In Your Element |
Featured
-
-
Article |
 Modular chemoenzymatic synthesis of ten fusicoccane diterpenoids
Modular chemoenzymatic synthesis of ten fusicoccane diterpenoids
Fusicoccane diterpenoids are complex natural products with intricate tricyclic skeletons and intriguing biological activities. Now a chemoenzymatic strategy has been developed for modularly synthesizing a number of compounds from the family. This approach combines de novo skeletal construction and hybrid C–H oxidations, allowing the synthesis of ten different natural products.
- Yanlong Jiang
- & Hans Renata
-
Article |
 Stereodivergent photobiocatalytic radical cyclization through the repurposing and directed evolution of fatty acid photodecarboxylases
Stereodivergent photobiocatalytic radical cyclization through the repurposing and directed evolution of fatty acid photodecarboxylases
Despite their intriguing photochemical activities, natural photoenzymes have not yet been repurposed for new-to-nature activities. Now, by leveraging the strongly oxidizing excited-state flavoquinone cofactor, fatty acid photodecarboxylases were engineered to catalyse unnatural decarboxylative radical cyclization with excellent chemo-, enantio- and diastereoselectivities.
- Shuyun Ju
- , Dian Li
- & Yang Yang
-
Article |
 Biocatalytic strategy for the construction of sp3-rich polycyclic compounds from directed evolution and computational modelling
Biocatalytic strategy for the construction of sp3-rich polycyclic compounds from directed evolution and computational modelling
The use of biocatalysis to support early-stage drug discovery campaigns remains largely untapped. Here, engineered biocatalysts enable the synthesis of sp3-rich polycyclic compounds through an intramolecular cyclopropanation of benzothiophenes, affording a class of complex scaffolds potentially useful for fragment-based drug discovery campaigns.
- David A. Vargas
- , Xinkun Ren
- & Rudi Fasan
-
Article |
 Remote stereocontrol with azaarenes via enzymatic hydrogen atom transfer
Remote stereocontrol with azaarenes via enzymatic hydrogen atom transfer
The inherent rigidity of the azaarene ring structure has made it challenging to achieve remote stereocontrol through asymmetric catalysis on these substrates. Now, through a photoenzymatic process, an ene-reductase system facilitates the production of diverse azaarenes with distant γ-stereocentres, highlighting the potential of biocatalysts for stereoselectivity at remote sites.
- Maolin Li
- , Wesley Harrison
- & Huimin Zhao
-
Article |
 Enhanced active-site electric field accelerates enzyme catalysis
Enhanced active-site electric field accelerates enzyme catalysis
The design and improvement of enzymes based on physical principles remain challenging. Now, the vibrational Stark effect has been used to demonstrate how an electrostatic model can unify the catalytic effects of distinct chemical forces in a quantitative manner and guide the design of enzyme variants that outperform their natural counterpart.
- Chu Zheng
- , Zhe Ji
- & Steven G. Boxer
-
Article
| Open Access Site-specific bioorthogonal protein labelling by tetrazine ligation using endogenous β-amino acid dienophiles
Site-specific bioorthogonal protein labelling by tetrazine ligation using endogenous β-amino acid dienophiles
An enzymatic reaction installs endogenous β-amino acids in proteins with unique reactivity. Now it has been shows that this reaction can be used for site-specific modification with tetrazine dienophiles to introduce labels onto target proteins. Applications include generation of a radiolabel chelator-modified Her2-binding Affibody and intracellular, fluorescently labelled cell division protein FtsZ.
- Daniel Richter
- , Edgars Lakis
- & Jörn Piel
-
Article |
 Tandem intermolecular [4 + 2] cycloadditions are catalysed by glycosylated enzymes for natural product biosynthesis
Tandem intermolecular [4 + 2] cycloadditions are catalysed by glycosylated enzymes for natural product biosynthesis
Two glycosylated enzymes, EupfF and PycR1, have now been characterized and shown to independently catalyse the tandem intermolecular [4 + 2] cycloaddition in the biosynthesis of bistropolone-sesquiterpenes. Through analysis of enzyme–substrate co-crystal structures, together with computational and mutational studies, the origins of their catalytic activity and stereoselectivity were elucidated.
