Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanically interlocked [c2]daisy chain backbone enabling advanced shape-memory polymeric materials
Mechanically interlocked [c2]daisy chain backbone enabling advanced shape-memory polymeric materials
Mechanically interlocked structures in polymer backbones can give interesting functionality, but can be challenging to prepare and control. Here, the authors report the development of polymers with a daisy chain unit in the backbone that are capable of shape memory behaviour.
- Shang-Wu Zhou
- , Danlei Zhou
- & Da-Hui Qu
-
Article
| Open Access Cross-catenation between position-isomeric metallacages
Cross-catenation between position-isomeric metallacages
The study of cross-catenated metallacages could provide facile insights into achieving more precise control over low-symmetry/high-complexity hierarchical assembly systems but is currently lacking. Here, the authors report a cross-catenane formed between two position-isomeric Pt(II) metallacages in the solid state.
- Yiliang Wang
- , Taotao Liu
- & Jun Li
-
Article
| Open Access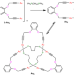 Self-assembly of the smallest and tightest molecular trefoil knot
Self-assembly of the smallest and tightest molecular trefoil knot
The synthesis of molecular knots remains challenging. Here, the authors report the synthesis of a chiral molecular trefoil metallaknot by self-assembly which contains only 54 atoms in the backbone.
- Zhiwen Li
- , Jingjing Zhang
- & Richard J. Puddephatt
-
Article
| Open Access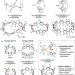 A dodecamethoxy[6]cycloparaphenylene consisting entirely of hydroquinone ethers: unveiling in-plane aromaticity through a rotaxane structure
A dodecamethoxy[6]cycloparaphenylene consisting entirely of hydroquinone ethers: unveiling in-plane aromaticity through a rotaxane structure
“Cycloparaphenylenes consisting of are cyclic π-conjugated structures presetting interesting physical properties upon functionalization. However, the ring strain and steric hindrance of the substituents hamper the functionalization of small sized cycloparaphenylenes. Here, the authors describe a [6]cycloparaphenylene with twelve methoxy units employed to form a rotaxane with in-plane aromaticity upon oxidation.”
- Naoki Narita
- , Yusuke Kurita
- & Yoshitaka Tsuchido
-
Article
| Open Access Selective synthesis of tightly- and loosely-twisted metallomacrocycle isomers towards precise control of helicity inversion motion
Selective synthesis of tightly- and loosely-twisted metallomacrocycle isomers towards precise control of helicity inversion motion
Molecular twist is a characteristic component of molecular machines. Here the authors report a kinetically selective synthesis of tightly- and loosely-twisted isomers of a trinuclear Pd-macrocycle and their markedly different molecular behaviours.
- Tomoki Nakajima
- , Shohei Tashiro
- & Mitsuhiko Shionoya
-
Article
| Open Access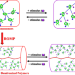 Stimuli-responsive rotaxane-branched dendronized polymers with tunable thermal and rheological properties
Stimuli-responsive rotaxane-branched dendronized polymers with tunable thermal and rheological properties
Enriching the toolbox of polymers, the design and construction of novel polymers with desired properties and functions remains an attractive topic in polymer chemistry. Here the authors demonstrate rotaxane-branched dendronized polymers with rotaxane-branched dendrons attached onto the polymer chains as polymers with attractive dynamic properties.
- Yu Zhu
- , Hanqiu Jiang
- & Hai-Bo Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Allosteric control of olefin isomerization kinetics via remote metal binding and its mechanochemical analysis
Allosteric control of olefin isomerization kinetics via remote metal binding and its mechanochemical analysis
The mechanisms by which changes in local geometries of receptor sites lower activation reaction barriers in electronically uncoupled, remote reaction moieties remain relatively unexplored. Here, the authors demonstrate allosteric acceleration in the thermal isomerization of an alkene triggered by the binding of a metal ion to a remote receptor site.
