Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Genomic data in the All of Us Research Program
Genomic data in the All of Us Research Program
A study describes the release of clinical-grade whole-genome sequence data for 245,388 diverse participants by the All of Us Research Program and characterizes the properties of the dataset.
- Alexander G. Bick
- , Ginger A. Metcalf
- & Joshua C. Denny
-
Article
| Open Access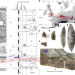 Homo sapiens reached the higher latitudes of Europe by 45,000 years ago
Homo sapiens reached the higher latitudes of Europe by 45,000 years ago
Through archaeological excavation, morphological and proteomic taxonomic identification, mitochondrial DNA analysis and direct radiocarbon dating of human remains, a study reports the presence of Homo sapiens in Germany north of the Alps more than 45,000 years ago.
- Dorothea Mylopotamitaki
- , Marcel Weiss
- & Jean-Jacques Hublin
-
Article |
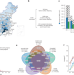 The Born in Guangzhou Cohort Study enables generational genetic discoveries
The Born in Guangzhou Cohort Study enables generational genetic discoveries
Analysis of data from the Born in Guangzhou Cohort Study comprising mainly of trios and mother–infant pairs reveals novel East Asian-specific genetic associations with maternal bile acid, gestational weight gain and infant cord blood traits.
- Shujia Huang
- , Siyang Liu
- & Xiu Qiu
-
Article
| Open Access 100 ancient genomes show repeated population turnovers in Neolithic Denmark
100 ancient genomes show repeated population turnovers in Neolithic Denmark
Integrated data, including 100 human genomes from the Mesolithic, Neolithic and Early Bronze Age periods show that two major population turnovers occurred over just 1,000 years in Neolithic Denmark, resulting in dramatic changes in the genes, diet and physical appearance of the local people, as well as the landscape in which they lived.
- Morten E. Allentoft
- , Martin Sikora
- & Eske Willerslev
-
Article
| Open Access Population genomics of post-glacial western Eurasia
Population genomics of post-glacial western Eurasia
An analysis involving the shotgun sequencing of more than 300 ancient genomes from Eurasia reveals a deep east–west genetic divide from the Black Sea to the Baltic, and provides insight into the distinct effects of the Neolithic transition on either side of this boundary.
- Morten E. Allentoft
- , Martin Sikora
- & Eske Willerslev
-
Article
| Open Access The selection landscape and genetic legacy of ancient Eurasians
The selection landscape and genetic legacy of ancient Eurasians
Analyses of imputed ancient genomes and of samples from the UK Biobank indicate that ancient selection and migration were large contributors to the distribution of phenotypic diversity in present-day Europeans.
- Evan K. Irving-Pease
- , Alba Refoyo-Martínez
- & Eske Willerslev
-
Article
| Open Access Elevated genetic risk for multiple sclerosis emerged in steppe pastoralist populations
Elevated genetic risk for multiple sclerosis emerged in steppe pastoralist populations
Analysis of a large ancient genome dataset shows that genetic risk for multiple sclerosis rose in steppe pastoralists, providing insight into how genetic ancestry from the Neolithic and Bronze Age has shaped modern immune responses.
- William Barrie
- , Yaoling Yang
- & Eske Willerslev
-
Article
| Open Access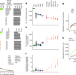 Indigenous Australian genomes show deep structure and rich novel variation
Indigenous Australian genomes show deep structure and rich novel variation
Analysis of the genomes of 159 individuals from four Indigenous communities in Australia shows a high level of genetic variation and demonstrates the need for greater representation of Indigenous Australians in reference panels and clinical databases.
- Matthew Silcocks
- , Ashley Farlow
- & Stephen Leslie
-
Article
| Open Access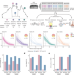 The landscape of genomic structural variation in Indigenous Australians
The landscape of genomic structural variation in Indigenous Australians
Population-scale whole-genome sequencing across four remote Indigenous Australian communities reveals a large fraction of structural variants that are unique to these populations, emphasizing the genetic distinctiveness of and diversity among Indigenous Australians.
