Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access From nanohole to ultralong straight nanochannel fabrication in graphene oxide with swift heavy ions
From nanohole to ultralong straight nanochannel fabrication in graphene oxide with swift heavy ions
While porous graphene oxide with nm-sized pores can be of great interest to biofluidic and energy storage applications, achieving precisely controlled porosity remains a technical challenge. Here, the authors exploit swift heavy ions to create uniform nanoholes and ultralong straight nanochannels in GO films.
- Andrzej Olejniczak
- & Ruslan A. Rymzhanov
-
Article
| Open Access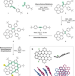 Synthesis of precisely functionalizable curved nanographenes via graphitization-induced regioselective chlorination in a mechanochemical Scholl Reaction
Synthesis of precisely functionalizable curved nanographenes via graphitization-induced regioselective chlorination in a mechanochemical Scholl Reaction
The synthesis of functionalizable nanographenes remains challenging. Here, the authors report that mechanochemical Scholl reaction allows access to regioselectively modifiable curved nanographenes in a high-yielding and general manner.
- Jovana Stanojkovic
- , Ronny William
- & Mihaiela C. Stuparu
-
Article
| Open Access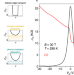 Phonon-mediated room-temperature quantum Hall transport in graphene
Phonon-mediated room-temperature quantum Hall transport in graphene
Monolayer graphene can support the quantum Hall effect up to room temperature. Here, the authors provide evidence that graphene encapsulated in hexagonal boron nitride realizes a novel transport regime where dissipation in the quantum Hall phase is mediated predominantly by electron-phonon scattering rather than disorder scattering.
- Daniel Vaquero
- , Vito Clericò
- & Sergio Pezzini
-
Article
| Open Access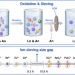 Ion sieving in graphene oxide membrane enables efficient actinides/lanthanides separation
Ion sieving in graphene oxide membrane enables efficient actinides/lanthanides separation
Separation of actinides from lanthanides is very important for the safe management of nuclear waste, however still challenging due to the chemical complexity of the f-elements. Here, authors report an efficient strategy with graphene oxide membranes for ion sieving of high valent actinyl ions and spherical lanthanide ions.
- Zhipeng Wang
- , Liqin Huang
- & Chao Xu
-
Article
| Open Access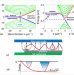 An epitaxial graphene platform for zero-energy edge state nanoelectronics
An epitaxial graphene platform for zero-energy edge state nanoelectronics
Here, the authors show robust edge state transport in patterned nanoribbon networks produced on epigraphene—graphene that is epitaxially grown on non-polar faces of SiC wafers. The edge state forms a zero-energy, one-dimensional ballistic network with dissipationless nodes at ribbon–ribbon junctions.
- Vladimir S. Prudkovskiy
- , Yiran Hu
- & Walt A. de Heer
-
Article
| Open Access Torsional periodic lattice distortions and diffraction of twisted 2D materials
Torsional periodic lattice distortions and diffraction of twisted 2D materials
In twisted 2D materials, spontaneous lattice reconstructions mean that twist angle alone provides an incomplete description. Here, using electron diffraction, the authors show that the displacement field in twisted bilayer graphene can be described as a superposition of three periodic lattice distortion (PLD) waves with wavevectors oriented at 120° from each other, forming a “torsional" PLD.
- Suk Hyun Sung
- , Yin Min Goh
- & Robert Hovden
-
Article
| Open Access Quantum criticality of excitonic Mott metal-insulator transitions in black phosphorus
Quantum criticality of excitonic Mott metal-insulator transitions in black phosphorus
The exciton Mott transition refers to a transition from an insulating state of gas-like excitons to strongly correlated electron-hole plasma phases in photoexcited semiconductors. Here the authors experimentally study such a transition in black phosphorus and reveal its quantum critical properties.
- Binjie Zheng
- , Junzhuan Wang
- & Xiaomu Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Perpendicular electric field drives Chern transitions and layer polarization changes in Hofstadter bands
Perpendicular electric field drives Chern transitions and layer polarization changes in Hofstadter bands
Moiré superlattices offer a rich platform fort the study of correlated and topological phases. Here, by using low-temperature magneto-transport measurements, the authors demonstrate electric-field induced switching between Chern states in twisted double-layer graphene in the Hofstadter regime.
