News & Views |
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Accessing elusive σ-type cyclopropenium cation equivalents through redox gold catalysis
Accessing elusive σ-type cyclopropenium cation equivalents through redox gold catalysis
The σ-type cyclopropenium cations (CPCs) are unstable species and currently underdeveloped. Now, an iodine(III)-based cyclopropenyl transfer reagent has been developed, which can generate electrophilic cyclopropenyl-gold(III) species as equivalents of σ-type CPCs. The synthetic potential has been demonstrated by the transfer of σ-type CPCs to terminal alkynes and vinylboronic acids.
- Xiangdong Li
- , Matthew D. Wodrich
- & Jérôme Waser
-
Article
| Open Access An air- and moisture-stable ruthenium precatalyst for diverse reactivity
An air- and moisture-stable ruthenium precatalyst for diverse reactivity
Despite the widespread utility of ruthenium catalysts, many protocols for their use require high temperatures or light irradiation. Now, the synthesis of an air- and moisture-stable ruthenium precatalyst has been reported. This versatile catalyst drives an array of transformations and enables rapid screening and optimization of reactions, revealing previously unknown in situ generated ruthenium complexes.
- Gillian McArthur
- , Jamie H. Docherty
- & Igor Larrosa
-
Research Briefing |
 Carbon isotope exchange for pharmaceutical radiolabelling through metal-catalysed functional group metathesis
Carbon isotope exchange for pharmaceutical radiolabelling through metal-catalysed functional group metathesis
A method for carbon isotope exchange involving a metal-catalysed metathesis reaction of in situ formed acyl chlorides is demonstrated. The platform provides access to 13C- or 14C-enriched carboxylic acids, including natural products and pharmaceuticals, without the need for radioactive gases, using a single carboxylic acid carbon donor.
-
Article |
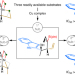 A catalytic process enables efficient and programmable access to precisely altered indole alkaloid scaffolds
A catalytic process enables efficient and programmable access to precisely altered indole alkaloid scaffolds
New drug leads can be developed through modification of a natural product’s framework, but this is possible only if the compound is abundant and contains modifiable moieties. Now a strategy is introduced for accessing a scarce indole alkaloid and several expanded, contracted and distorted analogues, one of which shows anti-cancer activity.
- Youming Huang
- , Xinghan Li
- & Amir H. Hoveyda
-
Article |
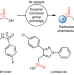 A metal-catalysed functional group metathesis approach to the carbon isotope labelling of carboxylic acids
A metal-catalysed functional group metathesis approach to the carbon isotope labelling of carboxylic acids
The preparation of 14C-labelled compounds is a crucial step in pharmaceutical development but typically requires using toxic, radioactive gases. Now a broadly applicable functional group metathesis reaction has been developed that forms 14C-labelled carboxylic acids in one pot, without added gases, via dynamic exchange with an easily handled carboxylic acid 14C source.
- R. Garrison Kinney
- , José Zgheib
- & Bruce A. Arndtsen
-
Article |
 Cooperative H2 activation at a nickel(0)–olefin centre
Cooperative H2 activation at a nickel(0)–olefin centre
Activation of H2 by a metal–olefin complex is characterized experimentally and computationally using a nickel pincer complex, showing that the reaction proceeds via a direct ligand-to-ligand hydrogen transfer mechanism. An application of this cooperative H2-activation mechanism is demonstrated in the nickel-catalysed semihydrogenation of diphenylacetylene.
- María L. G. Sansores-Paredes
- , Martin Lutz
- & Marc-Etienne Moret
-
News & Views |
 From feedstock to pharmaceuticals
From feedstock to pharmaceuticals
Fluoroalkyl fragments are ubiquitous motifs in pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals, but their introduction to a given molecule typically involves expensive or difficult-to-handle reagents. Now, the photocatalysed hydrofluoroalkylation of alkenes has been achieved using simple and readily available fluoroalkyl carboxylic acids.