- Jiawang Liu
- , Jiayan Lu
- & Youcai Hu
-
Article |
 Fragmentation and [4 + 3] cycloaddition in sodorifen biosynthesis
Fragmentation and [4 + 3] cycloaddition in sodorifen biosynthesis
The biosynthesis of the methylated sesquiterpene sodorifen, which features a cryptic methylation pattern, has now been studied through extensive labelling experiments and computational chemistry. The methyl group formation is now understood to come from methylene carbons of the substrate farnesyl diphosphate and the absolute configuration of the biosynthetic intermediate presodorifen diphosphate has been revised.
- Houchao Xu
- , Lukas Lauterbach
- & Jeroen S. Dickschat
-
Article |
 Activity-based directed evolution of a membrane editor in mammalian cells
Activity-based directed evolution of a membrane editor in mammalian cells
Cellular membranes contain numerous lipids, and efforts to understand the biological functions of individual lipids demand approaches for controlled modulation of membrane composition in situ. Now, click chemistry-based directed evolution of a microbial phospholipase within mammalian cells affords an editor for optogenetic, targeted modification of phospholipids in cell membranes.
- Reika Tei
- , Saket R. Bagde
- & Jeremy M. Baskin
-
News & Views |
 Selective cycloadditions
Selective cycloadditions
2+2-cycloaddition reactions have long been considered key transformations in the biosynthesis of cyclobutane-containing natural products, but enzymes for these reactions have not yet been identified. Now, a 2+2 cyclase has been discovered, characterized and bioengineered to catalyse cycloadditions with different selectivity.
- Bo Zhang
- & Hui Ming Ge
-
Article |
 A cyclase that catalyses competing 2 + 2 and 4 + 2 cycloadditions
A cyclase that catalyses competing 2 + 2 and 4 + 2 cycloadditions
Cycloaddition reactions are among the most useful reactions in chemical synthesis, but biosynthetic enzymes with 2 + 2 cyclase activity have yet to be observed. Now it is shown that a β-barrel-fold protein catalyses competitive 2 + 2 and 4 + 2 cycloaddition reactions. This protein can be engineered to preferentially produce the exo-2 + 2, exo-4 + 2 or endo-4 + 2 product.
- Hongbo Wang
- , Yike Zou
- & K. N. Houk
-
Article |
 An NmrA-like enzyme-catalysed redox-mediated Diels–Alder cycloaddition with anti-selectivity
An NmrA-like enzyme-catalysed redox-mediated Diels–Alder cycloaddition with anti-selectivity
A Diels–Alderase that catalyses the inherently disfavoured cycloaddition and forms a bicyclo[2.2.2]diazaoctane scaffold with a strict α-anti-selectivity has now been discovered. This Diels–Alderase, called CtdP, is an NmrA-like protein. Isotopic labelling, structural biology and computational studies reveal that the CtdP-catalysed Diels–Alder reaction involves a NADP+/NADPH-dependent redox mechanism.
- Zhiwen Liu
- , Sebastian Rivera
- & Xue Gao
-
Article |
 Using enzymes to tame nitrogen-centred radicals for enantioselective hydroamination
Using enzymes to tame nitrogen-centred radicals for enantioselective hydroamination
Expanding the biocatalysis toolbox for C–N bond formation is of great value. Now, a biocatalytic amination strategy using a new-to-nature mechanism involving nitrogen-centred radicals has been developed. The transformations are enabled by synergistic photoenzymatic catalysis, providing intra- and intermolecular hydroamination products with high yields and levels of enantioselectivity.
