Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Ten-electron count rule for the binding of adsorbates on single-atom alloy catalysts
Ten-electron count rule for the binding of adsorbates on single-atom alloy catalysts
Single-atom alloys have emerged as highly active and selective catalysts that do not follow the traditional models of heterogeneous catalysis. Now it has been shown that the binding of adsorbates at their surface abides by a simple 10-electron count rule, which can identify promising catalysts for various applications.
- Julia Schumann
- , Michail Stamatakis
- & Romain Réocreux
-
Article |
 Light-driven ammonia synthesis under mild conditions using lithium hydride
Light-driven ammonia synthesis under mild conditions using lithium hydride
Photon-driven dinitrogen reduction to ammonia is a promising but challenging reaction. Now it has been shown that lithium hydride undergoes photolysis upon ultraviolet illumination to yield long-lived photon-generated electrons residing in hydrogen vacancies, favouring the activation of the N≡N bond and achieving photocatalytic ammonia synthesis.
- Yeqin Guan
- , Hong Wen
- & Ping Chen
-
Article |
 Scalable and continuous access to pure cyclic polymers enabled by ‘quarantined’ heterogeneous catalysts
Scalable and continuous access to pure cyclic polymers enabled by ‘quarantined’ heterogeneous catalysts
Cyclic polymers are topologically interesting and envisioned as a lubricant material, but methods for the scalable synthesis of pure cyclic polymers are currently elusive. Now, a scalable process has been developed by leveraging heterogeneity of the catalysts with the help of compartmentalized custom glassware, namely, a cyclic polymer dispenser.
- Ki-Young Yoon
- , Jinkyung Noh
- & Robert H. Grubbs
-
News & Views |
 Catalytic site seeing
Catalytic site seeing
Understanding how surface structure affects catalyst selectivity is limited by the ability to synthesize atomically precise active-site ensembles. Now, by using intermetallic Pd–Zn, a series of well-defined multinuclear Pd–metal–Pd catalytic sites have been generated and studied, providing insights into their selectivity for the semi-hydrogenation of acetylene.
- Max Mortensen
- & Siris Laursen
-
Article |
 Atomic control of active-site ensembles in ordered alloys to enhance hydrogenation selectivity
Atomic control of active-site ensembles in ordered alloys to enhance hydrogenation selectivity
Advances in the design of heterogeneous catalysts are limited by our ability to synthesize atomically precise active-site ensembles. Now, the controlled synthesis of Pd–M–Pd catalytic sites (M = Zn, Pd, Cu, Ag and Au) has been demonstrated. Stoichiometric control identifies that Pd–Pd–Pd sites are active for ethylene hydrogenation, whereas Pd–Zn–Pd sites are not.
- Anish Dasgupta
- , Haoran He
- & Robert M. Rioux
-
Article
| Open Access Scalable and selective deuteration of (hetero)arenes
Scalable and selective deuteration of (hetero)arenes
A method for the selective deuteration of anilines, indoles, phenols and heterocyclic compounds, including natural products and other bioactive molecules, has been developed. The nanostructured iron catalyst that underpins this process is prepared by combining cellulose with iron salts and has been used for the preparation of deuterated compounds on up to a kilogram scale.
- Wu Li
- , Jabor Rabeah
- & Matthias Beller
-
News & Views |
 Two steps to sustainable polymers
Two steps to sustainable polymers
Medium-chain linear α-olefins are commodity chemicals; however, manufacturing α-olefins from biomass is challenging due to inefficient removal of the last oxygen atoms. Now, a two-step biological–chemical catalysis strategy to produce medium-chain linear α-olefins provides a route to sustainable polymers.
- Shaafique Chowdhury
- & Pamela Peralta-Yahya
-
Article |
 A short peptide synthon for liquid–liquid phase separation
A short peptide synthon for liquid–liquid phase separation
Liquid–liquid phase separation plays an important role in creating cellular compartments and protocells, but designing small-molecule models remains difficult. A peptide-based synthon for liquid–liquid phase separation consisting of two stickers and a flexible, polar spacer has now been presented. Condensates formed by these synthons can concentrate biomolecules and catalyse anabolic reactions.
