Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access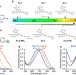 Photoswitchable polyynes for multiplexed stimulated Raman scattering microscopy with reversible light control
Photoswitchable polyynes for multiplexed stimulated Raman scattering microscopy with reversible light control
Bioimaging with photocontrol and multiplexing capability is vital for studying cellular interactions and dynamics, but multiplexed stimulated Raman scattering (SRS) imaging with reversible photocontrol is elusive. Here, the authors report SRS microscopy with Carbow-switch enabling multiplexed SRS imaging and tracking in live cells with reversible photocontrol and high spatiotemporal selectivity.
- Yueli Yang
- , Xueyang Bai
- & Fanghao Hu
-
Article
| Open Access In situ electrochemical regeneration of nanogap hotspots for continuously reusable ultrathin SERS sensors
In situ electrochemical regeneration of nanogap hotspots for continuously reusable ultrathin SERS sensors
SERS is a powerful analytical technique, but achieving reproducibility for continuous analysis a challenge. Here, the authors report a SERS substrate recycling method that enables direct analysis of complex samples without substrate contamination.
- Sarah May Sibug-Torres
- , David-Benjamin Grys
- & Jeremy J. Baumberg
-
Article
| Open Access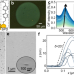 Extensive photochemical restructuring of molecule-metal surfaces under room light
Extensive photochemical restructuring of molecule-metal surfaces under room light
The nature of the molecule-metal interface is crucial for many technological applications. Here, the authors show that the photostability of the material can be sensitive to room light when coated with a single molecular layer, with implications for devices and processes.
- Chenyang Guo
- , Philip Benzie
- & Jeremy J. Baumberg
-
Article
| Open Access Visualization-enhanced under-oil open microfluidic system for in situ characterization of multi-phase chemical reactions
Visualization-enhanced under-oil open microfluidic system for in situ characterization of multi-phase chemical reactions
Under-oil open microfluidic systems have potential for studying multi-phase chemical reactions but have so far demonstrated largely only for biological applications. Here, the authors report the development of a system for in situ characterization of gas-liquid reactions by Raman spectroscopy.
- Qiyuan Chen
- , Hang Zhai
- & Bu Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Accessible hotspots for single-protein SERS in DNA-origami assembled gold nanorod dimers with tip-to-tip alignment
Accessible hotspots for single-protein SERS in DNA-origami assembled gold nanorod dimers with tip-to-tip alignment
The identification of individual proteins is highly desirable in diagnostics. Here, the authors report on DNA-origami assembled dimers of gold nanorod with accessible hotspots to capture and identify single proteins from solution by SERS.
- Francis Schuknecht
- , Karol Kołątaj
- & Theobald Lohmueller
-
Article
| Open Access Efficient optical plasmonic tweezer-controlled single-molecule SERS characterization of pH-dependent amylin species in aqueous milieus
Efficient optical plasmonic tweezer-controlled single-molecule SERS characterization of pH-dependent amylin species in aqueous milieus
Studying rare species in mixtures is challenging. Here, authors utilize on-and-off optical plasmonic trapping to control SERS-active nanocavity to analyse pH-dependent amylin species at single-molecule level, unveiling amyloid aggregation mechanisms.
- Wenhao Fu
- , Huanyu Chi
- & Jinqing Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Drug classification with a spectral barcode obtained with a smartphone Raman spectrometer
Drug classification with a spectral barcode obtained with a smartphone Raman spectrometer
Smartphones are ubiquitous devices that have permeated into our daily life. Here, the authors demonstrate that a Smartphone Raman spectrometer can be used for drug classification by using a convolutional neural network to process its spectral barcode.
- Un Jeong Kim
- , Suyeon Lee
- & Hyuck Choo
-
Article
| Open Access Probing hyperbolic and surface phonon-polaritons in 2D materials using Raman spectroscopy
Probing hyperbolic and surface phonon-polaritons in 2D materials using Raman spectroscopy
Hyperbolic phonon polaritons (HPhPs) in anisotropic van der Waals materials hold promise for nanophotonic applications, but their far-field characterization remains challenging. Here, the authors demonstrate the application of Raman spectroscopy in a backscattering configuration to determine the dispersion of HPhPs in thin GaSe crystals.
