Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access The AAA+ ATPase RavA and its binding partner ViaA modulate E. coli aminoglycoside sensitivity through interaction with the inner membrane
The AAA+ ATPase RavA and its binding partner ViaA modulate E. coli aminoglycoside sensitivity through interaction with the inner membrane
Membrane lipid composition is a key factor for bacterial stress adaptation. Here, authors show that ViaA and AAA+ ATPase RavA, alter lipid composition and modulate E. coli aminoglycoside sensitivity.
- Jan Felix
- , Ladislav Bumba
- & Irina Gutsche
-
Article
| Open Access Grain boundary structural transformation induced by co-segregation of aliovalent dopants
Grain boundary structural transformation induced by co-segregation of aliovalent dopants
The effect of aliovalent doping on grain boundary is not yet fully understood at the atomic level. Here, the authors report grain boundary structural transformation in α-Al2O3 is induced by co-segregation of multiple dopants using atomic-resolution electron microscopy and theoretical calculations.
- Toshihiro Futazuka
- , Ryo Ishikawa
- & Yuichi Ikuhara
-
Article
| Open Access Improved immunoassay sensitivity and specificity using single-molecule colocalization
Improved immunoassay sensitivity and specificity using single-molecule colocalization
A major challenge of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays is discriminating true signal from non-specific binding. Here the authors present a Single-Molecule Colocalization Assay (SiMCA) which eliminates such effects, enabling reproducible detection of picomolar protein concentrations.
- Amani A. Hariri
- , Sharon S. Newman
- & H. Tom Soh
-
Article
| Open Access The primeval optical evolving matter by optical binding inside and outside the photon beam
The primeval optical evolving matter by optical binding inside and outside the photon beam
Optical binding enables light-induced assembly of many particles within a focus area. Here, the authors demonstrate that optical binding can occur outside the irradiated area by scattered light interacting with the particles outside the focus, generating arc-shape potential wells for particle trapping.
- Chih-Hao Huang
- , Boris Louis
- & Hiroshi Masuhara
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrafast and hypersensitive phase imaging of propagating internodal current flows in myelinated axons and electromagnetic pulses in dielectrics
Ultrafast and hypersensitive phase imaging of propagating internodal current flows in myelinated axons and electromagnetic pulses in dielectrics
The authors introduce differentially enhanced compressed ultrafast photography, a phase imaging platform that combines high speed and sensitivity. They visualise propagation of passive current flows along myelinated axons, and electromagnetic pulses in lithium niobate.
- Yide Zhang
- , Binglin Shen
- & Lihong V. Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Structure and activity of particulate methane monooxygenase arrays in methanotrophs
Structure and activity of particulate methane monooxygenase arrays in methanotrophs
Particulate methane monooxygenase (pMMO) is the main enzyme used by methanotrophs. Here, the authors determined the native structure of pMMO by cryo-electron tomography, revealing lipid-stabilized features and a higher-order hexagonal array arrangement in intact cells.
- Yanan Zhu
- , Christopher W. Koo
- & Peijun Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Observation of formation and local structures of metal-organic layers via complementary electron microscopy techniques
Observation of formation and local structures of metal-organic layers via complementary electron microscopy techniques
Obtaining information about the structure of metal-organic layers (MOLs) using standard electron microscopy methods is challenging due to damage under electron beam irradiation. Here, the authors reveal a multistep formation process of MOLs and identify missing clusters, dislocations, loop and flat surface terminations and ligand connector of MOLs via complementary electron microscopy techniques.
- Xinxing Peng
- , Philipp M. Pelz
- & Mary C. Scott
-
Article
| Open Access Fast DNA-PAINT imaging using a deep neural network
Fast DNA-PAINT imaging using a deep neural network
DNA-PAINT image acquisition is limited by speed. Here the authors use the neural network DeepSTORM to predict fluorophore positions from high emitter density DNA-PAINT data in order to achieve image acquisition in one minute; they demonstrate multi-colour and large-area imaging of semi-thin neuronal tissue.
- Kaarjel K. Narayanasamy
- , Johanna V. Rahm
- & Mike Heilemann
-
Article
| Open Access Three-dimensional electron ptychography of organic–inorganic hybrid nanostructures
Three-dimensional electron ptychography of organic–inorganic hybrid nanostructures
The authors demonstrate electron ptychographic computed tomography by simultaneously recording high contrast data from both the organic- and inorganic components in a 3D DNA-origami framework hybrid nanostructure.