- Manzar Abbas
- , Wojciech P. Lipiński
- & Evan Spruijt
-
Article |
 Platinum incorporation into titanate perovskites to deliver emergent active and stable platinum nanoparticles
Platinum incorporation into titanate perovskites to deliver emergent active and stable platinum nanoparticles
Nanoparticulate platinum is a highly active catalyst, but it is scarce, expensive and not always sufficiently durable. Now, barium platinate has been used as a vehicle to preserve platinum as an oxide during the solid-state synthesis of a Pt-doped titanate perovskite; this enables the production of a structure with active and stable Pt nanoparticles on the perovskite surface that catalyses CO oxidation.
- Maadhav Kothari
- , Yukwon Jeon
- & John T. S. Irvine
-
Matters Arising |
 Reply to: Questioning the rate law in the analysis of water oxidation catalysis on haematite photoanodes
Reply to: Questioning the rate law in the analysis of water oxidation catalysis on haematite photoanodes
- Camilo A. Mesa
- , Reshma R. Rao
- & James R. Durrant
-
Article |
 Multihole water oxidation catalysis on haematite photoanodes revealed by operando spectroelectrochemistry and DFT
Multihole water oxidation catalysis on haematite photoanodes revealed by operando spectroelectrochemistry and DFT
The oxidation of water remains the kinetic bottleneck of solar-to-fuel synthesis. Now, spectroelectrochemical evidence together with density functional theory calculations show that charge accumulation determines the reaction mechanism on metal–oxide photoanodes. These insights reveal features that are common to the mechanisms of water oxidation carried out by other inorganic and biological systems.
- Camilo A. Mesa
- , Laia Francàs
- & James R. Durrant
-
Article |
 Single-atom gold oxo-clusters prepared in alkaline solutions catalyse the heterogeneous methanol self-coupling reactions
Single-atom gold oxo-clusters prepared in alkaline solutions catalyse the heterogeneous methanol self-coupling reactions
Generating stable single-atom catalysts is far from straightforward and can involve complicated preparation procedures. Now, mononuclear gold oxo-clusters formed in alkaline solutions through a facile one-pot synthesis are shown to catalyse the heterogeneous methanol self-coupling reaction to methyl formate and hydrogen. The intrinsic activity is the same for both supported and unsupported gold catalysts.
- Sufeng Cao
- , Ming Yang
- & Maria Flytzani-Stephanopoulos
-
Article |
 Identification of the strong Brønsted acid site in a metal–organic framework solid acid catalyst
Identification of the strong Brønsted acid site in a metal–organic framework solid acid catalyst
Solid acid heterogeneous catalysts are widely used in industrial chemical processes, but understanding the exact molecular structures responsible for catalytic activity has proved difficult. Now, the structure of the strong Brønsted acid site for a sulfated zirconium-based metal–organic framework has been shown to consist of a specific arrangement of adsorbed water and sulfate moieties on the zirconium clusters.
- Christopher A. Trickett
- , Thomas M. Osborn Popp
- & Omar M. Yaghi
-
News & Views |
 Staining a porous catalyst
Staining a porous catalyst
The structural features and catalytic performances of catalyst particles have now been correlated using a fluorescence microscopy approach, by tracking nanoprobes as well as fluorescent reaction products. Such mapping enables exploration of structure–function relationships, which is essential for the design of better catalysts.
- Wei Wang
-
Article |
 Visualizing pore architecture and molecular transport boundaries in catalyst bodies with fluorescent nanoprobes
Visualizing pore architecture and molecular transport boundaries in catalyst bodies with fluorescent nanoprobes
The accessibility of materials’ porous domains is typically explored through bulk, and often non-visual, measurements. Now, an integrated fluorescence microscopy approach has established a direct visual relationship between pore architecture (which depends on pore sizes and interconnectivity), molecular transport, and in turn catalytic performance in industrial-grade catalyst particles.
