Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Staggered structural dynamic-mediated selective adsorption of H2O/D2O on flexible graphene oxide nanosheets
Staggered structural dynamic-mediated selective adsorption of H2O/D2O on flexible graphene oxide nanosheets
Graphene oxide is a promising material for molecular separation technologies. Here, the authors propose a realistic staggered stacking structure that plays a crucial role in H/D recognition in water adsorption, as well as high mobilities of water.
- Ryusuke Futamura
- , Taku Iiyama
- & Katsumi Kaneko
-
Article
| Open Access Float-stacked graphene–PMMA laminate
Float-stacked graphene–PMMA laminate
To maximize composite reinforcing efficiency, a semi-infinite reinforcement should be aligned in the matrix. Here, the authors report a float-stacking strategy for graphene-PMMA laminate with precisely aligned monolayer graphene in a polymer matrix.
- Seung-Il Kim
- , Ji-Yun Moon
- & Jae-Hyun Lee
-
Article
| Open Access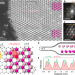 Alkali metal bilayer intercalation in graphene
Alkali metal bilayer intercalation in graphene
Here, the authors report a study of the structural properties of intercalated alkali metals in bilayer graphene and graphite via low-voltage scanning transmission electron microscopy, providing mechanistic insights for the development of energy storage applications.
- Yung-Chang Lin
- , Rika Matsumoto
- & Kazu Suenaga
-
Article
| Open Access Bidirectionally promoting assembly order for ultrastiff and highly thermally conductive graphene fibres
Bidirectionally promoting assembly order for ultrastiff and highly thermally conductive graphene fibres
Aligned 2D assembled fibres have been developed by drawing like 1D polymers, yet with disorders in cross-section. Here, the authors bidirectionally promote assembly order of graphene fibres, achieving high modulus and highly thermal conductivity.
- Peng Li
- , Ziqiu Wang
- & Chao Gao
-
Article
| Open Access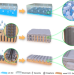 3D hierarchical graphene matrices enable stable Zn anodes for aqueous Zn batteries
3D hierarchical graphene matrices enable stable Zn anodes for aqueous Zn batteries
Uncontrolled dendrite growth and severe side reactions at high capacities and rates impede its practical application for zinc metal anodes. Here, the authors propose a composite zinc anode with 3D hierarchical graphene matrix as a multifunctional host to regulate zinc deposition for aqueous zinc batteries.
- Yongbiao Mu
- , Zheng Li
- & Lin Zeng
-
Article
| Open Access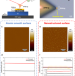 Robust microscale structural superlubricity between graphite and nanostructured surface
Robust microscale structural superlubricity between graphite and nanostructured surface
Structural superlubricity (SSL) is a state of nearly zero friction and no wear between two contacted solid surfaces. Here, authors show that, by preventing edge contact with the substrate, a microscale graphite flake can achieve robust SSL against nanostructured silicon surfaces under ambient condition.
- Xuanyu Huang
- , Tengfei Li
- & Quanshui Zheng
-
Article
| Open Access From nanohole to ultralong straight nanochannel fabrication in graphene oxide with swift heavy ions
From nanohole to ultralong straight nanochannel fabrication in graphene oxide with swift heavy ions
While porous graphene oxide with nm-sized pores can be of great interest to biofluidic and energy storage applications, achieving precisely controlled porosity remains a technical challenge. Here, the authors exploit swift heavy ions to create uniform nanoholes and ultralong straight nanochannels in GO films.
- Andrzej Olejniczak
- & Ruslan A. Rymzhanov
-
Article
| Open Access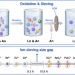 Ion sieving in graphene oxide membrane enables efficient actinides/lanthanides separation
Ion sieving in graphene oxide membrane enables efficient actinides/lanthanides separation
Separation of actinides from lanthanides is very important for the safe management of nuclear waste, however still challenging due to the chemical complexity of the f-elements. Here, authors report an efficient strategy with graphene oxide membranes for ion sieving of high valent actinyl ions and spherical lanthanide ions.
- Zhipeng Wang
- , Liqin Huang
- & Chao Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Torsional periodic lattice distortions and diffraction of twisted 2D materials
Torsional periodic lattice distortions and diffraction of twisted 2D materials
In twisted 2D materials, spontaneous lattice reconstructions mean that twist angle alone provides an incomplete description. Here, using electron diffraction, the authors show that the displacement field in twisted bilayer graphene can be described as a superposition of three periodic lattice distortion (PLD) waves with wavevectors oriented at 120° from each other, forming a “torsional" PLD.
- Suk Hyun Sung
- , Yin Min Goh
- & Robert Hovden
-
Article
| Open Access Unconventional non-local relaxation dynamics in a twisted trilayer graphene moiré superlattice
Unconventional non-local relaxation dynamics in a twisted trilayer graphene moiré superlattice
In moiré materials, structural relaxation phenomena can lead to unexpected and novel material properties. Here, the authors characterize an unconventional non-local relaxation process in twisted double trilayer graphene, in which an energy gain in one domain of the moiré lattice is paid for by a relaxation that occurs in the other.
- Dorri Halbertal
- , Simon Turkel
- & D. N. Basov
-
Article
| Open Access Unexpectedly efficient ion desorption of graphene-based materials
Unexpectedly efficient ion desorption of graphene-based materials
Desorption of ions from sorbents generally involves high acid or base concentrations and long desorption times, especially for multivalent ions. Here the authors report a rapid and efficient desorption of Co2+, Mn2+, and Sr2+ adsorbed on magnetite-graphene oxide that occurs by adding low amounts of Al3+, which is shown to interact with graphene more strongly than divalent ions.