- Pratap Chandra Adak
- , Subhajit Sinha
- & Mandar M. Deshmukh
-
Article
| Open Access Unconventional non-local relaxation dynamics in a twisted trilayer graphene moiré superlattice
Unconventional non-local relaxation dynamics in a twisted trilayer graphene moiré superlattice
In moiré materials, structural relaxation phenomena can lead to unexpected and novel material properties. Here, the authors characterize an unconventional non-local relaxation process in twisted double trilayer graphene, in which an energy gain in one domain of the moiré lattice is paid for by a relaxation that occurs in the other.
- Dorri Halbertal
- , Simon Turkel
- & D. N. Basov
-
Article
| Open Access Antifouling graphene oxide membranes for oil-water separation via hydrophobic chain engineering
Antifouling graphene oxide membranes for oil-water separation via hydrophobic chain engineering
Fouling is a continuous challenge for the effective application of membranes in oily wastewater treatment. Here, the authors present a hydrophobic chain engineering strategy to regulate the surface of graphene oxide-based membranes at a molecular scale for increased antifouling even at high permeance.
- Chao Yang
- , Mengying Long
- & Zhongyi Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access Unexpectedly efficient ion desorption of graphene-based materials
Unexpectedly efficient ion desorption of graphene-based materials
Desorption of ions from sorbents generally involves high acid or base concentrations and long desorption times, especially for multivalent ions. Here the authors report a rapid and efficient desorption of Co2+, Mn2+, and Sr2+ adsorbed on magnetite-graphene oxide that occurs by adding low amounts of Al3+, which is shown to interact with graphene more strongly than divalent ions.
- Xinming Xia
- , Feng Zhou
- & Haiping Fang
-
Article
| Open Access Covalent transfer of chemical gradients onto a graphenic surface with 2D and 3D control
Covalent transfer of chemical gradients onto a graphenic surface with 2D and 3D control
Covalent modification is an essential chemical method for altering the physicochemical properties of material interfaces. Here, the authors show that the no-slip conditions in microfluidic devices grant spatiotemporal control over molecular grafting.
- Yuanzhi Xia
- , Semih Sevim
- & Josep Puigmartí-Luis
-
Article
| Open Access Engineering high quality graphene superlattices via ion milled ultra-thin etching masks
Engineering high quality graphene superlattices via ion milled ultra-thin etching masks
Focused-ion beam (FIB) lithography enables high-resolution nanopatterning of 2D materials, but usually introduces significant damage. Here, the authors report a FIB-based fabrication technique to obtain high quality graphene superlattices with 18-nm pitch, which exhibit electronic transport properties similar to those of natural moiré systems.
- David Barcons Ruiz
- , Hanan Herzig Sheinfux
- & Frank H. L. Koppens
-
Article
| Open Access Accurate graphene quantum Hall arrays for the new International System of Units
Accurate graphene quantum Hall arrays for the new International System of Units
The 2019 redefinition of the International System of Units requires a 100 Ω quantum resistance standard for the ideal electrical realization of the kilogram via the Kibble Balance. Here, the authors report the realization of an array of 236 graphene quantum Hall bars, demonstrating a quantized resistance of 109 Ω with an accuracy of 0.2 nΩ/Ω over an extended range of bias currents.
- Hans He
- , Karin Cedergren
- & Gunnar Eklund
-
Article
| Open Access Explosive percolation yields highly-conductive polymer nanocomposites
Explosive percolation yields highly-conductive polymer nanocomposites
Materials with correlated localisation of percolating particles and emergent conductive paths can realise sharp transitions and high conductivities characteristic of the explosively-grown network. Here the authors exploit explosive percolation to realize a low-loading composite material with enhanced electrical properties by in-situ reduction of graphene oxide.
- Manuela Meloni
- , Matthew J. Large
- & Alan B. Dalton
-
Article
| Open Access Transfer learning enhanced water-enabled electricity generation in highly oriented graphene oxide nanochannels
Transfer learning enhanced water-enabled electricity generation in highly oriented graphene oxide nanochannels
Large-scale nanochannel integration and the multi-parameter coupling restrictive influence on electric generation are big challenges for effective energy harvesting from spontaneous water flow within artificial nanochannels. Here, authors apply transfer learning to overcome these and design optimized water-enabled generators.