- Gareth T. Whiting
- , Nikolaos Nikolopoulos
- & Bert M. Weckhuysen
-
Article |
 Structure–performance descriptors and the role of Lewis acidity in the methanol-to-propylene process
Structure–performance descriptors and the role of Lewis acidity in the methanol-to-propylene process
As of yet, no clear structure–performance descriptors have been developed to tune the catalytic activity of zeolitic methanol-to-olefin catalysts. Now it has been shown that introducing Lewis acidity into Brønsted acidic zeolites boosts their performance. Although Brønsted acidity is found to define propylene selectivity, Lewis acidity is responsible for prolonging lifetime.
- Irina Yarulina
- , Kristof De Wispelaere
- & Jorge Gascon
-
News & Views |
 Communicating catalysts
Communicating catalysts
The beauty and activity of enzymes inspire chemists to tailor new and better non-biological catalysts. Now, a study reveals that the active sites within heterogeneous catalysts actively cooperate in a fashion phenomenologically similar to, but mechanistically distinct, from enzymes.
- Bert M. Weckhuysen
-
Article |
 Cooperative communication within and between single nanocatalysts
Cooperative communication within and between single nanocatalysts
Nanocatalysts can undergo various dynamic phenomena that affect their activity, such as restructuring and spillover. Now, using spatially and temporally resolved imaging of individual catalytic reactions, cooperative communication between different sites within single palladium- and gold-based nanocatalysts, and between different nanocatalysts, has been observed during three distinct catalytic reactions.
- Ningmu Zou
- , Xiaochun Zhou
- & Peng Chen
-
Article |
 Evaluating differences in the active-site electronics of supported Au nanoparticle catalysts using Hammett and DFT studies
Evaluating differences in the active-site electronics of supported Au nanoparticle catalysts using Hammett and DFT studies
Understanding how a supporting material can change the surface chemistry of the nanoparticle catalysts that it hosts is critical to tuning catalytic properties. Experimental Hammett studies and density functional theory calculations show that differences in reactivity can be attributed to differences in the electron density at metal active sites, which arises from differences in electron donation from the support.
- Gaurav Kumar
- , Luke Tibbitts
- & Bert D. Chandler
-
Article |
 Pt/Cu single-atom alloys as coke-resistant catalysts for efficient C–H activation
Pt/Cu single-atom alloys as coke-resistant catalysts for efficient C–H activation
A renewed interest in C–H bond activation has developed on account of the recent increased availability of shale gas. Now, using a combination of surface science, microscopy, theory and nanoparticle studies, the ability of coke-resistant Pt/Cu single-atom alloys to efficiently activate C–H bonds in alkanes has been demonstrated under realistic catalytic conditions.
- Matthew D. Marcinkowski
- , Matthew T. Darby
- & E. Charles H. Sykes
-
News & Views |
 Popping up to the surface
Popping up to the surface
Merging the advantages of homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysts is a useful strategy for creating improved catalytic systems. Now, a concept has been developed that uses single Pd atoms — supported within liquid alloy droplets — that emerge from the droplet subsurface and interior to react with molecules approaching from the gas phase.
- Günther Rupprechter
-
Article |
 Gallium-rich Pd–Ga phases as supported liquid metal catalysts
Gallium-rich Pd–Ga phases as supported liquid metal catalysts
Creating systems that merge some of the advantages of both heterogeneous and molecular catalysis is a useful approach to developing improved catalysts. Following this strategy, a liquid mixture of gallium and palladium supported on porous glass has now been shown to form an active catalyst for alkane dehydrogenation that is resistant to coke formation and is thus highly stable.
- N. Taccardi
- , M. Grabau
- & P. Wasserscheid
-
Article |
 Direct conversion of CO2 into liquid fuels with high selectivity over a bifunctional catalyst
Direct conversion of CO2 into liquid fuels with high selectivity over a bifunctional catalyst
It is still a great challenge to synthesize value-added products with two or more carbons directly from CO2. Now, a bifunctional catalyst composed of reducible metal oxides (In2O3) and zeolites (HZSM-5) is prepared and yields high selectivity to gasoline-range hydrocarbons (78.6%) with a high octane number directly from CO2 hydrogenation.
