Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Convoluted micellar morphological transitions driven by tailorable mesogenic ordering effect from discotic mesogen-containing block copolymer
Convoluted micellar morphological transitions driven by tailorable mesogenic ordering effect from discotic mesogen-containing block copolymer
Assembly of block copolymers can be controlled to give varying morphologies and functionalities, but there are still aspects of the process that are not well understood. Here, the authors report convoluted self-assembly behaviours of block copolymers with discotic liquid crystalline moieties.
- Huanzhi Yang
- , Yunjun Luo
- & Xiaoyu Li
-
Article
| Open Access Scalable production of structurally colored composite films by shearing supramolecular composites of polymers and colloids
Scalable production of structurally colored composite films by shearing supramolecular composites of polymers and colloids
Structurally coloured composite films are flexible optical materials with potential in a range of applications, but their production is impacted by long time-frames and limited materials. Here, the authors report a method for the production of large scale films by shearing supramolecular composites.
- Miaomiao Li
- , Bolun Peng
- & Jintao Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access Creating amphiphilic porosity in two-dimensional covalent organic frameworks via steric-hindrance-mediated precision hydrophilic-hydrophobic microphase separation
Creating amphiphilic porosity in two-dimensional covalent organic frameworks via steric-hindrance-mediated precision hydrophilic-hydrophobic microphase separation
Creating different pore environments within a covalent organic framework (COF) leads to useful multicompartment structure and multiple functions. Here, the authors propose a strategy to construct amphiphilic COFs with separated hydrophilic and hydrophobic nanochannels by precisely controlling the distribution of hydrophilic and hydrophobic segments in two different kinds of pores.
- Shu-Yan Jiang
- , Zhi-Bei Zhou
- & Xin Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Biomimetic chiral hydrogen-bonded organic-inorganic frameworks
Biomimetic chiral hydrogen-bonded organic-inorganic frameworks
Assembly is an interesting strategy to build chiral hierarchies with premade properties and functionalities. Here, the authors present assembled chiral hydrogen-bonded organic-inorganic frameworks with dynamical chiroptical activities and employ them as powerful and recoverable platforms for enantioselective recognition of chiral aliphatic substrates.
- Jun Guo
- , Yulong Duan
- & Yi Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Thermo-responsive chiral micelles as recyclable organocatalyst for asymmetric Rauhut-Currier reaction in water
Thermo-responsive chiral micelles as recyclable organocatalyst for asymmetric Rauhut-Currier reaction in water
Developing eco-friendly chiral organocatalysts with the combined advantages of homogeneous catalysis and heterogeneous processes is challenging. Here, the authors present, a family of amphiphilic one handed helical polyisocyanides bearing phosphine pendants which self-assembled into well-defined chiral micelles in water and show thermo-responsiveness
- Lei Xu
- , Li Zhou
- & Zong-Quan Wu
-
Article
| Open Access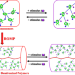 Stimuli-responsive rotaxane-branched dendronized polymers with tunable thermal and rheological properties
Stimuli-responsive rotaxane-branched dendronized polymers with tunable thermal and rheological properties
Enriching the toolbox of polymers, the design and construction of novel polymers with desired properties and functions remains an attractive topic in polymer chemistry. Here the authors demonstrate rotaxane-branched dendronized polymers with rotaxane-branched dendrons attached onto the polymer chains as polymers with attractive dynamic properties.
- Yu Zhu
- , Hanqiu Jiang
- & Hai-Bo Yang
-
Article
| Open Access A cage-on-MOF strategy to coordinatively functionalize mesoporous MOFs for manipulating selectivity in adsorption and catalysis
A cage-on-MOF strategy to coordinatively functionalize mesoporous MOFs for manipulating selectivity in adsorption and catalysis
Functionalising porous materials is a route to enhancing properties of hybrid materials. Here authors present a “Cage-on-MOF” strategy to modify the surface of mesoporous MOFs by using molecular cages to achieve selective dyes adsorption behavior and heterogeneous catalysis.
- Yu Liang
- , Xiaoxin Yang
- & Yu Fang
-
Article
| Open Access Saddles as rotational locks within shape-assisted self-assembled nanosheets
Saddles as rotational locks within shape-assisted self-assembled nanosheets
Self-assembly in the formation of two dimensional materials typically relies upon strong, directional interactions instead of covalent bonds but control over less directional forces remains challenging. Here, the authors show the process of shape-assisted self-assembly to be consistent across a range of derivatives that highlights the restriction of rotational motion.
