Featured
-
-
Article |
 Recycling of autophagosomal components from autolysosomes by the recycler complex
Recycling of autophagosomal components from autolysosomes by the recycler complex
Zhou and colleagues identify SNX4–SNX5–SNX17 as a multiunit complex that mediates the recycling of autophagosomal components from autolysosomes.
- Chuchu Zhou
- , Zhe Wu
- & Yueguang Rong
-
News & Views |
 Mitochondrial efficiency directs cell fate
Mitochondrial efficiency directs cell fate
Mitochondria are asymmetrically distributed to the daughter cells according to their age. A study now identifies metabolic features associated with mitochondrial age that regulate cell fate decisions.
- Jessica Brooke Spinelli
- & Elma Zaganjor
-
News & Views |
 Softening redox homeostasis in cancer cells
Softening redox homeostasis in cancer cells
Extracellular matrix (ECM) rigidity increases during tumour progression. In a recent study, Romani et al. delineated a connection between ECM stiffness and the redox response of disseminated tumour cells. Their results suggest that soft ECM promotes DRP1-mediated mitochondrial fission and an NRF2-dependent antioxidant response.
- Justin A. Powers
- & Iok In Christine Chio
-
Article |
 Mitochondrial fission links ECM mechanotransduction to metabolic redox homeostasis and metastatic chemotherapy resistance
Mitochondrial fission links ECM mechanotransduction to metabolic redox homeostasis and metastatic chemotherapy resistance
Romani et al. report that cells on soft extracellular matrix have increased mitochondrial fission, with subsequent production of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species and NRF2, which may increase resistance to reactive oxygen species-dependent chemotherapy drugs in breast cancer cells in vitro and in mouse lungs.
- Patrizia Romani
- , Nunzia Nirchio
- & Sirio Dupont
-
Article |
 LONP-1 and ATFS-1 sustain deleterious heteroplasmy by promoting mtDNA replication in dysfunctional mitochondria
LONP-1 and ATFS-1 sustain deleterious heteroplasmy by promoting mtDNA replication in dysfunctional mitochondria
Yang et al. report that ATFS-1 preferentially accumulates in dysfunctional mitochondria carrying mutated mitochondria DNA (∆mtDNA) and facilitates mtDNA replication by promoting POLG recruitment, resulting in the replicative advantage of ∆mtDNA and heteroplasmy maintenance.
- Qiyuan Yang
- , Pengpeng Liu
- & Cole M. Haynes
-
News & Views |
 Surveying the mitochondrial proteome
Surveying the mitochondrial proteome
Mitochondrial-derived vesicles (MDVs) transfer mitochondrial content to lysosomes and peroxisomes. A study now reveals that MDVs deliver β-barrel proteins and fully assembled mitochondrial complexes for lysosomal degradation, establishing an important role for MDVs in mitochondrial protein quality control.
- Dominic Winter
- & Thomas Becker
-
Article |
 MIROs and DRP1 drive mitochondrial-derived vesicle biogenesis and promote quality control
MIROs and DRP1 drive mitochondrial-derived vesicle biogenesis and promote quality control
By characterizing the composition of mitochondrial-derived vesicles (MDVs), König et al. define a MIRO1/2- and DRP1-dependent MDV biogenesis pathway and propose that MDVs maintain the mitochondrial proteome by shuttling assembled protein complexes to lysosomes.
- Tim König
- , Hendrik Nolte
- & Heidi M. McBride
-
News & Views |
 Mitochondrial UPR through generations
Mitochondrial UPR through generations
Neuronal mitochondria perturbation elicits a mitochondrial unfolded protein response (UPRmt) in peripheral tissues cell non-autonomously, dependent on the Wnt signalling pathway. A study now reveals that a Wnt-mediated increase in maternally inherited mitochondria DNA is responsible for transgenerational UPRmt induced by neuronal mitochondria perturbation.
