Featured
-
-
Editorial |
 Soft features for robotics
Soft features for robotics
Innovations in soft materials design and engineering are delivering promising functional components for advanced soft robotic applications.
-
News & Views |
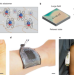 Energy supply from magnetoelastic composites
Energy supply from magnetoelastic composites
The giant magnetoelastic effect measured in magnetic elastomers enables new energy generators for wearable and implantable electronics.
- Denys Makarov
-
News & Views |
 Popping, locking robots
Popping, locking robots
An interplay between deswelling and buckling in a polymer gel is harnessed to achieve sequential snap events for repeatable jumping motion, opening the door to autonomously moving soft robots.
- Johannes T. B. Overvelde
-
Comment |
 Shaping the future of robotics through materials innovation
Shaping the future of robotics through materials innovation
New classes of functional soft materials show promise to revolutionize robotics. Now materials scientists must focus on realizing the predicted performance of these materials and developing effective and robust interfaces to integrate them into highly functional robotic systems that have a positive impact on human life.
- Philipp Rothemund
- , Yoonho Kim
- & Christoph Keplinger
-
News & Views |
 A photocurable bioelectronics–tissue interface
A photocurable bioelectronics–tissue interface
A functional bioadhesive has been developed to possess properties such as mechanical compliance, electrical conductivity and optical transparency, and is utilized for bonding electronic devices to various organs in the body for up to several months.
- Tsuyoshi Sekitani
-
Review Article |
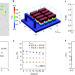 High-performance thermoelectrics and challenges for practical devices
High-performance thermoelectrics and challenges for practical devices
Thermoelectric materials can generate energy from a heat differential. This Review provides an overview of mid- to high-temperature thermoelectrics, their application in modules, and the issues that need to be addressed to enable commercial implementation of state-of-the-art materials.
- Qingyu Yan
- & Mercouri G. Kanatzidis
-
News & Views |
 The secret order of disorder
The secret order of disorder
A seemingly disordered network of nanowires governed by thermodynamics is used as the physical ‘reservoir’ in a memristive implementation of reservoir computing to process spatiotemporal information.
- Qiangfei Xia
- , J. Joshua Yang
- & Rivu Midya
-
Review Article |
 Strain analysis and engineering in halide perovskite photovoltaics
Strain analysis and engineering in halide perovskite photovoltaics
This Review provides an outlook on current understanding of the role of strain on the performance and stability of perovskite solar cells, as well as on tools to characterize strain in halide perovskite films and on strain management strategies.
- Dongtao Liu
- , Deying Luo
- & Wei Zhang
-
Letter |
 Broadband and pixelated camouflage in inflating chiral nematic liquid crystalline elastomers
Broadband and pixelated camouflage in inflating chiral nematic liquid crystalline elastomers
Pneumatically actuated membranes made from a chiral nematic liquid crystalline elastomer supported by poly(dimethylsiloxane) layers are assembled into pixelated colour devices, where each individual pixel can be tuned throughout the entire visible spectrum.
- Se-Um Kim
- , Young-Joo Lee
- & Shu Yang
-
Article |
 Two-dimensional hole gas in organic semiconductors
Two-dimensional hole gas in organic semiconductors
A two-dimensional hole gas with high carrier density is confined at the interface between a solution-processed, single-crystalline organic semiconducting film and the electric double layer formed by an ion gel on top of the film.
- Naotaka Kasuya
- , Junto Tsurumi
- & Jun Takeya
-
News & Views |
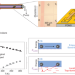 Precision doping to heal traps
Precision doping to heal traps
Passivation of traps via site-specific surface doping allows access to the intrinsic properties of organic semiconductors and leads to the observation of electron atmospheres in organic crystals.
- Oana D. Jurchescu
-
Article |
 Site-specific chemical doping reveals electron atmospheres at the surfaces of organic semiconductor crystals
Site-specific chemical doping reveals electron atmospheres at the surfaces of organic semiconductor crystals
Organic semiconductor crystals can be selectively doped at the crystallographic step edges, deactivating shallow traps and recovering band-like transport. The space charge induced by chemical doping is observed by scanning Kelvin probe microscopy.