- Yuxuan Ye
- , Jingzhe Cao
- & Todd K. Hyster
-
Article |
 Post-translational backbone-acyl shift yields natural product-like peptides bearing hydroxyhydrocarbon units
Post-translational backbone-acyl shift yields natural product-like peptides bearing hydroxyhydrocarbon units
Despite recent advances in engineering of in vitro translation systems, direct ribosomal incorporation of hydroxyhydrocarbon moieties—which can endow peptides with unique biochemical/folding properties—remains challenging. Now, incorporation of translation-compatible azide/hydroxy acids and their post-translational tandem backbone-acyl shifts have enabled in vitro ribosomal synthesis of peptides containing various hydroxyhydrocarbon units.
- Tomohiro Kuroda
- , Yichao Huang
- & Hiroaki Suga
-
News & Views |
 Warhead assembly in a lethal pathogen
Warhead assembly in a lethal pathogen
Malleicyprols are highly reactive polyketides responsible for virulence in some pathogenic bacteria. Now, the enzyme that constructs the cyclopropanol warhead of malleicyprols has been identified. This enzyme could represent a useful target for developing new antivirulence therapeutics.
- Elijah Abraham
- & Rebecca A. Butcher
-
Article |
 Chemoenzymatic synthesis of fluorinated polyketides
Chemoenzymatic synthesis of fluorinated polyketides
The introduction of fluorine into a drug molecule can alter the biological responses to it, including modulating bioavailability, pharmacokinetics and selectivity. Now, a hybrid polyketide/fatty acid synthase multienzyme has been designed to incorporate fluorinated precursors during polyketide biosynthesis in an approach that provides new chemoenzymatic access to fluorinated natural compounds.
- Alexander Rittner
- , Mirko Joppe
- & Martin Grininger
-
Review Article |
 Multistep enzyme cascades as a route towards green and sustainable pharmaceutical syntheses
Multistep enzyme cascades as a route towards green and sustainable pharmaceutical syntheses
Enzymes, either purified or as whole-cell biocatalysts, can be concatenated into catalytic cascades and used to produce pharmaceutically relevant molecules. This Review discusses the advantages and requirements of multistep enzyme cascades and also highlights how they can be harnessed to achieve highly sustainable and cost-efficient syntheses.
- Ana I. Benítez-Mateos
- , David Roura Padrosa
- & Francesca Paradisi
-
News & Views |
 Building enzymes from scratch
Building enzymes from scratch
Combining computational design with directed evolution has the potential to deliver enzymes with new functions, yet so far de novo catalysts have been limited to a handful of model transformations. Now, a primitive computationally designed enzyme has been remodelled into an efficient enantioselective catalyst for the Morita–Baylis–Hillman reaction.
- Elaine O’Reilly
-
Article |
 Engineering an efficient and enantioselective enzyme for the Morita–Baylis–Hillman reaction
Engineering an efficient and enantioselective enzyme for the Morita–Baylis–Hillman reaction
Directed evolution of a primitive computationally designed enzyme has produced an efficient and enantioselective biocatalyst for the Morita–Baylis–Hillman reaction. The engineered enzyme uses a designed histidine nucleophile operating in synergy with a catalytic arginine that emerged during evolution and serves as a genetically encoded surrogate of privileged bidentate hydrogen-bonding catalysts.
- Rebecca Crawshaw
- , Amy E. Crossley
- & Anthony P. Green
-
Article |
 A dual cellular–heterogeneous catalyst strategy for the production of olefins from glucose
A dual cellular–heterogeneous catalyst strategy for the production of olefins from glucose
A dual cellular-then-heterogeneous catalysis strategy has been used to produce olefins from glucose. 3-Hydroxy acids are made using an engineered microbial host. A hydrolytic step then provides the driving force for fatty acid deoxygenation by simple heterogeneous Lewis acid catalysis. This decarboxylation–dehydration route to olefinic products avoids the need for an additional redox input typically required for deoxygenation of unmodified fatty acids.
- Zhen Q. Wang
- , Heng Song
- & Michelle C. Y. Chang
-
Article |
 Dual-function enzyme catalysis for enantioselective carbon–nitrogen bond formation
Dual-function enzyme catalysis for enantioselective carbon–nitrogen bond formation
A haem protein that serves as a dual-function catalyst capable of inserting a carbene into a N–H bond to form α-amino lactones has been reported. The enzyme catalyses both carbene transfer and the subsequent proton transfer in a single active site. This transformation can proceed at the gram scale with high efficiency and enantioselective control.
