Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access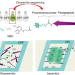 Rapid discovery of self-assembling peptides with one-bead one-compound peptide library
Rapid discovery of self-assembling peptides with one-bead one-compound peptide library
Self-assembling peptides have a range of potential applications but developing self-assembling sequences can be challenging. Here, the authors report on a one-bead one-compound combinatorial library where fluorescence is used to detect the potential for self-assembly and identified candidates are evaluated.
- Pei-Pei Yang
- , Yi-Jing Li
- & Kit S. Lam
-
Article
| Open Access Astral hydrogels mimic tissue mechanics by aster-aster interpenetration
Astral hydrogels mimic tissue mechanics by aster-aster interpenetration
The development of tissue-like materials which replicate the mechanical properties of tissue is of interest for a range of applications. Here, the authors report on the development of radial asters that form a gel network to stiffen in compression and soften in extension, resembling tissue mechanics.
- Qingqiao Xie
- , Yuandi Zhuang
- & Lingxiang Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access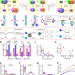 Integration of photocatalytic and dark-operating catalytic biomimetic transformations through DNA-based constitutional dynamic networks
Integration of photocatalytic and dark-operating catalytic biomimetic transformations through DNA-based constitutional dynamic networks
Nucleic acid-based constitutional dynamic networks (CDNs) enable control of various catalytic processes, but it is challenging to achieve intercommunication between different CDNs and by that mimic complex cell biology networks. Here, the authors report two CDNs that control the integration of photochemical and dark-operating processes, and show their intercommunication afforded by environmental components.
- Chen Wang
- , Michael P. O’Hagan
- & Itamar Willner
-
Article
| Open Access Self-assembly using a retro Diels-Alder reaction
Self-assembly using a retro Diels-Alder reaction
Despite their great utility in synthetic and materials chemistry, Diels-Alder and retro Diels-Alder reactions have been vastly unexplored in promoting self-assembly processes. Here the authors show the release of steric bulkiness associated with a bridged bicyclic Diels Alder adduct by the retro Diels-Alder reaction that allowed generation of two building blocks that spontaneously self-assembled to form a supramolecular polymer.
- Jaeyoung Park
- , Jung-Moo Heo
- & Jong-Man Kim
-
Article
| Open Access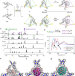 A curved host and second guest cooperatively inhibit the dynamic motion of corannulene
A curved host and second guest cooperatively inhibit the dynamic motion of corannulene
The preparation of artificial host–guest systems that display dynamic adaptation during guest binding is challenging. Here the authors report a chiral self-assembled tetrahedral cage featuring curved walls that reconfigures stereochemically to fit fullerene guests, regulates corannulene inversion, and enables the determination of co-guest enantiomeric excess by NMR spectroscopy.
- Yang Yang
- , Tanya K. Ronson
- & Jonathan R. Nitschke
-
Article
| Open Access Polymer cyclization for the emergence of hierarchical nanostructures
Polymer cyclization for the emergence of hierarchical nanostructures
Synthetic polymer nano-objects with well-defined hierarchical structures are important for a wide range of applications such as nanomaterial synthesis, catalysis, and therapeutics. Here the authors demonstrate the strategy of fabricating controlled hierarchical structures through self-assembly of folded synthetic polymers.
- Chaojian Chen
- , Manjesh Kumar Singh
- & Tanja Weil
-
Article
| Open Access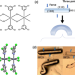 High-pressure reversibility in a plastically flexible coordination polymer crystal
High-pressure reversibility in a plastically flexible coordination polymer crystal
Mechanically flexible single crystals are promising materials for advanced technological applications. Here, the authors study the high pressure response of a plastically flexible coordination polymer and provide indication of an overall disparate mechanical response of bulk flexibility and quasi-hydrostatic compression within the same crystal lattice.
- Xiaojiao Liu
- , Adam A. L. Michalchuk
- & Colin R. Pulham
-
Article
| Open Access Self-assembly of an anion receptor with metal-dependent kinase inhibition and potent in vitro anti-cancer properties
Self-assembly of an anion receptor with metal-dependent kinase inhibition and potent in vitro anti-cancer properties
Artificial self-assembling systems such as anion receptors or ‘binders’ are largely unexplored for therapeutic applications. Here, the authors report self-assembling trimetallic cryptands containing copper, zinc or manganese that encapsulate a range of anions, are highly toxic to human cancer cell lines and show metal-dependent selectivity towards cancer vs. healthy cells linked to the selective inhibition of multiple kinases.