- Mooncheol Park
- & Meng C. Wang
-
Article |
 The memory of neuronal mitochondrial stress is inherited transgenerationally via elevated mitochondrial DNA levels
The memory of neuronal mitochondrial stress is inherited transgenerationally via elevated mitochondrial DNA levels
Zhang et al. report that the systemic mitochondrial unfolded protein response triggered by neuronal mitochondrial stress can be transmitted across multiple generations in Caenorhabditis elegans via a mechanism involving elevation in mitochondrial DNA levels in oocytes.
- Qian Zhang
- , Zihao Wang
- & Ye Tian
-
Article |
 A Golgi-derived vesicle potentiates PtdIns4P to PtdIns3P conversion for endosome fission
A Golgi-derived vesicle potentiates PtdIns4P to PtdIns3P conversion for endosome fission
Gong et al. uncover a role for the Golgi network in ER-associated endosome fission, showing that a Golgi-derived SEC14L2 compartment mediates ER-associated endosome fission by promoting PtdIns4P to PtdIns3P conversion.
- Bo Gong
- , Yuting Guo
- & Shunji Jia
-
Article |
 Lysosomal retargeting of Myoferlin mitigates membrane stress to enable pancreatic cancer growth
Lysosomal retargeting of Myoferlin mitigates membrane stress to enable pancreatic cancer growth
Gupta et al. show that the membrane repair factor Myoferlin protects against membrane damage of pancreatic cancer lysosomes to sustain enhanced lysosomal function and promote tumour growth.
- Suprit Gupta
- , Julian Yano
- & Rushika M. Perera
-
Article |
 LC3 lipidation is essential for TFEB activation during the lysosomal damage response to kidney injury
LC3 lipidation is essential for TFEB activation during the lysosomal damage response to kidney injury
Nakamura et al. find that the master transcriptional regulator of lysosomal biogenesis and autophagy TFEB is activated following LC3 lipidation during lysosomal damage and show the importance of this mechanism during kidney injury.
- Shuhei Nakamura
- , Saki Shigeyama
- & Tamotsu Yoshimori
-
News & Views |
 ESCRTs cut some slack
ESCRTs cut some slack
In this issue of Nature Cell Biology, Mercier et al. show that acute changes in membrane tension may be a physiological trigger for ESCRT assembly, which drives membrane scission, luminal vesicle budding, and a wide array of other membrane remodelling events throughout the cell.
- Robert C. Piper
-
Article |
 Mammalian Atg8 proteins and the autophagy factor IRGM control mTOR and TFEB at a regulatory node critical for responses to pathogens
Mammalian Atg8 proteins and the autophagy factor IRGM control mTOR and TFEB at a regulatory node critical for responses to pathogens
Kumar et al. show that mammalian Atg8 proteins along with IRGM regulate the lysosomal system via mTOR and TFEB, respectively, in the response to pathogens.
- Suresh Kumar
- , Ashish Jain
- & Vojo Deretic
-
Article |
 Endocytic regulation of cellular ion homeostasis controls lysosome biogenesis
Endocytic regulation of cellular ion homeostasis controls lysosome biogenesis
López-Hernández et al. show that exo-endocytosis of a Na+/H+ exchanger controls lysosome biogenesis through Ca2+/calcineurin-mediated activation of TFEB in response to osmotic stress.
- Tania López-Hernández
- , Dmytro Puchkov
- & Volker Haucke
-
Letter |
 Hrd1 forms the retrotranslocation pore regulated by auto-ubiquitination and binding of misfolded proteins
Hrd1 forms the retrotranslocation pore regulated by auto-ubiquitination and binding of misfolded proteins
Ubiquitin ligase Hrd1 is essential for endoplasmic-reticulum-associated protein degradation. Vasic et al. demonstrate that Hrd1 forms a retrotranslocation channel controlled by auto-ubiquitination and substrate binding.