- Joseph F. Woods
- , Lucía Gallego
- & Michel Rickhaus
-
Article
| Open Access A stretchable, mechanically robust polymer exhibiting shape-memory-assisted self-healing and clustering-triggered emission
A stretchable, mechanically robust polymer exhibiting shape-memory-assisted self-healing and clustering-triggered emission
Polymers formed with non-covalent bonds are increasingly being developed, but often show inferior mechanical properties. Here, the authors report the development of high performances polyurethane-urea elastomer with shape-memory assisted self-healing behaviour
- Xiaoyue Wang
- , Jing Xu
- & Xinrui Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Multi-chiral materials comprising metallosupramolecular and covalent helical polymers containing five axial motifs within a helix
Multi-chiral materials comprising metallosupramolecular and covalent helical polymers containing five axial motifs within a helix
The axial helical structure of supramolecular and covalent polymers provides communication mechanisms among monomer repeating units. Here, the authors present multi-helical materials comprising five axial motifs that combine information from both metallosupramolecular and covalent helical polymers
- Francisco Rey- Tarrío
- , Emilio Quiñoá
- & Félix Freire
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanosensitive non-equilibrium supramolecular polymerization in closed chemical systems
Mechanosensitive non-equilibrium supramolecular polymerization in closed chemical systems
Chemical fuel-driven supramolecular systems have been developed showing out of-equilibrium functions such as transient gelation and oscillations but these systems suffer from undesired waste accumulation and they function only in open systems. Here, the authors we report non-equilibrium supramolecular polymerizations in a closed system, which is built by viologens and pyranine in the presence of hydrazine hydrate.
- Xianhua Lang
- , Yingjie Huang
- & Hui Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access [2,2] Paracyclophanes-based double helicates for constructing artificial light-harvesting systems and white LED device
[2,2] Paracyclophanes-based double helicates for constructing artificial light-harvesting systems and white LED device
The construction of efficient artificial lightharvesting (ALH) systems is of vital importance in utilizing solar energy. Here, the authors report the non-covalent syntheses of double helicates by metalcoordination interaction and their applications in ALHSs and white LED device
- Zhe Lian
- , Jing He
- & Hua Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access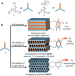 Hierarchical porous photosensitizers with efficient photooxidation
Hierarchical porous photosensitizers with efficient photooxidation
Photosensitizers (PS) with nano- or micro-sized pore provide a great promise in the conversion of light energy into chemical fuel but pore deformation and blocking often decreases the catalytic efficiency. Here, the authors prepare an ordered porous PSs by cross-linking hierarchical porous assemblies of hydrogen donating PSs and functionalized acceptors.
- Yajun Fang
- , Yuntian Yang
- & Zhegang Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Repurposing host-guest chemistry to sequester virulence and eradicate biofilms in multidrug resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Acinetobacter baumannii
Repurposing host-guest chemistry to sequester virulence and eradicate biofilms in multidrug resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Acinetobacter baumannii
Rapid antibiotic resistance in bacteria is putting pressure on both existing therapies as well as the development pipeline. Here, the authors present a dual-acting anti-virulence treatment that evades antibiotic resistance mechanisms and remains effective against Top Priority pathogens.
- Christopher Jonkergouw
- , Ngong Kodiah Beyeh
- & Markus B. Linder
-
Article
| Open Access A supramolecular gel-elastomer system for soft iontronic adhesives
A supramolecular gel-elastomer system for soft iontronic adhesives
Electroadhesion in soft robotics provides controllable interfacial attraction for robotic functionalities but materials selection is limited. Here, Gao et. al. present an iontronic adhesive to design a soft iontronic gripper with self-healability, tunable adhesion at reduced voltages and rapid release.
- Dace Gao
- , Gurunathan Thangavel
- & Pooi See Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Four distinct network patterns of supramolecular/polymer composite hydrogels controlled by formation kinetics and interfiber interactions
Four distinct network patterns of supramolecular/polymer composite hydrogels controlled by formation kinetics and interfiber interactions
Synthetic hydrogels composed of covalent polymers and supramolecular fibers have been investigated for controlled delivery of biopharmaceuticals, but characterisation of the structures and properties can be challenging. Here, the authors report an imaging study for the composite network, categorizing into four distinct patterns controlled by network formation kinetics and interactions between
- Keisuke Nakamura
- , Ryou Kubota
- & Itaru Hamachi
-
Article
| Open Access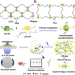 Polymerizable rotaxane hydrogels for three-dimensional printing fabrication of wearable sensors
Polymerizable rotaxane hydrogels for three-dimensional printing fabrication of wearable sensors
While hydrogels find applications in wearable sensors and electronic skins, they are prone to fatigue fractures upon deformation cycling. Xiong et al. report the synthesis of conductive polymerizable rotaxane hydrogels, exhibiting large fatigue resistance, for 3D printable flexible sensors.