- Simon J. Allison
- , Jaroslaw Bryk
- & Craig R. Rice
-
Article
| Open Access Active coacervate droplets are protocells that grow and resist Ostwald ripening
Active coacervate droplets are protocells that grow and resist Ostwald ripening
Active coacervate droplets are droplets coupled to a chemical reaction that maintains them out of equilibrium, which can be used to drive active processes, but coacervates are still subject to passive processes that compete with or mask growth. Here, the authors present a nucleotide-based model for active coacervate droplets that form and grow by fuel-driven synthesis of ATP, and, importantly, do not undergo Ostwald ripening.
- Karina K. Nakashima
- , Merlijn H. I. van Haren
- & Evan Spruijt
-
Article
| Open Access Efficient ethylene purification by a robust ethane-trapping porous organic cage
Efficient ethylene purification by a robust ethane-trapping porous organic cage
The removal of ethane from ethylene is of importance in the petrochemical industry, but similar physicochemical properties of these molecules makes separation a challenging task. Here, the authors demonstrate that a robust octahedral calix[4]resorcinarene-based porous organic cage can separate high-purity ethylene from ethane/ethylene mixtures.
- Kongzhao Su
- , Wenjing Wang
- & Daqiang Yuan
-
Article
| Open Access Order–disorder transition of a rigid cage cation embedded in a cubic perovskite
Order–disorder transition of a rigid cage cation embedded in a cubic perovskite
In hybrid perovskites, the driving forces of an order–disorder transition that arise from the organic cation and inorganic framework cannot be easily untangled. Here, the authors introduce a cage-in-framework structure in which reorientation of the cage cation does not alter the cubic symmetry of the perovskite lattice.
- Zhifang Shi
- , Zheng Fang
- & Qixi Mi
-
Article
| Open Access Intracellular artificial supramolecules based on de novo designed Y15 peptides
Intracellular artificial supramolecules based on de novo designed Y15 peptides
Self-assembling peptides (SAPs) can be used to build biomaterials, but genetically encoded SAPs have rarely been used as building blocks in cells. Here, the authors design a SAP that can be genetically fused to target proteins to induce their intracellular clustering and modulate their signaling functions.
- Takayuki Miki
- , Taichi Nakai
- & Hisakazu Mihara
-
Article
| Open Access Multimodal host–guest complexation for efficient and stable perovskite photovoltaics
Multimodal host–guest complexation for efficient and stable perovskite photovoltaics
It remains a challenge to achieve a balance between performance and stability, as well as addressing the environmental impact of perovskite solar cells. Here, the authors propose a multimodal host-guest complexation strategy enabling these shortcomings to be addressed simultaneously.
- Hong Zhang
- , Felix Thomas Eickemeyer
- & Michael Grätzel
-
Article
| Open Access Living supramolecular polymerization of fluorinated cyclohexanes
Living supramolecular polymerization of fluorinated cyclohexanes
Living supramolecular polymerization can produce precise covalent polymers, but the scope of monomers is still narrow. Here the authors show a molecular platform for living supramolecular polymerization that is based on the unique structure of all-cis 1,2,3,4,5,6- 22 hexafluorocyclohexane, the most polar aliphatic compound reported to date.
- Oleksandr Shyshov
- , Shyamkumar Vadakket Haridas
- & Max von Delius
-
Article
| Open Access Versatile non-luminescent color palette based on guest exchange dynamics in paramagnetic cavitands
Versatile non-luminescent color palette based on guest exchange dynamics in paramagnetic cavitands
Host-guest supramolecular chemistry can be used as a tool to develop multicolor displays. Here, the authors present a system based on lanthanide-cradled cyclodextrins that allows to construct MRI-readable and erasable artificial non-luminescent color palettes.
- Elad Goren
- , Liat Avram
- & Amnon Bar-Shir
-
Article
| Open Access Acceleration of lipid reproduction by emergence of microscopic motion
Acceleration of lipid reproduction by emergence of microscopic motion
Artificial molecular systems can show complex kinetics of reproduction, however their integration into larger ensembles remains a challenge towards evolving higher order functionality. Here authors use show that self-reproducing lipids can initiate and accelerate octanol droplet movement and that reciprocally chemotactic movement of these droplets increases the rate of lipid reproduction substantially.