- Ce Yang
- , Haiyan Wang
- & Liangti Qu
-
Article
| Open Access The composition and structure of the ubiquitous hydrocarbon contamination on van der Waals materials
The composition and structure of the ubiquitous hydrocarbon contamination on van der Waals materials
Here, the authors attribute the ambient surface contamination of van der Waals materials to a self-organized molecular layer of normal alkanes with lengths of 20-26 carbon atoms. The alkane adlayer displaces the manifold other airborne contaminant species, capping the surface of graphene, graphite, hBN and MoS2.
- András Pálinkás
- , György Kálvin
- & Péter Nemes-Incze
-
Article
| Open Access Gate-tunable Veselago interference in a bipolar graphene microcavity
Gate-tunable Veselago interference in a bipolar graphene microcavity
Charge carriers in graphene can be manipulated, e.g., collimated or focused, as in conventional optics but the efficiency of these processes remains low. Zhang et al. demonstrate interference of electrons in a novel graphene microcavity device and use it to enhance collimation efficiency of the electron flow.
- Xi Zhang
- , Wei Ren
- & Ke Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Differences in water and vapor transport through angstrom-scale pores in atomically thin membranes
Differences in water and vapor transport through angstrom-scale pores in atomically thin membranes
Understanding water transport through nanochannels is central to biology, separations and clean water. Here, the authors show transport of water vapor through Angstrom-scale pores (~2.8–6.6 Å in diameter) in atomically thin graphene membranes is orders of magnitude faster than liquid water, due to permeation occurring in different flow regimes.
- Peifu Cheng
- , Francesco Fornasiero
- & Piran R. Kidambi
-
Article
| Open Access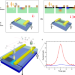 Strongly enhanced THz generation enabled by a graphene hot-carrier fast lane
Strongly enhanced THz generation enabled by a graphene hot-carrier fast lane
THz imaging and spectroscopy always request even more efficient components. Here the authors, thanks to a modified photoconductive switch that includes a graphene layer, demonstrate a high-speed photoconductive switch without sacrificing the generated power.
- Dehui Zhang
- , Zhen Xu
- & Zhaohui Zhong
-
Article
| Open Access Sliding nanomechanical resonators
Sliding nanomechanical resonators
The motion of a vibrating object is set by the way it is held. Here, the authors show a nanomechanical resonator reversibly slides on its supporting substrate as it vibrates and exploit this unconventional dynamics to quantify friction at the nanoscale.
- Yue Ying
- , Zhuo-Zhi Zhang
- & Guo-Ping Guo
-
Article
| Open Access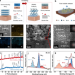 Dual interfacial engineering of a Chevrel phase electrode material for stable hydrogen evolution at 2500 mA cm−2
Dual interfacial engineering of a Chevrel phase electrode material for stable hydrogen evolution at 2500 mA cm−2
Stable electrodes which operate at large current density are essential for industrial water electrolysis. Here, a highly active Chevrel phase electrode is reported to achieve 2500 mA/cm−2 current density for 300 hours at small overpotentials.
- Heming Liu
- , Ruikuan Xie
- & Bilu Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Giant ferroelectric polarization in a bilayer graphene heterostructure
Giant ferroelectric polarization in a bilayer graphene heterostructure
Interfacial ferroelectricity may emerge in moiré superlattices. Here, the authors find that the polarized charge is much larger than the capacity of the moiré miniband and the associated anomalous screening exists outside the band.
- Ruirui Niu
- , Zhuoxian Li
- & Jianming Lu
-
Article
| Open Access Wien effect in interfacial water dissociation through proton-permeable graphene electrodes
Wien effect in interfacial water dissociation through proton-permeable graphene electrodes
Direct observation of electric field effects in the water dissociation reaction remains elusive. Here, the authors report an exponential acceleration of the reaction as function of the interfacial electric field using graphene electrodes decorated with Pt.
- J. Cai
- , E. Griffin
- & M. Lozada-Hidalgo
-
Article
| Open Access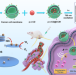 Near-infrared phosphorescent carbon dots for sonodynamic precision tumor therapy
Near-infrared phosphorescent carbon dots for sonodynamic precision tumor therapy
Combining sonodynamic properties and NIR fluorescence into a single material is desired for deep tissue applications. Here, the authors report on carbon dot sono-sensitizers engineered with a narrow bandgap and coated with cancer cell membrane for targeted NIR guided sonodynamic cancer therapy.