- Zhen Liu
- , Carla Calvó-Tusell
- & Frances H. Arnold
-
Article |
 Unnatural biosynthesis by an engineered microorganism with heterologously expressed natural enzymes and an artificial metalloenzyme
Unnatural biosynthesis by an engineered microorganism with heterologously expressed natural enzymes and an artificial metalloenzyme
Natural products are produced by living organisms practising nature’s chemical transformations. Now, an unnatural product has been generated by creating hybrid biosynthetic microorganisms. These microorganisms combine an unnatural chemical transformation—catalysis by an artificial metalloenzyme containing an iridium-based, unnatural cofactor—with a natural biosynthetic pathway within the same cell.
- Jing Huang
- , Zhennan Liu
- & John F. Hartwig
-
Article |
 Tracing the incorporation of the “ninth sulfur” into the nitrogenase cofactor precursor with selenite and tellurite
Tracing the incorporation of the “ninth sulfur” into the nitrogenase cofactor precursor with selenite and tellurite
Located in the catalytically important belt region, the ‘ninth sulfur’ of the nitrogenase cofactor has now been shown to be inserted through coordination of sulfite by two cluster iron atoms at a vacant belt site. This is followed by in situ reduction of sulfite to sulfide, which enables the subsequent transfer and functionalization of the cofactor.
- Kazuki Tanifuji
- , Andrew J. Jasniewski
- & Markus W. Ribbe
-
Article |
 Heat flows in rock cracks naturally optimize salt compositions for ribozymes
Heat flows in rock cracks naturally optimize salt compositions for ribozymes
The correct function of ribozymes in a prebiotic world would be dependent on the presence of optimal salt compositions and concentrations. Now, local heat fluxes have been shown to create an ideal salt habitat for ribozyme activity based on geologically plausible salt-leaching processes.
- T. Matreux
- , K. Le Vay
- & C. B. Mast
-
Article |
 Evolution of dynamical networks enhances catalysis in a designer enzyme
Evolution of dynamical networks enhances catalysis in a designer enzyme
Computationally designed enzymes can be substantially improved by directed evolution. Now, it has been shown that evolution can introduce a dynamic network that selectively tightens the transition-state ensemble, giving rise to a negative activation heat capacity. Targeting such transition state conformational dynamics may expedite de novo enzyme creation.
- H. Adrian Bunzel
- , J. L. Ross Anderson
- & Adrian J. Mulholland
-
Article |
 Mechanism of molybdate insertion into pterin-based molybdenum cofactors
Mechanism of molybdate insertion into pterin-based molybdenum cofactors
The molybdenum cofactor (Moco) is found in the active site of numerous enzymes, but the mechanism of molybdate insertion is not clear. Now, the mechanism of the final maturation step, in which adenylated molybdopterin and molybdate are the substrates, has been revealed. X-ray crystallography of an Mo-insertase identified adenylated Moco as an unexpected intermediate in this reaction sequence.
- Corinna Probst
- , Jing Yang
- & Tobias Kruse
-
Article |
 Integrating programmable DNAzymes with electrical readout for rapid and culture-free bacterial detection using a handheld platform
Integrating programmable DNAzymes with electrical readout for rapid and culture-free bacterial detection using a handheld platform
Methods to detect and identify bacteria typically rely on enrichment steps such as bacterial culture and nucleic acid amplification. Now, an assay for detecting bacteria based on a two-channel electrical chip that combines electroactive DNAzymes with an electrochemical readout, has been developed. This assay enables reagentless and culture-free detection of bacteria in clinical samples.
- Richa Pandey
- , Dingran Chang
- & Leyla Soleymani
-
News & Views |
 Hydride surprise
Hydride surprise
Harnessing the unique catalytic properties of enzymes for abiotic reactions is a prized goal that has inspired a variety of approaches in enzyme design and engineering. Now, the transfer hydrogenation of ketones with silanes has been reported, catalysed by a native carbonic anhydrase.