- Yichen Yu
- , Robert T. O’Neill
- & Stephen L. Craig
-
Article
| Open Access The host–guest inclusion driven by host-stabilized charge transfer for construction of sequentially red-shifted mechanochromic system
The host–guest inclusion driven by host-stabilized charge transfer for construction of sequentially red-shifted mechanochromic system
The understanding of the structure-property relationship of mechanochromic luminescent molecules remains challenging. Here, the authors elucidate the effect of host-guest interactions on the mechanochromic properties of organic molecules.
- Dongdong Sun
- , Yong Wu
- & Simin Liu
-
Article
| Open Access An approach to MOFaxanes by threading ultralong polymers through metal–organic framework microcrystals
An approach to MOFaxanes by threading ultralong polymers through metal–organic framework microcrystals
Mechanically interlocked architectures inspired the fabrication of numerous molecular systems, but the topological design of such architectures has not been fully explored from the nano- to the macroscopic scale. Here, the authors propose a MOFaxane, comprised of long chain molecules penetrating a microcrystal of metal– organic framework.
- Tomoya Iizuka
- , Hiroyuki Sano
- & Takashi Uemura
-
Article
| Open Access A supramolecular cucurbit[8]uril-based rotaxane chemosensor for the optical tryptophan detection in human serum and urine
A supramolecular cucurbit[8]uril-based rotaxane chemosensor for the optical tryptophan detection in human serum and urine
Sensing small biomolecules in biofluids using host-guest chemosensors remains challenging, in part due to the impact of interfering components. Here, the authors develop a dual-macrocyclic rotaxane for tryptophan detection which can function in biofluids such as human serum and urine.
- Joana Krämer
- , Laura M. Grimm
- & Frank Biedermann
-
Article
| Open Access Amplification of integrated microscopic motions of high-density [2]rotaxanes in mechanically interlocked networks
Amplification of integrated microscopic motions of high-density [2]rotaxanes in mechanically interlocked networks
Amplifying molecular motion to macroscopic material property is attractive but challenging. Here, the authors report mechanically interlocked networks with dense rotaxane backbones whose microscopic motion is integrated into decent mechanical properties of bulk materials.
- Xue Yang
- , Lin Cheng
- & Xuzhou Yan
-
Article
| Open Access An unexpected dual-emissive luminogen with tunable aggregation-induced emission and enhanced chiroptical property
An unexpected dual-emissive luminogen with tunable aggregation-induced emission and enhanced chiroptical property
Organic materials with both aggregation induced emission (AIE) and aggregation-caused quenching (ACQ) effects that can emit with multiple wavelengths in the solution and aggregated state are rarely reported. Here, the authors report a chiral dual-emissive bismacrocycle which shows the unique ACQ and AIE effects inducing redshift emission with near white-light emission.
- Xinyu Zhang
- , Huiqing Liu
- & Pingwu Du
-
Article
| Open Access Switchable bifunctional molecular recognition in water using a pH-responsive Endo-functionalized cavity
Switchable bifunctional molecular recognition in water using a pH-responsive Endo-functionalized cavity
The development of synthetic host-guest systems for stimuli-responsive molecular recognition in water is challenging. Here, the authors report a pair of water-soluble naphthotubes with a pH-responsive cavity for which switchable bifunctional recognition in water is achieved.
- Xiaoping Wang
- , Mao Quan
- & Wei Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access Paramagnetic relaxation enhancement NMR as a tool to probe guest binding and exchange in metallohosts
Paramagnetic relaxation enhancement NMR as a tool to probe guest binding and exchange in metallohosts
Paramagnetic metallohost systems are difficult to characterize. Here the authors report that the paramagnetic relaxation enhancement effect can be used to prove by nuclear magnetic resonance experiments that Mn(III) porphyrin cage compounds can bind and thread low molecular weight and polymeric guests.
- Anne Swartjes
- , Paul B. White
- & Roeland J. M. Nolte
-
Article
| Open Access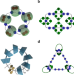 Mechanically interlocked networks cross-linked by a molecular necklace
Mechanically interlocked networks cross-linked by a molecular necklace
Constructing cross-linked networks with different topologies is attractive but challenging. Here the authors present mechanically interlocked networks cross-linked by a molecular necklace whose peculiar architectural and dynamic features endow the materials with robust yet mechanically adaptive properties.