- Dhanya Babu
- , Robert J. H. Scanes
- & Nathalie Katsonis
-
Article
| Open Access Hierarchical communication of chirality for aromatic oligoamide sequences
Hierarchical communication of chirality for aromatic oligoamide sequences
Communication of chirality at a molecular level is the fundamental for transmitting chirality information but one-step communication modes in many artificial systems limits further processing the chirality information. Here, the authors report chirality communication of aromatic oligoamide sequences within interpenetrated helicate architecture in a hierarchical manner.
- Jiajia Zhang
- , Dan Luo
- & Quan Gan
-
Article
| Open Access Oriented arrangement of simple monomers enabled by confinement: towards living supramolecular polymerization
Oriented arrangement of simple monomers enabled by confinement: towards living supramolecular polymerization
Using simple monomers in living supramolecular polymerization is difficult due to energy principles. Here the authors use confinement from a layered double hydroxide nanomaterial to successfully polymerise several simple monomers with length control and narrow dispersity.
- Yingtong Zong
- , Si-Min Xu
- & Chao Lu
-
Article
| Open Access Overtemperature-protection intelligent molecular chiroptical photoswitches
Overtemperature-protection intelligent molecular chiroptical photoswitches
Realizing overtemperature protection with a molecular device is challenging. Here, the authors demonstrate an overtemperature protection function by integrating thermo- and photoresponsive functions into a pillar[6]arene based pseudocatanene.
- Jiabin Yao
- , Wanhua Wu
- & Cheng Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Semi-conducting 2D rectangles with tunable length via uniaxial living crystallization-driven self-assembly of homopolymer
Semi-conducting 2D rectangles with tunable length via uniaxial living crystallization-driven self-assembly of homopolymer
Semi-conducting two-dimensional polymer nanoobjects are promising materials but examples of self-assembled 2D nanosheets with controlled dimensions has not been shown before. Here, the authors precisely tune the length of 2D sheets of conjugated polymers by using blending, heating, and seeded-growth strategies.
- Sanghee Yang
- , Sung-Yun Kang
- & Tae-Lim Choi
-
Article
| Open Access Ultraviolet irradiation-responsive dynamic ultralong organic phosphorescence in polymeric systems
Ultraviolet irradiation-responsive dynamic ultralong organic phosphorescence in polymeric systems
Efficient stimulus-responsive phosphorescence organic materials are attractive, but are extremely rare because of unclear design principles and intrinsically spin-forbidden intersystem crossing. Here, the authors present a facile strategy to achieve ultraviolet irradiation-responsive ultralong room-temperature phosphorescence in several simple amorphous polymer materials.
- Yongfeng Zhang
- , Liang Gao
- & Yanli Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Organic superstructure microwires with hierarchical spatial organisation
Organic superstructure microwires with hierarchical spatial organisation
Rationally designing and precisely constructing the dimensions, configurations and compositions of organic micro- and nanomaterials are key issues in material chemistry, but remain challenging. Here, the authors realize the fine synthesis of organic superstructure microwires via a hierarchical epitaxial-growth approach.
- Ming-Peng Zhuo
- , Guang-Peng He
- & Liang-Sheng Liao
-
Article
| Open Access Generating biomembrane-like local curvature in polymersomes via dynamic polymer insertion
Generating biomembrane-like local curvature in polymersomes via dynamic polymer insertion
Investigating biomembrane curvature formation is important for studying intracellular processes, but the instability of liposome models mimicking these membranes restricts exploration of membrane processes. Here, the authors demonstrate control over the curvature formation in polymersome membranes by insertion of PNIPAm as stimuli responsive polymer.
- Jiawei Sun
- , Sjoerd J. Rijpkema
- & Daniela A. Wilson
-
Article
| Open Access Photoactivated nanomotors via aggregation induced emission for enhanced phototherapy
Photoactivated nanomotors via aggregation induced emission for enhanced phototherapy
Induced motion has emerged as a method to increase the efficacy of delivery and therapeutic outcomes using nanomaterials. Here, the authors report on a Janus gold shell polymersome with aggregation-induced emission molecules for phototactic and photodynamic therapy applications.
