Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access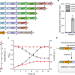 An l-2-hydroxyglutarate biosensor based on specific transcriptional regulator LhgR
An l-2-hydroxyglutarate biosensor based on specific transcriptional regulator LhgR
L-2-hydroxyglutarate (L-2-HG) is an important metabolite but its regulation is poorly understood. Here the authors report an L-2-HG FRET biosensor based on the allosteric transcription factor, LhgR, to monitor L-2-HG in cells and biological samples.
- Zhaoqi Kang
- , Manman Zhang
- & Ping Xu
-
Article
| Open Access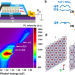 Strong interaction between interlayer excitons and correlated electrons in WSe2/WS2 moiré superlattice
Strong interaction between interlayer excitons and correlated electrons in WSe2/WS2 moiré superlattice
Heterobilayers of transition metal dichalcogenides host moiré superlattices that give rise to strong electron interactions. Here, the authors study the photoluminescence from interlayer excitons in a WS2/WSe2 heterobilayer to reveal the onset of various correlated insulating states.
- Shengnan Miao
- , Tianmeng Wang
- & Su-Fei Shi
-
Article
| Open Access Large Stokes shift fluorescence activation in an RNA aptamer by intermolecular proton transfer to guanine
Large Stokes shift fluorescence activation in an RNA aptamer by intermolecular proton transfer to guanine
Fluorogenic RNA aptamers such as Chili display strong fluorescence enhancement upon aptamer–ligand complex formation. Here, the authors provide insights into the mechanism of fluorescence activation of Chili by solving the crystal structures of Chili with its bound positively charged ligands DMHBO+ and DMHBI+, and they reveal that Chili uses an excited state proton transfer mechanism based on time-resolved optical spectroscopy measurements.
- Mateusz Mieczkowski
- , Christian Steinmetzger
- & Claudia Höbartner
-
Article
| Open Access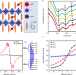 Manganese doping for enhanced magnetic brightening and circular polarization control of dark excitons in paramagnetic layered hybrid metal-halide perovskites
Manganese doping for enhanced magnetic brightening and circular polarization control of dark excitons in paramagnetic layered hybrid metal-halide perovskites
Combining magnetic and semiconducting properties in a single material offers great technological potential, all the more so if these are coupled with good optical properties. Here, Neumann et al. present a Manganese doped Ruddlesden-Popper perovskite with this trifecta of attributes.
- Timo Neumann
- , Sascha Feldmann
- & Felix Deschler
-
Article
| Open Access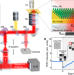 Adaptive tip-enhanced nano-spectroscopy
Adaptive tip-enhanced nano-spectroscopy
Tip-enhanced nano-spectroscopy suffers from inconsistent signal and difficulty in polarization-resolved measurement. Here, the authors present adaptive tip-enhanced nano-spectroscopy, which enables the additional signal enhancement and near-field polarization control via dynamic wavefront shaping.
- Dong Yun Lee
- , Chulho Park
- & Kyoung-Duck Park
-
Article
| Open Access Multiplexed live-cell profiling with Raman probes
Multiplexed live-cell profiling with Raman probes
Currently relatively few functional probes for Raman-based live-cell profiling exist. Here the authors build on their previous ultra-bright Raman dots to devise a 14-plexed Raman probe panel to quantify cell surface proteins, endocytosis activities and metabolic dynamics of single live cells.
- Chen Chen
- , Zhilun Zhao
- & Wei Min
-
Article
| Open Access Through bonds or contacts? Mapping protein vibrational energy transfer using non-canonical amino acids
Through bonds or contacts? Mapping protein vibrational energy transfer using non-canonical amino acids
Vibrational energy transfer (VET) is essential for protein function as it is responsible for efficient energy dissipation in reaction sites and is linked to pathways of allosteric communication. Here authors equipped a tryptophan zipper with a VET injector and a VET sensor for femtosecond pump probe experiments to map the VET.
- Erhan Deniz
- , Luis Valiño-Borau
- & Jens Bredenbeck
-
Article
| Open Access Switchable stimulated Raman scattering microscopy with photochromic vibrational probes
Switchable stimulated Raman scattering microscopy with photochromic vibrational probes
Probes with reversible fluorescence are useful in super-resolution microscopy, but lack sufficient chemical specificity. Here, the authors engineer alkyne tagged diarylethene to realize photo-switchable stimulated Raman scattering probes with high chemical resolution, for applications in living cells.