- Zhaoming Zhang
- , Jun Zhao
- & Xuzhou Yan
-
Article
| Open Access Selective photoinduced charge separation in perylenediimide-pillar[5]arene rotaxanes
Selective photoinduced charge separation in perylenediimide-pillar[5]arene rotaxanes
The development of complex molecular machinery requires a detailed appreciation of the factors that control energy pathways through the nanoscale scaffold. Here, the authors demonstrate that hetero-rotaxanes can be employed to create assemblies of different redox and photo-active components that enable selective tuning of energy transfer pathways.
- Nicholas Pearce
- , Katherine E. A. Reynolds
- & Neil R. Champness
-
Article
| Open Access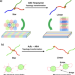 Topology-transformable block copolymers based on a rotaxane structure: change in bulk properties with same composition
Topology-transformable block copolymers based on a rotaxane structure: change in bulk properties with same composition
The topology of a polymer is normally a fixed property of the material, derived from the characteristic of the monomers and their linkages. Here the authors present a method to transform the topology of block copolymers containing rotaxane linkages via acetylation.
- Hiroki Sato
- , Daisuke Aoki
- & Toshikazu Takata
-
Article
| Open Access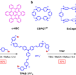 A contorted nanographene shelter
A contorted nanographene shelter
Encapsulating large and contorted nanographenes inside artificial receptors remain challenging. This work reports the synthesis, characterization and binding properties of a trigonal prismatic cage compound that can serve as a receptor for contorted nanographene derivatives.
- Huang Wu
- , Yu Wang
- & J. Fraser Stoddart
-
Article
| Open Access Hierarchical communication of chirality for aromatic oligoamide sequences
Hierarchical communication of chirality for aromatic oligoamide sequences
Communication of chirality at a molecular level is the fundamental for transmitting chirality information but one-step communication modes in many artificial systems limits further processing the chirality information. Here, the authors report chirality communication of aromatic oligoamide sequences within interpenetrated helicate architecture in a hierarchical manner.
- Jiajia Zhang
- , Dan Luo
- & Quan Gan
-
Article
| Open Access Overtemperature-protection intelligent molecular chiroptical photoswitches
Overtemperature-protection intelligent molecular chiroptical photoswitches
Realizing overtemperature protection with a molecular device is challenging. Here, the authors demonstrate an overtemperature protection function by integrating thermo- and photoresponsive functions into a pillar[6]arene based pseudocatanene.
- Jiabin Yao
- , Wanhua Wu
- & Cheng Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Enantioselective preparation of mechanically planar chiral rotaxanes by kinetic resolution strategy
Enantioselective preparation of mechanically planar chiral rotaxanes by kinetic resolution strategy
Since the discovery of mechanically planar chiral rotaxanes and topologically chiral catenanes, their asymmetric synthesis has been a long-standing challenge. Here, the authors report enantioselective preparation of mechanically planar chiral rotaxanes with up to 99.9% ee in 29% yield.
- Ayumi Imayoshi
- , Bhatraju Vasantha Lakshmi
- & Takeo Kawabata
-
Article
| Open Access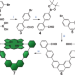 Ru(II)Porphyrinate-based molecular nanoreactor for carbene insertion reactions and quantitative formation of rotaxanes by active-metal-template syntheses
Ru(II)Porphyrinate-based molecular nanoreactor for carbene insertion reactions and quantitative formation of rotaxanes by active-metal-template syntheses
Selectivity in carbene insertion reactions promoted by Ru(II)porphyrinates is achieved only upon careful control of substrate stoichiometry. Here, the authors demonstrate that endotopic catalysis and formation of mechanical bonds enables carbene insertions to occur selectively and in quantitative yield regardless of substrate stoichiometry.
- Liniquer A. Fontana
- , Marlon P. Almeida
- & Jackson D. Megiatto Jr.