- Hans Martin Senn
-
News & Views |
 Designing in vivo active DNAzymes
Designing in vivo active DNAzymes
The therapeutic applications of DNAzymes are limited because of their low effectiveness in vivo. Now, a promising approach for constructing DNAzymes that show high gene-silencing efficiency in mammalian cells has been developed. This approach incorporates chemical modifications into an existing DNAzyme scaffold.
- Yifei Zhou
- & Chuanzheng Zhou
-
Article |
 Glycine-derived nitronates bifurcate to O-methylation or denitrification in bacteria
Glycine-derived nitronates bifurcate to O-methylation or denitrification in bacteria
O-methyl nitronate is a rare functional group in natural products. Now, the biosynthetic pathway to O-methyl nitronate, which involves O-methylation of a peptidyl carrier protein (PCP)-tethered nitronate, has been revealed. In some bacteria, the same PCP-tethered nitronate is shown to be oxidized by nitronate monooxygenases to provide nitrite and a PCP-tethered glyoxylate.
- Hai-Yan He
- & Katherine S. Ryan
-
Article |
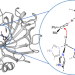 Abiotic reduction of ketones with silanes catalysed by carbonic anhydrase through an enzymatic zinc hydride
Abiotic reduction of ketones with silanes catalysed by carbonic anhydrase through an enzymatic zinc hydride
Enzymatic reactions involving mononuclear metal hydrides are unknown in nature, despite the prevalence of such intermediates in synthetic transition-metal catalysed reactions. Now, it has been shown that zinc-containing carbonic anhydrase enzymes can catalyse hydride transfers from silanes to ketones with high enantioselectivity and there is evidence to support the intermediacy of a mononuclear zinc hydride.
- Pengfei Ji
- , Jeeyoung Park
- & John F. Hartwig
-
Article |
 Efficient Lewis acid catalysis of an abiological reaction in a de novo protein scaffold
Efficient Lewis acid catalysis of an abiological reaction in a de novo protein scaffold
A de novo designed zinc-binding protein has been converted into a highly active, stereoselective catalyst for a hetero-Diels–Alder reaction. Design and directed evolution were used to effectively harness Lewis acid catalysis and create an enzyme more proficient than other reported Diels–Alderases.
- Sophie Basler
- , Sabine Studer
- & Donald Hilvert
-
Article |
 Screening and characterization of a diverse panel of metagenomic imine reductases for biocatalytic reductive amination
Screening and characterization of a diverse panel of metagenomic imine reductases for biocatalytic reductive amination
High-throughput biocatalytic screening and metagenomics have been used to discover over 300 imine reductases (IREDs) and subsequently produce a sequence-diverse panel of IREDs suitable for optimizing the synthesis of chiral amines. Additional characterization identified biocatalysts that accommodate structurally demanding amines and ketones for enzymatic reductive aminations.
- James R. Marshall
- , Peiyuan Yao
- & Nicholas J. Turner
-
News & Views |
 Challenging nature’s preference for methylation
Challenging nature’s preference for methylation
Enzymes that methylate using S-adenosyl-l-methionine — nature’s methyliodide — are abundant and often promiscuous; however, a preference for alkylation over methylation has been neither observed in nature nor engineered. Now, carboxymethylation has been demonstrated using engineered methyltransferases.
- Jennifer N. Andexer
- & Andrea Rentmeister
-
Article |
 Directional conformer exchange in dihydrofolate reductase revealed by single-molecule nanopore recordings
Directional conformer exchange in dihydrofolate reductase revealed by single-molecule nanopore recordings
Single-molecule nanopore measurements have revealed ligand-induced conformational changes in the catalytic cycle of dihydrofolate reductase, and showed that the enzyme adopts distinctive conformers, which have different affinities for substrates and products. Crossing the transition state facilitates conformer exchange, suggesting that the chemical step catalyses the switch between conformers to obtain a more efficient product release.