- Jianpeng Ao
- , Xiaofeng Fang
- & Minbiao Ji
-
Article
| Open Access All-dielectric chiral-field-enhanced Raman optical activity
All-dielectric chiral-field-enhanced Raman optical activity
Raman optical activity (ROA) is useful for studying conformational structure and behavior of chiral molecules, but is limited by the weak signals. Here, the authors demonstrate 100x signal enhancement via an all-dielectric approach, using a silicon nanodisk array and exploiting its dark mode.
- Ting-Hui Xiao
- , Zhenzhou Cheng
- & Keisuke Goda
-
Article
| Open Access Microsecond fingerprint stimulated Raman spectroscopic imaging by ultrafast tuning and spatial-spectral learning
Microsecond fingerprint stimulated Raman spectroscopic imaging by ultrafast tuning and spatial-spectral learning
The authors employ a polygon-based ultrafast delay scanner and a deep learning framework for acquiring stimulated Raman scattering spectrum with high spectral and temporal resolution. They demonstrate high-speed imaging and tracking of multiple biomolecules in the fingerprint region.
- Haonan Lin
- , Hyeon Jeong Lee
- & Ji-Xin Cheng
-
Article
| Open Access Electromechanical coupling mechanism for activation and inactivation of an HCN channel
Electromechanical coupling mechanism for activation and inactivation of an HCN channel
Sea urchin hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated (spHCN) ion channels channels are activated by membrane hyperpolarization instead of depolarization and undergo inactivation with hyperpolarization. Here authors apply transition metal ion FRET, patch-clamp fluorometry and Rosetta modeling to measure differences in the structural rearrangements between activation and inactivation of spHCN channels.
- Gucan Dai
- , Teresa K. Aman
- & William N. Zagotta
-
Article
| Open Access Probing subwavelength in-plane anisotropy with antenna-assisted infrared nano-spectroscopy
Probing subwavelength in-plane anisotropy with antenna-assisted infrared nano-spectroscopy
s-SNOM is a powerful tool, but it is less sensitive to in-plane variations. Here the authors present a method to improve this with a metallic microdisk antenna, which they demonstrate by probing in-plane phonon responses.
- Ziheng Yao
- , Xinzhong Chen
- & Mengkun Liu
-
Article
| Open Access A rich catalog of C–C bonded species formed in CO2 reduction on a plasmonic photocatalyst
A rich catalog of C–C bonded species formed in CO2 reduction on a plasmonic photocatalyst
In situ vibrational spectroscopy affords a powerful tool for probing elementary chemical processes on catalytic surfaces. Using surface enhanced Raman scattering, authors identify an array of multicarbon species formed on a Ag nanoparticle catalyst in plasmon-driven reduction of CO2 in water.
- Dinumol Devasia
- , Andrew J. Wilson
- & Prashant K. Jain
-
Article
| Open Access Quantification of FRET-induced angular displacement by monitoring sensitized acceptor anisotropy using a dim fluorescent donor
Quantification of FRET-induced angular displacement by monitoring sensitized acceptor anisotropy using a dim fluorescent donor
The FRET efficiency usually predominantly depends on the proximity of donor and acceptor. Here the authors report an anisotropy-based mode of FRET detection, FRET-induced Angular Displacement Evaluation via Dim donor (FADED), to allow quantification of the relative angle between donor and acceptor.
- Danai Laskaratou
- , Guillermo Solís Fernández
- & Hideaki Mizuno
-
Article
| Open Access The molecular pH-response mechanism of the plant light-stress sensor PsbS
The molecular pH-response mechanism of the plant light-stress sensor PsbS
Photosystem II subunit S (PsbS) senses thylakoid lumen acidification when plants are exposed to excess light. Here the authors use NMR and IR spectroscopy to show that low pH causes repositioning of an amphipathic helix and folding of a loop involving critical pH sensing glutamate residues in PsbS.
- Maithili Krishnan-Schmieden
- , Patrick E. Konold
- & Anjali Pandit
-
Article
| Open Access Exciton-acoustic phonon coupling revealed by resonant excitation of single perovskite nanocrystals
Exciton-acoustic phonon coupling revealed by resonant excitation of single perovskite nanocrystals
In order to develop perovskite nanocrystals as a single-photon source, there is a need to understand the complex exciton photo-physics. Here, the authors employ resonant and near-resonant excitation technique to study single CsPbI3 nanocrystal that allows them to probe the continuous and size-quantised acoustic-phonon modes.
