Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Recurrent repeat expansions in human cancer genomes
Recurrent repeat expansions in human cancer genomes
An atlas explores the landscape of recurrent repeat expansions in human cancer genomes.
- Graham S. Erwin
- , Gamze Gürsoy
- & Michael P. Snyder
-
Article |
 Autonomous rhythmic activity in glioma networks drives brain tumour growth
Autonomous rhythmic activity in glioma networks drives brain tumour growth
A population of highly interconnected cells in glioblastoma makes these tumours resistant to general damage but vulnerable to targeted disruption of this small fraction of cells and their rhythmic Ca2+ oscillations.
- David Hausmann
- , Dirk C. Hoffmann
- & Frank Winkler
-
Research Highlight |
 Deadly skin cancer can shrink or vanish after T cells join the fray
Deadly skin cancer can shrink or vanish after T cells join the fray
Immune-cell-based therapy quashed tumour growth in some people with treatment-resistant melanoma.
-
Article |
 Structural variants drive context-dependent oncogene activation in cancer
Structural variants drive context-dependent oncogene activation in cancer
Results are presented that indicate that alterations to gene regulatory three-dimensional architecture are a critical mechanism that enables structural variant-based oncogene activation in cancer genomes and sheds light on the essential elements for such gene activation events.
- Zhichao Xu
- , Dong-Sung Lee
- & Jesse R. Dixon
-
Article
| Open Access Dendritic cells direct circadian anti-tumour immune responses
Dendritic cells direct circadian anti-tumour immune responses
Rhythmic trafficking of dendritic cells to the tumour draining lymph node governs a circadian response of tumour-antigen-specific CD8+ T cells that is dependent on the circadian expression of the co-stimulatory molecule CD80.
- Chen Wang
- , Coline Barnoud
- & Christoph Scheiermann
-
Article
| Open Access Ras drives malignancy through stem cell crosstalk with the microenvironment
Ras drives malignancy through stem cell crosstalk with the microenvironment
Aberrant crosstalk between cancer stem cells and their microenvironment triggers angiogenesis and TGFβ signalling, creating conditions that are conducive for hijacking leptin and leptin receptor signalling, which in turn launches downstream PI3K–AKT–mTOR signalling during the benign-to-malignant transition.
- Shaopeng Yuan
- , Katherine S. Stewart
- & Elaine Fuchs
-
Article |
 Genomic signature of Fanconi anaemia DNA repair pathway deficiency in cancer
Genomic signature of Fanconi anaemia DNA repair pathway deficiency in cancer
Defective DNA interstrand crosslink repair in Fanconi anaemia drives extensive genomic rearrangements, thereby substantially increasing the risk of cancer development.
- Andrew L. H. Webster
- , Mathijs A. Sanders
- & Agata Smogorzewska
-
Article |
 Human fetal cerebellar cell atlas informs medulloblastoma origin and oncogenesis
Human fetal cerebellar cell atlas informs medulloblastoma origin and oncogenesis
Integrated single-cell atlases of human fetal cerebella and MBs show potential cell populations predisposed to transformation and regulatory circuitries underlying tumour cell states and oncogenesis, highlighting hitherto unrecognized transitional progenitor intermediates predictive of disease prognosis.
- Zaili Luo
- , Mingyang Xia
- & Q. Richard Lu
-
News & Views |
 Folate transporter offers clues for anticancer drugs
Folate transporter offers clues for anticancer drugs
Structural insights into a long-studied folate-transport protein provide evidence that might lead to entirely new targeted anticancer treatments, or boost the success of immunotherapy approaches to tackling tumours.
- Larry H. Matherly
- & Zhanjun Hou
-
Article |
 MYC multimers shield stalled replication forks from RNA polymerase
MYC multimers shield stalled replication forks from RNA polymerase
MYC dissociation from active promoters alters its interactions with proteins involved in transcription termination and RNA processing, influencing DNA repair and thus, potentially, tumour cell growth.
- Daniel Solvie
- , Apoorva Baluapuri
- & Martin Eilers
-
News & Views |
 Uncoordinated protein coordinates cell migration
Uncoordinated protein coordinates cell migration
Mounting evidence suggests that developing neurons and metastatic cancer cells migrate through similar mechanisms. Characterization of a previously unknown complex involved in cell migration confirms this idea.
