair comparisons. Here, we discuss this topic, focusing on battery materials.
- Nella M. Vargas-Barbosa
-
Research Briefing |
 Spinning nanomotor with a DNA clutch
Spinning nanomotor with a DNA clutch
An encodable DNA clutch with the ability to recognize microenvironmental molecular inputs intelligently complements the remote control of a 200-nm sized magnetic nanomachine. This nanomachine interacts with biological machinery in vitro when the encoded clutch selectively engages the engine with the rotor while external magnetic fields power the rotation.
-
Research Briefing |
 High-fidelity initialization and control of multiple nuclear spin qubits in silicon
High-fidelity initialization and control of multiple nuclear spin qubits in silicon
A robust initialization protocol has been demonstrated for a four-qubit nuclear spin register in silicon. The protocol, driven electrically through electric-dipole spin resonance, enables high-fidelity qubit control and hence a route to a register-based quantum computer that exploits the exceptional coherence properties of atom qubits in silicon.
-
-
Article
| Open Access High-fidelity initialization and control of electron and nuclear spins in a four-qubit register
High-fidelity initialization and control of electron and nuclear spins in a four-qubit register
An electric dipole spin resonance protocol making use of hyperfine interaction enacts high-fidelity initialization of a four-qubit nuclear spin register in silicon. This protocol allows for high-fidelity qubit control and a path towards a register-based quantum computer using the exceptional coherence properties of donors in silicon.
- J. Reiner
- , Y. Chung
- & M. Y. Simmons
-
Article |
 A magnetically powered nanomachine with a DNA clutch
A magnetically powered nanomachine with a DNA clutch
The nanospace confinement of a magnetic nanoparticle within a porous cage, coupled with an encodable DNA clutch interface, enables a remotely powered and controlled rotary nanomotor that is autoresponsive to its microenvironment.
- Mouhong Lin
- , Jung-uk Lee
- & Jinwoo Cheon
-
News & Views |
 An optical imager that can compute
An optical imager that can compute
An intelligent meta-imager can perform multi-channel convolutions to accelerate machine vision for incoherent light.
- Zheng Huang
- & Hongwei Chen
-
Comment |
 How nanoparticles are counted in global regulatory nanomaterial definitions
How nanoparticles are counted in global regulatory nanomaterial definitions
The legal definition of a nanomaterial differs around the world, meaning that the same material may be classified as a nanomaterial, or not, depending on the country where it is classified. The first steps towards converging on an international definition are to recognize the differences between existing nanomaterial definitions and to agree on particle counting methods. Meanwhile, we propose a naming convention that indicates the key criteria of a specific definition of a nanomaterial.
- Kirsten Rasmussen
- , Juan Riego Sintes
- & Hubert Rauscher
-
Article |
 Coherent electronic coupling in quantum dot solids induces cooperative enhancement of nonlinear optoelectronic responses
Coherent electronic coupling in quantum dot solids induces cooperative enhancement of nonlinear optoelectronic responses
Synchronized dynamics of quantum dot ensembles are essential for the generation of giant optical responses. To this end, coherent electronic coupling in quantum dot solids induces cooperative enhancement of nonlinear optoelectronic responses.
- Hirokazu Tahara
- , Masanori Sakamoto
- & Yoshihiko Kanemitsu

 Tuning light by the vibes
Tuning light by the vibes Roeland Nolte (1944–2024)
Roeland Nolte (1944–2024) Ian Manners (1961–2023)
Ian Manners (1961–2023)