Featured
-
-
Article |
 Photochemical single-step synthesis of β-amino acid derivatives from alkenes and (hetero)arenes
Photochemical single-step synthesis of β-amino acid derivatives from alkenes and (hetero)arenes
The majority of methods to prepare β-amino acid derivatives require metal-mediated multistep manipulations of pre-functionalized substrates. Now, a metal-free, energy-transfer enabled, highly regioselective aminocarboxylation reaction has been developed, for the single-step installation of both amine and ester functionalities into alkenes or (hetero)arenes. An oxime oxalate ester is used as a bifunctional reagent, supplying C-centred ester and N-centred iminyl radicals.
- Guangying Tan
- , Mowpriya Das
- & Frank Glorius
-
News & Views |
 Warhead assembly in a lethal pathogen
Warhead assembly in a lethal pathogen
Malleicyprols are highly reactive polyketides responsible for virulence in some pathogenic bacteria. Now, the enzyme that constructs the cyclopropanol warhead of malleicyprols has been identified. This enzyme could represent a useful target for developing new antivirulence therapeutics.
- Elijah Abraham
- & Rebecca A. Butcher
-
News & Views |
 Radical ring formation
Radical ring formation
N-heterocycles are valuable motifs in pharmaceuticals and materials, but divergent synthetic strategies are lacking. Now, bifunctional sulfilimines have been shown to form nitrogen-centred radicals under photocatalytic conditions, and subsequent coupling with olefins enables the synthesis of diverse N-heterocycles.
- Prabagar Baskaran
- & Wei Li
-
Article
| Open Access Bifunctional sulfilimines enable synthesis of multiple N-heterocycles from alkenes
Bifunctional sulfilimines enable synthesis of multiple N-heterocycles from alkenes
Intermolecular cyclization reactions using nitrogen-containing building blocks are scarce. Now, bifunctional sulfilimines have been shown to enable the modular construction of a diverse range of N-heterocycles by reacting with alkenes in a single photocatalysed step. Both sulfilimines and alkenes are easily accessible, providing access to a wide range of N-heterocycles with different ring types, ring sizes and substituents on the skeleton.
- Qiang Cheng
- , Zibo Bai
- & Tobias Ritter
-
Article |
 Chemoenzymatic synthesis of fluorinated polyketides
Chemoenzymatic synthesis of fluorinated polyketides
The introduction of fluorine into a drug molecule can alter the biological responses to it, including modulating bioavailability, pharmacokinetics and selectivity. Now, a hybrid polyketide/fatty acid synthase multienzyme has been designed to incorporate fluorinated precursors during polyketide biosynthesis in an approach that provides new chemoenzymatic access to fluorinated natural compounds.
- Alexander Rittner
- , Mirko Joppe
- & Martin Grininger
-
News & Views |
 N2O revalorization
N2O revalorization
Nitrous oxide is traditionally considered to be an inert molecule, and methods for its activation and utilization are currently limited. Now, a strategy has been developed — involving an organometallic Baeyer–Villiger step — for the conversion of aryl halides to phenols under mild conditions, using N2O as the oxygen source.
- Jun-Jie Chen
- & Huan-Ming Huang
-
Article |
 Tunable and recyclable polyesters from CO2 and butadiene
Tunable and recyclable polyesters from CO2 and butadiene
The direct copolymerization of carbon dioxide and commodity olefins has been a long-standing challenge in polymer science. Now, an indirect approach has been developed in which hydrogenated disubstituted valerolactones derived from telomerization of CO2 and butadiene can undergo ring-opening polymerization, yielding chemically recyclable and degradable aliphatic polyesters with high CO2 content.
- Rachel M. Rapagnani
- , Rachel J. Dunscomb
- & Ian A. Tonks
-
Article |
 Nickel-catalysed asymmetric hydrogenation of oximes
Nickel-catalysed asymmetric hydrogenation of oximes
The asymmetric hydrogenation of oximes to chiral hydroxylamines is a long-standing challenge because of the labile N–O bond and inert C=N bond. Now, it has been shown that this reaction can be catalysed with a chiral nickel complex, and the weak interactions between catalyst and substrate are found to play a crucial role.
- Bowen Li
- , Jianzhong Chen
- & Wanbin Zhang
-
Article |
 Selective visible-light photocatalysis of acetylene to ethylene using a cobalt molecular catalyst and water as a proton source
Selective visible-light photocatalysis of acetylene to ethylene using a cobalt molecular catalyst and water as a proton source
The acetylene contaminant present in ethylene feeds used to produce polymers is typically removed by thermal hydrogenation. Now, it has been shown that the conversion of acetylene to ethylene at room temperature can be achieved in a visible-light-driven process using an earth-abundant metal (cobalt) catalyst and a water proton source.