- Vedran Vasic
- , Niels Denkert
- & Michael Meinecke
-
Article |
 A perinuclear microtubule-organizing centre controls nuclear positioning and basement membrane secretion
A perinuclear microtubule-organizing centre controls nuclear positioning and basement membrane secretion
Zheng et al. discover a type of perinuclear microtubule-organizing center, which is assembled by multiple factors and regulates retrograde endosomal trafficking and plasma membrane growth.
- Yiming Zheng
- , Rebecca A. Buchwalter
- & Timothy L. Megraw
-
Article |
 FERARI is required for Rab11-dependent endocytic recycling
FERARI is required for Rab11-dependent endocytic recycling
Solinger et al. show that FERARI is a conserved tethering platform that mediates Rab11-dependent recycling at sorting endosomes.
- Jachen A. Solinger
- , Harun-Or Rashid
- & Anne Spang
-
Article |
 Mitochondria-localised ZNFX1 functions as a dsRNA sensor to initiate antiviral responses through MAVS
Mitochondria-localised ZNFX1 functions as a dsRNA sensor to initiate antiviral responses through MAVS
Wang et al. identify ZNFX1 as a mitochondria-localised sensor that recognizes viral dsRNA and induces a type I interferon response, thereby restricting virus infection.
- Yao Wang
- , Shaochun Yuan
- & Anlong Xu
-
Article |
 Phagolysosome resolution requires contacts with the endoplasmic reticulum and phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate signalling
Phagolysosome resolution requires contacts with the endoplasmic reticulum and phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate signalling
Levin-Konigsberg et al. show that resorption of the phagolysosome after degradation of its contents requires transfer of PI4P and tethering to the ER, both mediated by oxysterol-binding protein-related protein 1L (ORP1L).
- Roni Levin-Konigsberg
- , Fernando Montaño-Rendón
- & Sergio Grinstein
-
News & Views |
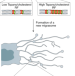 Migrasomes take center stage
Migrasomes take center stage
Migrasomes are a recently discovered type of extracellular vesicles that are characteristically generated along retraction fibers in migrating cells. Two studies now show how migrasomes are formed and how they function in the physiologically relevant context of the developing zebrafish embryo.
- Stefania Tavano
- & Carl-Philipp Heisenberg
-
Article |
 Migrasomes provide regional cues for organ morphogenesis during zebrafish gastrulation
Migrasomes provide regional cues for organ morphogenesis during zebrafish gastrulation
Yu and colleagues report the formation of migrasomes during zebrafish gastrulation. Migrasomes provide signalling molecules to guide the migration of dorsal forerunner cells, thus controlling organ morphogenesis.
- Dong Jiang
- , Zheng Jiang
- & Li Yu
-
Article |
 Asymmetric inheritance of spindle microtubule-organizing centres preserves replicative lifespan
Asymmetric inheritance of spindle microtubule-organizing centres preserves replicative lifespan
Yeast cells segregate the old spindle pole body into the bud. Manzano-López et al. report that inverted segregation accelerates ageing due to aberrant partition of protein aggregates and damaged mitochondria.
- Javier Manzano-López
- , Laura Matellán
- & Fernando Monje-Casas
-
Article |
 Mitochondrial fusion regulates lipid homeostasis and stem cell maintenance in the Drosophila testis
Mitochondrial fusion regulates lipid homeostasis and stem cell maintenance in the Drosophila testis
Demarco et al. demonstrate that a block in mitochondrial fusion leads to a loss of male germline stem cells in Drosophila, a disruption of lipid homeostasis and activation of TOR signalling.
- Rafael Sênos Demarco
- , Bradley S. Uyemura
- & D. Leanne Jones
-
News & Views |
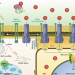 IRE1α modulates ER and mitochondria crosstalk
IRE1α modulates ER and mitochondria crosstalk
IRE1α is an endoplasmic reticulum (ER) transmembrane protein known for a crucial role in regulating the unfolding protein response. A study now shows that IRE1α interacts with the main ER Ca2+ channel InsP3Rs and facilitates the transfer of Ca2+ from the ER into mitochondria, thus driving cellular metabolism.