- Alain Chédotal
-
Article
| Open Access Effect of the intratumoral microbiota on spatial and cellular heterogeneity in cancer
Effect of the intratumoral microbiota on spatial and cellular heterogeneity in cancer
Spatial profiling and single-cell RNA sequencing are used to map the spatial distribution of the microbiota within human tumours, revealing how intratumoral microbial communities contribute to tumour heterogeneity and cancer progression.
- Jorge Luis Galeano Niño
- , Hanrui Wu
- & Susan Bullman
-
News & Views |
 A spatial perspective on bacteria in tumours
A spatial perspective on bacteria in tumours
Bacteria are frequently present in human cancers. The use of state-of-the-art methods for tumour analysis that capture spatial information and single-cell molecular profiles paves the way to clarifying the roles of these microorganisms.
- Ilana Livyatan
- & Ravid Straussman
-
Article |
 Colon tumour cell death causes mTOR dependence by paracrine P2X4 stimulation
Colon tumour cell death causes mTOR dependence by paracrine P2X4 stimulation
Chemotherapy-induced death of colon cancer cells causes ATP release triggering P2X4 to mediate an mTOR-dependent pro-survival program in neighbouring cancer cells, which renders them sensitive to mTOR inhibition.
- Mark Schmitt
- , Fatih Ceteci
- & Florian R. Greten
-
Article |
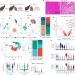 T cells specific for α-myosin drive immunotherapy-related myocarditis
T cells specific for α-myosin drive immunotherapy-related myocarditis
Cytotoxic CD8+ T cells specific for α-myosin are identified as pivotal players in myocarditis associated with immune checkpoint inhibitor anticancer therapies.
- Margaret L. Axelrod
- , Wouter C. Meijers
- & Justin M. Balko
-
Article |
 Ferroptosis of tumour neutrophils causes immune suppression in cancer
Ferroptosis of tumour neutrophils causes immune suppression in cancer
Pathologically activated neutrophils, termed myeloid-derived suppressor cells, in the tumour microenvironment spontaneously undergo ferroptosis, which negatively regulates anti-tumour immunity through the release of oxygenated lipids, therefore limiting the activity of human and mouse T cells.
- Rina Kim
- , Ayumi Hashimoto
- & Dmitry I. Gabrilovich
-
News |
 CRISPR cancer trial success paves the way for personalized treatments
CRISPR cancer trial success paves the way for personalized treatments
‘Most complicated therapy ever’ tailors bespoke, genome-edited immune cells to attack tumours.
- Heidi Ledford
-
Article
| Open Access Non-viral precision T cell receptor replacement for personalized cell therapy
Non-viral precision T cell receptor replacement for personalized cell therapy
A first-in-human phase I clinical trial demonstrates the feasibility and safety of non-viral precision genome-engineering of a personalized adoptive cell transfer anticancer therapeutic.
- Susan P. Foy
- , Kyle Jacoby
- & Stefanie J. Mandl
-
Article |
 Liver tumour immune microenvironment subtypes and neutrophil heterogeneity
Liver tumour immune microenvironment subtypes and neutrophil heterogeneity
Tumour-associated neutrophil populations enriched in the myeloid-cell-enriched tumour immune microenvironment subtype are associated with unfavourable prognosis in humans and mice with liver cancer.
- Ruidong Xue
- , Qiming Zhang
- & Ning Zhang
-
News & Views |
 Spatial maps of genetically diverse breast cancer cells
Spatial maps of genetically diverse breast cancer cells
The generation of spatial maps that detail molecular and genetic information for the diverse cells and tissue environment of breast tumours offers insight into the factors that drive cancer progression.
- Ghamdan Al-Eryani
- & Alexander Swarbrick
-
Article
| Open Access Spatial genomics maps the structure, nature and evolution of cancer clones
Spatial genomics maps the structure, nature and evolution of cancer clones
A workflow centred around base-specific in situ sequencing generates detailed maps of, and can phenotypically characterize, the unique set of subclones of cancers.