- Peng Gao
- , Shenggang Li
- & Yuhan Sun
-
News & Views |
 Giving catalysts a hand
Giving catalysts a hand
Using chiral modifiers on the surfaces of heterogeneous catalysts is a potentially fruitful route to practical stereoselective chemistry. Now, a study of the dynamics of prochiral adsorbates on modified surfaces has shown that they can rapidly interconvert between adsorption states of different prochirality.
- Wilfred T. Tysoe
-
Article |
 Monitoring interconversion between stereochemical states in single chirality-transfer complexes on a platinum surface
Monitoring interconversion between stereochemical states in single chirality-transfer complexes on a platinum surface
A chiral molecule on a metal surface can set up a prochiral molecule for an enantioselective reaction step by forming a hydrogen-bonded complex that imposes a specific adsorption geometry. Time-lapsed scanning tunnelling microscopy and density functional theory studies reveal that such complexes can sometimes switch between states of opposing prochirality.
- Guillaume Goubert
- , Yi Dong
- & Peter H. McBreen
-
Article |
 MoS2 monolayer catalyst doped with isolated Co atoms for the hydrodeoxygenation reaction
MoS2 monolayer catalyst doped with isolated Co atoms for the hydrodeoxygenation reaction
Converting oxygen-rich biomass into fuels requires the removal of oxygen groups through hydrodeoxygenation. MoS2 monolayer sheets decorated with isolated Co atoms bound to sulfur vacancies in the basal plane have now been synthesized that exhibit superior catalytic activity, selectivity and stability for the hydrodeoxygenation of 4-methylphenol to toluene when compared to conventionally prepared materials.
- Guoliang Liu
- , Alex W. Robertson
- & Shik Chi Edman Tsang
-
News & Views |
 An extra layer of complexity
An extra layer of complexity
Strong interactions between oxide supports and catalytic metal particles can lead to inhibitive oxide layers forming over the active metal catalyst. Now, adsorbate-induced metal–support interactions have been shown to lead to a porous overlayer in the Rh/TiO2 system that tunes catalyst activity, improving its selectivity for the partial reduction of CO2.
- Bert D. Chandler
-
Article |
 Ballbot-type motion of N-heterocyclic carbenes on gold surfaces
Ballbot-type motion of N-heterocyclic carbenes on gold surfaces
STM investigations and first principles calculations provide an understanding of the microscopic mechanism behind the mobility of N-heterocyclic carbenes (NHCs) on gold surfaces. Now, it is shown that a ballbot-type motion allows the formation of self-assembled monolayers due to the NHC extracting a gold atom from the surface, leading to a ligated gold adatom.
- Gaoqiang Wang
- , Andreas Rühling
- & Harald Fuchs
-
News & Views |
 More than skimming the surface
More than skimming the surface
The high temperatures and pressures used in heterogeneous catalysis make it difficult to observe catalysts using conventional techniques. Now, adsorbed product molecules on the surface of a single-crystal model catalyst have been observed during catalysis using a custom-built scanning tunnelling microscope that can work in situ.
- Franklin (Feng) Tao
- & Yu Tang
-
Article |
 In situ observation of self-assembled hydrocarbon Fischer–Tropsch products on a cobalt catalyst
In situ observation of self-assembled hydrocarbon Fischer–Tropsch products on a cobalt catalyst
During the Fischer-Tropsch catalytic reaction, alkanes are synthesized from carbon monoxide and hydrogen at high pressure and temperature. Now it is shown using scanning tunnelling imaging of a cobalt surface during reaction that linear alkane product molecules of a specific length self-assemble on terraces, facilitating the desorption of new product molecules created at step sites.
- Violeta Navarro
- , Matthijs A. van Spronsen
- & Joost W. M. Frenken
-
Article |
 Adsorbate-mediated strong metal–support interactions in oxide-supported Rh catalysts
Adsorbate-mediated strong metal–support interactions in oxide-supported Rh catalysts
Developing approaches to tune the reactivity and selectivity of supported-metal heterogeneous catalysts is critical for designing environmentally friendly chemical conversion processes. A reversible structural catalyst transformation has now been identified that involves the adsorbate-mediated encapsulation of Rh nanoparticles by their oxide support and enables dynamic tuning of the selectivity of CO2 reduction.