- Zhiyuan Ding
- , Si Gao
- & Peng Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Evidence for a HURP/EB free mixed-nucleotide zone in kinetochore-microtubules
Evidence for a HURP/EB free mixed-nucleotide zone in kinetochore-microtubules
Microtubules are built from GDP-tubulin lattices with small GTP caps at their plus-ends. Here, the authors reveal that microtubules that attach to kinetochores in mitosis contain, in addition to the GTP-cap and the GDP-lattices, a dynamic micron-sized mixed-nucleotide zone.
- Cédric Castrogiovanni
- , Alessio V. Inchingolo
- & Patrick Meraldi
-
Article
| Open Access A quantitative analysis of various patterns applied in lattice light sheet microscopy
A quantitative analysis of various patterns applied in lattice light sheet microscopy
Light sheet microscopes reduce phototoxicity and background while improving imaging speed compared to widefield and confocal microscopes. Here the authors quantify the differences between Gaussian and lattice light sheets using simulations and experimental data in fixed and live cells.
- Yu Shi
- , Timothy A. Daugird
- & Wesley R. Legant
-
Article
| Open Access Flexible-type ultrathin holographic endoscope for microscopic imaging of unstained biological tissues
Flexible-type ultrathin holographic endoscope for microscopic imaging of unstained biological tissues
Lensless fibre endoscopes are minimally invasive, but are often rigid and require calibration and fluorescence labelling. Here, the authors present a flexible endoscope based on a bare fibre bundle and a lensless Fourier holographic imaging configuration to detect weak reflections from unstained biological tissues.
- Wonjun Choi
- , Munkyu Kang
- & Wonshik Choi
-
Article
| Open Access Real-time 3D analysis during electron tomography using tomviz
Real-time 3D analysis during electron tomography using tomviz
High-throughput electron tomography has been challenging due to time-consuming alignment and reconstruction. Here, the authors demonstrate real-time tomography with dynamic 3D tomographic visualization integrated in tomviz, an open-source 3D data analysis tool.
- Jonathan Schwartz
- , Chris Harris
- & Robert Hovden
-
Article
| Open Access A density-based enrichment measure for assessing colocalization in single-molecule localization microscopy data
A density-based enrichment measure for assessing colocalization in single-molecule localization microscopy data
Full information gained from single-molecule localisation microscopy (SMLM) isn't exploited by current analysis tools. Here the authors report relative enrichment which uses a density-based colocalisation measure for both 2D and 3D SMLM data; they apply it to both simulated data and cultured neurons.
- Aske L. Ejdrup
- , Matthew D. Lycas
- & Ulrik Gether
-
Article
| Open Access UV photonic integrated circuits for far-field structured illumination autofluorescence microscopy
UV photonic integrated circuits for far-field structured illumination autofluorescence microscopy
Here, the authors develop a UV-compatible photonic integrated circuit for structured illumination microscopy on a conventional wide-field microscope. Operating at a wavelength of 360 nm, they generate switchable far-field fringe patterns, and demonstrate autofluorescence imaging of yeast cells.
- Chupao Lin
- , Juan Santo Domingo Peñaranda
- & Nicolas Le Thomas
-
Article
| Open Access Actin nano-architecture of phagocytic podosomes
Actin nano-architecture of phagocytic podosomes
Podosomes are actin structures important in multiple cell functions. Here, the authors use iPALM microscopy to reveal an “hourglass” shape of the podosome actin core, a protruding “knob” at the bottom of the core, and two actin networks extending from it.
- J. Cody Herron
- , Shiqiong Hu
- & Klaus M. Hahn
-
Article
| Open Access Sub-nanometer mapping of strain-induced band structure variations in planar nanowire core-shell heterostructures
Sub-nanometer mapping of strain-induced band structure variations in planar nanowire core-shell heterostructures
Planar growth of nanowire arrays involves interactions between materials that affect the electronic behavior of the effective heterojunction. Here, authors show how core curvature and cross-section morphology affect shell growth, demonstrating how strain at the core-shell interface induces electronic band modulations in ZnSe@ZnTe nanowires.