- Shoupeng Cao
- , Jingxin Shao
- & Jan C. M. van Hest
-
Matters Arising
| Open Access Oxalate production via oxidation of ascorbate rather than reduction of carbon dioxide
Oxalate production via oxidation of ascorbate rather than reduction of carbon dioxide
- Fatemeh Khamespanah
- , Maximilian Marx
- & Matthias Beller
-
Article
| Open Access Stereoselectivity in spontaneous assembly of rolled incommensurate carbon bilayers
Stereoselectivity in spontaneous assembly of rolled incommensurate carbon bilayers
Incommensurate pairing is a type of stereoisomerism, observed in carbon bilayers, that arises from the twisted orientations of the graphitic layers. Here, the authors create a finite molecular version of an incommensurate carbon bilayer in the form of two concentrically assembled cylindrical molecules.
- Taisuke Matsuno
- , Yutaro Ohtomo
- & Hiroyuki Isobe
-
Article
| Open Access Near quantitative synthesis of urea macrocycles enabled by bulky N-substituent
Near quantitative synthesis of urea macrocycles enabled by bulky N-substituent
Macrocycles are molecular structures extensively used in the design of catalysts, therapeutics and supramolecular assemblies but synthesis procedures that can produce macrocycles in high yield under high reaction concentrations are rare. Here the authors report the use of dynamic hindered urea bond for the construction of urea macrocycles with high efficiency.
- Yingfeng Yang
- , Hanze Ying
- & Jianjun Cheng
-
Article
| Open Access Photoresponsive supramolecular coordination polyelectrolyte as smart anticounterfeiting inks
Photoresponsive supramolecular coordination polyelectrolyte as smart anticounterfeiting inks
Photoluminescence printing is a widely applied anticounterfeiting technique but there are still challenges in developing new generation anticounterfeiting materials providing a high security level. Here, the authors demonstrate coordination dependent photochromic luminescence in a supramolecular coordination polyelectrolyte for multiple information authentication.
- Zhiqiang Li
- , Xiao Liu
- & Yanli Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular cannibalism: Sacrificial materials as precursors for hollow and multidomain single crystals
Molecular cannibalism: Sacrificial materials as precursors for hollow and multidomain single crystals
The coexistence of single-crystallinity with a multidomain morphology is a paradoxical crystallographic phenomenon. Here, the authors introduce a crystallographic morphology never reported before. The single-crystals with a curved and hollow morphology offer opportunities to generate a class of synthetic multidomain crystals.
- Maria Chiara di Gregorio
- , Merna Elsousou
- & Milko E. van der Boom
-
Article
| Open Access Digital navigation of energy–structure–function maps for hydrogen-bonded porous molecular crystals
Digital navigation of energy–structure–function maps for hydrogen-bonded porous molecular crystals
Energy–structure–function (ESF) maps can facilitate functional materials discovery. Here the authors provide a protocol for the digital navigation of ESF maps, as demonstrated for hydrogen-bonded organic frameworks constructed from triptycene- and spiro-biphenyl-based molecular building block.
- Chengxi Zhao
- , Linjiang Chen
- & Andrew I. Cooper
-
Article
| Open Access Ferroelectric columnar assemblies from the bowl-to-bowl inversion of aromatic cores
Ferroelectric columnar assemblies from the bowl-to-bowl inversion of aromatic cores
Organic ferroelectrics are of potential use in state-of-the-art ferroelectric devices but mechanistic insight in generating ferroelectricity remains limited. Here, the authors demonstrate that a bowl-to-bowl inversion of a bowl shaped organic molecule generates ferroelectric dipole relaxation, extending the concept of ferroelectricity in small organic molecules.
- Shunsuke Furukawa
- , Jianyun Wu
- & Tomoyuki Akutagawa
-
Article
| Open Access Physical networks from entropy-driven non-covalent interactions
Physical networks from entropy-driven non-covalent interactions
Physical networks typically employ enthalpy-dominated crosslinking interactions that become more dynamic at elevated temperatures. Here, the authors report an entropy-driven physical network based on polymer-nanoparticle interactions that exhibits mechanical properties that are invariant with temperature.
- Anthony C. Yu
- , Huada Lian
- & Eric A. Appel
-
Article
| Open Access Enantioselective preparation of mechanically planar chiral rotaxanes by kinetic resolution strategy
Enantioselective preparation of mechanically planar chiral rotaxanes by kinetic resolution strategy
Since the discovery of mechanically planar chiral rotaxanes and topologically chiral catenanes, their asymmetric synthesis has been a long-standing challenge. Here, the authors report enantioselective preparation of mechanically planar chiral rotaxanes with up to 99.9% ee in 29% yield.