- Nicole Stéphanie Galenkamp
- , Annemie Biesemans
- & Giovanni Maglia
-
Perspective |
 Proteomimetics as protein-inspired scaffolds with defined tertiary folding patterns
Proteomimetics as protein-inspired scaffolds with defined tertiary folding patterns
The complexity of proteins has inspired chemists to seek artificial mimetics of protein structure and function. Historically, most such work has focused on analogues of small, isolated segments; however, there is growing interest in mimicry of larger, intact tertiary folds. This Perspective surveys the emerging body of work on these agents, termed ‘proteomimetics’, discusses their construction and outlines some of the remaining challenges.
- W. Seth Horne
- & Tom N. Grossmann
-
News & Views |
 A radical approach to diverse meroterpenoids
A radical approach to diverse meroterpenoids
Meroterpenoids are mixed terpenoid–polyketide natural products with a variety of biological activities. Now, a synthetic approach that combines biocatalytic oxidation with a range of other radical-based reactions enables the divergent synthesis of eight oxidized meroterpenoid natural products and one analogue.
- Andrew Gomm
- & Adam Nelson
-
Article |
 Confluence of theory and experiment reveals the catalytic mechanism of the Varkud satellite ribozyme
Confluence of theory and experiment reveals the catalytic mechanism of the Varkud satellite ribozyme
The Varkud satellite ribozyme, which catalyses site-specific RNA cleavage and ligation, is an important model to understand RNA catalysis. Now, a combination of theoretical and experimental work has revealed new details about its catalytic mechanism. Mg2+ is shown to play an important role in organizing the active site, and the proton transfers in the transition state have also been identified.
- Abir Ganguly
- , Benjamin P. Weissman
- & Darrin M. York
-
Article |
 Merging chemoenzymatic and radical-based retrosynthetic logic for rapid and modular synthesis of oxidized meroterpenoids
Merging chemoenzymatic and radical-based retrosynthetic logic for rapid and modular synthesis of oxidized meroterpenoids
Meroterpenoids are mixed terpenoid–polyketide natural products that exhibit a range of biological activities. A hybrid synthetic strategy that combines biocatalytic and radical-based methods has now been developed and it enables eight different oxidized meroterpenoids to be made in just 7–12 steps from commercially available materials.
- Jian Li
- , Fuzhuo Li
- & Hans Renata
-
Article |
 Asymmetric redox-neutral radical cyclization catalysed by flavin-dependent ‘ene’-reductases
Asymmetric redox-neutral radical cyclization catalysed by flavin-dependent ‘ene’-reductases
Flavin-dependent ‘ene’-reductases have now been shown to catalyse redox-neutral radical cyclizations of α-haloamides to form enantioenriched oxindoles. Mechanistic studies indicate the reaction proceeds via the flavin semiquinone/quinone redox couple, where a ground state flavin semiquinone provides the electron for substrate reduction and flavin quinone oxidizes the radical formed after cyclization.
- Michael J. Black
- , Kyle F. Biegasiewicz
- & Todd K. Hyster
-
News & Views |
 Identifying an iodinase
Identifying an iodinase
Flavin-dependent halogenases catalyse the regioselective formation of carbon–chlorine and carbon–bromine bonds using oxygen and inorganic halide salts. Now, genome mining has led to the discovery of a previously unknown viral halogenase that catalyses the iodination of arenes, thereby providing a rare biocatalytic tool for the formation of carbon–iodine bonds.
- Christian Schnepel
- & Nicholas J. Turner
-
Article |
 A marine viral halogenase that iodinates diverse substrates
A marine viral halogenase that iodinates diverse substrates
A flavin-dependent halogenase with a remarkable preference for iodination has now been discovered. The halogenase (VirX1) was discovered using a bioinformatics-based approach and comes from a cyanophage. Structural characterization and kinetic studies show that VirX1 possesses broad substrate tolerance, making it an attractive tool for synthesis.