- Francesca Arcudi
- , Luka Ðorđević
- & Emily A. Weiss
-
In Your Element |
 The fruit fly of photophysics
The fruit fly of photophysics
The tris(2,2′-bipyridine)ruthenium(II) cation, or ‘rubipy’ to its friends, has had a significant influence on our understanding of the photophysics of transition metal complexes, and has also helped revolutionize organic photochemistry, explains Daniela M. Arias-Rotondo.
- Daniela M. Arias-Rotondo
-
News & Views |
 Trisubstituted triumph
Trisubstituted triumph
Trisubstituted macrocyclic alkenes are prominent moieties in natural products, and although ring-closing metathesis reactions can be used to access such targets, the yields are typically suboptimal and the stereochemical outcome is unpredictable. Now, a methodology has been developed that tackles both of these challenges.
- Damian W. Young
- & Srinivas Chamakuri
-
News & Views |
 Complex networks at life’s origins
Complex networks at life’s origins
Explaining the controlled emergence and growth of molecular complexity at life’s origins is one of prebiotic chemistry’s grand challenges. Now, it has been shown that we can observe how the self-organization of a complex carbohydrate network can be modulated by its environment.
- Quentin Dherbassy
- & Kamila B. Muchowska
-
Article |
 Low-temperature liquid platinum catalyst
Low-temperature liquid platinum catalyst
The cost-effective use of platinum as a catalyst has led to an evolving set of systems ranging from nanoparticles to single atoms on a variety of solid supports. It has now been shown that the dissolution of platinum atoms in a liquid gallium matrix generates a liquid catalyst that functions at low temperature with high activity.
- Md. Arifur Rahim
- , Jianbo Tang
- & Kourosh Kalantar-Zadeh
-
News & Views |
 Tungsten’s tandem transformation
Tungsten’s tandem transformation
Being able to run two reactions concurrently enables synthetic methods to be streamlined, but simultaneously controlling the selectivity of both reactions is an enormous challenge. Now, a directing group is used to reinvent a classic tandem reaction, activating specific sp3 C–H bonds with pinpoint accuracy.
- Sarah E. Jenny
- & Graham E. Dobereiner
-
Article |
 Low-valent tungsten redox catalysis enables controlled isomerization and carbonylative functionalization of alkenes
Low-valent tungsten redox catalysis enables controlled isomerization and carbonylative functionalization of alkenes
The regioselectivity of tandem isomerization/hydrocarbonylation reactions is typically dictated by thermodynamics and there are limitations on the isomerization of internal alkenes. Now, it has been shown that a low-valent-tungsten catalyst controls the isomerization of alkenes to classically challenging unactivated internal positions and, with the aid of a directing group, enables subsequent addition of hydrogen and carbon monoxide.
- Tanner C. Jankins
- , William C. Bell
- & Keary M. Engle
-
Article |
 Mechanism-based ligand design for copper-catalysed enantioconvergent C(sp3)–C(sp) cross-coupling of tertiary electrophiles with alkynes
Mechanism-based ligand design for copper-catalysed enantioconvergent C(sp3)–C(sp) cross-coupling of tertiary electrophiles with alkynes
A general copper-catalysed enantioconvergent C(sp3)–C(sp) cross-coupling of diverse racemic tertiary alkyl halides with terminal alkynes has been developed, forging all-carbon quaternary stereocentres. Key to the success is the rational design of chiral anionic N,N,N-ligands tailor-made for the computationally predicted outer-sphere radical group transfer pathway.
- Fu-Li Wang
- , Chang-Jiang Yang
- & Xin-Yuan Liu
-
Article |
 E- and Z-trisubstituted macrocyclic alkenes for natural product synthesis and skeletal editing
E- and Z-trisubstituted macrocyclic alkenes for natural product synthesis and skeletal editing
Many bioactive compounds are trisubstituted macrocyclic alkenes, but use of current methods often results in poor yields and low stereoselectivity. Now, a ring-closing metathesis strategy has been developed that enables these compounds to be prepared efficiently and in either stereoisomeric form: an approach that may prove useful in the late stages of total syntheses, for skeletal editing and in drug discovery.