- Sara Martí-Sánchez
- , Marc Botifoll
- & Jordi Arbiol
-
Article
| Open Access Instant diagnosis of gastroscopic biopsy via deep-learned single-shot femtosecond stimulated Raman histology
Instant diagnosis of gastroscopic biopsy via deep-learned single-shot femtosecond stimulated Raman histology
Diagnosis of gastric cancer currently requires gastroscopic biopsy, which requires time and expertize to perform. Here, the authors demonstrate a femto-SRS imaging method which showed high accuracy in diagnosing gastric cancer without the need for pathologistbased diagnosis.
- Zhijie Liu
- , Wei Su
- & Minbiao Ji
-
Article
| Open Access Optimal acceleration voltage for near-atomic resolution imaging of layer-stacked 2D polymer thin films
Optimal acceleration voltage for near-atomic resolution imaging of layer-stacked 2D polymer thin films
High-resolution imaging of organic 2D materials using transmission electron microscopes is challenging. Here, the authors find the optimal electron acceleration voltage, and demonstrate 1.9 Å resolution, enabling detection of interstitial defects and functional groups in 2D polymer thin films.
- Baokun Liang
- , Yingying Zhang
- & Haoyuan Qi
-
Article
| Open Access Nuclear speed and cycle length co-vary with local density during syncytial blastoderm formation in a cricket
Nuclear speed and cycle length co-vary with local density during syncytial blastoderm formation in a cricket
Early in insect embryo development, many nuclei share one large cell, travel varied paths and self-organize into a single layer. Donoughe et al. illuminate this process with live-imaging, modeling, and experimental changes to the embryo’s shape.
- Seth Donoughe
- , Jordan Hoffmann
- & Cassandra G. Extavour
-
Article
| Open Access Scanning gradiometry with a single spin quantum magnetometer
Scanning gradiometry with a single spin quantum magnetometer
Scanning NV center magnetometry enables imaging of weak magnetic fields at the nanoscale. Huxter et al. achieve an order-of-magnitude improvement in sensitivity by converting a spatial field gradient into an AC field by mechanical oscillations of the sensor, and image stray fields from atomic steps in an antiferromagnet.
- W. S. Huxter
- , M. L. Palm
- & C. L. Degen
-
Article
| Open Access Surface plasmons induce topological transition in graphene/α-MoO3 heterostructures
Surface plasmons induce topological transition in graphene/α-MoO3 heterostructures
Hyperbolic phonon polaritons – mixed states of photons and anisotropic lattice vibrations – offer appealing properties for nanophotonic applications. Here, the authors show that the plasmon-phonon hybridization upon electronic doping in graphene/α-MoO3 heterostructures can induce topological transitions of the polariton wavefront.
- Francesco L. Ruta
- , Brian S. Y. Kim
- & D. N. Basov
-
Article
| Open Access Assembly dynamics of FtsZ and DamX during infection-related filamentation and division in uropathogenic E. coli
Assembly dynamics of FtsZ and DamX during infection-related filamentation and division in uropathogenic E. coli
A subset of uropathogenic Escherichia coli are able to halt division and grow into highly filamentous cells during infection of bladder epithelial cells. Here, authors aim to determine the mechanism, and understand the dynamics of cell division machinery during infection-related filamentation.
- Bill Söderström
- , Matthew J. Pittorino
- & Iain G. Duggin
-
Article
| Open Access DNA damage-induced transcription stress triggers the genome-wide degradation of promoter-bound Pol II
DNA damage-induced transcription stress triggers the genome-wide degradation of promoter-bound Pol II
DNA damage inhibits elongating RNA polymerase II, but also initiates genome-wide transcriptional responses. Here the authors reveal that particularly promoter-bound Pol II is degraded upon DNA damage in a GSK3 signaling-mediated response.
- Barbara Steurer
- , Roel C. Janssens
- & Jurgen Marteijn
-
Article
| Open Access Probing TDP-43 condensation using an in silico designed aptamer
Probing TDP-43 condensation using an in silico designed aptamer
Here, the authors generated an artificial RNA molecule, or aptamer, specific for the Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis protein TDP-43. By interacting avidly with its target, the aptamer can be exploited to track TDP-43 phase transition in vitro and in cells.
- Elsa Zacco
- , Owen Kantelberg
- & Gian Gaetano Tartaglia
-
Article
| Open Access The architecture and operating mechanism of a cnidarian stinging organelle
The architecture and operating mechanism of a cnidarian stinging organelle
The venomous stinging cells of jellyfish, anemones, and corals contain an organelle, the nematocyst, which explosively discharges a venom-laden thread. Here, the authors describe the nematocyst thread and its sub-structures in the sea anemone N. vectensis, revealing a complexity and sophistication underpinning this cellular weapon.