-
Article
| Open Access Highly efficient synthesis of non-planar macrocycles possessing intriguing self-assembling behaviors and ethene/ethyne capture properties
Highly efficient synthesis of non-planar macrocycles possessing intriguing self-assembling behaviors and ethene/ethyne capture properties
The design of covalent macrocycles which show characteristic self-assembly behaviour and host-guest properties is challenging. Here, the authors demonstrate the synthesis of diphenylamine[n]arenes through a one-pot synthesis and demonstrate the π-π pi stacking of the non-planar rings as well as ethane/ethyne host-guest interactions.
- Lijun Mao
- , Yang Hu
- & Xueliang Shi
-
Article
| Open Access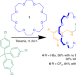 Weak functional group interactions revealed through metal-free active template rotaxane synthesis
Weak functional group interactions revealed through metal-free active template rotaxane synthesis
Weak interactions between functional groups are often difficult to characterize in host–guest complexes. Here, the authors report the metal-free active template synthesis of a series of rotaxanes that permit a range of kinetically stabilized, weak crown ether-axle interactions to be characterized in solution and the solid state.
- Chong Tian
- , Stephen D. P. Fielden
- & David A. Leigh
-
Article
| Open Access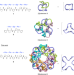 A metal–peptide capsule by multiple ring threading
A metal–peptide capsule by multiple ring threading
Constructing molecular cages from entangled molecules is a complex task requiring precise topological control. Here, the authors thread together six metal-peptide rings into a giant cubic molecular capsule with a defined cavity and 24 crossover points.
- Tomohisa Sawada
- , Yuuki Inomata
- & Makoto Fujita
-
Perspective
| Open Access Kinetic asymmetry allows macromolecular catalysts to drive an information ratchet
Kinetic asymmetry allows macromolecular catalysts to drive an information ratchet
The mechanism by which macromolecular catalysts use energy from exergonic reactions to move, adapt, and assemble has been unclear. In this Perspective article, R. Dean Astumian shows that in addition to disequilibrium of the catalyzed reaction, kinetic asymmetry is the essential feature required to drive non-equilibrium response by an information ratchet mechanism.
- R. Dean Astumian
-
Article
| Open Access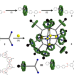 A [13]rotaxane assembled via a palladium molecular capsule
A [13]rotaxane assembled via a palladium molecular capsule
Mechanically interlocked molecules and molecular cages are two important themes in supramolecular chemistry. Here, the authors combine these concepts to construct a giant [13]rotaxane built around a palladium capsule, one of the most complex metallosupramolecular assemblies yet.
- Jesus Ferrando-Soria
- , Antonio Fernandez
- & Richard E. P. Winpenny
-
Article
| Open Access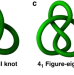 Coordination-driven self-assembly of a molecular figure-eight knot and other topologically complex architectures
Coordination-driven self-assembly of a molecular figure-eight knot and other topologically complex architectures
Molecular knots and links continue to fascinate synthetic chemists. Here, the authors use stacking and hydrogen-bonding interactions between a set of similar building blocks to construct several complex molecular topologies, including a figure-eight knot and a trefoil knot.
- Li-Long Dang
- , Zhen-Bo Sun
- & Guo-Xin Jin
-
Article
| Open Access Metal–peptide rings form highly entangled topologically inequivalent frameworks with the same ring- and crossing-numbers
Metal–peptide rings form highly entangled topologically inequivalent frameworks with the same ring- and crossing-numbers
For interlocking ring structures, knot theory predicts that the number of topologically different links increases with ring and crossing number. Here, the authors use a peptide folding-and-assembly strategy to selectively realize two highly entangled catenanes with 4 rings and 12 crossings, representing two of the 100 predicted topologies with this complexity.
- Tomohisa Sawada
- , Ami Saito
- & Makoto Fujita
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular Russian dolls
Molecular Russian dolls
Hierarchical non-intertwined ring-in-ring complexes are intriguing but challenging supramolecular targets. Here, the authors describe a box-in-box assembly based on radical-pairing interactions between two rigid diradical dicationic cyclophanes; the inner box can further accommodate guests to form Russian doll-like assemblies.