- Yucheng Mu
- , Felix W. W. Hartrampf
- & Amir H. Hoveyda
-
News & Views |
 Catalytic site seeing
Catalytic site seeing
Understanding how surface structure affects catalyst selectivity is limited by the ability to synthesize atomically precise active-site ensembles. Now, by using intermetallic Pd–Zn, a series of well-defined multinuclear Pd–metal–Pd catalytic sites have been generated and studied, providing insights into their selectivity for the semi-hydrogenation of acetylene.
- Max Mortensen
- & Siris Laursen
-
Review Article |
 Multistep enzyme cascades as a route towards green and sustainable pharmaceutical syntheses
Multistep enzyme cascades as a route towards green and sustainable pharmaceutical syntheses
Enzymes, either purified or as whole-cell biocatalysts, can be concatenated into catalytic cascades and used to produce pharmaceutically relevant molecules. This Review discusses the advantages and requirements of multistep enzyme cascades and also highlights how they can be harnessed to achieve highly sustainable and cost-efficient syntheses.
- Ana I. Benítez-Mateos
- , David Roura Padrosa
- & Francesca Paradisi
-
Article |
 A two-directional vibrational probe reveals different electric field orientations in solution and an enzyme active site
A two-directional vibrational probe reveals different electric field orientations in solution and an enzyme active site
Preorganized electric fields may be essential for the extraordinary catalytic power of enzymes. Now, it has been demonstrated how electric field strengths can be monitored along two directions using a vibrational Stark probe, enabling the observation of distinct electric field orientations in an enzyme active site compared with those in simple solvents.
- Chu Zheng
- , Yuezhi Mao
- & Steven G. Boxer
-
Article |
 Binding methane to a metal centre
Binding methane to a metal centre
Catalytic transformations of methane frequently involve the formation of a metal–methane complex, but these compounds are challenging to observe. Now, a relatively long-lived osmium–methane complex has been characterized using NMR spectroscopy and forms from the direct binding of methane to a photolytically generated, coordinatively unsaturated cationic osmium–carbonyl complex dissolved in an inert hydrofluorocarbon solvent at –90 °C.
- James. D. Watson
- , Leslie. D. Field
- & Graham. E. Ball
-
Article |
 Ion-pair reorganization regulates reactivity in photoredox catalysts
Ion-pair reorganization regulates reactivity in photoredox catalysts
Ion pairing is ubiquitous in low-dielectric-constant solvents, but whether it influences the reactivity of common cationic photoredox catalysts has been unclear. However, it has now been shown that ion pairing is responsible for a 4-fold modulation in reactivity in a prototypical Ir(III) complex and is explained by excited-state ion-pair reorganization.
- J. D. Earley
- , A. Zieleniewska
- & G. Rumbles
-
Article |
 Stereocontrolled 1,3-nitrogen migration to access chiral α-amino acids
Stereocontrolled 1,3-nitrogen migration to access chiral α-amino acids
A straightforward method for synthesizing optically active α-amino acids from abundant carboxylic acids has been developed. Based on a nitrene-mediated stereocontrolled 1,3-nitrogen shift, this approach provides access to a large variety of unnatural α-amino acids with aryl, allyl, propargyl and alkyl side chains and enables late-stage amination of carboxylic-acid-containing drugs.
- Chen-Xi Ye
- , Xiang Shen
- & Eric Meggers
-
Article |
 Cobalt(II)–tetraphenylporphyrin-catalysed carbene transfer from acceptor–acceptor iodonium ylides via N-enolate–carbene radicals
Cobalt(II)–tetraphenylporphyrin-catalysed carbene transfer from acceptor–acceptor iodonium ylides via N-enolate–carbene radicals
Although cobalt–carbene radicals have proved to be highly versatile intermediates for homogeneous catalysis, their spectroscopic detection and characterization have been limited. Now, by using hypervalent iodonium ylides, the formation and spectroscopic detection of a biscarbenoid N-enolate–carbene radical—which undergoes a complex catalytic pathway involving reversible N-enolate formation—has been demonstrated.
- Roel F. J. Epping
- , Mees M. Hoeksma
- & Bas de Bruin
-
Article |
 Reversible C–C bond formation using palladium catalysis
Reversible C–C bond formation using palladium catalysis
Although carbometallation reactions have been thoroughly investigated, understanding the factors responsible for the reverse reaction (β-carbon elimination) is an emerging area of research. Now, a series of substrates has been investigated to study the key factors that promote β-carbon elimination under palladium catalysis.