- Tao He
- , Matthias Stolte
- & C. Daniel Frisbie
-
News & Views |
 Silicon goes heavyweight
Silicon goes heavyweight
A substantial spin–orbit interaction is introduced in a purely silicon heterostructure and can be tuned through an applied gate voltage.
- Christopher H. Marrows
-
Article |
 Photocurable bioresorbable adhesives as functional interfaces between flexible bioelectronic devices and soft biological tissues
Photocurable bioresorbable adhesives as functional interfaces between flexible bioelectronic devices and soft biological tissues
A functional interfacial material has been developed for soft integration of bioelectronic devices with biological tissues. This has been applied in battery-free optoelectronic systems for deep-brain optogenetics and subdermal phototherapy as well as wireless millimetre-scale pacemakers and flexible multielectrode epicardial arrays.
- Quansan Yang
- , Tong Wei
- & John A. Rogers
-
Article |
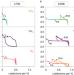 Extending insertion electrochemistry to soluble layered halides with superconcentrated electrolytes
Extending insertion electrochemistry to soluble layered halides with superconcentrated electrolytes
Insertion compounds in layered oxide or sulfide electrodes provide the fundamental basis of current commercialized Li-ion batteries. The feasibility of reversibly intercalating Li+ electrochemically into halide compounds via the use of superconcentrated electrolytes is now demonstrated.
- Nicolas Dubouis
- , Thomas Marchandier
- & Alexis Grimaud
-
News & Views |
 Magic under the microscope
Magic under the microscope
Four-dimensional scanning transmission electron microscopy is demonstrated to be a powerful technique for interrogating local strain of twisted graphene bilayers, revealing a two-regime lattice reconstruction process below the ‘magic’ angle.
- S. J. Haigh
- & R. Gorbachev
-
Letter |
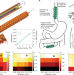 Kirigami-inspired stents for sustained local delivery of therapeutics
Kirigami-inspired stents for sustained local delivery of therapeutics
A kirigami-inspired stent-based system has been developed for extended local drug delivery to the gastrointestinal and respiratory tracts as well as the vascular system.
- Sahab Babaee
- , Yichao Shi
- & Giovanni Traverso
-
Review Article |
 Emerging perovskite monolayers
Emerging perovskite monolayers
Metal-halide and oxide perovskites are a rich playground for fundamental studies and applications. This Review focuses on the opportunities opened by reducing the dimensionality of these materials to two-dimensional monolayers.
- Antonio Gaetano Ricciardulli
- , Sheng Yang
- & Michael Saliba
-
Article |
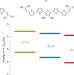 Band gap engineering in blended organic semiconductor films based on dielectric interactions
Band gap engineering in blended organic semiconductor films based on dielectric interactions
Changes in dielectric constant due to intimate mixing of thiophene molecules with different gaps between ionization energy and electron affinity induce gap variations at the single-particle level, finely tunable by controlling the mixture ratio.
- Katrin Ortstein
- , Sebastian Hutsch
- & Karl Leo
-
Article |
 Solid-state rigid-rod polymer composite electrolytes with nanocrystalline lithium ion pathways
Solid-state rigid-rod polymer composite electrolytes with nanocrystalline lithium ion pathways
Developing safe electrolytes compatible with high-energy-density electrodes is key for the next generation of lithium-based batteries. Stable solid-state rigid-rod polymer composite electrolytes with nanocrystalline lithium ion pathways are now proposed.
- Ying Wang
- , Curt J. Zanelotti
- & Louis A. Madsen
-
Article |
 Mechano-tunable chiral metasurfaces via colloidal assembly
Mechano-tunable chiral metasurfaces via colloidal assembly
Stacked elastomeric arrays containing plasmonic nanoparticles show efficient chiral responses that can be fully controlled by mechanical compression and stack rotation. These simple layered materials may be useful modulators for photonic applications.