- Fabio Juliá
-
Article |
 Photocatalytic hydrofluoroalkylation of alkenes with carboxylic acids
Photocatalytic hydrofluoroalkylation of alkenes with carboxylic acids
Alkene hydrofluoroalkylation offers a promising route to diverse fluoroalkylated compounds but current methods have limitations, such as needing expensive fluoroalkylating reagents. Now, leveraging iron photocatalysis and hydrogen-atom-transfer catalysis, a hydrofluoroalkylation method has been developed that utilizes feedstock chemicals such as trifluoroacetic acid as direct fluoroalkyl radical precursors, providing a redox-neutral, general protocol to introduce fluoroalkyl moieties.
- Kang-Jie Bian
- , Yen-Chu Lu
- & Julian G. West
-
Article |
 A crystalline aluminium–carbon-based ambiphile capable of activation and catalytic transfer of ammonia in non-aqueous media
A crystalline aluminium–carbon-based ambiphile capable of activation and catalytic transfer of ammonia in non-aqueous media
The reversible N–H activation and catalytic transformations of ammonia are a challenge. Now, a hidden frustrated Lewis pair is shown to activate non-aqueous ammonia thermoneutrally and split the N–H bond reversibly at ambient temperature. The N–H-activated ammonia was also utilized as an atom-economical nitrogen source for catalytic NH3 transfer reactions.
- Felix Krämer
- , Jan Paradies
- & Frank Breher
-
News & Views |
 Hydrogenative double-bond deuteration
Hydrogenative double-bond deuteration
Deuterated compounds are used in many applications such as mass-spectrometry standards, drugs or in organic light-emitting diodes. Now, hydrogen-activated homogeneous pincer complex catalysts can be used to perform selective alkene deuteration with the cheapest available deuterium source, D2O.
- Anika Tarasewicz
- & Volker Derdau
-
News & Views |
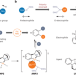 Aryl ortho methoxylation
Aryl ortho methoxylation
Aryl ethers are useful intermediates in organic synthesis and are found in countless biologically active compounds. Now, through palladium/norbornene cooperative catalysis and incorporation of a polarity-reversed N–O reagent as the O-electrophile, an efficient arene methoxylation approach has been successfully developed.
- Kun Zhao
- & Zhenhua Gu
-
Article |
 Hydrogenative alkene perdeuteration aided by a transient cooperative ligand
Hydrogenative alkene perdeuteration aided by a transient cooperative ligand
Deuterogenation methods typically introduce only two deuterium atoms per unsaturation. Now the single-step hydrogenative perdeuteration of alkenes has been achieved using H2 and D2O, with incorporation of up to 4.9 D atoms per C=C double bond. The reaction is catalysed by a ruthenium pincer complex with a catalytic amount of thiol, which serves as a transient cooperative ligand.
- Jie Luo
- , Lijun Lu
- & David Milstein
-
Article |
 Ortho-C–H methoxylation of aryl halides enabled by a polarity-reversed N–O reagent
Ortho-C–H methoxylation of aryl halides enabled by a polarity-reversed N–O reagent
Pd/norbornene cooperative catalysis provides a strategy for arene functionalization, but the electrophile scope is typically limited to ‘soft’ elements such as carbon, nitrogen and sulfur. Now the ortho-C–H methoxylation of aryl halides has been realized using a polarity-reversed N−O reagent and facilitated by a C7-bromo-substituted norbornene mediator.
- Xin Liu
- , Yue Fu
- & Guangbin Dong
-
Article |
 Copper-catalysed difluorocarbene transfer enables modular synthesis
Copper-catalysed difluorocarbene transfer enables modular synthesis
Although several transition-metal carbene complexes have been isolated and used for catalytic carbene transfer reactions, few metal difluorocarbene complexes have been reported. Now, the synthesis, characterization and reactivity of isolable copper(I) difluorocarbene complexes has been reported, which has enabled the development of a copper-catalysed difluorocarbene transfer reaction to access fluorinated compounds from simple chemical feedstocks.