- Alaric Bergeron
- , Clément Gradziel
- & Sébastien Francoeur
-
Article
| Open Access Coherent Stokes Raman scattering microscopy (CSRS)
Coherent Stokes Raman scattering microscopy (CSRS)
Coherent Stokes Raman scattering (CSRS) has never been explored previously for chemical imaging due to a strong fluorescence background. Here, the authors demonstrate the first fluorescence-free CSRS laser scanning microscope and predict CSRS’ unique backscattering properties.
- Sandro Heuke
- & Hervé Rigneault
-
Article
| Open Access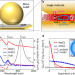 Giant optomechanical spring effect in plasmonic nano- and picocavities probed by surface-enhanced Raman scattering
Giant optomechanical spring effect in plasmonic nano- and picocavities probed by surface-enhanced Raman scattering
Extreme confinement of light in plasmonic nanocavities strongly enhances the optomechanical coupling of light with molecular vibrations. Here, the authors use a giant optical spring effect to reversibly weaken molecular bonds.
- Lukas A. Jakob
- , William M. Deacon
- & Jeremy J. Baumberg
-
Article
| Open Access Measurement-induced collective vibrational quantum coherence under spontaneous Raman scattering in a liquid
Measurement-induced collective vibrational quantum coherence under spontaneous Raman scattering in a liquid
Spontaneous Raman scattering is classically understood as an incoherent process. Here, the authors demonstrate that macroscopic quantum coherence among billions of vibrating molecules in a liquid is generated when single photon detection and single spatio-temporal mode excitation are implemented.
- Valeria Vento
- , Santiago Tarrago Velez
- & Christophe Galland
-
Article
| Open Access Spectroscopic visualization and phase manipulation of chiral charge density waves in 1T-TaS2
Spectroscopic visualization and phase manipulation of chiral charge density waves in 1T-TaS2
Two-dimensional charge density waves in layered semiconductors may exhibit chirality. Here, the authors utilize thermal annealing to reversibly switch the in-plane chirality of charge density waves in 1T-TaS2 and demonstrate a vertical chirality-locking effect between the van der Waals-stacked layers.
- Yan Zhao
- , Zhengwei Nie
- & Jin Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Two-dimensional infrared-Raman spectroscopy as a probe of water’s tetrahedrality
Two-dimensional infrared-Raman spectroscopy as a probe of water’s tetrahedrality
Direct spectroscopic probes of the impact of structure on dynamical processes in liquids remain scarce. Here, the authors use molecular dynamics simulations to show that the correlation between vibrational coupling and the local tetrahedral structure of liquid water can be studied via hybrid terahertz- and infrared-Raman spectroscopy.
- Tomislav Begušić
- & Geoffrey A. Blake
-
Article
| Open Access Quantum interference between dark-excitons and zone-edged acoustic phonons in few-layer WS2
Quantum interference between dark-excitons and zone-edged acoustic phonons in few-layer WS2
Here, the authors investigate the Raman spectra of few-layered WS2 when the excitation energy is in resonance with the dark exciton, and observe a Fano resonance between dark excitonsand zone-edge acoustic phonons.
- Qing-Hai Tan
- , Yun-Mei Li
- & Jun Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Rapid, label-free histopathological diagnosis of liver cancer based on Raman spectroscopy and deep learning
Rapid, label-free histopathological diagnosis of liver cancer based on Raman spectroscopy and deep learning
Biopsy is recommended for definitive diagnosis of liver carcinoma, however, this process requires staining and expert pathologists to confirm diagnosis. Here, the authors employ a portable Raman spectroscopy system combined with deep learning to detect carcinoma from normal tissue in real time.
- Liping Huang
- , Hongwei Sun
- & Yi Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Lossless enrichment of trace analytes in levitating droplets for multiphase and multiplex detection
Lossless enrichment of trace analytes in levitating droplets for multiphase and multiplex detection
Efficient enrichment of molecules from liquids, solid objects, or the gas phase is critical for their detection at trace concentrations. Here, the authors report on the lossless enrichment of analytes in droplets using acoustic levitation for multiphase and multiplex SERS detection.
- Xueyan Chen
- , Qianqian Ding
- & Shikuan Yang
-
Article
| Open Access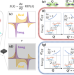 Absolute excited state molecular geometries revealed by resonance Raman signals
Absolute excited state molecular geometries revealed by resonance Raman signals
Physical or chemical reactions driven by light absorption are ruled by excited-state multidimensional energy surfaces displaced with respect to the ground state. Here the authors introduce a nonlinear Raman experiment to access an elusive aspect of the excited-state displacements: their sensed directions relative to the ground-state.