- Danai S. Gkotsi
- , Hannes Ludewig
- & Rebecca J. M. Goss
-
Article |
 An enzymatic platform for the asymmetric amination of primary, secondary and tertiary C(sp3)–H bonds
An enzymatic platform for the asymmetric amination of primary, secondary and tertiary C(sp3)–H bonds
Stereoselective functionalization of C(sp3)–H bonds could greatly simplify the construction of complex molecular scaffolds. Now, a series of enzyme catalysts derived from a cytochrome P450 have been developed using directed evolution. The catalysts enable the enantioselective amination of primary, secondary and tertiary C(sp3)–H bonds.
- Yang Yang
- , Inha Cho
- & Frances H. Arnold
-
Article |
 Enzymatic control of cycloadduct conformation ensures reversible 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition in a prFMN-dependent decarboxylase
Enzymatic control of cycloadduct conformation ensures reversible 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition in a prFMN-dependent decarboxylase
The UbiD family of reversible decarboxylases interconvert propenoic or aromatic acids with the corresponding alkenes or aromatic compounds, using a transient 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition between the substrate and the prenylated flavin mononucleotide cofactor. Atomic-resolution crystallography shows targeted destabilization of the intermediate covalent adducts, allowing the enzyme to harness 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition as a readily reversible reaction.
- Samuel S. Bailey
- , Karl A. P. Payne
- & David Leys
-
Article |
 Genome mining- and synthetic biology-enabled production of hypermodified peptides
Genome mining- and synthetic biology-enabled production of hypermodified peptides
Polytheonamides are potently cytotoxic hypermodified ribosomal peptides that are produced by an uncultivated bacterium. Now, a bioinformatic mining strategy has enabled the development of a bacterial production host that can be cultivated in a laboratory. The host generates polytheonamide-like compounds within 2 days, and can efficiently introduce multiple d-amino acids, asparagine N-methylations and C-methyl groups into various peptides.
- Agneya Bhushan
- , Peter J. Egli
- & Jörn Piel
-
Article |
 A catalytically active [Mn]-hydrogenase incorporating a non-native metal cofactor
A catalytically active [Mn]-hydrogenase incorporating a non-native metal cofactor
Natural hydrogenases exclusively utilize Ni and/or Fe to activate or produce hydrogen. Now, a catalytically active [Mn]-hydrogenase has been prepared by incorporating a synthetic Mn complex into the apoenzyme of [Fe]-Hydrogenase. The semi-synthetic [Mn]-hydrogenase shows higher activity than the corresponding Fe analogue.
- Hui-Jie Pan
- , Gangfeng Huang
- & Xile Hu
-
Article |
 Radical polymerization inside living cells
Radical polymerization inside living cells
A strategy for directly synthesizing unnatural polymers in cells through radical polymerization has now been developed. This approach provides a platform to manipulate, track and control cellular behaviour by the in cellulo generation of macromolecules and a variety of nanostructures.
- Jin Geng
- , Weishuo Li
- & Mark Bradley
-
Article |
 A genetically encoded photosensitizer protein facilitates the rational design of a miniature photocatalytic CO2-reducing enzyme
A genetically encoded photosensitizer protein facilitates the rational design of a miniature photocatalytic CO2-reducing enzyme
A 27 kDa photosensitizer protein (PSP) has now been developed and used to design a miniature photocatalytic CO2-reducing enzyme. Visible light drives the PSP efficiently to the long-lived triplet excited state (PSP*), and then to a super-reducing radical (PSP•), which is strong enough to reduce many CO2-reducing catalysts. The 3D structure of PSP• at 1.8 Å resolution was determined by X-ray crystallography.
- Xiaohong Liu
- , Fuying Kang
- & Jiangyun Wang
-
Article |
 Enzyme-powered motility in buoyant organoclay/DNA protocells
Enzyme-powered motility in buoyant organoclay/DNA protocells
Organoclay/DNA semipermeable microcapsules with catalase-powered oxygen gas bubble-dependent buoyancy are prepared and exploited as synthetic protocells capable of programmed motility and sustained oscillatory movement.
- B. V. V. S. Pavan Kumar
- , Avinash J. Patil
- & Stephen Mann

 Deciding the future of adipic acid
Deciding the future of adipic acid