- Andre L. M. Reis
- , Melissa Rapadas
- & Ira W. Deveson
-
Article |
 A genomic mutational constraint map using variation in 76,156 human genomes
A genomic mutational constraint map using variation in 76,156 human genomes
A genomic constraint map for the human genome constructed using data from 76,156 human genomes from the Genome Aggregation Database shows that non-coding constrained regions are enriched for regulatory elements and variants associated with complex diseases and traits.
- Siwei Chen
- , Laurent C. Francioli
- & Konrad J. Karczewski
-
Article
| Open Access The genetic legacy of the expansion of Bantu-speaking peoples in Africa
The genetic legacy of the expansion of Bantu-speaking peoples in Africa
We gathered genetic data for 1,763 individuals from 147 populations across 14 African countries, and 12 Late Iron Age individuals, to trace the expansion of Bantu-speaking peoples over the past 6,000 years.
- Cesar A. Fortes-Lima
- , Concetta Burgarella
- & Carina M. Schlebusch
-
Article
| Open Access Identification of constrained sequence elements across 239 primate genomes
Identification of constrained sequence elements across 239 primate genomes
Whole-genome alignment of 239 primate species reveals noncoding regulatory elements that are under selective constraint in primates but not in other placental mammals, that are enriched for variants that affect human gene expression and complex traits in diseases.
- Lukas F. K. Kuderna
- , Jacob C. Ulirsch
- & Kyle Kai-How Farh
-
Article |
 Genetic continuity and change among the Indigenous peoples of California
Genetic continuity and change among the Indigenous peoples of California
Genome-wide analyses of ancient DNA from individuals from California and Mexico shed light on the spread of Mexican ancestry to California and how it correlates with linguistic flow.
- Nathan Nakatsuka
- , Brian Holguin
- & David Reich
-
Article
| Open Access Genotyping, sequencing and analysis of 140,000 adults from Mexico City
Genotyping, sequencing and analysis of 140,000 adults from Mexico City
Genotype and exome sequencing of 150,000 participants and whole-genome sequencing of 9,950 selected individuals recruited into the Mexico City Prospective Study constitute a valuable, publicly available resource of non-European sequencing data.
- Andrey Ziyatdinov
- , Jason Torres
- & Roberto Tapia-Conyer
-
Article
| Open Access Mexican Biobank advances population and medical genomics of diverse ancestries
Mexican Biobank advances population and medical genomics of diverse ancestries
Nationwide genomic biobank in Mexico unravels demographic history and complex trait architecture from 6,057 individuals.
- Mashaal Sohail
- , María J. Palma-Martínez
- & Andrés Moreno-Estrada
-
Article
| Open Access Large-scale plasma proteomics comparisons through genetics and disease associations
Large-scale plasma proteomics comparisons through genetics and disease associations
Comparisons of phenotypic and genetic association with protein levels from Icelandic and UK Biobank cohorts show that using multiple analysis platforms and stratifying populations by ancestry improves the detection of associations and allows the refinement of their location within the genome.
- Grimur Hjorleifsson Eldjarn
- , Egil Ferkingstad
- & Kari Stefansson
-
Article
| Open Access Rare variant associations with plasma protein levels in the UK Biobank
Rare variant associations with plasma protein levels in the UK Biobank
A set of three papers in Nature reports a new proteomics resource from the UK Biobank and initial analysis of common and rare genetic variant associations with plasma protein levels.
- Ryan S. Dhindsa
- , Oliver S. Burren
- & Slavé Petrovski
-
Article
| Open Access Plasma proteomic associations with genetics and health in the UK Biobank
Plasma proteomic associations with genetics and health in the UK Biobank
The Pharma Proteomics Project generates the largest open-access plasma proteomics dataset to date, offering insights into trans protein quantitative trait loci across multiple biological domains, and highlighting genetic influences on ligand–receptor interactions and pathway perturbations across a diverse collection of cytokines and complement networks.
- Benjamin B. Sun
- , Joshua Chiou
- & Christopher D. Whelan
-
Review Article |
 From target discovery to clinical drug development with human genetics
From target discovery to clinical drug development with human genetics
This Review provides a perspective on the development of non-cancer therapies based on human genetics studies and suggests measures that can be taken to streamline the pipeline from initial genetic discovery to approved therapy.