- Giovanni Batignani
- , Emanuele Mai
- & Tullio Scopigno
-
Article
| Open Access Electron-phonon coupling and vibrational properties of size-selected linear carbon chains by resonance Raman scattering
Electron-phonon coupling and vibrational properties of size-selected linear carbon chains by resonance Raman scattering
H-capped polyynes are the simplest system to observe finite-length effects in carbyne. Here, the authors exploit synchrotron-based UV resonance Raman spectroscopy to explain a peculiar intensity behavior of multiple phonons scattering and show a size-dependent electron-phonon coupling.
- P. Marabotti
- , M. Tommasini
- & C. S. Casari
-
Article
| Open Access Single-droplet surface-enhanced Raman scattering decodes the molecular determinants of liquid-liquid phase separation
Single-droplet surface-enhanced Raman scattering decodes the molecular determinants of liquid-liquid phase separation
The authors introduce a unique single-droplet surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) methodology that illuminates a wealth of molecular information within the mesoscopic liquid condensed phase of Fused in Sarcoma in the absence and presence of RNA.
- Anamika Avni
- , Ashish Joshi
- & Samrat Mukhopadhyay
-
Article
| Open Access Conformational heterogeneity of molecules physisorbed on a gold surface at room temperature
Conformational heterogeneity of molecules physisorbed on a gold surface at room temperature
Tip-enhanced vibrational spectroscopy at room temperature is complicated by molecular conformational dynamics, photobleaching, contaminations, and chemical reactions in air. This study demonstrates that a sub-nm protective layer of Al2O3 provides robust conditions for probing single-molecule conformations.
- Mingu Kang
- , Hyunwoo Kim
- & Kyoung-Duck Park
-
Article
| Open Access Magnons and magnetic fluctuations in atomically thin MnBi2Te4
Magnons and magnetic fluctuations in atomically thin MnBi2Te4
MnBi2Te4, referred to as MBT, is a van der Waals material combining topological electron bands with magnetic order. Here, Lujan et al study collective spin excitations in MBT, and show that magnetic fluctuations increase as samples reduce in thickness, implying less robust magnetic order.
- David Lujan
- , Jeongheon Choe
- & Xiaoqin Li
-
Article
| Open Access Intracavity Raman scattering couples soliton molecules with terahertz phonons
Intracavity Raman scattering couples soliton molecules with terahertz phonons
Here, the authors demonstrate intra-cavity excitation and time-domain sampling of coherent optical phonons inside an active laser oscillator. They discover that Terahertz crystal vibrations link successive ultrashort solitons which offers an approach to highspeed Raman spectroscopy inside laser cavities.
- Alexandra Völkel
- , Luca Nimmesgern
- & Georg Herink
-
Article
| Open Access The stability of covalent dative bond significantly increases with increasing solvent polarity
The stability of covalent dative bond significantly increases with increasing solvent polarity
Non covalent complexes are often considerably destabilized in the solvent. Here the authors combine vibrational Raman and NMR spectroscopy with a coupled-cluster computational investigation to show that the solvent polarity enhance the complex stability of a Me3NBH3 complex.
- Rabindranath Lo
- , Debashree Manna
- & Pavel Hobza
-
Article
| Open Access Chemically identifying single adatoms with single-bond sensitivity during oxidation reactions of borophene
Chemically identifying single adatoms with single-bond sensitivity during oxidation reactions of borophene
Here, the authors report the use of ultrahigh vacuum tip-enhanced Raman spectroscopy to characterize the oxidation processes of monolayer borophene with atomic-scale resolution and single-bond sensitivity, demonstrating the potential of the technique for probing the local chemistry of surface adsorbates on low-dimensional materials.
- Linfei Li
- , Jeremy F. Schultz
- & Nan Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access Hollow-core optical fibre sensors for operando Raman spectroscopy investigation of Li-ion battery liquid electrolytes
Hollow-core optical fibre sensors for operando Raman spectroscopy investigation of Li-ion battery liquid electrolytes
New analytical tools are needed to identify chemical degradation and failure mechanisms in Li-ion batteries. Here, the authors report an operando Raman spectroscopy method, based on hollow-core optical fibres, that enables monitoring the chemistry of liquid electrolytes during battery cycling.