- Xueru Xiong
- , Yunhua Chen
- & Yanli Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access High-efficiency gold recovery by additive-induced supramolecular polymerization of β-cyclodextrin
High-efficiency gold recovery by additive-induced supramolecular polymerization of β-cyclodextrin
Eco-friendly, efficient, and selective gold recovery technologies are urgently desired to satisfy the increasing demand for gold. Here, the authors report one such technology based on the supramolecular polymerization of second-sphere coordinated adducts formed between β-cyclodextrin and tetrabromoaurate anions.
- Huang Wu
- , Yu Wang
- & J. Fraser Stoddart
-
Article
| Open Access Bioinspired crowding directs supramolecular polymerisation
Bioinspired crowding directs supramolecular polymerisation
Crowding effects have long been established as powerful guiding forces in natural assembly processes. Here the authors report a bioinspired approach translating this phenomenon to artificial supramolecular polymers.
- Nils Bäumer
- , Eduardo Castellanos
- & Gustavo Fernández
-
Article
| Open Access Supramolecular framework membrane for precise sieving of small molecules, nanoparticles and proteins
Supramolecular framework membrane for precise sieving of small molecules, nanoparticles and proteins
Synthetic framework materials are appealing candidates for the fabrication of separation membranes but realizing precise control of aperture distribution and separation threshold remains challenging. Here, the authors show a two-dimensional processible supramolecular framework which can be used in the fabrication of separation membranes by integrating directional organic host-guest motifs and inorganic functional polyanionic clusters.
- Guohua Zhang
- , Xinyue Li
- & Lixin Wu
-
Article
| Open Access Stereoisomeric engineering of aggregation-induced emission photosensitizers towards fungal killing
Stereoisomeric engineering of aggregation-induced emission photosensitizers towards fungal killing
Fungal infections are often major causes of disease in immune compromised patients and photodynamic therapy offers and attractive treatment. Here, the authors develop stereoisomeric photosensitizers via supramolecular assembly and demonstrate aggregation-induced photodynamic action against fungi.
- Wenping Zhu
- , Ying Li
- & Ben Zhong Tang
-
Article
| Open Access Amplification of integrated microscopic motions of high-density [2]rotaxanes in mechanically interlocked networks
Amplification of integrated microscopic motions of high-density [2]rotaxanes in mechanically interlocked networks
Amplifying molecular motion to macroscopic material property is attractive but challenging. Here, the authors report mechanically interlocked networks with dense rotaxane backbones whose microscopic motion is integrated into decent mechanical properties of bulk materials.
- Xue Yang
- , Lin Cheng
- & Xuzhou Yan
-
Article
| Open Access Formation of supramolecular channels by reversible unwinding-rewinding of bis(indole) double helix via ion coordination
Formation of supramolecular channels by reversible unwinding-rewinding of bis(indole) double helix via ion coordination
Synthetic supramolecular double-stranded helical systems that can undergo reversible unwinding are rare. Here, the authors report bis(indole)-based double helix systems that unwind in the presence of chloride, forming supramolecular ion channels; Addition of silver enables the regeneration of the double helix.
- Debashis Mondal
- , Manzoor Ahmad
- & Pinaki Talukdar
-
Article
| Open Access Supramolecular photodynamic agents for simultaneous oxidation of NADH and generation of superoxide radical
Supramolecular photodynamic agents for simultaneous oxidation of NADH and generation of superoxide radical
Tumour hypoxia is a major issue for conventional photodynamic therapies, Here, the authors report on the supramolecular assembly of electron acceptors with photosensitizers which have improved reactive oxygen species production and are able to directly oxidise NHDH and demonstrate application against hypoxic tumours.
- Kun-Xu Teng
- , Li-Ya Niu
- & Qing-Zheng Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Cholesterol-stabilized membrane-active nanopores with anticancer activities
Cholesterol-stabilized membrane-active nanopores with anticancer activities
Bacterial cells utilize cholesterol-enhanced pore formation to specifically target eukaryotic cells. Here, the authors present a class of bio-inspired, cholesterol-enhanced nanopores which display anticancer activities in vitro.