- Kang Cai
- , Mark C. Lipke
- & J. Fraser Stoddart
-
Article
| Open Access Cramming versus threading of long amphiphilic oligomers into a polyaromatic capsule
Cramming versus threading of long amphiphilic oligomers into a polyaromatic capsule
Molecular capsules typically bind only guests with volumes smaller than their cavities. Here, the authors find that a polyaromatic capsule accommodates linear amphiphilic oligomers in a length-dependent manner, whereas short chains are fully crammed into the cavity, long chains can be incorporated into the capsule in a threaded fashion.
- Masahiro Yamashina
- , Shunsuke Kusaba
- & Michito Yoshizawa
-
Article
| Open Access Dual stimuli-responsive rotaxane-branched dendrimers with reversible dimension modulation
Dual stimuli-responsive rotaxane-branched dendrimers with reversible dimension modulation
Mechanically interlocked molecules are extensively applied as artificial molecular machines but rotaxane-branched dendrimers are rarely explored because of synthetic challenges. Here the authors present the construction of dual stimuli-responsive rotaxane-branched dendrimer which can be stimulated by DMSO or acetate ions.
- Xu-Qing Wang
- , Wei Wang
- & Hai-Bo Yang
-
Article
| Open Access An isolable catenane consisting of two Möbius conjugated nanohoops
An isolable catenane consisting of two Möbius conjugated nanohoops
Molecules exhibiting Möbius topology are fascinating but challenging synthetic targets. Here, the authors report the elegant synthesis and crystal structure of a catenane formed from two fully conjugated, interlocked Möbius nanohoops, and use theoretical calculations to understand its conformational stability and aromaticity.
- Yang-Yang Fan
- , Dandan Chen
- & Huan Cong
-
Article
| Open Access High-throughput discovery of organic cages and catenanes using computational screening fused with robotic synthesis
High-throughput discovery of organic cages and catenanes using computational screening fused with robotic synthesis
Supramolecular assemblies remain of great importance to a variety of fields, yet their targeted design and synthesis remains highly challenging. Here, Cooper and colleagues combine computational screening with high-throughput robotic synthesis and discover 33 new organic cage molecules that form cleanly in one-pot syntheses.
- R. L. Greenaway
- , V. Santolini
- & A. I. Cooper
-
Article
| Open Access Positive and negative regulation of carbon nanotube catalysts through encapsulation within macrocycles
Positive and negative regulation of carbon nanotube catalysts through encapsulation within macrocycles
Doping carbon nanomaterials with heteroatoms is the most common way to change their catalytic activity. Here, the authors show that the catalytic properties of single-walled carbon nanotubes can be modified by non-covalently encapsulating them within electron-accepting or electron-donating macrocycles to form rotaxane-like structures.
- Matías Blanco
- , Belén Nieto-Ortega
- & Emilio M. Pérez
-
Article
| Open Access Thermally triggered polyrotaxane translational motion helps proton transfer
Thermally triggered polyrotaxane translational motion helps proton transfer
Proton exchange is critical in many applications, such as in conductive proton exchange membranes, but achieving fast proton exchange still remains a challenge. Here the authors report fast proton exchange in a rotaxane based polymer by exploiting thermally triggered translational motion of the mechanically bonded rotaxane.
- Xiaolin Ge
- , Yubin He
- & Tongwen Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Coulombic-enhanced hetero radical pairing interactions
Coulombic-enhanced hetero radical pairing interactions
Homo radical spin-pairing interactions between two identical aromatic radicals are common in supramolecular chemistry, but hetero interactions between two different aromatic radicals are seldom observed. Here, the authors find that hetero radical pairing between a radical cation and a radical anion, together with Coulombic attraction, can drive host-guest recognition, representing a new supramolecular recognition motif.