- Ermanno Miele
- , Wesley M. Dose
- & Tijmen G. Euser
-
Article
| Open Access Quantum interference directed chiral raman scattering in two-dimensional enantiomers
Quantum interference directed chiral raman scattering in two-dimensional enantiomers
Quantum interference among elementary Raman processes has only been observed in few materials under specific excitation configurations. Here, the authors show that quantum interference can lead to significant chiral Raman response in a monolayer material of transitional metal dichalcogenide with triclinic symmetry.
- Shishu Zhang
- , Jianqi Huang
- & Jin Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Ultra-rapid and highly efficient enrichment of organic pollutants via magnetic mesoporous nanosponge for ultrasensitive nanosensors
Ultra-rapid and highly efficient enrichment of organic pollutants via magnetic mesoporous nanosponge for ultrasensitive nanosensors
The authors demonstrate a sensing approach for effectively monitoring organic micropollutants in water. They first use mesoporous nanosponge and magnetic nanoparticles for fast enrichment of micropollutants, and demonstrate SERS-based sensing with 2-3 orders of magnitude improvement in detection limits.
- Lingling Zhang
- , Yu Guo
- & Jixiang Fang
-
Article
| Open Access Resolving sub-angstrom ambient motion through reconstruction from vibrational spectra
Resolving sub-angstrom ambient motion through reconstruction from vibrational spectra
Tracking single molecule movements is a challenging task, but highly desired for applications and fundamental studies. Here the authors reconstruct the sub-angstrom relative movements of a molecule interacting with a metal adatom, by measuring its vibrational spectrum in a self-assembled monolayer, continuously modified by the adatom in a nanoparticle-on-mirror construct.
- Jack Griffiths
- , Tamás Földes
- & Jeremy J. Baumberg
-
Article
| Open Access Non-invasive hydrodynamic imaging in plant roots at cellular resolution
Non-invasive hydrodynamic imaging in plant roots at cellular resolution
Existing methods for non-invasively monitoring water flow in plants have limited spatial/temporal resolution. Here, the authors report that Raman microspectroscopy, complemented by hydrodynamic modelling, can monitor hydrodynamics within living root tissues at cell- and sub-second-scale resolutions.
- Flavius C. Pascut
- , Valentin Couvreur
- & Kevin F. Webb
-
Article
| Open Access In-situ nanospectroscopic imaging of plasmon-induced two-dimensional [4+4]-cycloaddition polymerization on Au(111)
In-situ nanospectroscopic imaging of plasmon-induced two-dimensional [4+4]-cycloaddition polymerization on Au(111)
Here, the authors use tip-enhanced Raman spectroscopy for in-situ investigation of plasmon-induced [4+4]-cycloaddition polymerization on Au(111). They find that this occurs by a hot electron tunneling mechanism, while crosslinks form via a self-stimulating growth mechanism.
- Feng Shao
- , Wei Wang
- & Renato Zenobi
-
Article
| Open Access 9-Cyanopyronin probe palette for super-multiplexed vibrational imaging
9-Cyanopyronin probe palette for super-multiplexed vibrational imaging
The authors develop a method to build Manhattan Raman Scattering (MARS) probes based on different core atoms, conjugation ring numbers, and stable isotope substitutions. A quantitative model predicts vibrational frequencies of MARS dyes from structures, which are used in supermultiplexed vibrational imaging.
- Yupeng Miao
- , Naixin Qian
- & Wei Min
-
Article
| Open Access Super-resolution label-free volumetric vibrational imaging
Super-resolution label-free volumetric vibrational imaging
Super-resolution microscopy is often limited by photobleaching or uneven distribution of fluorophores. The authors present a label-free superresolution method termed VISTA, combining sample-expansion and vibrational imaging, with resolution down to 78 nm in protein-rich biological structures in cells and tissues.
- Chenxi Qian
- , Kun Miao
- & Lu Wei
-
Article
| Open Access Adaptive tip-enhanced nano-spectroscopy
Adaptive tip-enhanced nano-spectroscopy
Tip-enhanced nano-spectroscopy suffers from inconsistent signal and difficulty in polarization-resolved measurement. Here, the authors present adaptive tip-enhanced nano-spectroscopy, which enables the additional signal enhancement and near-field polarization control via dynamic wavefront shaping.