- Ahmet Karabulut
- , Melainia McClain
- & Matthew C. Gibson
-
Article
| Open Access Light-sheet photonic force optical coherence elastography for high-throughput quantitative 3D micromechanical imaging
Light-sheet photonic force optical coherence elastography for high-throughput quantitative 3D micromechanical imaging
The authors introduce photonic force optical coherence elastography that uses a light-sheet for parallelised and localised mechanical loading. They demonstrate the combination of 3D imaging of extracellular matrix mechanics with cellular-scale resolution and dynamic monitoring of cell-mediated changes.
- Yuechuan Lin
- , Nichaluk Leartprapun
- & Steven G. Adie
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis of rapid actin dynamics in the evolutionarily divergent Leishmania parasite
Structural basis of rapid actin dynamics in the evolutionarily divergent Leishmania parasite
The authors report here the structure-function analysis of highly divergent actin from Leishmania parasite. The study reveals remarkably rapid dynamics of parasite actin as well as the underlying molecular basis, thus providing insight into evolution of the actin cytoskeleton.
- Tommi Kotila
- , Hugo Wioland
- & Pekka Lappalainen
-
Article
| Open Access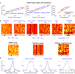 Photon-free (s)CMOS camera characterization for artifact reduction in high- and super-resolution microscopy
Photon-free (s)CMOS camera characterization for artifact reduction in high- and super-resolution microscopy
Pixel-to-pixel variations in sCMOS cameras lead to image artifacts in widefield fluorescence microscopy, and algorithmic corrections require thorough camera characterization. Here, the authors present an open source automated pipeline for camera characterization based solely on thermally generated signal.
- Robin Diekmann
- , Joran Deschamps
- & Jonas Ries
-
Article
| Open Access Embryo-scale epithelial buckling forms a propagating furrow that initiates gastrulation
Embryo-scale epithelial buckling forms a propagating furrow that initiates gastrulation
Drosophila mesoderm invagination begins with the formation of a furrow. Here they show that a long-range mechanism, powered by actomyosin contraction between the embryo polar caps, works like a ‘cheese-cutter wire’ indenting the tissue surface and folding it into a propagating furrow.
- Julien Fierling
- , Alphy John
- & Matteo Rauzi
-
Article
| Open Access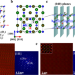 Direct investigation of the atomic structure and decreased magnetism of antiphase boundaries in garnet
Direct investigation of the atomic structure and decreased magnetism of antiphase boundaries in garnet
Iron garnets are widely used in magneto-optical devices, but knowledge of the effects of common defects on performance is limited. Here, using high-resolution microscopy and spectroscopy, the authors find that magnetism is weakened near these defects causing reduced performance, but can be avoided by tuning the growth rate.
- Kun Xu
- , Ting Lin
- & Jing Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access Tailoring electron beams with high-frequency self-assembled magnetic charged particle micro optics
Tailoring electron beams with high-frequency self-assembled magnetic charged particle micro optics
Electron beam manipulation is important for their application in microscopes, lithography instruments, and colliders. Here the authors report a wafer scale, self-assembled, microcoil electrically-driven magnetic charge particle optic device that can be implemented into different configurations for controlling of electron beams.
- R. Huber
- , F. Kern
- & A. Lubk
-
Article
| Open Access Deep learning enables reference-free isotropic super-resolution for volumetric fluorescence microscopy
Deep learning enables reference-free isotropic super-resolution for volumetric fluorescence microscopy
Volumetric fluorescence microscopy is often limited by anisotropic spatial resolution. Here, the authors present an unsupervised deep-learning approach that enhances axial resolution by learning from high-resolution lateral images, and demonstrate isotropic resolution and restoration of suppressed visual details.
- Hyoungjun Park
- , Myeongsu Na
- & Jong Chul Ye
-
Article
| Open Access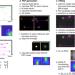 Global fitting for high-accuracy multi-channel single-molecule localization
Global fitting for high-accuracy multi-channel single-molecule localization
Multi-channel SMLM imaging is powerful. Here the authors report globLoc, a GPU-based global fitting algorithm, to extract maximum information from multichannel single molecule data; this gives improved localisation precision for biplane and 4Pi-SMLM and colour assignment in multi-colour astigmatic SMLM.