- Austin D. Marchese
- , Bijan Mirabi
- & Mark Lautens
-
News & Views |
 Sustainable and degradable plastics
Sustainable and degradable plastics
Plastics that are developed from renewable resources and can be recycled are highly environmentally desirable alternatives to current petroleum-based non-degradable polymers. Now, an effective and robust industrially relevant strategy towards high-performance biomass-derived degradable poly(γ-thiobutyrolactone)s has been developed.
- Sophie M. Guillaume
-
Article |
 Fast CO2 hydration kinetics impair heterogeneous but improve enzymatic CO2 reduction catalysis
Fast CO2 hydration kinetics impair heterogeneous but improve enzymatic CO2 reduction catalysis
Carbonic anhydrase enzymatically catalyses CO2 hydration, and its effect on enzymatic and heterogeneous CO2 reduction has now been studied. Through the co-immobilization of carbonic anhydrase, it has been shown that faster CO2 hydration kinetics are beneficial for enzymatic catalysis (using formate dehydrogenase) but detrimental for heterogeneous catalysts, such as gold.
- Samuel J. Cobb
- , Vivek M. Badiani
- & Erwin Reisner
-
Article |
 Stereodefined alkenes with a fluoro-chloro terminus as a uniquely enabling compound class
Stereodefined alkenes with a fluoro-chloro terminus as a uniquely enabling compound class
Stereochemically defined trisubstituted alkenyl fluorides are important compounds for drug discovery, agrochemical development and materials science, but their preparation is challenging. Now, a practical and widely applicable catalytic strategy enables access to a large assortment of olefins bearing a fluoro-chloro terminus. Subsequent cross-coupling generates the corresponding trisubstituted alkenyl fluorides.
- Qinghe Liu
- , Yucheng Mu
- & Amir H. Hoveyda
-
Article |
 Atomic control of active-site ensembles in ordered alloys to enhance hydrogenation selectivity
Atomic control of active-site ensembles in ordered alloys to enhance hydrogenation selectivity
Advances in the design of heterogeneous catalysts are limited by our ability to synthesize atomically precise active-site ensembles. Now, the controlled synthesis of Pd–M–Pd catalytic sites (M = Zn, Pd, Cu, Ag and Au) has been demonstrated. Stoichiometric control identifies that Pd–Pd–Pd sites are active for ethylene hydrogenation, whereas Pd–Zn–Pd sites are not.
- Anish Dasgupta
- , Haoran He
- & Robert M. Rioux
-
News & Views |
 Building enzymes from scratch
Building enzymes from scratch
Combining computational design with directed evolution has the potential to deliver enzymes with new functions, yet so far de novo catalysts have been limited to a handful of model transformations. Now, a primitive computationally designed enzyme has been remodelled into an efficient enantioselective catalyst for the Morita–Baylis–Hillman reaction.
- Elaine O’Reilly
-
Article |
 Catalytic remote hydrohalogenation of internal alkenes
Catalytic remote hydrohalogenation of internal alkenes
The hydrohalogenation of alkenes generally forms branched alkyl halides. Now, a palladium-catalysed method has been developed for the remote hydrohalogenation of internal and terminal alkenes, enabling the efficient synthesis of linear alkyl halides. The method uses an engineered Pyox ligand with a hydroxy group, which is essential for accelerating the oxidative halogenation.
- Xiang Li
- , Jianbo Jin
- & Guosheng Liu
-
Article |
 A photosensitizer–polyoxometalate dyad that enables the decoupling of light and dark reactions for delayed on-demand solar hydrogen production
A photosensitizer–polyoxometalate dyad that enables the decoupling of light and dark reactions for delayed on-demand solar hydrogen production
Decoupling the processes of light harvesting and catalytic hydrogen evolution could be a potentially important step in storing solar energy. This has now been achieved with a single molecular unit: a light-harvesting ruthenium complex–polyoxometalate dyad that absorbs light, separates and stores charge and then generates hydrogen on demand following the addition of a proton donor.
- Sebastian Amthor
- , Sebastian Knoll
- & Carsten Streb
-
Article
| Open Access Scalable and selective deuteration of (hetero)arenes
Scalable and selective deuteration of (hetero)arenes
A method for the selective deuteration of anilines, indoles, phenols and heterocyclic compounds, including natural products and other bioactive molecules, has been developed. The nanostructured iron catalyst that underpins this process is prepared by combining cellulose with iron salts and has been used for the preparation of deuterated compounds on up to a kilogram scale.