- Artem Lomakin
- , Jessica Svedlund
- & Lucy R. Yates
-
Research Briefing |
 Cancer cells move and spread faster in thicker extracellular fluids
Cancer cells move and spread faster in thicker extracellular fluids
The viscosity of extracellular fluid is a key physical cue, but its impact on cell function and cancer-cell dissemination has remained largely unknown. Experiments in various systems reveal that cancer cells sense, respond to and develop memory of the viscosity of extracellular fluid, with high viscosities increasing cell motility and promoting cancer dissemination.
-
Article
| Open Access Nociceptor neurons affect cancer immunosurveillance
Nociceptor neurons affect cancer immunosurveillance
Melanoma cells interact with pain-mediating sensory neurons by increasing their release of the neuropeptide CGRP, which increases the exhaustion of CD8+ T cells and thus promotes the survival of cancer cells.
- Mohammad Balood
- , Maryam Ahmadi
- & Sebastien Talbot
-
Article
| Open Access Extracellular fluid viscosity enhances cell migration and cancer dissemination
Extracellular fluid viscosity enhances cell migration and cancer dissemination
Elevated viscosity counterintuitively increases the motility of various cell types in vitro and imprints mechanical memory to tumour cells, which enables them to disseminate more efficiently in vivo.
- Kaustav Bera
- , Alexander Kiepas
- & Konstantinos Konstantopoulos
-
Article
| Open Access Single-cell genomic variation induced by mutational processes in cancer
Single-cell genomic variation induced by mutational processes in cancer
Single-cell whole-genome sequencing shows that 'foreground' cell-to-cell structural variation and alterations in copy number are associated with genomic diversity and evolution in triple-negative breast and high-grade serous ovarian cancers.
- Tyler Funnell
- , Ciara H. O’Flanagan
- & Samuel Aparicio
-
Article
| Open Access The co-evolution of the genome and epigenome in colorectal cancer
The co-evolution of the genome and epigenome in colorectal cancer
A study maps genetic and epigenetic heterogeneity of primary colorectal adenomas and cancers at single-clone resolution through spatial multi-omic profiling of individual glands and adjacent normal tissue.
- Timon Heide
- , Jacob Househam
- & Andrea Sottoriva
-
Article
| Open Access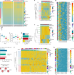 Phenotypic plasticity and genetic control in colorectal cancer evolution
Phenotypic plasticity and genetic control in colorectal cancer evolution
Intratumour genetic ancestry only infrequently affects gene expression traits and subclonal evolution in colorectal cancer, with most genetic intratumour variation having no detected phenotypic consequence and transcriptional plasticity being widespread within a tumour.
- Jacob Househam
- , Timon Heide
- & Trevor A. Graham
-
Clinical Briefing |
 Preoperative immune-therapy combination shows promise in skin cancer
Preoperative immune-therapy combination shows promise in skin cancer
Treatment with the drugs relatlimab and nivolumab before the surgical removal of a type of cancer called melanoma resulted in tumours becoming inviable in 57% of individuals, and no severe adverse effects were observed. People with a favourable treatment response had a better survival outcome than did those who did not respond.
-
Article |
 Subtype-specific 3D genome alteration in acute myeloid leukaemia
Subtype-specific 3D genome alteration in acute myeloid leukaemia
Extensive genomic analyses of the chromatin architecture in acute myeloid leukaemia reveals several characteristics, including subtype-specific distal enhancers and silencers, that may represent new anticancer therapeutic targets.
- Jie Xu
- , Fan Song
- & Feng Yue
-
Article
| Open Access Neoadjuvant relatlimab and nivolumab in resectable melanoma
Neoadjuvant relatlimab and nivolumab in resectable melanoma
Patients with resectable clinical stage III or oligometastatic stage IV melanoma were given neoadjuvant relatlimab and nivolumab combination immunotherapy, which induced a high pathologic complete response rate, indicating the efficacy and safety of this regimen.
- Rodabe N. Amaria
- , Michael Postow
- & Hussein A. Tawbi
-
World View |
 Cancer research needs better databases
Cancer research needs better databases
Progress on one of the world’s biggest killers will stall without big registries linking scattered records.