- Yiming Li
- , Wei Shi
- & Jonas Ries
-
Article
| Open Access Measuring and directing charge transfer in heterogenous catalysts
Measuring and directing charge transfer in heterogenous catalysts
Precise control of charge transfer between catalyst nanoparticles and supports presents a unique opportunity to enhance catalytic performance. Here the authors demonstrate a scanning transmission electron microscopy method to visualize atomic-scale structure and sub-nanometer-scale charge distribution in heterogeneous catalysts, shedding light on the atomic-scale mechanisms behind their highly active perimeter sites.
- Michael J. Zachman
- , Victor Fung
- & Miaofang Chi
-
Article
| Open Access Observation of a phase transition within the domain walls of ferromagnetic Co3Sn2S2
Observation of a phase transition within the domain walls of ferromagnetic Co3Sn2S2
In the Bloch or Neel domain walls in ferromagnets, the magnetization rotates smoothly from up to down, preserving its magnitude. Here, Lee et al show that Co3Sn2S2 exhibits a phase transition within its domain walls to a state in which the magnetization passes through zero rather than rotating as the wall is traversed.
- Changmin Lee
- , Praveen Vir
- & Joseph Orenstein
-
Article
| Open Access Open-source personal pipetting robots with live-cell incubation and microscopy compatibility
Open-source personal pipetting robots with live-cell incubation and microscopy compatibility
Liquid handling and pipetting tools can automate repetitive tasks but are far from universally used. Here the authors report the Pipetting Helper Imaging Lid (PHIL), an open-source liquid handling robot designed for inexperienced users, that they use for automated pipetting.
- Philip Dettinger
- , Tobias Kull
- & Timm Schroeder
-
Article
| Open Access Modulating inherent lewis acidity at the intergrowth interface of mortise-tenon zeolite catalyst
Modulating inherent lewis acidity at the intergrowth interface of mortise-tenon zeolite catalyst
The acid sites are important local structures to determine catalytic performances of zeolites. Here, the authors expand the interface engineering to the field of porous zeolites through the lattice mismatch of the intergrown zeolite to enrich the inherent Lewis acid sites at the interface of a mortise-tenon ZSM-5 catalyst.
- Huiqiu Wang
- , Boyuan Shen
- & Weizhong Qian
-
Article
| Open Access Seeing structural evolution of organic molecular nano-crystallites using 4D scanning confocal electron diffraction (4D-SCED)
Seeing structural evolution of organic molecular nano-crystallites using 4D scanning confocal electron diffraction (4D-SCED)
Studying organic molecular nanocrystals with electron microscopy has been challenging due to complex structures and radiation sensitivity. Here, the authors present 4D-scanning confocal electron diffraction, and demonstrate direct in situ observation of structural evolution of bulk heterojunction thin films.
- Mingjian Wu
- , Christina Harreiß
- & Erdmann Spiecker
-
Article
| Open Access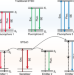 Achieving low-power single-wavelength-pair nanoscopy with NIR-II continuous-wave laser for multi-chromatic probes
Achieving low-power single-wavelength-pair nanoscopy with NIR-II continuous-wave laser for multi-chromatic probes
The authors introduce stimulated-emission induced excitation depletion (STExD) nanoscopy using a single pair of low-power, near-infrared, continue-wave lasers. Emission of multichromatic probes is inhibited by cascade amplified depletion in lanthanide upconversion systems induced by manipulating their common sensitizer.
- Xin Guo
- , Rui Pu
- & Qiuqiang Zhan
-
Article
| Open Access Entropy and crystal-facet modulation of P2-type layered cathodes for long-lasting sodium-based batteries
Entropy and crystal-facet modulation of P2-type layered cathodes for long-lasting sodium-based batteries
The use of Mn-rich layered cathodes in Na-based batteries is hindered by inadequate cycling reversibility and sluggish anionic redox kinetics. Here, the authors report a strategy to stabilize the structure and promote anionic redox via configurational entropy and ion-diffusion structural tuning.
- Fang Fu
- , Xiang Liu
- & Gui-Liang Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Phase separation and zinc-induced transition modulate synaptic distribution and association of autism-linked CTTNBP2 and SHANK3
Phase separation and zinc-induced transition modulate synaptic distribution and association of autism-linked CTTNBP2 and SHANK3
Autism impacts synapses. This study reports that autism-linked mutations of CTTNBP2 regulate phase separation to control synaptic enrichment of that protein. A zinc-induced liquid-to-gel transition improves synaptic retention of CTTNBP2 and SHANK3.