- Yan Lv
- , Chunyang Yin
- & Min Xiao
-
Article
| Open Access Precisely spun super rotors
Precisely spun super rotors
Optical pulses can be useful to create and control molecules in higher quantum states. Here the authors use optical pumping to create rotationally excited states of SiO+ molecular ion into super rotor ensemble.
- Ivan O. Antonov
- , Patrick R. Stollenwerk
- & Brian C. Odom
-
Article
| Open Access In-situ plasmonic tracking oxygen evolution reveals multistage oxygen diffusion and accumulating inhibition
In-situ plasmonic tracking oxygen evolution reveals multistage oxygen diffusion and accumulating inhibition
Understanding mass transfer processes concomitant with gas evolution reactions is important in energy research. Here, the authors show diffusion tracking of dissolved oxygen on copper nanostructured interface with plasmonic signal, and provide a direct observation of the interfacial mass transfer processes.
- Jun-Gang Wang
- , Lifang Shi
- & Di Li
-
Article
| Open Access Proximity control of interlayer exciton-phonon hybridization in van der Waals heterostructures
Proximity control of interlayer exciton-phonon hybridization in van der Waals heterostructures
Here, the authors demonstrate proximity-controlled strong-coupling between Coulomb correlations and lattice dynamics in neighbouring van der Waals materials (WSe2 and a gypsum layer), creating electrically neutral hybrid exciton-phonon eigenmodes called excitonic Lyman polarons.
- Philipp Merkl
- , Chaw-Keong Yong
- & Rupert Huber
-
Article
| Open Access Nano-imaging photoresponse in a moiré unit cell of minimally twisted bilayer graphene
Nano-imaging photoresponse in a moiré unit cell of minimally twisted bilayer graphene
Here, the authors use a nanoscale probe to study the photoresponse within a single moiré unit cell of minimally twisted bilayer graphene, and observe an intricate photo-thermoelectric response attributed to the Seebeck coefficient variation at AB-BA domain boundaries.
- Niels C. H. Hesp
- , Iacopo Torre
- & Frank H. L. Koppens
-
Article
| Open Access Stability of person-specific blood-based infrared molecular fingerprints opens up prospects for health monitoring
Stability of person-specific blood-based infrared molecular fingerprints opens up prospects for health monitoring
Health status transitions are reflected as characteristic changes in molecular composition of biofluids. Here, the authors apply infrared molecular fingerprinting and reveal that blood-based phenotypes are sufficiently stable over time, providing the basis for time- and cost-effective health monitoring.
- Marinus Huber
- , Kosmas V. Kepesidis
- & Mihaela Žigman
-
Article
| Open Access Thermochromic aggregation-induced dual phosphorescence via temperature-dependent sp3-linked donor-acceptor electronic coupling
Thermochromic aggregation-induced dual phosphorescence via temperature-dependent sp3-linked donor-acceptor electronic coupling
Aggregation-induced emission (AIE) has proven to be a viable strategy to achieve highly efficient room temperature phosphorescence (RTP) in bulk by restricting molecular motions. Here, the authors present an RTP design strategy by combining the concept of AIE and donor-acceptor motif and demonstrate unusual thermochromic dual phosphorescence.
- Tao Wang
- , Zhubin Hu
- & Guoqing Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Ultra-bright Raman dots for multiplexed optical imaging
Ultra-bright Raman dots for multiplexed optical imaging
Raman-based imaging of biomarkers is often challenging due to low sensitivity. Here, the authors use a swelling-diffusion approach to develop a series of Raman probes that are both ultra-bright and compact in size, and demonstrate multiplexed imaging of specific protein targets in cells and tissue slices.
- Zhilun Zhao
- , Chen Chen
- & Wei Min
-
Article
| Open Access Optical tweezers-controlled hotspot for sensitive and reproducible surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy characterization of native protein structures
Optical tweezers-controlled hotspot for sensitive and reproducible surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy characterization of native protein structures
It is currently challenging to identify protein structures at low concentrations. Here the authors report optical tweezers-coupled Raman spectroscopy to generate tunable and reproducible SERS enhancements with single-molecule level sensitivity and use the method to detect protein structural features.