- Xin Zeng
- , Yao Li
- & Xingang Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Bismuth radical catalysis in the activation and coupling of redox-active electrophiles
Bismuth radical catalysis in the activation and coupling of redox-active electrophiles
The use of main-group elements in radical cross-coupling reactions has been little explored. Now, a low-valency bismuth complex has been shown to emulate the behaviour of first-row transition metals and undergo single-electron-transfer oxidative addition to redox-active electrophiles, leading to the development of a bismuth-catalysed C–N coupling reaction between amines and carboxylic acids.
- Mauro Mato
- , Davide Spinnato
- & Josep Cornella
-
Article |
 Multi-site programmable functionalization of alkenes via controllable alkene isomerization
Multi-site programmable functionalization of alkenes via controllable alkene isomerization
The diverse site-selective functionalization, including multi-functionalization, of C=C double bonds and C(sp3)–H bonds remains a largely unmet challenge. Now, a palladium-catalysed aerobic oxidative method has been developed for the multi-site programmable functionalization of terminal olefins via a strategy that controls the reaction sequence between alkene isomerization and oxidative functionalization.
- Zhengxing Wu
- , Jingjie Meng
- & Wanbin Zhang
-
Article |
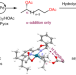 Regio- and enantioselective remote dioxygenation of internal alkenes
Regio- and enantioselective remote dioxygenation of internal alkenes
Functionalization of unsymmetrical internal alkenes usually takes place with low regioselectivity, giving a mixture of isomers. Now, a highly regio- and enantioselective remote 1,n-dioxygenation of internal alkenes using a palladium catalyst has been developed for the synthesis of chiral 1,n-diols. Regioselectivity tuning was demonstrated by altering the rate-determining step, enabled by the phenyl-substituted Pyox ligand.
- Xiaonan Li
- , Tilong Yang
- & Guosheng Liu
-
Article |
 Nature-inspired methylated polyhydroxybutyrates from C1 and C4 feedstocks
Nature-inspired methylated polyhydroxybutyrates from C1 and C4 feedstocks
Polyhydroxyalkanoates are potential substitutes for non-degradable polyolefin plastics. Now, it has been shown that structurally related methylated polyhydroxybutyrates, synthesized from carbon monoxide and 2-butenes, can provide a full suite of polyolefin-like polymers. These materials can be recycled or upcycled, and their properties can be easily tuned by varying the cis/trans ratio of the starting materials.
- Zhiyao Zhou
- , Anne M. LaPointe
- & Geoffrey W. Coates
-
Article |
 Catalytic undirected borylation of tertiary C–H bonds in bicyclo[1.1.1]pentanes and bicyclo[2.1.1]hexanes
Catalytic undirected borylation of tertiary C–H bonds in bicyclo[1.1.1]pentanes and bicyclo[2.1.1]hexanes
Borylated bicyclopentanes and bicyclohexanes are valuable compounds in drug research but are difficult to prepare. Now, an iridium-catalysed method has been developed for the borylation of the bridgehead tertiary C–H bonds in bicyclopentanes and bicyclohexanes, providing access to a variety of highly decorated bicyclic cores.
- Isaac F. Yu
- , Jenna L. Manske
- & John F. Hartwig
-
Article |
 Cu-catalysed enantioselective radical heteroatomic S–O cross-coupling
Cu-catalysed enantioselective radical heteroatomic S–O cross-coupling
Heteroatom–heteroatom cross-couplings have so far remained elusive. Now, a copper-catalysed enantioselective S–O cross-coupling of diverse diols or triols with sulfonyl chlorides has been realized via a single-electron reductive elimination manifold. The reaction provides access to value-added chiral C3 building blocks and inositol phosphates through enantioselective desymmetrization of biomass-derived alcohols.
- Yong-Feng Cheng
- , Zhang-Long Yu
- & Xin-Yuan Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Inverse hydride shuttle catalysis enables the stereoselective one-step synthesis of complex frameworks
Inverse hydride shuttle catalysis enables the stereoselective one-step synthesis of complex frameworks
The rapid assembly of complex scaffolds in a single step from simple precursors would be an ideal reaction in terms of efficiency and sustainability. Now, the single-step construction of alkaloid-like frameworks from three dynamically assembled precursors has been reported. Using a dual-catalytic system, the transformation involves a hydride shuttle process initiated by a hydride donation event.