- Ayumi Imayoshi
- , Bhatraju Vasantha Lakshmi
- & Takeo Kawabata
-
Article
| Open Access A DNA origami-based aptamer nanoarray for potent and reversible anticoagulation in hemodialysis
A DNA origami-based aptamer nanoarray for potent and reversible anticoagulation in hemodialysis
Safe haemodialysis is essential for patients with acute kidney injury and renal failure. Here the authors present a DNA origami-based approach with high affinity and specificity to thrombin, inhibiting coagulation.
- Shuai Zhao
- , Run Tian
- & Baoquan Ding
-
Article
| Open Access Self-assembled organic nanomedicine enables ultrastable photo-to-heat converting theranostics in the second near-infrared biowindow
Self-assembled organic nanomedicine enables ultrastable photo-to-heat converting theranostics in the second near-infrared biowindow
Organic agents with activity in the second near infrared region (NIR-II) are needed for precise treatment of cancer. Here, the authors develop boron difluoride formazanate nanosystem as a theranostic agent active in the NIR-II region for treating deep-seated hepatocellular carcinoma in mice.
- Huijing Xiang
- , Lingzhi Zhao
- & Yanli Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Biomimetic selenocystine based dynamic combinatorial chemistry for thiol-disulfide exchange
Biomimetic selenocystine based dynamic combinatorial chemistry for thiol-disulfide exchange
Thiol-disulfide exchange is an extensively used reversible reaction in dynamic combinatorial chemistry, but usually requires long time to reach equilibrium. Here, the authors employ selenocystine as a catalyst of thiol-disulfide exchange at low temperatures and basic pH, and show that it can promote disulfide bond formation during folding of a scrambled RNase A.
- Andrea Canal-Martín
- & Ruth Pérez-Fernández
-
Article
| Open Access Biomimetic caged platinum catalyst for hydrosilylation reaction with high site selectivity
Biomimetic caged platinum catalyst for hydrosilylation reaction with high site selectivity
Design of artificial catalysts to mimic enzyme activity and selectivity is a challenge in the catalysis field. Here, the authors design a platinum catalyst with a porous cage ligand which shows enzyme-like properties, such as high hydrosilylation activity and substrate size selectivity, while being recyclable.
- Ganghuo Pan
- , Chunhua Hu
- & Yuzhou Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Ru(II)Porphyrinate-based molecular nanoreactor for carbene insertion reactions and quantitative formation of rotaxanes by active-metal-template syntheses
Ru(II)Porphyrinate-based molecular nanoreactor for carbene insertion reactions and quantitative formation of rotaxanes by active-metal-template syntheses
Selectivity in carbene insertion reactions promoted by Ru(II)porphyrinates is achieved only upon careful control of substrate stoichiometry. Here, the authors demonstrate that endotopic catalysis and formation of mechanical bonds enables carbene insertions to occur selectively and in quantitative yield regardless of substrate stoichiometry.
- Liniquer A. Fontana
- , Marlon P. Almeida
- & Jackson D. Megiatto Jr.
-
Article
| Open Access Programmed spatial organization of biomacromolecules into discrete, coacervate-based protocells
Programmed spatial organization of biomacromolecules into discrete, coacervate-based protocells
Mimicking the crowded cytosol of cells in synthetic cells has been a major limitation to the functionality. Here, the authors used the interaction between nickel, nitrilotriacetic acid and histidine tagged proteins to control loading of macromolecules into spatially programmed coacervate-based protocells.
- Wiggert J. Altenburg
- , N. Amy Yewdall
- & Jan C. M. van Hest
-
Article
| Open Access Xenon binding by a tight yet adaptive chiral soft capsule
Xenon binding by a tight yet adaptive chiral soft capsule
Xenon binding carries potential for xenon separation and emerging applications in magnetic resonance imaging. Here, the authors report a rare example of a tight yet soft capsule, assembled from two chiral bisurea-bisthiourea macrocycle components, that can efficiently and adaptively bind xenon in both the solid state and solution.
- Shi-Xin Nie
- , Hao Guo
- & Qi-Qiang Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Light-directed trapping of metastable intermediates in a self-assembly process
Light-directed trapping of metastable intermediates in a self-assembly process
Knowledge about kinetically favored intermediate states in self-assembly processes can provide information about the self-assembly process but trapping these states without changing the reaction conditions is challenging. Here, the authors report a method for trapping metastable intermediates in self-assembly processes that is based on a photopolymerization strategy.