- Jie Shen
- , Yongting Gu
- & Huaqiang Zeng
-
Article
| Open Access Phase-locked constructing dynamic supramolecular ionic conductive elastomers with superior toughness, autonomous self-healing and recyclability
Phase-locked constructing dynamic supramolecular ionic conductive elastomers with superior toughness, autonomous self-healing and recyclability
Stretchable ionic conductors are attractive candidates for flexible ionotronics but combining high conductivity with excellent mechanical properties is challenging. Herein, the authors combine these properties in a dynamic supramolecular ionic conductive elastomer enabling lithium-ion transport in the soft phase and dynamic disulfide and supramolecular hydrogen bonding in the hard segments.
- Jing Chen
- , Yiyang Gao
- & Shujiang Ding
-
Article
| Open Access Shape-assisted self-assembly
Shape-assisted self-assembly
Self-assembly and molecular recognition usually depend on strong, directional non-covalent interactions but also topography can play a role in the formation of supramolecular constructs which makes it nearly impossible to discern the potential of shape and motion in the creation of complexity. Here, the authors demonstrate that long-range order in supramolecular constructs can be assisted by the topography of the individual units even in the absence of highly directional interactions.
- Joseph F. Woods
- , Lucía Gallego
- & Michel Rickhaus
-
Article
| Open Access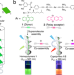 A bioinspired sequential energy transfer system constructed via supramolecular copolymerization
A bioinspired sequential energy transfer system constructed via supramolecular copolymerization
Sequential energy transfer is ubiquitous in natural light harvesting systems, but most artificial mimics have unsatisfactory energy transfer efficiency. Here, authors synthesize a sequential energy transfer system with overall efficiency of 87.4% via supramolecular copolymerization mimicking the aggregation mode of bacteriochlorophyll pigments in green photosynthetic bacteria.
- Yifei Han
- , Xiaolong Zhang
- & Feng Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Lateral growth of cylinders
Lateral growth of cylinders
Precise control of the microstructure of nanomaterials is of interest but living lateral growth of cylinders is still very challenging. Here, the authors propose a crystallization-driven fusion-induced particle assembly strategy to prepare cylinders with growing diameters by controlled fusion of spherical micelles self-assembled from an amphiphilic homopolymer.
- Hui Sun
- , Shuai Chen
- & Jianzhong Du
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular communications in complex systems of dynamic supramolecular polymers
Molecular communications in complex systems of dynamic supramolecular polymers
The dynamic structure of supramolecular polymers is challenging to determine both in experiments and in simulations. Here the authors use coarse-grained molecular models to provide a comprehensive analysis of the molecular communication in these complex molecular systems.
- Martina Crippa
- , Claudio Perego
- & Giovanni M. Pavan
-
Article
| Open Access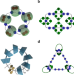 Mechanically interlocked networks cross-linked by a molecular necklace
Mechanically interlocked networks cross-linked by a molecular necklace
Constructing cross-linked networks with different topologies is attractive but challenging. Here the authors present mechanically interlocked networks cross-linked by a molecular necklace whose peculiar architectural and dynamic features endow the materials with robust yet mechanically adaptive properties.
- Zhaoming Zhang
- , Jun Zhao
- & Xuzhou Yan
-
Article
| Open Access Tough, stable and self-healing luminescent perovskite-polymer matrix applicable to all harsh aquatic environments
Tough, stable and self-healing luminescent perovskite-polymer matrix applicable to all harsh aquatic environments
Fabrication of perovskite-polymer composites that simultaneously possesses strong mechanical strength, high stretchability, high stability towards harsh aqueous environments and self-healing properties is challenging. Here, the authors report a luminescent composite that is simultaneously transparent, tough and can autonomously self-heal in both dry and wet conditions.
- Yuncong Liu
- , Tao Chen
- & Chao Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Oscillating the local milieu of polymersome interiors via single input-regulated bilayer crosslinking and permeability tuning
Oscillating the local milieu of polymersome interiors via single input-regulated bilayer crosslinking and permeability tuning
Permselectivity of cellular membranes is crucial to normal cellular function but this has been hard to replicate in artificial cells. Here, the authors use pH-responsive polymersomes containing Schiff base moieties which can be used to control mesh size allowing for selective permeability control creating responsive systems.