- Immo Klose
- , Giovanni Di Mauro
- & Nuno Maulide
-
News & Views |
 Isolating intermediates
Isolating intermediates
Noyori-type catalysts and inorganic bases are frequently used together for homogeneous hydrogenation, but key intermediates have not yet been isolated. Now, the structure and reactivity of a long-postulated intermediate — the alkali metal amidate complex — have been reported through experimental and computational studies.
- Pavel A. Dub
-
Article |
 Structure, reactivity and catalytic properties of manganese-hydride amidate complexes
Structure, reactivity and catalytic properties of manganese-hydride amidate complexes
Noyori-type hydrogenation catalysts consist of an N–H moiety coordinated to a metal centre. Now, a metal-hydride amidate complex (HMn–NLi) has been isolated and found to have superior reactivity and catalytic performance compared with the corresponding HMn–NH complex, highlighting the superiority of M/NM′ bifunctional catalysis over the classic M/NH bifunctional catalysis for hydrogenation reactions.
- Yujie Wang
- , Shihan Liu
- & Qiang Liu
-
Article |
 Palladium-catalysed selective oxidative amination of olefins with Lewis basic amines
Palladium-catalysed selective oxidative amination of olefins with Lewis basic amines
Given the importance of amine compounds, methods for their synthesis continue to be in high demand. Now, a palladium-catalysed strategy has been developed for the selective oxidative amination of unactivated olefins with Lewis basic amines, via C(sp3)–H activation, forming architecturally versatile and functionally diverse allylamines in a single step.
- Yangbin Jin
- , Yaru Jing
- & Huanfeng Jiang
-
News & Views |
 Hopping protons in supramolecular catalysis
Hopping protons in supramolecular catalysis
Supramolecular catalysis can emulate many features of enzymatic transformations. Now, a complex proton wire mechanism — enabling the dual activation of a nucleophile and an electrophile through reciprocal proton transfer — has been shown to operate during the β-glycosylation of sugars within a self-assembled capsule.
- Cally J. E. Haynes
- & Larissa K. S. von Krbek
-
Article |
 Palladium-catalysed construction of butafulvenes
Palladium-catalysed construction of butafulvenes
Butafulvene is a constitutional isomer of benzene, comprising a cyclobutene skeleton bearing two exocyclic conjugated methylene units. Strategies for the synthesis of butafulvene compounds are currently limited due to its intrinsic high strain energy and anti-aromaticity. Now, palladium-catalysed couplings have been developed for the rapid assembly of symmetric and non-symmetric anti-aromatic butafulvene derivatives.
- Xin Huang
- , Bing-Zhi Chen
- & Shengming Ma
-
News & Views |
 N2O revalorization
N2O revalorization
Nitrous oxide is traditionally considered to be an inert molecule, and methods for its activation and utilization are currently limited. Now, a strategy has been developed — involving an organometallic Baeyer–Villiger step — for the conversion of aryl halides to phenols under mild conditions, using N2O as the oxygen source.
- Jun-Jie Chen
- & Huan-Ming Huang
-
News & Views |
 Tungsten’s tandem transformation
Tungsten’s tandem transformation
Being able to run two reactions concurrently enables synthetic methods to be streamlined, but simultaneously controlling the selectivity of both reactions is an enormous challenge. Now, a directing group is used to reinvent a classic tandem reaction, activating specific sp3 C–H bonds with pinpoint accuracy.
- Sarah E. Jenny
- & Graham E. Dobereiner
-
Article |
 Low-valent tungsten redox catalysis enables controlled isomerization and carbonylative functionalization of alkenes
Low-valent tungsten redox catalysis enables controlled isomerization and carbonylative functionalization of alkenes
The regioselectivity of tandem isomerization/hydrocarbonylation reactions is typically dictated by thermodynamics and there are limitations on the isomerization of internal alkenes. Now, it has been shown that a low-valent-tungsten catalyst controls the isomerization of alkenes to classically challenging unactivated internal positions and, with the aid of a directing group, enables subsequent addition of hydrogen and carbon monoxide.