- Wu Li
- , Jabor Rabeah
- & Matthias Beller
-
Article |
 Engineering an efficient and enantioselective enzyme for the Morita–Baylis–Hillman reaction
Engineering an efficient and enantioselective enzyme for the Morita–Baylis–Hillman reaction
Directed evolution of a primitive computationally designed enzyme has produced an efficient and enantioselective biocatalyst for the Morita–Baylis–Hillman reaction. The engineered enzyme uses a designed histidine nucleophile operating in synergy with a catalytic arginine that emerged during evolution and serves as a genetically encoded surrogate of privileged bidentate hydrogen-bonding catalysts.
- Rebecca Crawshaw
- , Amy E. Crossley
- & Anthony P. Green
-
Article |
 Arene radiofluorination enabled by photoredox-mediated halide interconversion
Arene radiofluorination enabled by photoredox-mediated halide interconversion
A photoredox-mediated SNAr reaction has now been developed for the direct radiofluorination of unactivated aryl halides. A series of arenes can be radiofluorinated in a site-selective manner from readily available aryl halide precursors under mild conditions. This strategy allows efficient 19F/18F isotopic exchange, enabling rapid PET probe diversification and clinical tracer preparation.
- Wei Chen
- , Hui Wang
- & Zibo Li
-
Article |
 Directing-group-free catalytic dicarbofunctionalization of unactivated alkenes
Directing-group-free catalytic dicarbofunctionalization of unactivated alkenes
Without directing auxiliaries, the addition of carbogenic groups to unactivated alkenes is typically inefficient and suffers from poor regioselectivity. Now, a directing-group-free, nickel catalyst-controlled strategy has been developed, enabling the site-selective dicarbofunctionalization of a broad array of activated and unactivated alkenes.
- Hongyu Wang
- , Chen-Fei Liu
- & Ming Joo Koh
-
News & Views |
 Two steps to sustainable polymers
Two steps to sustainable polymers
Medium-chain linear α-olefins are commodity chemicals; however, manufacturing α-olefins from biomass is challenging due to inefficient removal of the last oxygen atoms. Now, a two-step biological–chemical catalysis strategy to produce medium-chain linear α-olefins provides a route to sustainable polymers.
- Shaafique Chowdhury
- & Pamela Peralta-Yahya
-
Article |
 A dual cellular–heterogeneous catalyst strategy for the production of olefins from glucose
A dual cellular–heterogeneous catalyst strategy for the production of olefins from glucose
A dual cellular-then-heterogeneous catalysis strategy has been used to produce olefins from glucose. 3-Hydroxy acids are made using an engineered microbial host. A hydrolytic step then provides the driving force for fatty acid deoxygenation by simple heterogeneous Lewis acid catalysis. This decarboxylation–dehydration route to olefinic products avoids the need for an additional redox input typically required for deoxygenation of unmodified fatty acids.
- Zhen Q. Wang
- , Heng Song
- & Michelle C. Y. Chang
-
Article |
 Spontaneous N2 formation by a diruthenium complex enables electrocatalytic and aerobic oxidation of ammonia
Spontaneous N2 formation by a diruthenium complex enables electrocatalytic and aerobic oxidation of ammonia
The use of ammonia as an alternative fuel relies on its electrochemical conversion to dinitrogen in a fuel cell. Now a stable metal–metal bonded diruthenium complex is shown to spontaneously produce dinitrogen from ammonia under ambient conditions and is also able to electrocatalyse the oxidation of ammonia to dinitrogen at low potentials.
- Michael J. Trenerry
- , Christian M. Wallen
- & John F. Berry
-
Article |
 Visible light-driven conjunctive olefination
Visible light-driven conjunctive olefination
A conjunctive olefination between aldehydes and carboxylic acids has been developed by merging photoredox catalysis with the Wittig reaction. The process uses a readily available phosphonium salt to join together complex molecular fragments with high functional group tolerance and minimal use of protecting groups, enabling access to coupling products with user-defined geometries.
- Dario Filippini
- & Mattia Silvi
-
Article |
 Dual-function enzyme catalysis for enantioselective carbon–nitrogen bond formation
Dual-function enzyme catalysis for enantioselective carbon–nitrogen bond formation
A haem protein that serves as a dual-function catalyst capable of inserting a carbene into a N–H bond to form α-amino lactones has been reported. The enzyme catalyses both carbene transfer and the subsequent proton transfer in a single active site. This transformation can proceed at the gram scale with high efficiency and enantioselective control.