- Katerina Trajanoska
- , Claude Bhérer
- & Vincent Mooser
-
Article |
 The complete sequence of a human Y chromosome
The complete sequence of a human Y chromosome
We present the complete 62,460,029-base-pair sequence of a human Y chromosome from the HG002 genome (T2T-Y) that corrects multiple errors in GRCh38-Y and adds over 30 million base pairs of sequence to the reference.
- Arang Rhie
- , Sergey Nurk
- & Adam M. Phillippy
-
Article
| Open Access Nuclear genetic control of mtDNA copy number and heteroplasmy in humans
Nuclear genetic control of mtDNA copy number and heteroplasmy in humans
We quantify mitochondrial DNA copy number and heteroplasmy levels and study their association with nuclear genetic loci in population-scale biobanks.
- Rahul Gupta
- , Masahiro Kanai
- & Vamsi K. Mootha
-
Article
| Open Access Dissecting human population variation in single-cell responses to SARS-CoV-2
Dissecting human population variation in single-cell responses to SARS-CoV-2
Population differences in immune responses to SARS-CoV-2 can be explained by environmental exposures, but also by local adaptation acting through genetic variants acquired after admixture with archaic hominin forms.
- Yann Aquino
- , Aurélie Bisiaux
- & Lluis Quintana-Murci
-
Article
| Open Access Extensive pedigrees reveal the social organization of a Neolithic community
Extensive pedigrees reveal the social organization of a Neolithic community
The burial community at Gurgy ‘les Noisats’ (France) was genetically connected by two main pedigrees, spanning seven generations, that were patrilocal and patrilineal, with evidence for female exogamy and exchange with genetically close neighbouring groups.
- Maïté Rivollat
- , Adam Benjamin Rohrlach
- & Wolfgang Haak
-
Article
| Open Access Early contact between late farming and pastoralist societies in southeastern Europe
Early contact between late farming and pastoralist societies in southeastern Europe
Archaeogenetic analysis of 135 individuals from the zone between southeastern Europe and the northwestern Black Sea region indicates contacts between farming and pastoralist populations at the end of the Copper Age.
- Sandra Penske
- , Adam B. Rohrlach
- & Wolfgang Haak
-
Article
| Open Access A pangenome reference of 36 Chinese populations
A pangenome reference of 36 Chinese populations
A study reports data from the first phase of the Chinese Pangenome Consortium including 116 de novo assemblies from 58 core samples representing 36 minority Chinese ethnic groups.
- Yang Gao
- , Xiaofei Yang
- & Shuhua Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Northwest African Neolithic initiated by migrants from Iberia and Levant
Northwest African Neolithic initiated by migrants from Iberia and Levant
Genome sequencing of nine individuals shows ancestry shifts in the Neolithization of northwestern Africa that probably mirrored a heterogeneous economic and cultural landscape in a more multifaceted process than observed in other regions.
- Luciana G. Simões
- , Torsten Günther
- & Mattias Jakobsson
-
Article
| Open Access ERα-associated translocations underlie oncogene amplifications in breast cancer
ERα-associated translocations underlie oncogene amplifications in breast cancer
An analysis of 780 breast cancer genomes shows that focal amplifications are frequently preceded by dicentric chromosome formation from inter-chromosomal translocations associated with oestrogen receptor binding, which leads to chromosome bridge formation and breakage, initiating the amplification process.
- Jake June-Koo Lee
- , Youngsook Lucy Jung
- & Peter J. Park
-
Article |
 A weakly structured stem for human origins in Africa
A weakly structured stem for human origins in Africa
An analysis of models of human populations in Africa, using some newly sequenced genomes, finds that human origins in the continent can best be described by a weakly structured stem model.
- Aaron P. Ragsdale
- , Timothy D. Weaver
- & Simon Gravel
-
Article
| Open Access Increased mutation and gene conversion within human segmental duplications
Increased mutation and gene conversion within human segmental duplications
A study comparing the pattern of single-nucleotide variation between unique and duplicated regions of the human genome shows that mutation rate and interlocus gene conversion are elevated in duplicated regions.