- Xin Dai
- , Wenhao Fu
- & Jinqing Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Probing intramolecular vibronic coupling through vibronic-state imaging
Probing intramolecular vibronic coupling through vibronic-state imaging
Vibronic coupling is a key feature of molecular electronic transitions, but its visualization in real space is an experimental challenge. Here the authors, using scanning tunneling microscopy induced luminescence, resolve the effect of vibronic coupling with different modes on the electron distributions in real space in a single pentacene molecule.
- Fan-Fang Kong
- , Xiao-Jun Tian
- & J. G. Hou
-
Article
| Open Access A digital single-molecule nanopillar SERS platform for predicting and monitoring immune toxicities in immunotherapy
A digital single-molecule nanopillar SERS platform for predicting and monitoring immune toxicities in immunotherapy
There is a clinical need to monitor immune-related toxicities of immune checkpoint blockade therapy. Here, the authors develop a digital SERS platform for multiplexed single cytokine counting to track immune-toxicities and demonstrate the ability to use pre-screening to identify patients at higher risk.
- Junrong Li
- , Alain Wuethrich
- & Matt Trau
-
Article
| Open Access Optoelectronic frequency-modulated continuous-wave terahertz spectroscopy with 4 THz bandwidth
Optoelectronic frequency-modulated continuous-wave terahertz spectroscopy with 4 THz bandwidth
Time-domain spectroscopy with terahertz frequencies typically requires complex and bulky systems. Here, the authors present an opto-electronics-based, frequency-domain terahertz sensing technique which offers competitive measurement performance in a much simpler system.
- Lars Liebermeister
- , Simon Nellen
- & Björn Globisch
-
Article
| Open Access Exciton–phonon coupling strength in single-layer MoSe2 at room temperature
Exciton–phonon coupling strength in single-layer MoSe2 at room temperature
The exciton–phonon coupling (EXPC) affects the opto-electronic properties of atomically thin semiconductors. Here, the authors develop two-dimensional micro-spectroscopy to determine the EXPC of monolayer MoSe2.
- Donghai Li
- , Chiara Trovatello
- & Tobias Brixner
-
Article
| Open Access Measuring the frequency chirp of extreme-ultraviolet free-electron laser pulses by transient absorption spectroscopy
Measuring the frequency chirp of extreme-ultraviolet free-electron laser pulses by transient absorption spectroscopy
Free-electron laser pulses generated from self-amplification of spontaneous emission scheme vary from one another in their characteristics. Here the authors demonstrate a transient absorption spectroscopy method to characterize the frequency chirp of the FEL pulses.
- Thomas Ding
- , Marc Rebholz
- & Thomas Pfeifer
-
Article
| Open Access The multi-photon induced Fano effect
The multi-photon induced Fano effect
Fano resonances occur in many platforms that have auto-ionizing states. Here the authors show that auto-ionizing states are not required for multi-photon Fano resonance in a Si:P system with significant screening by using a pump-probe method.
- K. L. Litvinenko
- , Nguyen H. Le
- & B. N. Murdin
-
Article
| Open Access Excited-state vibration-polariton transitions and dynamics in nitroprusside
Excited-state vibration-polariton transitions and dynamics in nitroprusside
Here the authors report spectroscopy and dynamics of cavity coupled NO band of sodium nitroprusside using 2D infrared and transient spectroscopy employing pump-probe technique. They find signatures of third-order nonlinearity, incoherent and strong coupling effects of vibrational polaritons.
- Andrea B. Grafton
- , Adam D. Dunkelberger
- & Jeffrey C. Owrutsky
-
Article
| Open Access Giant topological longitudinal circular photo-galvanic effect in the chiral multifold semimetal CoSi
Giant topological longitudinal circular photo-galvanic effect in the chiral multifold semimetal CoSi
Quantized circular photogalvanic effect (CPGE) is predicted in chiral topological semimetals, but the experimental observation remains challenging. Here, Ni et al. observe a large topological longitudinal photocurrent in CoSi, which is much larger than the photocurrent in any other chiral crystals, indicating quantized CPGE within reach upon doping and increase of the hot-carrier lifetime.
- Zhuoliang Ni
- , K. Wang
- & Liang Wu
-
Article
| Open Access Spread spectrum SERS allows label-free detection of attomolar neurotransmitters
Spread spectrum SERS allows label-free detection of attomolar neurotransmitters
Identification of neurotransmitters remains challenging for surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) due to presence of noise. Here, the authors present spread spectrum SERS, which by encoding excited light and decoding SERS signals enables detection of unlabelled neurotransmitters at attomolar concentrations.