- Tanner C. Jankins
- , William C. Bell
- & Keary M. Engle
-
Article |
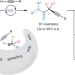 Mechanism-based ligand design for copper-catalysed enantioconvergent C(sp3)–C(sp) cross-coupling of tertiary electrophiles with alkynes
Mechanism-based ligand design for copper-catalysed enantioconvergent C(sp3)–C(sp) cross-coupling of tertiary electrophiles with alkynes
A general copper-catalysed enantioconvergent C(sp3)–C(sp) cross-coupling of diverse racemic tertiary alkyl halides with terminal alkynes has been developed, forging all-carbon quaternary stereocentres. Key to the success is the rational design of chiral anionic N,N,N-ligands tailor-made for the computationally predicted outer-sphere radical group transfer pathway.
- Fu-Li Wang
- , Chang-Jiang Yang
- & Xin-Yuan Liu
-
Article |
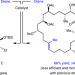 E- and Z-trisubstituted macrocyclic alkenes for natural product synthesis and skeletal editing
E- and Z-trisubstituted macrocyclic alkenes for natural product synthesis and skeletal editing
Many bioactive compounds are trisubstituted macrocyclic alkenes, but use of current methods often results in poor yields and low stereoselectivity. Now, a ring-closing metathesis strategy has been developed that enables these compounds to be prepared efficiently and in either stereoisomeric form: an approach that may prove useful in the late stages of total syntheses, for skeletal editing and in drug discovery.
- Yucheng Mu
- , Felix W. W. Hartrampf
- & Amir H. Hoveyda
-
Article |
 Cobalt(II)–tetraphenylporphyrin-catalysed carbene transfer from acceptor–acceptor iodonium ylides via N-enolate–carbene radicals
Cobalt(II)–tetraphenylporphyrin-catalysed carbene transfer from acceptor–acceptor iodonium ylides via N-enolate–carbene radicals
Although cobalt–carbene radicals have proved to be highly versatile intermediates for homogeneous catalysis, their spectroscopic detection and characterization have been limited. Now, by using hypervalent iodonium ylides, the formation and spectroscopic detection of a biscarbenoid N-enolate–carbene radical—which undergoes a complex catalytic pathway involving reversible N-enolate formation—has been demonstrated.
- Roel F. J. Epping
- , Mees M. Hoeksma
- & Bas de Bruin
-
Article |
 Reversible C–C bond formation using palladium catalysis
Reversible C–C bond formation using palladium catalysis
Although carbometallation reactions have been thoroughly investigated, understanding the factors responsible for the reverse reaction (β-carbon elimination) is an emerging area of research. Now, a series of substrates has been investigated to study the key factors that promote β-carbon elimination under palladium catalysis.
- Austin D. Marchese
- , Bijan Mirabi
- & Mark Lautens
-
Article |
 Stereodefined alkenes with a fluoro-chloro terminus as a uniquely enabling compound class
Stereodefined alkenes with a fluoro-chloro terminus as a uniquely enabling compound class
Stereochemically defined trisubstituted alkenyl fluorides are important compounds for drug discovery, agrochemical development and materials science, but their preparation is challenging. Now, a practical and widely applicable catalytic strategy enables access to a large assortment of olefins bearing a fluoro-chloro terminus. Subsequent cross-coupling generates the corresponding trisubstituted alkenyl fluorides.
- Qinghe Liu
- , Yucheng Mu
- & Amir H. Hoveyda
-
Article |
 Catalytic remote hydrohalogenation of internal alkenes
Catalytic remote hydrohalogenation of internal alkenes
The hydrohalogenation of alkenes generally forms branched alkyl halides. Now, a palladium-catalysed method has been developed for the remote hydrohalogenation of internal and terminal alkenes, enabling the efficient synthesis of linear alkyl halides. The method uses an engineered Pyox ligand with a hydroxy group, which is essential for accelerating the oxidative halogenation.