- Mitchell R. Vollger
- , Philip C. Dishuck
- & Evan E. Eichler
-
Article
| Open Access Recombination between heterologous human acrocentric chromosomes
Recombination between heterologous human acrocentric chromosomes
Comparisons within the human pangenome establish that homologous regions on short arms of heterologous human acrocentric chromosomes actively recombine, leading to the high rate of Robertsonian translocation breakpoints in these regions.
- Andrea Guarracino
- , Silvia Buonaiuto
- & Erik Garrison
-
Article
| Open Access Ancient human DNA recovered from a Palaeolithic pendant
Ancient human DNA recovered from a Palaeolithic pendant
A non-destructive DNA isolation method for the stepwise release of DNA trapped in ancient tooth and bone artefacts is developed.
- Elena Essel
- , Elena I. Zavala
- & Matthias Meyer
-
Article
| Open Access Entwined African and Asian genetic roots of medieval peoples of the Swahili coast
Entwined African and Asian genetic roots of medieval peoples of the Swahili coast
Analysis of ancient human DNA from the Swahili coast reveals that predominantly African female ancestors and Asian male ancestors formed families after around ad 1000 and lived in elite communities in coastal stone towns.
- Esther S. Brielle
- , Jeffrey Fleisher
- & Chapurukha M. Kusimba
-
Article |
 An atlas of genetic scores to predict multi-omic traits
An atlas of genetic scores to predict multi-omic traits
A machine learning approach is used to analyse multi-omics (proteomics, metabolomics and transcriptomics) data, producing genetic scores for more than 17,000 biomolecular traits in human blood, and identifying possible associations with disease.
- Yu Xu
- , Scott C. Ritchie
- & Michael Inouye
-
Article
| Open Access Palaeogenomics of Upper Palaeolithic to Neolithic European hunter-gatherers
Palaeogenomics of Upper Palaeolithic to Neolithic European hunter-gatherers
Combined analysis of new genomic data from 116 ancient hunter-gatherer individuals together with previously published data provides insights into the genetic structure and demographic shifts of west Eurasian forager populations over a period of 30,000 years.
- Cosimo Posth
- , He Yu
- & Johannes Krause
-
Article |
 Polygenic architecture of rare coding variation across 394,783 exomes
Polygenic architecture of rare coding variation across 394,783 exomes
An analysis of rare coding variants across 22 common traits and diseases indicates that these variants will contribute substantially to biological insights but modestly to population risk stratification.
- Daniel J. Weiner
- , Ajay Nadig
- & Luke J. O’Connor
-
Article
| Open Access FinnGen provides genetic insights from a well-phenotyped isolated population
FinnGen provides genetic insights from a well-phenotyped isolated population
Genome-wide association studies of individuals from an isolated population (data from the Finnish biobank study FinnGen) and consequent meta-analyses facilitate the identification of previously unknown coding variant associations for both rare and common diseases.
- Mitja I. Kurki
- , Juha Karjalainen
- & Aarno Palotie
-
Article
| Open Access Recurrent repeat expansions in human cancer genomes
Recurrent repeat expansions in human cancer genomes
An atlas explores the landscape of recurrent repeat expansions in human cancer genomes.
- Graham S. Erwin
- , Gamze Gürsoy
- & Michael P. Snyder
-
Article
| Open Access Semi-automated assembly of high-quality diploid human reference genomes
Semi-automated assembly of high-quality diploid human reference genomes
Which combination of current genome sequencing and assembly approaches results in high-quality, complete diploid genome assemblies is determined.
- Erich D. Jarvis
- , Giulio Formenti
- & Karen H. Miga
-
Article
| Open Access Genetic insights into the social organization of Neanderthals
Genetic insights into the social organization of Neanderthals
Genetic data for 13 Neanderthals from 2 Middle Palaeolithic sites in the Altai Mountains of southern Siberia presented provide insights into the social organization of an isolated Neanderthal community at the easternmost extent of their known range.