- Patrick T. Probst
- , Martin Mayer
- & Andreas Fery
-
Article |
 Adduct-based p-doping of organic semiconductors
Adduct-based p-doping of organic semiconductors
Adducts of dimethyl sulfoxide and hydrobromic acid demonstrate efficient p-doping of various organic semiconductors and compatibility with other counterions used to improve stability and other performance parameters of organic-based optoelectronic devices.
- Nobuya Sakai
- , Ross Warren
- & Henry J. Snaith
-
Article |
 High-rate nanofluidic energy absorption in porous zeolitic frameworks
High-rate nanofluidic energy absorption in porous zeolitic frameworks
Porous materials can absorb energy by water infiltration, but studies at industrially relevant high-rate intrusions are rare. Here, high-rate experiments are performed on ZIFs showing high energy storage capacity, while molecular simulations allow design rules to be formulated for absorption materials.
- Yueting Sun
- , Sven M. J. Rogge
- & Jin-Chong Tan
-
Article |
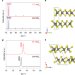 Metastable 1T′-phase group VIB transition metal dichalcogenide crystals
Metastable 1T′-phase group VIB transition metal dichalcogenide crystals
A general method for the synthesis of high-purity crystals of metastable 1T′-phase transition metal dichalcogenides is reported, providing a source of phase-engineered materials that can be used to systematically explore their intrinsic properties.
- Zhuangchai Lai
- , Qiyuan He
- & Hua Zhang
-
Article |
 Two-dimensional overdamped fluctuations of the soft perovskite lattice in CsPbBr3
Two-dimensional overdamped fluctuations of the soft perovskite lattice in CsPbBr3
Neutron and X-ray scattering measurements provide further insight into the anharmonic behaviour of lead halide perovskites, revealing that rotations of PbBr6 octahedra in CsPbBr3 crystals occur in a correlated fashion along two-dimensional planes.
- T. Lanigan-Atkins
- , X. He
- & O. Delaire
-
Article |
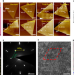 Van der Waals epitaxial growth of air-stable CrSe2 nanosheets with thickness-tunable magnetic order
Van der Waals epitaxial growth of air-stable CrSe2 nanosheets with thickness-tunable magnetic order
CrSe2 nanosheets grown on WSe2 show no apparent change in surface roughness or magnetic properties after months of exposure in air. Calculations suggest that charge transfer from the WSe2 substrate and interlayer coupling within CrSe2 play a critical role.
- Bo Li
- , Zhong Wan
- & Xiangfeng Duan
-
News & Views |
 Liquid assets for soft electronics
Liquid assets for soft electronics
Liquid-metal networks have been developed that can be stretched to extreme deformations with minimal change in electrical resistance, ushering in approaches for breathable and integrated soft and stretchable electronic devices.
- Michael D. Bartlett
-
Article |
 Highly stretchable multilayer electronic circuits using biphasic gallium-indium
Highly stretchable multilayer electronic circuits using biphasic gallium-indium
Conductors made of a mixture of liquid and solid domains of Ga–In alloy can be stretched over 1,000%, keeping almost constant conductivity, and used to connect commercial electronic components and realize stretchable multilayer printed circuit boards.
- Shanliangzi Liu
- , Dylan S. Shah
- & Rebecca Kramer-Bottiglio
-
Article |
 Permeable superelastic liquid-metal fibre mat enables biocompatible and monolithic stretchable electronics
Permeable superelastic liquid-metal fibre mat enables biocompatible and monolithic stretchable electronics
Coating of liquid metals on electrospun elastomeric fibre mats leads to the realization of conducting buckled meshes that can be stretched up to 1,800% strain while preserving both stable electrical properties and permeability to air and moisture.
- Zhijun Ma
- , Qiyao Huang
- & Zijian Zheng
-
Article |
 Coupled liquid crystalline oscillators in Huygens’ synchrony
Coupled liquid crystalline oscillators in Huygens’ synchrony
Upon light stimulation, two jointed liquid crystalline network oscillators affect the movement of each other, achieving synchronized in-phase and anti-phase oscillations that can be explored to generate soft actuators with collective responses.