- Dong Yun Lee
- , Chulho Park
- & Kyoung-Duck Park
-
Article
| Open Access Multiplexed live-cell profiling with Raman probes
Multiplexed live-cell profiling with Raman probes
Currently relatively few functional probes for Raman-based live-cell profiling exist. Here the authors build on their previous ultra-bright Raman dots to devise a 14-plexed Raman probe panel to quantify cell surface proteins, endocytosis activities and metabolic dynamics of single live cells.
- Chen Chen
- , Zhilun Zhao
- & Wei Min
-
Article
| Open Access Switchable stimulated Raman scattering microscopy with photochromic vibrational probes
Switchable stimulated Raman scattering microscopy with photochromic vibrational probes
Probes with reversible fluorescence are useful in super-resolution microscopy, but lack sufficient chemical specificity. Here, the authors engineer alkyne tagged diarylethene to realize photo-switchable stimulated Raman scattering probes with high chemical resolution, for applications in living cells.
- Jianpeng Ao
- , Xiaofeng Fang
- & Minbiao Ji
-
Article
| Open Access All-dielectric chiral-field-enhanced Raman optical activity
All-dielectric chiral-field-enhanced Raman optical activity
Raman optical activity (ROA) is useful for studying conformational structure and behavior of chiral molecules, but is limited by the weak signals. Here, the authors demonstrate 100x signal enhancement via an all-dielectric approach, using a silicon nanodisk array and exploiting its dark mode.
- Ting-Hui Xiao
- , Zhenzhou Cheng
- & Keisuke Goda
-
Article
| Open Access Microsecond fingerprint stimulated Raman spectroscopic imaging by ultrafast tuning and spatial-spectral learning
Microsecond fingerprint stimulated Raman spectroscopic imaging by ultrafast tuning and spatial-spectral learning
The authors employ a polygon-based ultrafast delay scanner and a deep learning framework for acquiring stimulated Raman scattering spectrum with high spectral and temporal resolution. They demonstrate high-speed imaging and tracking of multiple biomolecules in the fingerprint region.
- Haonan Lin
- , Hyeon Jeong Lee
- & Ji-Xin Cheng
-
Article
| Open Access A rich catalog of C–C bonded species formed in CO2 reduction on a plasmonic photocatalyst
A rich catalog of C–C bonded species formed in CO2 reduction on a plasmonic photocatalyst
In situ vibrational spectroscopy affords a powerful tool for probing elementary chemical processes on catalytic surfaces. Using surface enhanced Raman scattering, authors identify an array of multicarbon species formed on a Ag nanoparticle catalyst in plasmon-driven reduction of CO2 in water.
- Dinumol Devasia
- , Andrew J. Wilson
- & Prashant K. Jain
-
Article
| Open Access Ultra-bright Raman dots for multiplexed optical imaging
Ultra-bright Raman dots for multiplexed optical imaging
Raman-based imaging of biomarkers is often challenging due to low sensitivity. Here, the authors use a swelling-diffusion approach to develop a series of Raman probes that are both ultra-bright and compact in size, and demonstrate multiplexed imaging of specific protein targets in cells and tissue slices.
- Zhilun Zhao
- , Chen Chen
- & Wei Min
-
Article
| Open Access Optical tweezers-controlled hotspot for sensitive and reproducible surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy characterization of native protein structures
Optical tweezers-controlled hotspot for sensitive and reproducible surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy characterization of native protein structures
It is currently challenging to identify protein structures at low concentrations. Here the authors report optical tweezers-coupled Raman spectroscopy to generate tunable and reproducible SERS enhancements with single-molecule level sensitivity and use the method to detect protein structural features.
- Xin Dai
- , Wenhao Fu
- & Jinqing Huang
-
Article
| Open Access A digital single-molecule nanopillar SERS platform for predicting and monitoring immune toxicities in immunotherapy
A digital single-molecule nanopillar SERS platform for predicting and monitoring immune toxicities in immunotherapy
There is a clinical need to monitor immune-related toxicities of immune checkpoint blockade therapy. Here, the authors develop a digital SERS platform for multiplexed single cytokine counting to track immune-toxicities and demonstrate the ability to use pre-screening to identify patients at higher risk.