- Bijiang Geng
- , Jinyan Hu
- & Longxiang Shen
-
Article
| Open Access Understanding water transport through graphene-based nanochannels via experimental control of slip length
Understanding water transport through graphene-based nanochannels via experimental control of slip length
Water transport through graphene oxide membranes (GOMs) is thought to originate from frictionless movement through graphene-based channels. Here authors study the effects of cation intercalation and show flux in GOMs is governed by interactions between water molecules and impurities on channel walls.
- Xinyue Wen
- , Tobias Foller
- & Rakesh Joshi
-
Article
| Open Access Integrated wafer-scale ultra-flat graphene by gradient surface energy modulation
Integrated wafer-scale ultra-flat graphene by gradient surface energy modulation
Defect-free integration of 2D materials onto semiconductor wafers is desired to implement heterogeneous electronic devices. Here, the authors report a method to transfer high-quality graphene on target wafers via gradient surface energy modulation, leading to improved structural and electronic properties.
- Xin Gao
- , Liming Zheng
- & Hailin Peng
-
Article
| Open Access Determination of topological edge quantum numbers of fractional quantum Hall phases by thermal conductance measurements
Determination of topological edge quantum numbers of fractional quantum Hall phases by thermal conductance measurements
The knowledge of quantum numbers of the edge modes is essential for understanding fractional Hall states containing counter-propagating downstream and upstream modes. Here the authors identify the edge quantum numbers by probing a crossover from non-equilibrated to equilibrated edge mode regime in thermal conductance.
- Saurabh Kumar Srivastav
- , Ravi Kumar
- & Anindya Das
-
Article
| Open Access Integrated biosensor platform based on graphene transistor arrays for real-time high-accuracy ion sensing
Integrated biosensor platform based on graphene transistor arrays for real-time high-accuracy ion sensing
The potential of 2D materials for biosensing applications is often limited by large device-to-device variation. Here, the authors report a calibration method and a machine learning approach leveraging the redundancy of a sensing platform based on 256 integrated graphene transistors to enhance the system accuracy in real-time ion classification.
- Mantian Xue
- , Charles Mackin
- & Tomás Palacios
-
Article
| Open Access A polymer electrolyte design enables ultralow-work-function electrode for high-performance optoelectronics
A polymer electrolyte design enables ultralow-work-function electrode for high-performance optoelectronics
Ambient-stable solution-processed conductive materials with a low work function are essential to facilitate electron injection. Here, the authors design and synthesise polymer electrolyte with work function down to 2.2 eV for applications in high-performance light-emitting diodes and solar cells.
- Bo Tong
- , Jinhong Du
- & Wencai Ren
-
Article
| Open Access Flexible iontronics based on 2D nanofluidic material
Flexible iontronics based on 2D nanofluidic material
Osmotic power source based on 2D nanofluidic graphene oxide could overcome humidity and temperature limitations due to high areal power density purely from ion gradient. Here, authors couple it with triboelectric nanogenerator, and demonstrate a self-chargeable conformable tribo-iontronic device.
- Di Wei
- , Feiyao Yang
- & Zhonglin Wang
-
Article
| Open Access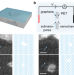 Multifunctional graphene heterogeneous nanochannel with voltage-tunable ion selectivity
Multifunctional graphene heterogeneous nanochannel with voltage-tunable ion selectivity
Nanoporous 2D materials have shown promising potential for ion sieving applications due to their physical and chemical properties. Here authors develop a heterogeneous graphene-based polyethylene terephthalate nanochannel with ion sieving ability that is controlled by adjusting the applied voltage.
- Shihao Su
- , Yifan Zhang
- & Jianming Xue
-
Article
| Open Access Superelastic graphene aerogel-based metamaterials
Superelastic graphene aerogel-based metamaterials
Graphene aerogels are highly porous and have very low density; despite this they also exhibit high mechanical strength. Here the authors present a laser-engraving strategy for producing graphene meta-aerogels with different configurations and properties.