- T. S. Karin Eisinger-Mathason
-
News Feature |
 Cancer drugs are closing in on some of the deadliest mutations
Cancer drugs are closing in on some of the deadliest mutations
The protein KRAS, mutated in many cancers, was deemed ‘undruggable’. Now scientists are hoping to save lives with a batch of new compounds that target it.
- Heidi Ledford
-
Nature Index |
 Pandemic’s cancer backlogs receive treatment from AI innovation
Pandemic’s cancer backlogs receive treatment from AI innovation
Solutions are emerging for unmanageable clinical workloads, but experts warn of ethical issues.
- Bianca Nogrady
-
News Round-Up |
 AI mathematician, tumour fungi and Africa’s coronavirus genomes
AI mathematician, tumour fungi and Africa’s coronavirus genomes
The latest science news, in brief.
-
Article
| Open Access Collagenolysis-dependent DDR1 signalling dictates pancreatic cancer outcome
Collagenolysis-dependent DDR1 signalling dictates pancreatic cancer outcome
Cleaved and intact type I collagen have different effects on pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), and remodelling of type I collagen—mediated through DDR1 signalling—is a prognostic indicator for the survival of patients with PDAC.
- Hua Su
- , Fei Yang
- & Michael Karin
-
Spotlight |
 Blood vessel growth in benign tumours can illuminate malignant ones
Blood vessel growth in benign tumours can illuminate malignant ones
Joyce Bischoff studies infant haemangiomas to glean insights into potential cancer drugs.
- Helen Santoro
-
Spotlight |
 Seeking better cancer outcomes in Kenya
Seeking better cancer outcomes in Kenya
Research oncologist Peter Mulatya has a job that takes him from conducting clinical trials to long discussions with patients and families.
- Helen Santoro
-
Article |
 Opposing roles of hepatic stellate cell subpopulations in hepatocarcinogenesis
Opposing roles of hepatic stellate cell subpopulations in hepatocarcinogenesis
Subpopulations of cytokine-producing and myofibroblastic hepatic stellate cells, identified by single-cell RNA sequencing, protect against or promote the development of hepatocellular carcinoma via high expression of hepatocyte growth factor or type I collagen, respectively..
- Aveline Filliol
- , Yoshinobu Saito
- & Robert F. Schwabe
-
Article |
 STING-induced regulatory B cells compromise NK function in cancer immunity
STING-induced regulatory B cells compromise NK function in cancer immunity
Systemic treatment of pancreatic cancer with STING agonist stimulates regulatory B cells to express immunosuppressive cytokine IL-35, which weakens the anti-tumour function of natural killer cells.
- Sirui Li
- , Bhalchandra Mirlekar
- & Jenny P.-Y. Ting
-
Article
| Open Access Nuclear-embedded mitochondrial DNA sequences in 66,083 human genomes
Nuclear-embedded mitochondrial DNA sequences in 66,083 human genomes
A study examining DNA transfer from mitochondria to the nucleus using whole-genome sequences from 66,083 people shows that this is an ongoing dynamic process in normal cells with distinct roles in different types of cancer.
- Wei Wei
- , Katherine R. Schon
- & Patrick F. Chinnery
-
News |
 Do fungi lurking inside cancers speed their growth?
Do fungi lurking inside cancers speed their growth?
Studies that scrutinized thousands of tumour samples provide the clearest link yet between cancer and fungi — but more research is needed.
- Max Kozlov
-
Article
| Open Access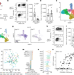 LRRC15+ myofibroblasts dictate the stromal setpoint to suppress tumour immunity
LRRC15+ myofibroblasts dictate the stromal setpoint to suppress tumour immunity
LRRC15-positive cancer-associated fibroblasts constitute a pivotal axis in tumorigenesis and are potential therapeutic targets to improve responses to immune checkpoint blockade.