- Joonsik Seo
- , Joonyoung F. Joung
- & Jong-Man Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Using antibodies to control DNA-templated chemical reactions
Using antibodies to control DNA-templated chemical reactions
DNA-templated synthesis takes advantage of sequence-specific hybridization to accelerate chemical reactions. Here, the authors present templated synthesis controlled through antibody-antigen interactions.
- Lorena Baranda Pellejero
- , Malihe Mahdifar
- & Francesco Ricci
-
Article
| Open Access Structural order enhances charge carrier transport in self-assembled Au-nanoclusters
Structural order enhances charge carrier transport in self-assembled Au-nanoclusters
The collective properties of atomically precise nanoclusters bear vast potential for electronic materials by design. Here, the authors describe the self-assembly of Au32 nanoclusters into micro-crystals, which improves the electric conductivity and invokes new optical transitions caused by the high structural order.
- Florian Fetzer
- , Andre Maier
- & Marcus Scheele
-
Article
| Open Access Three host peculiarities of a cycloalkane-based micelle toward large metal-complex guests
Three host peculiarities of a cycloalkane-based micelle toward large metal-complex guests
Typical micelles are molecular assemblies composed of amphiphiles bearing linear alkyl chains. Herein, the authors present an uncommon type of cycloalkane-based bent amphiphile and its micelle which encapsulates large metal- complexes with high uptake efficiency, selectivity, and emissivity in water.
- Mamiko Hanafusa
- , Yamato Tsuchida
- & Michito Yoshizawa
-
Article
| Open Access Photosynthetic hydrogen production by droplet-based microbial micro-reactors under aerobic conditions
Photosynthetic hydrogen production by droplet-based microbial micro-reactors under aerobic conditions
The development of techniques capable of orchestrating the assembly of living cells into multicellular ensembles with synergistic and function is challenge. Here, the authors construct algal or algal/bacterial cells-based core shell-like structure based on aqueous two-phase system for synergic photosynthetic H2 production.
- Zhijun Xu
- , Shengliang Wang
- & Stephen Mann
-
Article
| Open Access Synthesis and X-ray characterization of 15- and 16-vertex closo-carboranes
Synthesis and X-ray characterization of 15- and 16-vertex closo-carboranes
The synthesis of closo-carboranes with more than 14 vertexes is challenging, and no examples have been reported to date. Herein, the authors present the long-sought 15- and 16-vertex closo-carboranes, in which the introduction of silyl groups to the two cage carbons is crucial; this finding might enable the synthesis of even larger carborane analogs in the future.
- Fangrui Zheng
- , Tsz Hin Yui
- & Zuowei Xie
-
Article
| Open Access Self-assembled Möbius strips with controlled helicity
Self-assembled Möbius strips with controlled helicity
Different to exploring molecular topology, the development of supramolecular topology has been limited due to a lack of reliable synthetic methods. Here, the authors describe a supramolecular strategy to access Möbius strips through bending and cyclization of twisted nanofibers self-assembled from chiral glutamate amphiphiles.
- Guanghui Ouyang
- , Lukang Ji
- & Minghua Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Highly efficient synthesis of non-planar macrocycles possessing intriguing self-assembling behaviors and ethene/ethyne capture properties
Highly efficient synthesis of non-planar macrocycles possessing intriguing self-assembling behaviors and ethene/ethyne capture properties
The design of covalent macrocycles which show characteristic self-assembly behaviour and host-guest properties is challenging. Here, the authors demonstrate the synthesis of diphenylamine[n]arenes through a one-pot synthesis and demonstrate the π-π pi stacking of the non-planar rings as well as ethane/ethyne host-guest interactions.
- Lijun Mao
- , Yang Hu
- & Xueliang Shi
-
Article
| Open Access Control of self-assembly pathways toward conglomerate and racemic supramolecular polymers
Control of self-assembly pathways toward conglomerate and racemic supramolecular polymers
Homo- and heterochiral aggregation is a process of interest to prebiotic and chiral separation chemistry. Here, the authors analyze the self-assembly of a racemic mixture into 1D supramolecular polymers and find homochiral aggregation into conglomerates under kinetic control, while under thermodynamic control a racemic polymer is formed.
- Marius Wehner
- , Merle Insa Silja Röhr
- & Frank Würthner

 Light-fueled transient supramolecular assemblies in water as fluorescence modulators
Light-fueled transient supramolecular assemblies in water as fluorescence modulators