- Pu-Yun Shih
- , Yu-Lun Fang
- & Yi-Ping Hsueh
-
Article
| Open Access In vitro reconstitution of Escherichia coli divisome activation
In vitro reconstitution of Escherichia coli divisome activation
In E. coli, FtsA and FtsZ control the place and time of cell division. Here, the authors use in vitro experiments to show how FtsA can follow FtsZ treadmilling and that downstream proteins form dynamic copolymers with FtsA to initiate division.
- Philipp Radler
- , Natalia Baranova
- & Martin Loose
-
Article
| Open Access Gasdermin-A3 pore formation propagates along variable pathways
Gasdermin-A3 pore formation propagates along variable pathways
Gasdermin-A3 pore formation propagates along diverse pathways. It begins with membrane attachment and oligomeric pre-assembly. Once inserted in the membrane, the oligomers re-assemble into various shapes and sizes, which open their lytic pores.
- Stefania A. Mari
- , Kristyna Pluhackova
- & Daniel J. Müller
-
Article
| Open Access PICASSO allows ultra-multiplexed fluorescence imaging of spatially overlapping proteins without reference spectra measurements
PICASSO allows ultra-multiplexed fluorescence imaging of spatially overlapping proteins without reference spectra measurements
Ultra-multiplexed fluorescence imaging is currently difficult. Here the authors report PICASSO which enables 15-colour imaging of spatially overlapping proteins in a single-round of imaging; they combine it with cyclic immunofluorescence to achieve 45-colour imaging of the mouse brain in 3 cycles.
- Junyoung Seo
- , Yeonbo Sim
- & Jae-Byum Chang
-
Article
| Open Access Mre11-Rad50 oligomerization promotes DNA double-strand break repair
Mre11-Rad50 oligomerization promotes DNA double-strand break repair
The Mre11-Rad50 (MR) complex has key functions in the detection, signaling and repair of DNA breaks. Here the authors use transmission electron microscopy to show MR oligomerization is governed by a small beta-sheet protruding from the head domain of Rad50 at the base of the MR structure, and reveal MR head domain oligomerization is required for efficient DNA end resection.
- Vera M. Kissling
- , Giordano Reginato
- & Matthias Peter
-
Article
| Open Access Evanescent scattering imaging of single protein binding kinetics and DNA conformation changes
Evanescent scattering imaging of single protein binding kinetics and DNA conformation changes
Single molecule detection based on evanescent illumination usually require specially designed nanomaterials. Here, the authors show that single molecule detection can be realised on a plain glass surface via interference between the evanescent lights scattered by molecules and the natural roughness of the glass.
- Pengfei Zhang
- , Lei Zhou
- & Shaopeng Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Enabling high energy lithium metal batteries via single-crystal Ni-rich cathode material co-doping strategy
Enabling high energy lithium metal batteries via single-crystal Ni-rich cathode material co-doping strategy
Li-ion cathode active materials are transitioning from poly- to single-crystal structures. However, the performance of high Ni-content single-crystal cathodes remains below expectations. Here, via Al/Zr co-doping, the authors propose a strategy to mitigate structural degradation in this class of materials.
- Xing Ou
- , Tongchao Liu
- & Jun Lu
-
Article
| Open Access Enabling reactive microscopy with MicroMator
Enabling reactive microscopy with MicroMator
In microscopy, applications in which reactiveness is needed are multifarious. Here the authors report MicroMator, a Python software package for reactive experiments, which they use for applications requiring real-time tracking and light-targeting at the single-cell level.
- Zachary R. Fox
- , Steven Fletcher
- & Gregory Batt
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Atomic force microscopy
- Ca2+ imaging
- Confocal microscopy
- Cryoelectron microscopy
- Interference microscopy
- Light-sheet microscopy
- Multiphoton microscopy
- Phase-contrast microscopy
- Polarization microscopy
- Scanning electron microscopy
- Scanning probe microscopy
- Super-resolution microscopy
- Total internal reflection microscopy
- Transmission electron microscopy
- Transmission light microscopy
- Wide-field fluorescence microscopy

 Synchronous quantitative analysis of chiral mesostructured inorganic crystals by 3D electron diffraction tomography
Synchronous quantitative analysis of chiral mesostructured inorganic crystals by 3D electron diffraction tomography