- Guhuan Liu
- , Jiajia Tan
- & Shiyong Liu
-
Article
| Open Access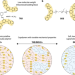 Mechanically robust supramolecular polymer co-assemblies
Mechanically robust supramolecular polymer co-assemblies
Reversible assembly of supramolecular polymers renders these materials with healing and recycling properties but mechanical properties are often inferior to those of conventional plastics. Here, the authors demonstrate that strong and tough but healable materials can be accessed through the combination of metallosupramolecular polymers with complementary mechanical properties that feature the same metal-ligand complex as binding motif
- Julien Sautaux
- , Franziska Marx
- & Stephen Schrettl
-
Article
| Open Access Controlling the length of porphyrin supramolecular polymers via coupled equilibria and dilution-induced supramolecular polymerization
Controlling the length of porphyrin supramolecular polymers via coupled equilibria and dilution-induced supramolecular polymerization
Controlling multicomponent systems is difficult due to convoluted behavior, pathway complexity, and coupled equilibria. Here the authors showed modulation of aggregate morphology in a zinc porphyrin-based supramolecular system via judicious capping with a manganese porphyrin monomer, in which the monomer’s chirality can influence the supramolecular behavior.
- Elisabeth Weyandt
- , Luigi Leanza
- & E. W. Meijer
-
Article
| Open Access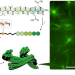 Supramolecular fibrillation of peptide amphiphiles induces environmental responses in aqueous droplets
Supramolecular fibrillation of peptide amphiphiles induces environmental responses in aqueous droplets
One-dimensional (1D) supramolecular polymers are commonly found in natural and synthetic systems but very little is currently known about the physico-chemical consequences and functional role of 1D supramolecular polymerisation confined in aqueous compartments. Here, the authors describe the different phenomena that resulted from the chemically triggered supramolecular fibrillation of synthetic peptide amphiphiles inside water microdroplets.
- Richard Booth
- , Ignacio Insua
- & Javier Montenegro
-
Article
| Open Access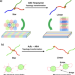 Topology-transformable block copolymers based on a rotaxane structure: change in bulk properties with same composition
Topology-transformable block copolymers based on a rotaxane structure: change in bulk properties with same composition
The topology of a polymer is normally a fixed property of the material, derived from the characteristic of the monomers and their linkages. Here the authors present a method to transform the topology of block copolymers containing rotaxane linkages via acetylation.
- Hiroki Sato
- , Daisuke Aoki
- & Toshikazu Takata
-
Article
| Open Access Self-assembly using a retro Diels-Alder reaction
Self-assembly using a retro Diels-Alder reaction
Despite their great utility in synthetic and materials chemistry, Diels-Alder and retro Diels-Alder reactions have been vastly unexplored in promoting self-assembly processes. Here the authors show the release of steric bulkiness associated with a bridged bicyclic Diels Alder adduct by the retro Diels-Alder reaction that allowed generation of two building blocks that spontaneously self-assembled to form a supramolecular polymer.
- Jaeyoung Park
- , Jung-Moo Heo
- & Jong-Man Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Living supramolecular polymerization of fluorinated cyclohexanes
Living supramolecular polymerization of fluorinated cyclohexanes
Living supramolecular polymerization can produce precise covalent polymers, but the scope of monomers is still narrow. Here the authors show a molecular platform for living supramolecular polymerization that is based on the unique structure of all-cis 1,2,3,4,5,6- 22 hexafluorocyclohexane, the most polar aliphatic compound reported to date.
- Oleksandr Shyshov
- , Shyamkumar Vadakket Haridas
- & Max von Delius
-
Article
| Open Access Oriented arrangement of simple monomers enabled by confinement: towards living supramolecular polymerization
Oriented arrangement of simple monomers enabled by confinement: towards living supramolecular polymerization
Using simple monomers in living supramolecular polymerization is difficult due to energy principles. Here the authors use confinement from a layered double hydroxide nanomaterial to successfully polymerise several simple monomers with length control and narrow dispersity.
- Yingtong Zong
- , Si-Min Xu
- & Chao Lu
-
Article
| Open Access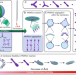 Generating biomembrane-like local curvature in polymersomes via dynamic polymer insertion
Generating biomembrane-like local curvature in polymersomes via dynamic polymer insertion
Investigating biomembrane curvature formation is important for studying intracellular processes, but the instability of liposome models mimicking these membranes restricts exploration of membrane processes. Here, the authors demonstrate control over the curvature formation in polymersome membranes by insertion of PNIPAm as stimuli responsive polymer.