- Wonkyoung Lee
- , Byoung-Hoon Kang
- & Ki-Hun Jeong
-
Article
| Open Access In vivo biomolecular imaging of zebrafish embryos using confocal Raman spectroscopy
In vivo biomolecular imaging of zebrafish embryos using confocal Raman spectroscopy
Raman spectroscopic imaging (RSI) can provide information on the chemical composition of a sample, but application to living organisms has lacked sufficient spatial resolution and signal strength. Here the authors apply confocal RSI to whole-mount zebrafish embryos to distinguish different infectious bacteria and to living zebrafish embryos to monitor the wound healing process.
- Håkon Høgset
- , Conor C. Horgan
- & Molly M. Stevens
-
Article
| Open Access Natural optical activity as the origin of the large chiroptical properties in π-conjugated polymer thin films
Natural optical activity as the origin of the large chiroptical properties in π-conjugated polymer thin films
Polymer thin films that emit and absorb circularly polarised light are promising in achieving important technological advances, but the origin of the large chiroptical effects in such films has remained elusive. Here the authors demonstrate that in non-aligned polymer thin films, large chiroptical effects are caused by magneto-electric coupling, not structural chirality as previously assumed.
- Jessica Wade
- , James N. Hilfiker
- & Matthew J. Fuchter
-
Article
| Open Access The role of mixed vibronic Qy-Qx states in green light absorption of light-harvesting complex II
The role of mixed vibronic Qy-Qx states in green light absorption of light-harvesting complex II
The green component of the solar spectrum can efficiently drive natural photosynthesis, but the process has been little investigated due to the complexity of the excited states involved. Here the authors utilize polarization-dependent two-dimensional electronic-vibrational spectroscopy to define the origin and dynamics of these states in light-harvesting complex II.
- Eric A. Arsenault
- , Yusuke Yoneda
- & Graham R. Fleming
-
Article
| Open Access Attosecond spectroscopy reveals alignment dependent core-hole dynamics in the ICl molecule
Attosecond spectroscopy reveals alignment dependent core-hole dynamics in the ICl molecule
Here the authors report a study measuring lifetimes of core-hole states of ICl molecule using attosecond transient absorption spectroscopy. They find that lifetimes depend on the alignment of the orbital relative to the molecular axis.
- Hugo J. B. Marroux
- , Ashley P. Fidler
- & Daniel M. Neumark
-
Article
| Open Access The smfBox is an open-source platform for single-molecule FRET
The smfBox is an open-source platform for single-molecule FRET
Broad uptake of smFRET has been hindered by high instrument costs and a lack of open-source hardware and acquisition software. Here, the authors present the smfBox, a cost-effective open-source platform capable of measuring precise FRET efficiencies between dyes on freely diffusing single molecules.
- Benjamin Ambrose
- , James M. Baxter
- & Timothy D. Craggs
-
Article
| Open Access Snapshot multidimensional photography through active optical mapping
Snapshot multidimensional photography through active optical mapping
Multidimensional photography has traditionally been restricted by their static optical architectures and measurement schemes. Here, the authors present a tunable multidimensional photography approach employing active optical mapping, which allows them to adapt the acquisition schemes to the scene.
- Jongchan Park
- , Xiaohua Feng
- & Liang Gao
-
Article
| Open Access Conformational disorder of organic cations tunes the charge carrier mobility in two-dimensional organic-inorganic perovskites
Conformational disorder of organic cations tunes the charge carrier mobility in two-dimensional organic-inorganic perovskites
Understanding the correlation between molecular structure and properties of 2D hybrid perovskites is crucial for material design and device performance. Here, the authors reveal that conformation of organic cations in the inorganic cages has strong effects on charge mobility and broadband emission behaviour.
- Chuanzhao Li
- , Jin Yang
- & Shuji Ye
-
Article
| Open Access Infrared spectroscopic study of hydrogen bonding topologies in the smallest ice cube
Infrared spectroscopic study of hydrogen bonding topologies in the smallest ice cube
Spectroscopic studies of water clusters provide insight into the hydrogen bond structure of water and ice. The authors measure infrared spectra of neutral water octamers using a threshold photoionization technique based on a tunable vacuum-UV free electron laser, identifying two cubic isomers in addition to those previously observed.