- Laurits Skov
- , Stéphane Peyrégne
- & Benjamin M. Peter
-
Article
| Open Access The Anglo-Saxon migration and the formation of the early English gene pool
The Anglo-Saxon migration and the formation of the early English gene pool
Archaeogenetic study of ancient DNA from medieval northwestern Europeans reveals substantial increase of continental northern European ancestry in Britain, suggesting mass migration across the North Sea during the Early Middle Ages.
- Joscha Gretzinger
- , Duncan Sayer
- & Stephan Schiffels
-
Article
| Open Access The sequences of 150,119 genomes in the UK Biobank
The sequences of 150,119 genomes in the UK Biobank
To measure selection on variants, whole-genome sequencing of approximately 150,000 individuals from the UK Biobank is used to rank sequence variants by their level of depletion.
- Bjarni V. Halldorsson
- , Hannes P. Eggertsson
- & Kari Stefansson
-
Article
| Open Access Grey wolf genomic history reveals a dual ancestry of dogs
Grey wolf genomic history reveals a dual ancestry of dogs
DNA from ancient wolves spanning 100,000 years sheds light on wolves’ evolutionary history and the genomic origin of dogs.
- Anders Bergström
- , David W. G. Stanton
- & Pontus Skoglund
-
Article |
 A natural mutator allele shapes mutation spectrum variation in mice
A natural mutator allele shapes mutation spectrum variation in mice
Natural variation in the mouse gene Mutyh influences the rate of C>A germline mutations.
- Thomas A. Sasani
- , David G. Ashbrook
- & Kelley Harris
-
Article |
 Reduced reproductive success is associated with selective constraint on human genes
Reduced reproductive success is associated with selective constraint on human genes
Human genetic variants that impair genes that are intolerant of damaging genetic variation are associated with lower reproductive success that is probably mediated by genetically associated cognitive and behavioural traits, particularly in males.
- Eugene J. Gardner
- , Matthew D. C. Neville
- & Matthew E. Hurles
-
Article
| Open Access Ancient DNA and deep population structure in sub-Saharan African foragers
Ancient DNA and deep population structure in sub-Saharan African foragers
DNA analysis of 6 individuals from eastern and south-central Africa spanning the past approximately 18,000 years, and of 28 previously published ancient individuals, provides genetic evidence supporting hypotheses of increasing regionalization at the end of the Pleistocene.
- Mark Lipson
- , Elizabeth A. Sawchuk
- & Mary E. Prendergast
-
Article
| Open Access Genetic associations of protein-coding variants in human disease
Genetic associations of protein-coding variants in human disease
A meta-analysis combining whole-exome sequencing data from UK Biobank participants and imputed genotypes from FinnGen participants enables identification of genetic associations with human disease in the rare and low-frequency allelic spectrum
- Benjamin B. Sun
- , Mitja I. Kurki
- & Heiko Runz
-
Article
| Open Access Mutation bias reflects natural selection in Arabidopsis thaliana
Mutation bias reflects natural selection in Arabidopsis thaliana
Data on de novo mutations in Arabidopsis thaliana reveal that mutations do not occur randomly; instead, epigenome-associated mutation bias reduces the occurrence of deleterious mutations.
- J. Grey Monroe
- , Thanvi Srikant
- & Detlef Weigel
-
Article |
 A high-resolution picture of kinship practices in an Early Neolithic tomb
A high-resolution picture of kinship practices in an Early Neolithic tomb
Archaeological and ancient DNA analyses of 35 individuals entombed at Hazleton North long cairn approximately 5,700 years ago are used to reconstruct kinship practices in Early Neolithic Britain.
- Chris Fowler
- , Iñigo Olalde
- & David Reich
-
Article |
 Large-scale migration into Britain during the Middle to Late Bronze Age
Large-scale migration into Britain during the Middle to Late Bronze Age
Genome-wide ancient DNA data from individuals from the Middle Bronze Age to Iron Age documents large-scale movement of people from the European continent between 1300 and 800 bc that was probably responsible for spreading early Celtic languages to Britain.
- Nick Patterson
- , Michael Isakov
- & David Reich

 Network of large pedigrees reveals social practices of Avar communities
Network of large pedigrees reveals social practices of Avar communities