- Zhen Liu
- , Carla Calvó-Tusell
- & Frances H. Arnold
-
Article |
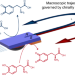 Direct dynamic read-out of molecular chirality with autonomous enzyme-driven swimmers
Direct dynamic read-out of molecular chirality with autonomous enzyme-driven swimmers
Self-propelled artificial chemical swimmers have previously been developed for chemical sensing. Now, hybrid bioelectrochemical swimmers, capable of translating chiral molecular information into macroscopic motion, have been developed. Diastereomeric interactions between enantiopure oligomers immobilized on the swimmer and a chiral molecule present in solution control the trajectory of the device.
- Serena Arnaboldi
- , Gerardo Salinas
- & Alexander Kuhn
-
Article |
 Unnatural biosynthesis by an engineered microorganism with heterologously expressed natural enzymes and an artificial metalloenzyme
Unnatural biosynthesis by an engineered microorganism with heterologously expressed natural enzymes and an artificial metalloenzyme
Natural products are produced by living organisms practising nature’s chemical transformations. Now, an unnatural product has been generated by creating hybrid biosynthetic microorganisms. These microorganisms combine an unnatural chemical transformation—catalysis by an artificial metalloenzyme containing an iridium-based, unnatural cofactor—with a natural biosynthetic pathway within the same cell.
- Jing Huang
- , Zhennan Liu
- & John F. Hartwig
-
Article |
 A directive Ni catalyst overrides conventional site selectivity in pyridine C–H alkenylation
A directive Ni catalyst overrides conventional site selectivity in pyridine C–H alkenylation
Selective C–H alkenylation of pyridines at the C3 position, with the pyridine as the limiting reagent, is a long-standing synthetic challenge. Now, it has been shown that this can be achieved using a bifunctional N-heterocyclic carbene-ligated Ni–Al catalyst that overrides the intrinsic C2/4 selectivity of pyridines and enables the selective late-stage functionalization of a range of complex pyridyl-containing motifs.
- Tao Zhang
- , Yu-Xin Luan
- & Jin-Quan Yu
-
Article |
 Asymmetric dearomatization catalysed by chiral Brønsted acids via activation of ynamides
Asymmetric dearomatization catalysed by chiral Brønsted acids via activation of ynamides
Chiral Brønsted acid catalysis is mostly limited to the activation of imine and carbonyl moieties. Now, by direct activation of alkynes, chiral Brønsted acids have been used to enable the catalytic asymmetric dearomatization of naphthol-, phenol- and pyrrole-ynamides for the construction of various spirocyclic enones and 2H-pyrroles bearing a chiral quaternary carbon stereocentre.
- Ying-Qi Zhang
- , Yang-Bo Chen
- & Long-Wu Ye
-
Article |
 A short peptide synthon for liquid–liquid phase separation
A short peptide synthon for liquid–liquid phase separation
Liquid–liquid phase separation plays an important role in creating cellular compartments and protocells, but designing small-molecule models remains difficult. A peptide-based synthon for liquid–liquid phase separation consisting of two stickers and a flexible, polar spacer has now been presented. Condensates formed by these synthons can concentrate biomolecules and catalyse anabolic reactions.
- Manzar Abbas
- , Wojciech P. Lipiński
- & Evan Spruijt
-
-
Article |
 Evolution of dynamical networks enhances catalysis in a designer enzyme
Evolution of dynamical networks enhances catalysis in a designer enzyme
Computationally designed enzymes can be substantially improved by directed evolution. Now, it has been shown that evolution can introduce a dynamic network that selectively tightens the transition-state ensemble, giving rise to a negative activation heat capacity. Targeting such transition state conformational dynamics may expedite de novo enzyme creation.
- H. Adrian Bunzel
- , J. L. Ross Anderson
- & Adrian J. Mulholland
-
News & Views |
 Mastering mono-bond metathesis
Mastering mono-bond metathesis
Carbon–carbon single bonds are generally among the least reactive chemical bonds. While olefin metathesis reactions are well established, direct metathesis of C–C single bonds is rare. Now, a C–C single bond metathesis reaction has been developed, forming cross-biaryl products from unstrained homo-biaryl compounds.
- Michael M. Gilbert
- & Daniel J. Weix

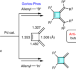 Palladium-catalysed construction of butafulvenes
Palladium-catalysed construction of butafulvenes Deconvoluting double layers
Deconvoluting double layers