- Xiang Li
- , Jianbo Jin
- & Guosheng Liu
-
Article |
 A photosensitizer–polyoxometalate dyad that enables the decoupling of light and dark reactions for delayed on-demand solar hydrogen production
A photosensitizer–polyoxometalate dyad that enables the decoupling of light and dark reactions for delayed on-demand solar hydrogen production
Decoupling the processes of light harvesting and catalytic hydrogen evolution could be a potentially important step in storing solar energy. This has now been achieved with a single molecular unit: a light-harvesting ruthenium complex–polyoxometalate dyad that absorbs light, separates and stores charge and then generates hydrogen on demand following the addition of a proton donor.
- Sebastian Amthor
- , Sebastian Knoll
- & Carsten Streb
-
Article
| Open Access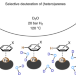 Scalable and selective deuteration of (hetero)arenes
Scalable and selective deuteration of (hetero)arenes
A method for the selective deuteration of anilines, indoles, phenols and heterocyclic compounds, including natural products and other bioactive molecules, has been developed. The nanostructured iron catalyst that underpins this process is prepared by combining cellulose with iron salts and has been used for the preparation of deuterated compounds on up to a kilogram scale.
- Wu Li
- , Jabor Rabeah
- & Matthias Beller
-
Article |
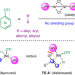 Directing-group-free catalytic dicarbofunctionalization of unactivated alkenes
Directing-group-free catalytic dicarbofunctionalization of unactivated alkenes
Without directing auxiliaries, the addition of carbogenic groups to unactivated alkenes is typically inefficient and suffers from poor regioselectivity. Now, a directing-group-free, nickel catalyst-controlled strategy has been developed, enabling the site-selective dicarbofunctionalization of a broad array of activated and unactivated alkenes.
- Hongyu Wang
- , Chen-Fei Liu
- & Ming Joo Koh
-
Article |
 A directive Ni catalyst overrides conventional site selectivity in pyridine C–H alkenylation
A directive Ni catalyst overrides conventional site selectivity in pyridine C–H alkenylation
Selective C–H alkenylation of pyridines at the C3 position, with the pyridine as the limiting reagent, is a long-standing synthetic challenge. Now, it has been shown that this can be achieved using a bifunctional N-heterocyclic carbene-ligated Ni–Al catalyst that overrides the intrinsic C2/4 selectivity of pyridines and enables the selective late-stage functionalization of a range of complex pyridyl-containing motifs.
- Tao Zhang
- , Yu-Xin Luan
- & Jin-Quan Yu
-
News & Views |
 Mastering mono-bond metathesis
Mastering mono-bond metathesis
Carbon–carbon single bonds are generally among the least reactive chemical bonds. While olefin metathesis reactions are well established, direct metathesis of C–C single bonds is rare. Now, a C–C single bond metathesis reaction has been developed, forming cross-biaryl products from unstrained homo-biaryl compounds.
- Michael M. Gilbert
- & Daniel J. Weix
-
Article |
 Orthogonal cross-coupling through intermolecular metathesis of unstrained C(aryl)–C(aryl) single bonds
Orthogonal cross-coupling through intermolecular metathesis of unstrained C(aryl)–C(aryl) single bonds
Metathesis reactions involving carbon–carbon double bonds have been well established, but direct metathesis of carbon–carbon single bonds is extremely rare. Now, a ruthenium-catalysed carbon–carbon single-bond metathesis reaction has been developed with unstrained homo-biaryl substrates. The reaction shows wide functional group tolerance and operates via an ‘olefin-metathesis-like’ mechanism.
- Jun Zhu
- , Rui Zhang
- & Guangbin Dong
-
Article |
 A ring expansion strategy towards diverse azaheterocycles
A ring expansion strategy towards diverse azaheterocycles
Using synergistic bimetallic catalysis, a general ring expansion strategy has been developed for cross-dimerization between three-membered aza heterocycles and three- and four-membered-ring ketones. This method provides a straightforward and broadly applicable route for the assembly of 3-benzazepinones, dihydropyridinones and uracils, which are versatile units in numerous drugs and biologically active compounds.