- Akshay T. Krishnamurty
- , Justin A. Shyer
- & Shannon J. Turley
-
Article
| Open Access PD-1-cis IL-2R agonism yields better effectors from stem-like CD8+ T cells
PD-1-cis IL-2R agonism yields better effectors from stem-like CD8+ T cells
Binding of the PD1-IL2v immunocytokine to PD-1 and IL-2Rβγ on the same cell leads to an alternative differentiation of stem-like CD8+ T cells into better effectors rather than exhausted T cells in models of both chronic infection and cancer.
- Laura Codarri Deak
- , Valeria Nicolini
- & Pablo Umaña
-
Article |
 A mechanism for oxidative damage repair at gene regulatory elements
A mechanism for oxidative damage repair at gene regulatory elements
The nuclear mitotic apparatus protein NuMA helps to protect genes from oxidative damage by occupying regions around transcription start sites, binding DNA repair factors and promoting transcription following damage.
- Swagat Ray
- , Arwa A. Abugable
- & Sherif F. El-Khamisy
-
Article |
 A cellular hierarchy in melanoma uncouples growth and metastasis
A cellular hierarchy in melanoma uncouples growth and metastasis
A hierarchical model of melanoma tumour growth mirrors the cellular and molecular logic of cell-fate specification and differentiation of the underlying embryonic neural crest, and suggests that the ability to support growth and metastasis are limited to distinct pools of cells.
- Panagiotis Karras
- , Ignacio Bordeu
- & Jean-Christophe Marine
-
Article |
 Unified rhombic lip origins of group 3 and group 4 medulloblastoma
Unified rhombic lip origins of group 3 and group 4 medulloblastoma
Multi-omic mapping shows that group 3 and group 4 medulloblastomas have a common, human-specific developmental origin in the cerebellar rhombic lip, providing a basis for their ambiguous molecular features and overlapping anatomical location, and for the difficulty of modelling these tumours in mice.
- Kyle S. Smith
- , Laure Bihannic
- & Paul A. Northcott
-
News & Views |
 The origins of medulloblastoma tumours in humans
The origins of medulloblastoma tumours in humans
How certain subgroups of a childhood brain tumour called a medulloblastoma arise has been unclear. Evidence now implicates a cell type found only in developing human brains as the originator of these tumours.
- Timothy N. Phoenix
-
Article
| Open Access Antibody targeting of E3 ubiquitin ligases for receptor degradation
Antibody targeting of E3 ubiquitin ligases for receptor degradation
Membrane-bound E3 ubiquitin ligases RNF43 and ZNRF3 are overexpressed in colorectal cancer, and can be repurposed using proteolysis-targeting antibodies (PROTABs) to selectively degrade cell-surface receptors in tumours.
- Hadir Marei
- , Wen-Ting K. Tsai
- & Felipe de Sousa e Melo
-
Article |
 Failure of human rhombic lip differentiation underlies medulloblastoma formation
Failure of human rhombic lip differentiation underlies medulloblastoma formation
Derailed differentiation of human-specific progenitors of the developing cerebellar rhombic lip is the cause of group 4 medulloblastoma, the most common childhood brain tumour.
- Liam D. Hendrikse
- , Parthiv Haldipur
- & Michael D. Taylor
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Bone cancer
- Breast cancer
- Cancer epidemiology
- Cancer genetics
- Cancer genomics
- Cancer imaging
- Cancer metabolism
- Cancer microenvironment
- Cancer models
- Cancer of unknown primary
- Cancer prevention
- Cancer screening
- Cancer stem cells
- Cancer therapy
- CNS cancer
- Cysts
- Embryonal neoplasms
- Endocrine cancer
- Eye cancer
- Gastrointestinal cancer
- Germ cell tumours
- Gynaecological cancer
- Haematological cancer
- Hamartoma
- Head and neck cancer
- Lung cancer
- Mesothelioma
- Metastasis
- Oncogenes
- Oral cancer
- Paediatric cancer
- Sarcoma
- Skin cancer
- Testicular cancer
- Tumour angiogenesis
- Tumour biomarkers
- Tumour heterogeneity
- Tumour immunology
- Tumour-suppressor proteins
- Tumour virus infections
- Urological cancer

 Ovarian cancer mutational processes drive site-specific immune evasion
Ovarian cancer mutational processes drive site-specific immune evasion