- Gang Li
- , Yang-Yang Zhang
- & Ling Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access Shortwave-infrared meso-patterned imaging enables label-free mapping of tissue water and lipid content
Shortwave-infrared meso-patterned imaging enables label-free mapping of tissue water and lipid content
Quantifying lipid and water content in tissues non-invasively is difficult, and no method exists to quantify lipids in blood non-invasively. Here the authors develop an imaging approach called shortwave infrared meso-patterned imaging (SWIR-MPI) to detect and spatially map tissue water and lipids in preclinical models.
- Yanyu Zhao
- , Anahita Pilvar
- & Darren Roblyer
-
Article
| Open Access The ultrafast onset of exciton formation in 2D semiconductors
The ultrafast onset of exciton formation in 2D semiconductors
The formation dynamics of excitons in 2D transition metal dichalcogenides are challenging to probe directly because of their inherently fast timescales. Here, the authors use extremely short optical pulses to excite an electron-hole plasma, and show the formation of 2D excitons in MoS2 on the timescale of 30 fs.
- Chiara Trovatello
- , Florian Katsch
- & Stefano Dal Conte
-
Article
| Open Access Porous carbon nanowire array for surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy
Porous carbon nanowire array for surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy
SERS can be unreliable for biomedical use. The authors demonstrate a metal-free nanostructure composed of porous carbon nanowires in an array as a SERS substrate. It offers 106 signal enhancement due to strong broadband charge-transfer resonance and substrate-to-substrate, spot-to-spot and time-to-time consistency in the SERS spectrum.
- Nan Chen
- , Ting-Hui Xiao
- & Keisuke Goda
-
Article
| Open Access Raman-guided subcellular pharmaco-metabolomics for metastatic melanoma cells
Raman-guided subcellular pharmaco-metabolomics for metastatic melanoma cells
Single-cell metabolomics can offer deep insights into the metabolic reprogramming that accompanies disease states. Here, the authors use Raman spectro-microscopy for non-invasive metabolite analysis and identification of druggable metabolic susceptibilities in single live melanoma cells.
- Jiajun Du
- , Yapeng Su
- & Lu Wei
-
Article
| Open Access Optical gap and fundamental gap of oligoynes and carbyne
Optical gap and fundamental gap of oligoynes and carbyne
Carbyne, a linear sp-hybridized carbon allotrope, is synthetically inaccessible and its properties are extrapolated from those of defined oligomers. Here the authors analyze weak optical bands in two series of oligoynes and reassess the optical and fundamental gap of carbyne to lower values than previously suggested.
- Johannes Zirzlmeier
- , Stephen Schrettl
- & Holger Frauenrath
-
Article
| Open Access Probing the heterogeneous structure of eumelanin using ultrafast vibrational fingerprinting
Probing the heterogeneous structure of eumelanin using ultrafast vibrational fingerprinting
Eumelanin protects cells from sun damage and is promising for energy conversion applications, but its structure and excited state dynamics are elusive. Here the authors shed light on both aspects combining selective excitation of UV- and visible-absorbing chromophores with time-resolved infrared spectroscopy.
- Christopher Grieco
- , Forrest R. Kohl
- & Bern Kohler
-
Article
| Open Access Polariton-driven phonon laser
Polariton-driven phonon laser
Efficient generation of phonons is an important ingredient for a prospective electrically-driven phonon laser for coherent control of quantum systems. Here, the authors report on laser-like phonon emission in a hybrid semiconductor microcavity that optomechanically couples BEC polaritons with phonons.
- D. L. Chafatinos
- , A. S. Kuznetsov
- & A. Fainstein
-
Article
| Open Access Chiroptical spectroscopy of a freely diffusing single nanoparticle
Chiroptical spectroscopy of a freely diffusing single nanoparticle
Chirality of nanostructures may be determined by ensemble measurements in solution or on single immobilized nanoparticles, with loss of detail or interference from the substrate. Here the authors demonstrate that circular differential scattering intensity spectra of freely diffusing single nanoparticles provide chiroptical spectra which reflect their intrinsic chirality.
- Johannes Sachs
- , Jan-Philipp Günther
- & Peer Fischer

 Super-resolution label-free volumetric vibrational imaging
Super-resolution label-free volumetric vibrational imaging