- Ruirui Li
- , Bo Li
- & Dongbing Zhao
-
Article |
 Visible light enables catalytic formation of weak chemical bonds with molecular hydrogen
Visible light enables catalytic formation of weak chemical bonds with molecular hydrogen
The formation of weak chemical bonds at or near thermodynamic potential is a challenge in chemical synthesis and catalysis. A bifunctional iridium hydride catalyst has now been discovered that absorbs visible light and promotes proton-coupled electron transfer to a range of substrates—creating element–hydrogen bonds—using dihydrogen as the terminal reductant.
- Yoonsu Park
- , Sangmin Kim
- & Paul J. Chirik
-
Article |
 Isolation of a Ru(iv) side-on peroxo intermediate in the water oxidation reaction
Isolation of a Ru(iv) side-on peroxo intermediate in the water oxidation reaction
Obtaining mechanistic data after the rate-determining step of a chemical reaction is difficult but essential for its understanding. Now, a Ru(iv) side-on peroxo complex has been isolated following the rate-determining step of the water oxidation reaction (O–O bond formation) carried out using a Ru-based molecular catalyst.
- Carla Casadevall
- , Vlad Martin-Diaconescu
- & Julio Lloret-Fillol
-
Article |
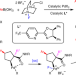 C–C bond activation enabled by dyotropic rearrangement of Pd(iv) species
C–C bond activation enabled by dyotropic rearrangement of Pd(iv) species
Many C–C bond activation methods involve strain-releasing cleavage of small rings to compensate for unfavourable kinetics and thermodynamics. Now, the 1,2-positional interchange of vicinal C–C and C–Pd bonds has been reported, giving access to quaternary carbon–palladium bonds. This dyotropic rearrangement has been used for the enantioselective synthesis of functionalized fluorinated cyclopentanes.
- Jian Cao
- , Hua Wu
- & Jieping Zhu
-
Article |
 Synthesis of monophosphines directly from white phosphorus
Synthesis of monophosphines directly from white phosphorus
State-of-the-art industrial methods for transforming P4 into useful phosphorus compounds currently rely on indirect, multi-step strategies. It has now been shown that straightforward one-pot reactions can convert P4 directly into industrially relevant products while requiring only mild conditions and simple, inexpensive reagents—and can also functionalize P4 catalytically.
- Daniel J. Scott
- , Jose Cammarata
- & Robert Wolf
-
Article |
 Nitrene-mediated intermolecular N–N coupling for efficient synthesis of hydrazides
Nitrene-mediated intermolecular N–N coupling for efficient synthesis of hydrazides
Although many natural products and drug molecules contain N–N linkages, the chemistry of N–N coupling is somewhat underdeveloped. Now, a nitrene-mediated intermolecular N–N coupling of dioxazolones and arylamines that relies on iridium or iron catalysis has been developed. These reactions offer a simple and efficient method for the synthesis of hydrazides from readily available precursors.
- Hao Wang
- , Hoimin Jung
- & Gong Chen
-
News & Views |
 Fragmentation and reassembly
Fragmentation and reassembly
Metal-catalysed hydroformylations efficiently convert feedstock alkenes into aldehydes, though typically relatively simple ones. Now, the palladium-catalysed fragmentation of acid chlorides followed by reassembly with alkynes and silanes has been shown to form valuable, highly substituted α,β-unsaturated aldehydes.
- José Zgheib
- & Bruce A. Arndtsen
-
Article |
 Enantioselective C(sp3)–C(sp3) cross-coupling of non-activated alkyl electrophiles via nickel hydride catalysis
Enantioselective C(sp3)–C(sp3) cross-coupling of non-activated alkyl electrophiles via nickel hydride catalysis
Methods for producing organic molecules rich in sp3-hybridized carbon centres can be particularly useful for drug development. Now, it has been shown that the enantioselective cross-coupling of non-activated alkyl halides with alkenyl boronates enables the synthesis of chiral alkyl boronates. The reaction proceeds via nickel hydride insertion into an internal alkene followed by nickel-catalysed alkyl–alkyl cross-coupling.
- Srikrishna Bera
- , Runze Mao
- & Xile Hu

 Cyclopropenium functionalization
Cyclopropenium functionalization