- Xujun Zheng
- , Yang Zhang
- & Hao Li
-
Article
| Open Access A multistage rotational speed changing molecular rotor regulated by pH and metal cations
A multistage rotational speed changing molecular rotor regulated by pH and metal cations
Molecular rotors with rotational speed modulation have not yet been well established. Here, the authors report a pH and metal cation triggered molecular rotor, which allows for a four stage speed modulation in the slow-to-fast frequency range.
- Yingying Wu
- , Guangxia Wang
- & Ying Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Higher-generation type III-B rotaxane dendrimers with controlling particle size in three-dimensional molecular switching
Higher-generation type III-B rotaxane dendrimers with controlling particle size in three-dimensional molecular switching
The complexity of rotaxane dendrimers poses a great synthetic challenge and the synthesis of higher generation rotaxane dendrimers has therefore rarely been reported. Here the authors report the synthesis of acid-base switchable rotaxane dendrimers up to generation 4 and demonstrate the uptake and release of guest molecules.
- Chak-Shing Kwan
- , Rundong Zhao
- & Ken Cham-Fai Leung
-
Article
| Open Access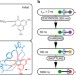 Transient two-dimensional vibrational spectroscopy of an operating molecular machine
Transient two-dimensional vibrational spectroscopy of an operating molecular machine
A deeper understanding of the mechanics of molecular machines is limited by the fast motions which are in the nanosecond or picosecond timescale. Here the authors present a real-time observation of structural changes in a rotaxane-based molecular shuttle by transient two-dimensional infrared spectroscopy.
- Matthijs R. Panman
- , Chris N. van Dijk
- & Sander Woutersen
-
Article
| Open Access Synthesis of spiro quasi[1]catenanes and quasi[1]rotaxanes via a templated backfolding strategy
Synthesis of spiro quasi[1]catenanes and quasi[1]rotaxanes via a templated backfolding strategy
Spiro compounds contain two or more rings linked together through one common atom. Here the authors provide a method to backfold both rings, producing spiro quasi[1]catenanes, via a strategy of temporarily linking the linear intermediates with covalent bonds.
- Luuk Steemers
- , Martin J. Wanner
- & Jan H. van Maarseveen
-
Article
| Open Access Synthesizing topological structures containing RNA
Synthesizing topological structures containing RNA
In vivo, complex topologies have been identified in proteins and DNA, while their existence in RNA is still unclear. Here, the authors design synthetic topological structures containing single stranded RNA, offering tools for investigating biologically relevant questions about RNA topology.
- Di Liu
- , Yaming Shao
- & Yossi Weizmann
-
Article
| Open Access Rapid and reversible photoinduced switching of a rotaxane crystal
Rapid and reversible photoinduced switching of a rotaxane crystal
Crystalline phase transition can be used to detect changes in the solid state properties of materials. Here, the authors describe the mechanical response of a crystal composed of ferrocene-containing rotaxane to laser irradiation.
- Kai-Jen Chen
- , Ya-Ching Tsai
- & Masaki Horie
-
Article
| Open Access Long-range movement of large mechanically interlocked DNA nanostructures
Long-range movement of large mechanically interlocked DNA nanostructures
Rotaxanes are interlocked molecules that can undergo sliding and rotational movements and can be used in artificial molecular machines and motors. Here, Simmel and co-workers show a rigid rotaxane structures consisting of DNA origami subunits that can slide over several hundreds of nanometres.
- Jonathan List
- , Elisabeth Falgenhauer
- & Friedrich C. Simmel
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanically selflocked chiral gemini-catenanes
Mechanically selflocked chiral gemini-catenanes
Mechanically locked molecules provide interesting topological structures and can present challenging synthetic targets. Here the authors report the synthesis of mechanically self-locked molecules, including chiral endo-spirobicyclics containing multiply interlocked rings within a single molecule.
- Sheng-Hua Li
- , Heng-Yi Zhang
- & Yu Liu

 Dynamic mechanostereochemical switching of a co-conformationally flexible [2]catenane controlled by specific ionic guests
Dynamic mechanostereochemical switching of a co-conformationally flexible [2]catenane controlled by specific ionic guests