- Roland Malli
- & Wolfgang F. Graier
-
Article |
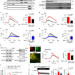 Non-canonical function of IRE1α determines mitochondria-associated endoplasmic reticulum composition to control calcium transfer and bioenergetics
Non-canonical function of IRE1α determines mitochondria-associated endoplasmic reticulum composition to control calcium transfer and bioenergetics
Carreras-Sureda et al. uncover a non-canonical role for IRE1α as a scaffold that stabilizes InsP3Rs at MAMs to control calcium uptake, fine-tunes ER–mitochondrial communication and regulates energy metabolism via AMPK.
- Amado Carreras-Sureda
- , Fabián Jaña
- & Claudio Hetz
-
Technical Report |
 The light-sensitive dimerizer zapalog reveals distinct modes of immobilization for axonal mitochondria
The light-sensitive dimerizer zapalog reveals distinct modes of immobilization for axonal mitochondria
Gutnick et al. design a light-sensitive small molecule, zapalog, which reversibly dimerizes any two proteins. Tethering mitochondria to active kinesin motors uncovers distinct modes of mitochondrial motility in axons.
- Amos Gutnick
- , Matthew R. Banghart
- & Thomas L. Schwarz
-
News & Views |
 GPCRs join the mTORC1 regulatory network
GPCRs join the mTORC1 regulatory network
Rag GTPases play a crucial role in mTORC1 activation by promoting its recruitment to the lysosomal surface in a nutrient-dependent manner. A study now identifies a family of lysosomal G-protein-coupled receptors as modulators of Rag GTPases localization and activation, adding one more component to the fast-growing mTOR regulatory network.
- Rosa Puertollano
-
Article |
 The lysosomal GPCR-like protein GPR137B regulates Rag and mTORC1 localization and activity
The lysosomal GPCR-like protein GPR137B regulates Rag and mTORC1 localization and activity
Gan et al. identify the GPCR-like protein GPR137B that interacts with Rag GTPases to recruit mTORC1 to lysosomes. They show that GPR137B controls dynamic Rag and mTORC1 activity as well as lysosome morphology.
- Lin Gan
- , Akiko Seki
- & Tobias Meyer
-
Article |
 Ultrastructure and dynamics of the actin−myosin II cytoskeleton during mitochondrial fission
Ultrastructure and dynamics of the actin−myosin II cytoskeleton during mitochondrial fission
Using platinum replica electron microscopy, Yang and Svitkina find how myosin II enhances actin-mediated mitochondrial constriction and fission.
- Changsong Yang
- & Tatyana M. Svitkina
-
Article |
 Mitochondrial protein-induced stress triggers a global adaptive transcriptional programme
Mitochondrial protein-induced stress triggers a global adaptive transcriptional programme
Boos et al. show that impairing mitochondrial protein import induces a global transcriptional response to activate the ubiquitin–proteasome system and heat stress response and repress oxidative phosphorylation genes.
- Felix Boos
- , Lena Krämer
- & Johannes M. Herrmann
-
Review Article |
 The lysosome as a cellular centre for signalling, metabolism and quality control
The lysosome as a cellular centre for signalling, metabolism and quality control
In this Review, Lawrence and Zoncu discuss the central role of the lysosome in cellular metabolism, including in macromolecular catabolism and nutrient recycling, and organelle crosstalk. They highlight the emerging function of the lysosome as a centre for nutrient sensing and metabolic signal transduction.
- Rosalie E. Lawrence
- & Roberto Zoncu
-
News & Views |
 Memory of ancestral mitochondrial stress
Memory of ancestral mitochondrial stress
Ancestral experience of mitochondrial stress is now found to render progeny of the roundworm Caenorhabditis elegans more resistant to the same insult for up to four generations. A DNA modification, N6-methyldeoxyadenine, is implicated in the inheritance of this stress adaptation.