- Mingmao Wu
- , Hongya Geng
- & Liangti Qu
-
Article
| Open Access Highly efficient and selective extraction of gold by reduced graphene oxide
Highly efficient and selective extraction of gold by reduced graphene oxide
High extraction capacity with precise selectivity to trace amounts of gold over a wide range of co-existing elements remains a challenge for effective e-waste recycling. Here, authors demonstrate the excellent performance of rGO for gold extraction from e-waste leachate, even at minute concentrations.
- Fei Li
- , Jiuyi Zhu
- & Hui-Ming Cheng
-
Article
| Open Access Large-area transfer of two-dimensional materials free of cracks, contamination and wrinkles via controllable conformal contact
Large-area transfer of two-dimensional materials free of cracks, contamination and wrinkles via controllable conformal contact
Reliable transfer techniques are critical for the integration of 2D materials with arbitrary substrates. Here, the authors describe a method to transfer 4-inch and A4-sized defect-free graphene films onto rigid and flexible substrates with controllable conformal contact, leading to improved electrical properties and uniformity.
- Yixuan Zhao
- , Yuqing Song
- & Zhongfan Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Organic covalent modification to improve thermoelectric properties of TaS2
Organic covalent modification to improve thermoelectric properties of TaS2
The improvement of thermoelectric performance of materials by reducing lattice thermal conductivity is challenging. Here, the authors find the side chains covalent modification of transition metal disulfides reducing the lattice thermal conductivity.
- Shaozhi Wang
- , Xiao Yang
- & Jian Zheng
-
Article
| Open Access Metaplastic and energy-efficient biocompatible graphene artificial synaptic transistors for enhanced accuracy neuromorphic computing
Metaplastic and energy-efficient biocompatible graphene artificial synaptic transistors for enhanced accuracy neuromorphic computing
Designing biocompatible and flexible electronic devices for neuromrophic applications remains a challenge. Here, Kireev et al. propose graphene-based artificial synaptic transistors with low-energy switching, long-term potentiation, and metaplasticity for future bio-interfaced neural networks.
- Dmitry Kireev
- , Samuel Liu
- & Jean Anne C. Incorvia
-
Article
| Open Access High-temperature flexible WSe2 photodetectors with ultrahigh photoresponsivity
High-temperature flexible WSe2 photodetectors with ultrahigh photoresponsivity
High-temperature photodetectors are desired for aerospace applications and harsh-environment robotics, but their responsivity is usually limited. Here, the authors report flexible hBN-encapsulated graphite/WSe2 photodetectors which can endure temperatures up to 700 °C in air with enhanced photoresponsivity.
- Yixuan Zou
- , Zekun Zhang
- & Peng Li
-
Article
| Open Access A reconfigurable and magnetically responsive assembly for dynamic solar steam generation
A reconfigurable and magnetically responsive assembly for dynamic solar steam generation
Despite a promising water harvesting approach solar steam generation low efficiency remains a challenging obstacle. Here, authors present a macro- and microscopically reconfigurable and magnetically responsive assembly towards a dynamic evaporation system with improved performance and salt resistance.
- Yajie Hu
- , Hongyun Ma
- & Liangti Qu
-
Article
| Open Access Dirac-source diode with sub-unity ideality factor
Dirac-source diode with sub-unity ideality factor
While different types of low-power transistors have been investigated, low voltage rectifiers able to overcome the thermionic limit have not been proposed yet. Here, the authors report the realization of Dirac-source diodes based on graphene/MoS2/graphite heterostructures, showing ideality factors <1 and rectifying ratios exceeding 108 at room temperature.
- Gyuho Myeong
- , Wongil Shin
- & Sungjae Cho
-
Article
| Open Access Gas permeation through graphdiyne-based nanoporous membranes
Gas permeation through graphdiyne-based nanoporous membranes
2D nanoporous membranes are predicted to provide highly selective gas transport in combination with extreme permeance. Here authors demonstrate gas separation performance and transport mechanisms through membranes of graphdiyne, a quasi 2D material with a graphene-like structure.
- Zhihua Zhou
- , Yongtao Tan
- & Sheng Hu
-
Article
| Open Access Light sources with bias tunable spectrum based on van der Waals interface transistors
Light sources with bias tunable spectrum based on van der Waals interface transistors
Here, the authors report the realization of light-emitting field-effect transistors based on van der Waals heterostructures with conduction and valence band edges at the Γ-point of the Brillouin zone, showing electrically tunable and material-dependent electroluminescence spectra at room temperature.