- John C. Matsubu
- , Shuyi Zhang
- & Phillip Christopher
-
Article |
 Breaking scaling relations to achieve low-temperature ammonia synthesis through LiH-mediated nitrogen transfer and hydrogenation
Breaking scaling relations to achieve low-temperature ammonia synthesis through LiH-mediated nitrogen transfer and hydrogenation
The existence of linear scaling relations between the adsorption energies of reaction intermediates on transition-metal surfaces prevents their independent optimization and limits catalytic activity. It has now been shown that using a catalytic LiH site alongside a transition-metal catalyst can break these intrinsic scaling relations, leading to unprecedented lower-temperature ammonia-synthesis activity.
- Peikun Wang
- , Fei Chang
- & Ping Chen
-
News & Views |
 Intermediate identification
Intermediate identification
The slow kinetics of light-driven water oxidation on haematite is an important factor limiting the material's efficiency. Now, an intermediate of the water-splitting reaction has been identified offering hope that the full mechanism will soon be resolved.
- Alexander J. Cowan
-
Article |
 Determination of photoelectrochemical water oxidation intermediates on haematite electrode surfaces using operando infrared spectroscopy
Determination of photoelectrochemical water oxidation intermediates on haematite electrode surfaces using operando infrared spectroscopy
Photoelectrochemical water oxidation with haematite is known to be associated with a build-up of holes at the electrode surface. Infrared spectra acquired during photoelectrochemical water oxidation have now allowed these holes to be identified as high-valent iron–oxo intermediate species involved in the water oxidation reaction.
- Omid Zandi
- & Thomas W. Hamann
-
Article |
 Catalyst design for natural-gas upgrading through oxybromination chemistry
Catalyst design for natural-gas upgrading through oxybromination chemistry
Efficiently and selectively activating the C–H bonds within the light alkanes of natural gas is a challenge that must be overcome if we are to make the most of Earth's abundant reserves. An oxybromination method that functionalizes methane under mild conditions has now been developed and vanadium phosphate was identified as the best catalyst for this reaction.
- Vladimir Paunović
- , Guido Zichittella
- & Javier Pérez-Ramírez
-
Article |
 Controlling activity and selectivity using water in the Au-catalysed preferential oxidation of CO in H2
Controlling activity and selectivity using water in the Au-catalysed preferential oxidation of CO in H2
The preferential oxidation of CO is a potentially efficient means of purifying industrial hydrogen, however, no catalytic systems are known with sufficiently high activity and selectivity. Now Au/Al2O3 catalysts are shown to have outstanding activity and selectivity when both the feed flow-rate and the amount of surface water are carefully controlled.
- Johnny Saavedra
- , Todd Whittaker
- & Bert D. Chandler
-
Review Article |
 Substrate channelling as an approach to cascade reactions
Substrate channelling as an approach to cascade reactions
In enzyme-catalysed metabolic pathways, substrate channelling often directs the movement of intermediates from one active site to the next. Intramolecular tunnels, electrostatic interactions and chemical swing arms pass intermediates from one enzyme to the next, enhancing pathway catalysis. Introducing mechanisms of bounded diffusion in chemical cascades can increase selectivity, transient rates and overall yield.
- Ian Wheeldon
- , Shelley D. Minteer
- & Matthew Sigman
-
Article |
 Efficient green methanol synthesis from glycerol
Efficient green methanol synthesis from glycerol
Impure glycerol is obtained as a significant by-product of biodiesel production. Now it is shown that this crude glycerol can be reacted with water over very simple basic or redox oxide catalysts to produce methanol in high yields, together with other useful chemicals, in a one-step low pressure process.
- Muhammad H. Haider
- , Nicholas F. Dummer
- & Graham J. Hutchings
-
News & Views |
 Scaling the rough heights
Scaling the rough heights
Scaling relations between the molecular structures of reactive intermediates and the strength of the bonds they form with flat surfaces have now been extended to also predict how bonding strength is affected by surface topography. These relations can be applied to design more efficient nanoparticle catalysts.