- Sarah-Lena Offenburger
- , Marcos Francisco Perez
- & Ben Lehner
-
Letter |
 N6-methyldeoxyadenine is a transgenerational epigenetic signal for mitochondrial stress adaptation
N6-methyldeoxyadenine is a transgenerational epigenetic signal for mitochondrial stress adaptation
Ma et al. show that exposure of Caenorhabditis elegans to mitochondrial stress triggers stress adaptation in offspring, which is mediated by 6mA DNA modification at mitochondrial unfolded-protein-response genes.
- Chengchuan Ma
- , Rong Niu
- & Ying Liu
-
News & Views |
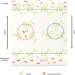 CLN8 safeguards lysosome biogenesis
CLN8 safeguards lysosome biogenesis
Newly synthesised lysosomal proteins are sorted from other cargo on the secretory pathway for delivery to endolysosomal compartments. A study now shows that the Batten disease protein, CLN8, acts as a recycling receptor to sort soluble lysosomal enzymes for export from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi.
- J. Paul Luzio
-
Letter |
 CLN8 is an endoplasmic reticulum cargo receptor that regulates lysosome biogenesis
CLN8 is an endoplasmic reticulum cargo receptor that regulates lysosome biogenesis
di Ronza et al. identify CLN8 as a cargo receptor for lysosomal enzymes required for their endoplasmic-reticulum-to-Golgi transport, linking Batten disease caused by CLN8 mutations to defects in organelle biogenesis.
- Alberto di Ronza
- , Lakshya Bajaj
- & Marco Sardiello
-
News & Views |
 A mitochondria–paraspeckle crosstalk
A mitochondria–paraspeckle crosstalk
Paraspeckles are nuclear bodies built on the long noncoding RNA, NEAT1, that regulate cellular homeostasis, but how they sense and help under stress is unclear. A study now shows mitochondrial stress modulates paraspeckles by altering NEAT1 expression with a feedback loop that influences mitochondrial homeostasis.
- Archa H. Fox
-
Article |
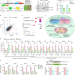 Genome-wide screening of NEAT1 regulators reveals cross-regulation between paraspeckles and mitochondria
Genome-wide screening of NEAT1 regulators reveals cross-regulation between paraspeckles and mitochondria
Wang et al. show that mitochondrial stress alters paraspeckle number and morphology through regulating the transcription and processing of lncRNA NEAT1, retaining mRNAs of mitochondrial proteins in paraspeckles.
- Yang Wang
- , Shi-Bin Hu
- & Ling-Ling Chen
-
Letter |
 Single particle trajectories reveal active endoplasmic reticulum luminal flow
Single particle trajectories reveal active endoplasmic reticulum luminal flow
Using super-resolution microscopy, tracking of single particle trajectories of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) luminal proteins traversing tubular ER, and measuring ER dynamics, Holcman et al. show that ER content is propelled by active luminal flow.
- David Holcman
- , Pierre Parutto
- & Edward Avezov
-
News & Views |
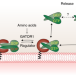 Lysosomal catch-and-release controls mTORC1
Lysosomal catch-and-release controls mTORC1
Rag GTPases facilitate mTORC1 activation by recruiting it to Rheb at the lysosome when amino acids are abundant. A study now shows that the amino acid-induced change in the GTP/GDP-binding state of the Rag heterodimer paradoxically increases its dynamic release from the Ragulator at the lysosome and may limit mTORC1 activation.
- Aaron M. Hosios
- & Brendan D. Manning
-
Review Article |
 Mechanisms of mitophagy in cellular homeostasis, physiology and pathology
Mechanisms of mitophagy in cellular homeostasis, physiology and pathology
In this Review, Tavernarakis and colleagues describe recent advances in delineating the molecular mechanisms that mediate mitophagy, and discuss the complex roles of this pathway in physiological and pathological contexts.