- Junrong Li
- , Alain Wuethrich
- & Matt Trau
-
Article
| Open Access Spread spectrum SERS allows label-free detection of attomolar neurotransmitters
Spread spectrum SERS allows label-free detection of attomolar neurotransmitters
Identification of neurotransmitters remains challenging for surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) due to presence of noise. Here, the authors present spread spectrum SERS, which by encoding excited light and decoding SERS signals enables detection of unlabelled neurotransmitters at attomolar concentrations.
- Wonkyoung Lee
- , Byoung-Hoon Kang
- & Ki-Hun Jeong
-
Article
| Open Access In vivo biomolecular imaging of zebrafish embryos using confocal Raman spectroscopy
In vivo biomolecular imaging of zebrafish embryos using confocal Raman spectroscopy
Raman spectroscopic imaging (RSI) can provide information on the chemical composition of a sample, but application to living organisms has lacked sufficient spatial resolution and signal strength. Here the authors apply confocal RSI to whole-mount zebrafish embryos to distinguish different infectious bacteria and to living zebrafish embryos to monitor the wound healing process.
- Håkon Høgset
- , Conor C. Horgan
- & Molly M. Stevens
-
Article
| Open Access Porous carbon nanowire array for surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy
Porous carbon nanowire array for surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy
SERS can be unreliable for biomedical use. The authors demonstrate a metal-free nanostructure composed of porous carbon nanowires in an array as a SERS substrate. It offers 106 signal enhancement due to strong broadband charge-transfer resonance and substrate-to-substrate, spot-to-spot and time-to-time consistency in the SERS spectrum.
- Nan Chen
- , Ting-Hui Xiao
- & Keisuke Goda
-
Article
| Open Access Raman-guided subcellular pharmaco-metabolomics for metastatic melanoma cells
Raman-guided subcellular pharmaco-metabolomics for metastatic melanoma cells
Single-cell metabolomics can offer deep insights into the metabolic reprogramming that accompanies disease states. Here, the authors use Raman spectro-microscopy for non-invasive metabolite analysis and identification of druggable metabolic susceptibilities in single live melanoma cells.
- Jiajun Du
- , Yapeng Su
- & Lu Wei
-
Article
| Open Access Raman image-activated cell sorting
Raman image-activated cell sorting
Most current cell sorting methods are based on fluorescence detection with no imaging capability. Here the authors generate and use Raman image-activated cell sorting with a throughput of around 100 events per second, providing molecular images with no need for labeling.
- Nao Nitta
- , Takanori Iino
- & Keisuke Goda
-
Article
| Open Access A library of ab initio Raman spectra for automated identification of 2D materials
A library of ab initio Raman spectra for automated identification of 2D materials
The authors develop a first-principles workflow for calculating Raman spectra of 733 monolayers from the computational 2D materials database. After benchmarking results against experimental data for 15 monolayers, an automatic procedure for identifying a material from its Raman spectrum is proposed.
- Alireza Taghizadeh
- , Ulrik Leffers
- & Kristian S. Thygesen
-
Article
| Open Access Buoyant particulate strategy for few-to-single particle-based plasmonic enhanced nanosensors
Buoyant particulate strategy for few-to-single particle-based plasmonic enhanced nanosensors
Plasmonic-enhanced nanosensors are limited in practical applications, as it remains challenging to detect molecules at low concentrations. Here, the authors introduce a buoyant particulate strategy in order to enrich analytes in the plasmonic hot spots.
- Dongjie Zhang
- , Leqin Peng
- & Jixiang Fang
-
Article
| Open Access Irreversible accumulated SERS behavior of the molecule-linked silver and silver-doped titanium dioxide hybrid system
Irreversible accumulated SERS behavior of the molecule-linked silver and silver-doped titanium dioxide hybrid system
The authors report that near-infrared light induces an irreversible accumulated Surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) behavior of a molecule/metal–semiconductor hybrid system. They investigate the underlying mechanism and show that it is attributed to crystallinity, charge transfer and reorientation.
- Lu Zhou
- , Jun Zhou
- & Pasquale Mormile

 Optics miniaturization strategy for demanding Raman spectroscopy applications
Optics miniaturization strategy for demanding Raman spectroscopy applications