- J. Will Medlin
- & Matthew M. Montemore
-
Article |
 Introducing structural sensitivity into adsorption–energy scaling relations by means of coordination numbers
Introducing structural sensitivity into adsorption–energy scaling relations by means of coordination numbers
Scaling relations between the adsorption energies of reaction intermediates facilitate the computational design of catalysts. However, these relations are restricted to low-index surfaces and how they differ from surface to surface cannot be predicted. Structural sensitivity has now been incorporated into scaling relations by elucidating how they are affected by the coordination number of an adsorption site.
- Federico Calle-Vallejo
- , David Loffreda
- & Philippe Sautet
-
Article |
 High-performance Ag–Co alloy catalysts for electrochemical oxygen reduction
High-performance Ag–Co alloy catalysts for electrochemical oxygen reduction
The oxygen reduction reaction limits fuel cell performance and currently requires costly electrocatalysts with high platinum content to achieve adequate power densities. Now a silver–cobalt surface alloy electrocatalyst has been developed for the oxygen reduction reaction that is stable in alkaline electrolytes and is more economical than traditional platinum-based materials.
- Adam Holewinski
- , Juan-Carlos Idrobo
- & Suljo Linic
-
-
Article |
 Discovery of a Ni-Ga catalyst for carbon dioxide reduction to methanol
Discovery of a Ni-Ga catalyst for carbon dioxide reduction to methanol
A Ni-Ga catalyst that reduces CO2 to methanol at ambient pressure has been discovered through a descriptor-based computational analysis, and has been shown experimentally to be particularly active and selective. This represents a first step towards the development of small-scale low-pressure processes for CO2 reduction to methanol from distributed hydrogen production.
- Felix Studt
- , Irek Sharafutdinov
- & Jens K. Nørskov
-
-
-
Article |
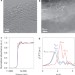 Exceptional oxidation activity with size-controlled supported gold clusters of low atomicity
Exceptional oxidation activity with size-controlled supported gold clusters of low atomicity
The catalytic activity of gold nanoparticles is known to be dependent on size, but less is known about the activity of even smaller gold clusters. It is now shown that clusters with 5 to 10 atoms supported on multiwalled carbon nanotubes are as active as enzymes for the oxidation of thiophenol to disulfide with O2.
- Avelino Corma
- , Patricia Concepción
- & Alvaro Mayoral
-
Article |
 Heterogenized cobalt oxide catalysts for nitroarene reduction by pyrolysis of molecularly defined complexes
Heterogenized cobalt oxide catalysts for nitroarene reduction by pyrolysis of molecularly defined complexes
Pyrolysis of defined nitrogen-ligated cobalt acetate complexes onto a commercial carbon support transforms the complexes into heterogeneous Co3O4 materials. These reusable non-noble-metal catalysts are highly selective for the industrially important hydrogenation of structurally diverse and functionalized nitroarenes to anilines.
- Felix A. Westerhaus
- , Rajenahally V. Jagadeesh
- & Matthias Beller
-
News & Views |
 Teaching an old material new tricks
Teaching an old material new tricks
A classic calcium aluminate has been modified to create an inorganic electride that can be used as a promoter of the catalytic synthesis of ammonia.
- Elio Giamello
-
Review Article |
 Heterogeneities of individual catalyst particles in space and time as monitored by spectroscopy
Heterogeneities of individual catalyst particles in space and time as monitored by spectroscopy
This Review describes the general trends and implications of heterogeneities within individual catalyst particles as observed by modern spatiotemporal spectroscopy. It discusses how catalytic materials have been found to display heterogeneities in structure, composition and reactivity in space and time. The implications of these findings for future catalyst design are also described.
- Inge L. C. Buurmans
- & Bert M. Weckhuysen

 Upcycling of polyethylene to gasoline through a self-supplied hydrogen strategy in a layered self-pillared zeolite
Upcycling of polyethylene to gasoline through a self-supplied hydrogen strategy in a layered self-pillared zeolite