- Konstantinos Palikaras
- , Eirini Lionaki
- & Nektarios Tavernarakis
-
Article |
 A nutrient-induced affinity switch controls mTORC1 activation by its Rag GTPase–Ragulator lysosomal scaffold
A nutrient-induced affinity switch controls mTORC1 activation by its Rag GTPase–Ragulator lysosomal scaffold
Lawrence et al. show that mTORC1 capture and activation at the lysosome are regulated by nutrients that destabilize Rag GTPase–Ragulator binding, and delineate how cancer-specific Rag mutants increase mTORC1 signalling.
- Rosalie E. Lawrence
- , Kelvin F. Cho
- & Roberto Zoncu
-
Review Article |
 Mitochondrial dynamics in adaptive and maladaptive cellular stress responses
Mitochondrial dynamics in adaptive and maladaptive cellular stress responses
Mitochondria sense and respond to many stressors and can support cell survival or death through energy production and signalling pathways. Mitochondrial responses depend on fusion–fission dynamics that dilute and segregate damaged mitochondria. Mitochondrial motility and inter-organellar interactions, such as with the endoplasmic reticulum, also function in cellular adaptation to stress. In this Review, we discuss how stressors influence these components, and how they contribute to the complex adaptive and pathological responses that lead to disease.
- Verónica Eisner
- , Martin Picard
- & György Hajnóczky
-
News & Views |
 Pro-tumorigenic AMPK in glioblastoma
Pro-tumorigenic AMPK in glioblastoma
AMPK is a key metabolic sensor promoting cellular energy homeostasis under low-nutrient conditions and other stresses. However, its role in cancer is context-dependent and not fully understood. A study now shows that glioma stem cells co-opt an AMPK-dependent pathway to rewire metabolism, promoting tumour growth.
- Nektaria Maria Leli
- & Constantinos Koumenis
-
Article |
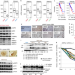 AMP kinase promotes glioblastoma bioenergetics and tumour growth
AMP kinase promotes glioblastoma bioenergetics and tumour growth
Signalling by the energy sensor kinase AMPK is generally tumour suppressive, but Chhipa et al. show that AMPK is upregulated in glioblastoma, where it phosphorylates CREB1 to enhance HIF1α and GABPA transcription and to support tumour bioenergetics.
- Rishi Raj Chhipa
- , Qiang Fan
- & Biplab Dasgupta
-
Perspective |
 A brief history of autophagy from cell biology to physiology and disease
A brief history of autophagy from cell biology to physiology and disease
A history of autophagy. In this Perspective, Mizushima describes the leaps and bounds in the history of autophagy and discusses unanswered questions driving the field forward.
- Noboru Mizushima
-
News & Views |
 Mitochondrial OXPHOS complex assembly lines
Mitochondrial OXPHOS complex assembly lines
Mitochondria are critical for cellular energy generation and house oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) complexes, which are under dual genetic control. A study finds that transcript translation and complex assembly are partitioned, and OXPHOS complexes III, IV and V are built at spatially defined regions of the mitochondrial inner membrane.
- Luke E. Formosa
- & Michael T. Ryan
-
Letter |
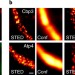 Spatial orchestration of mitochondrial translation and OXPHOS complex assembly
Spatial orchestration of mitochondrial translation and OXPHOS complex assembly
Using super-resolution microscopy and cryo-electron microscopy, Stoldt et al. show that mitochondrial transcript translation and OXPHOS complex assembly are spatially partitioned within the mitochondrial membrane.
- Stefan Stoldt
- , Dirk Wenzel
- & Stefan Jakobs
-

 Membrane surfaces regulate assembly of ribonucleoprotein condensates
Membrane surfaces regulate assembly of ribonucleoprotein condensates