- Ghislaine Vantomme
- , Lars C. M. Elands
- & Dirk J. Broer
-
News & Views |
 Restriction boosts piezoelectricity
Restriction boosts piezoelectricity
Large reversible shear strain has been achieved by electric-field-driven bipolar switching in a hybrid ferroelectric, facilitating development of shape-memory-type actuators with outstanding figures of merit.
- Sarah Guerin
- & Damien Thompson
-
Article |
 A molecular interaction–diffusion framework for predicting organic solar cell stability
A molecular interaction–diffusion framework for predicting organic solar cell stability
Studies on the morphology stability of polymer donor–small-molecule acceptor blends relevant to solar cell stability reveal relationships between their intermolecular interactions and the thermodynamic, kinetic, thermal and mechanical properties.
- Masoud Ghasemi
- , Nrup Balar
- & Harald Ade
-
Letter |
 Ferroelastic-switching-driven large shear strain and piezoelectricity in a hybrid ferroelectric
Ferroelastic-switching-driven large shear strain and piezoelectricity in a hybrid ferroelectric
Reversible strains are widely used in high-technology systems, with piezoelectrics showing fast response but low strain. Here, ferroelectric C6H5N(CH3)3CdCl3 is shown to produce a strain of 21.5%, two orders of magnitude larger than other piezoelectrics, due to organic molecules preventing 180° polarization switching.
- Yuzhong Hu
- , Lu You
- & Junling Wang
-
Article |
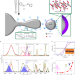 Hydrogen-doped viscoplastic liquid metal microparticles for stretchable printed metal lines
Hydrogen-doped viscoplastic liquid metal microparticles for stretchable printed metal lines
Hydrogen doping and polymer adsorption at the oxide surface of liquid metal microparticles increase the conductivity and viscoplastic behaviour of the oxide, leading to liquid-metal-based printed circuits with stable resistance up to 500% strain.
- Selvaraj Veerapandian
- , Woosun Jang
- & Unyong Jeong
-
Review Article |
 Triple ionic–electronic conducting oxides for next-generation electrochemical devices
Triple ionic–electronic conducting oxides for next-generation electrochemical devices
Triple ionic–electronic conductors can be used in electrochemical devices, including fuel cells, membrane reactors and electrolysis cells. Current understanding in single-phase conductors including defect formation and conduction mechanisms are now discussed.
- Meagan Papac
- , Vladan Stevanović
- & Ryan O’Hayre
-
Perspective |
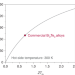 Thermoelectric cooling materials
Thermoelectric cooling materials
Thermoelectric materials can generate electricity from waste heat but can also use electricity for cooling. This Perspective discusses coefficients of performance for these systems and the state-of-the-art for materials, and suggests strategies for the discovery of improved thermoelectric materials.
- Jun Mao
- , Gang Chen
- & Zhifeng Ren
-
Article |
 Synergistically integrated phosphonated poly(pentafluorostyrene) for fuel cells
Synergistically integrated phosphonated poly(pentafluorostyrene) for fuel cells
Phosphonated polymers have been proposed as anhydrous proton conductors for fuel cells but anhydride formation of phosphonic acid functional groups lowers conductivity. A synergistically integrated phosphonated poly(pentafluorostyrene) is shown to maintain high protonic conductivity above 200 °C.
- Vladimir Atanasov
- , Albert S. Lee
- & Yu Seung Kim
-
Article |
 Intrinsic efficiency limits in low-bandgap non-fullerene acceptor organic solar cells
Intrinsic efficiency limits in low-bandgap non-fullerene acceptor organic solar cells
A systematic analysis of a series of donor–acceptor organic blends shows that in solar cells based on low-bandgap non-fullerene acceptors an ionization energy offset of about 0.5 eV is required to ensure efficient charge separation.
- Safakath Karuthedath
- , Julien Gorenflot
- & Frédéric Laquai
-
Perspective |
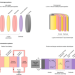 Water electrolysers with closed and open electrochemical systems
Water electrolysers with closed and open electrochemical systems
Although low-temperature water electrolysers are crucial for decarbonizing the industrial sector, substantial improvements in performance and deployment rates are needed. Recent developments in devices with modified architectures and designs, and practical challenges hampering large-scale deployment are discussed.