- Jiawei Sun
- , Sjoerd J. Rijpkema
- & Daniela A. Wilson
-
Article
| Open Access Photoresponsive supramolecular coordination polyelectrolyte as smart anticounterfeiting inks
Photoresponsive supramolecular coordination polyelectrolyte as smart anticounterfeiting inks
Photoluminescence printing is a widely applied anticounterfeiting technique but there are still challenges in developing new generation anticounterfeiting materials providing a high security level. Here, the authors demonstrate coordination dependent photochromic luminescence in a supramolecular coordination polyelectrolyte for multiple information authentication.
- Zhiqiang Li
- , Xiao Liu
- & Yanli Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Physical networks from entropy-driven non-covalent interactions
Physical networks from entropy-driven non-covalent interactions
Physical networks typically employ enthalpy-dominated crosslinking interactions that become more dynamic at elevated temperatures. Here, the authors report an entropy-driven physical network based on polymer-nanoparticle interactions that exhibits mechanical properties that are invariant with temperature.
- Anthony C. Yu
- , Huada Lian
- & Eric A. Appel
-
Article
| Open Access Self-assembled Möbius strips with controlled helicity
Self-assembled Möbius strips with controlled helicity
Different to exploring molecular topology, the development of supramolecular topology has been limited due to a lack of reliable synthetic methods. Here, the authors describe a supramolecular strategy to access Möbius strips through bending and cyclization of twisted nanofibers self-assembled from chiral glutamate amphiphiles.
- Guanghui Ouyang
- , Lukang Ji
- & Minghua Liu
-
Article
| Open Access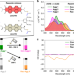 Control of self-assembly pathways toward conglomerate and racemic supramolecular polymers
Control of self-assembly pathways toward conglomerate and racemic supramolecular polymers
Homo- and heterochiral aggregation is a process of interest to prebiotic and chiral separation chemistry. Here, the authors analyze the self-assembly of a racemic mixture into 1D supramolecular polymers and find homochiral aggregation into conglomerates under kinetic control, while under thermodynamic control a racemic polymer is formed.
- Marius Wehner
- , Merle Insa Silja Röhr
- & Frank Würthner
-
Article
| Open Access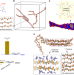 Homopolymer self-assembly of poly(propylene sulfone) hydrogels via dynamic noncovalent sulfone–sulfone bonding
Homopolymer self-assembly of poly(propylene sulfone) hydrogels via dynamic noncovalent sulfone–sulfone bonding
Natural biomolecules such as peptides and DNA can dynamically self-organize into diverse hierarchical structures. Here the authors report experiments and simulations on the dynamic network self-assembly and subsequent collapse of the synthetic homopolymer poly(propylene sulfone).
- Fanfan Du
- , Baofu Qiao
- & Evan Alexander Scott
-
Article
| Open Access Straightforward preparation of supramolecular Janus nanorods by hydrogen bonding of end-functionalized polymers
Straightforward preparation of supramolecular Janus nanorods by hydrogen bonding of end-functionalized polymers
Janus cylinders are useful as building blocks for advanced functional materials but challenging to prepare. Here, the authors describe a robust strategy to form micrometer long Janus nanorods by self-assembly in water of end-functionalized polymers.
- Shuaiyuan Han
- , Sandrine Pensec
- & Laurent Bouteiller
-
Article
| Open Access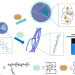 Ultralong purely organic aqueous phosphorescence supramolecular polymer for targeted tumor cell imaging
Ultralong purely organic aqueous phosphorescence supramolecular polymer for targeted tumor cell imaging
Room-temperature phosphorescence has attracted attention for bioimaging, but quenching in aqueous systems is an issue. Here, the authors report on the synthesis of a water soluble organic phosphorescent polymer and demonstrate application is cancer cell targeting and imaging.
- Wei-Lei Zhou
- , Yong Chen
- & Yu Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Control of seed formation allows two distinct self-sorting patterns of supramolecular nanofibers
Control of seed formation allows two distinct self-sorting patterns of supramolecular nanofibers
Regulation of self-sorted nanofiber network patterns in double network hydrogels comprising supramolecular nanofibers is considered as key for potential applications. Here, the authors describe a selective construction of two distinct self-sorting network patterns, by controlling the kinetics of seed formation with dynamic covalent chemistry.
- Ryou Kubota
- , Kazutoshi Nagao
- & Itaru Hamachi

 Highly robust supramolecular polymer networks crosslinked by a tiny amount of metallacycles
Highly robust supramolecular polymer networks crosslinked by a tiny amount of metallacycles