- Hugo Henck
- , Diego Mauro
- & Alberto F. Morpurgo
-
Article
| Open Access Waveguide-integrated mid-infrared photodetection using graphene on a scalable chalcogenide glass platform
Waveguide-integrated mid-infrared photodetection using graphene on a scalable chalcogenide glass platform
Mid-infrared photonic integrated circuits (PICs) are important for sensing and optical communications, but their operational wavelengths are usually limited below 4 μm. Here, the authors report the realization of photothermoelectric graphene photodetectors incorporated in a chalcogenide glass-on-CaF2 PIC operating at 5.2 μm, showing promising results for gas sensing applications.
- Jordan Goldstein
- , Hongtao Lin
- & Dirk Englund
-
Article
| Open Access Surface plasmons induce topological transition in graphene/α-MoO3 heterostructures
Surface plasmons induce topological transition in graphene/α-MoO3 heterostructures
Hyperbolic phonon polaritons – mixed states of photons and anisotropic lattice vibrations – offer appealing properties for nanophotonic applications. Here, the authors show that the plasmon-phonon hybridization upon electronic doping in graphene/α-MoO3 heterostructures can induce topological transitions of the polariton wavefront.
- Francesco L. Ruta
- , Brian S. Y. Kim
- & D. N. Basov
-
Article
| Open Access Sustainable wood electronics by iron-catalyzed laser-induced graphitization for large-scale applications
Sustainable wood electronics by iron-catalyzed laser-induced graphitization for large-scale applications
Ecologically friendly wood electronics will help alleviating the shortcomings of state-of-art cellulose-based green electronics. Here, the authors introduce iron-catalyzed laser-induced graphitization (IC-LIG) as an innovative approach for engraving large-scale electrically conductive structures on wood with high quality and efficiency.
- Christopher H. Dreimol
- , Huizhang Guo
- & Guido Panzarasa
-
Article
| Open Access Spin relaxation in a single-electron graphene quantum dot
Spin relaxation in a single-electron graphene quantum dot
Graphene has long been considered to be a promising host for spin qubits, however a demonstration of long spin relaxation times for a potential qubit has been lacking. Here, the authors report the electrical measurement of the single-electron spin relaxation time exceeding 200 μs in a bilayer graphene quantum dot.
- L. Banszerus
- , K. Hecker
- & C. Stampfer
-
Article
| Open Access Berry curvature-induced local spin polarisation in gated graphene/WTe2 heterostructures
Berry curvature-induced local spin polarisation in gated graphene/WTe2 heterostructures
Spin-based electronics offers significantly improved efficiency, but a major challenge is the electric manipulation of spin. Here, Powalla et al find a large gate induced spinpolarization in graphene/WTe2 heterostructures, illustrating the potential of such heterostructures for spintronics.
- Lukas Powalla
- , Jonas Kiemle
- & Marko Burghard
-
Article
| Open Access Nonlinear co-generation of graphene plasmons for optoelectronic logic operations
Nonlinear co-generation of graphene plasmons for optoelectronic logic operations
Nano-photonic devices based on 2D materials offer a potential solution for the miniaturization of optical computing technologies. Here, the authors demonstrate the implementation of high-speed logic operations via the all-optical generation and electrical control of multiple plasmon polaritons in a hybrid graphene device.
- Yiwei Li
- , Ning An
- & Baicheng Yao
-
Article
| Open Access Graphene nanoribbons initiated from molecularly derived seeds
Graphene nanoribbons initiated from molecularly derived seeds
The authors report on harnessing sp2-organic molecules as a basis for uniformly initiating the homoepitaxial-like, size-controlled, synthesis of sub-5 nm semiconducting graphene nanoribbons for electronics via chemical vapor deposition.
- Austin J. Way
- , Robert M. Jacobberger
- & Michael S. Arnold

 Microwave-assisted design of nanoporous graphene membrane for ultrafast and switchable organic solvent nanofiltration
Microwave-assisted design of nanoporous graphene membrane for ultrafast and switchable organic solvent nanofiltration