- Marie Francine Lagadec
- & Alexis Grimaud
-
Article |
 Observation of fluctuation-mediated picosecond nucleation of a topological phase
Observation of fluctuation-mediated picosecond nucleation of a topological phase
Time-resolved X-ray scattering is utilized to demonstrate an ultrafast 300 ps topological phase transition to a skyrmionic phase. This transition is enabled by the formation of a transient topological fluctuation state.
- Felix Büttner
- , Bastian Pfau
- & Stefan Eisebitt
-
Article |
 Electrical bioadhesive interface for bioelectronics
Electrical bioadhesive interface for bioelectronics
A graphene nanocomposite hydrogel showing anisotropic swelling is used to realize an electrically conducting and removable bioadhesive that improves the mechanical and electrical integration of bioelectronics devices with wet dynamic tissues.
- Jue Deng
- , Hyunwoo Yuk
- & Xuanhe Zhao
-
News & Views |
 The looks of a million-year-old polymer glass
The looks of a million-year-old polymer glass
Polymeric glasses with significant thermodynamic and kinetic stability have been fabricated using physical vapour deposition, providing a mean to gather insight into the properties of glasses aged for millions of years.
- Juan J. de Pablo
-
Article |
 Towards chirality control of graphene nanoribbons embedded in hexagonal boron nitride
Towards chirality control of graphene nanoribbons embedded in hexagonal boron nitride
Oriented trenches are created in h-BN using different catalysts, and used as templates to grow seamlessly integrated armchair and zigzag graphene nanoribbons with chirality-dependent electrical and magnetic conductance properties.
- Hui Shan Wang
- , Lingxiu Chen
- & Xiaoming Xie
-
Article |
 Entanglement and control of single nuclear spins in isotopically engineered silicon carbide
Entanglement and control of single nuclear spins in isotopically engineered silicon carbide
Isotope engineering of silicon carbide leads to control of nuclear spins associated with single divacancy centres and extended electron spin coherence.
- Alexandre Bourassa
- , Christopher P. Anderson
- & David D. Awschalom
-
News & Views |
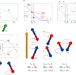 Flipping handedness in ferrimagnets
Flipping handedness in ferrimagnets
Controlling the handedness of magnetic excitations in magnetic materials is crucial for magnonic applications. Ferrimagnets provide a promising route.
- Satoshi Okamoto
-
News & Views |
 Crystallographic design for energy storage
Crystallographic design for energy storage
A crystallographic brick wall design for polycrystalline dielectric ceramics now allows the application of high electric fields at minimal misfit strain, yielding supreme reliability and high energy density.
- Jürgen Rödel
-
Article |
 Monolithic digital patterning of polydimethylsiloxane with successive laser pyrolysis
Monolithic digital patterning of polydimethylsiloxane with successive laser pyrolysis
A laser-based patterning method enables the fast fabrication of high-quality two- and three-dimensional features in polydimethylsiloxane for microfluidics and biomedical applications.
- Jaeho Shin
- , Jihoon Ko
- & Seung Hwan Ko
-
Article |
 Predictive modelling of structure formation in semiconductor films produced by meniscus-guided coating
Predictive modelling of structure formation in semiconductor films produced by meniscus-guided coating
Numerical simulations allow the prediction of domain morphology, from aligned to stretched and isotropic, in crystalline organic thin films formed by meniscus-guided coating, as a function of various deposition parameters.
- Jasper J. Michels
- , Ke Zhang
- & Tomasz Marszalek
-
Article |
 Biosynthetic self-healing materials for soft machines
Biosynthetic self-healing materials for soft machines
Protein-based materials for soft robotics that self-heal within a second while maintaining the high strength of the damaged area are reported.
- Abdon Pena-Francesch
- , Huihun Jung
- & Metin Sitti

 Flexible automation accelerates materials discovery
Flexible automation accelerates materials discovery