- Xinming Xia
- , Feng Zhou
- & Haiping Fang
-
Article
| Open Access Dual interfacial engineering of a Chevrel phase electrode material for stable hydrogen evolution at 2500 mA cm−2
Dual interfacial engineering of a Chevrel phase electrode material for stable hydrogen evolution at 2500 mA cm−2
Stable electrodes which operate at large current density are essential for industrial water electrolysis. Here, a highly active Chevrel phase electrode is reported to achieve 2500 mA/cm−2 current density for 300 hours at small overpotentials.
- Heming Liu
- , Ruikuan Xie
- & Bilu Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Superelastic graphene aerogel-based metamaterials
Superelastic graphene aerogel-based metamaterials
Graphene aerogels are highly porous and have very low density; despite this they also exhibit high mechanical strength. Here the authors present a laser-engraving strategy for producing graphene meta-aerogels with different configurations and properties.
- Mingmao Wu
- , Hongya Geng
- & Liangti Qu
-
Article
| Open Access A reconfigurable and magnetically responsive assembly for dynamic solar steam generation
A reconfigurable and magnetically responsive assembly for dynamic solar steam generation
Despite a promising water harvesting approach solar steam generation low efficiency remains a challenging obstacle. Here, authors present a macro- and microscopically reconfigurable and magnetically responsive assembly towards a dynamic evaporation system with improved performance and salt resistance.
- Yajie Hu
- , Hongyun Ma
- & Liangti Qu
-
Article
| Open Access General synthesis of ultrafine metal oxide/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites for ultrahigh-flux nanofiltration membrane
General synthesis of ultrafine metal oxide/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites for ultrahigh-flux nanofiltration membrane
Graphene oxide nanofiltration membranes with tunable interlayer spacing tend to be either unstable in water or have low water permeation rates. Here the authors report a general synthetic method to achieve ultrafine metal oxide - reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites for dye filtration, achieving high water permeability and selectivity.
- Wanyu Zhang
- , Hai Xu
- & Donghui Long
-
Article
| Open Access Imaging moiré deformation and dynamics in twisted bilayer graphene
Imaging moiré deformation and dynamics in twisted bilayer graphene
Local variations of twist angle and strain in twisted bilayer graphene (TBG) can produce relevant changes in the electronic properties of the system. Here, high-resolution low energy electron microscopy is used to characterize the spatial and temporal deformations of moiré patterns in TBG at high temperatures, showing the stability of these structures up to 600 ∘C.
- Tobias A. de Jong
- , Tjerk Benschop
- & Sense Jan van der Molen
-
Article
| Open Access Elastocapillary cleaning of twisted bilayer graphene interfaces
Elastocapillary cleaning of twisted bilayer graphene interfaces
Here, the authors investigate the long-range interaction and coalescence mechanism of water and ethanol nanopockets encapsulated in twisted bilayer graphene, showing the complete recovery of moiré patterns after the motion of the contaminants.
- Yuan Hou
- , Zhaohe Dai
- & Zhong Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Water friction in nanofluidic channels made from two-dimensional crystals
Water friction in nanofluidic channels made from two-dimensional crystals
Flow through nanometer scale channels facilitates an unmasked study of water-surface molecular interactions. Here, Keerthi et al. show with conduits made from graphite and hexagonal boron nitride that strong hydrophobicity does not rule out enhanced stickiness and friction.
- Ashok Keerthi
- , Solleti Goutham
- & Boya Radha
-
Article
| Open Access Tuning nonlinear damping in graphene nanoresonators by parametric–direct internal resonance
Tuning nonlinear damping in graphene nanoresonators by parametric–direct internal resonance
Nonlinear dissipation is frequently observed in nanomechanical resonators, but its microscopic origin remains unclear. Here, nonlinear damping is found to be enhanced in graphene nanodrums close to internal resonance conditions, providing insights on the mechanisms at the basis of this phenomenon.
- Ata Keşkekler
- , Oriel Shoshani
- & Farbod Alijani
-
Article
| Open Access Large-area integration of two-dimensional materials and their heterostructures by wafer bonding
Large-area integration of two-dimensional materials and their heterostructures by wafer bonding
The existing integration approaches for 2D materials often degrade material properties and are not compatible with industrial processing. Here, the authors devise an adhesive wafer bonding strategy to transfer and stack monolayers, suitable for back end of the line integration of 2D materials.
- Arne Quellmalz
- , Xiaojing Wang
- & Frank Niklaus
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular embroidering of graphene
Molecular embroidering of graphene
Covalently 2D-patterning graphene with different chemical functionalities is an attractive way to tailor its physical and chemical properties. Here, the authors realize spatially defined 2D-hetereoarchitectures of graphene via a strategy of molecular embroidering.
- Tao Wei
- , Malte Kohring
- & Andreas Hirsch
-
Article
| Open Access Controlling nanochannel orientation and dimensions in graphene-based nanofluidic membranes
Controlling nanochannel orientation and dimensions in graphene-based nanofluidic membranes
Vertically stacked graphene oxide sheets are promising structures for molecular sieving technologies. By folding large planar sheets in an accordion-like manner, Liu et al. fabricate a thin robust filter with near-vertically aligned nanochannels geared towards commercial separation membranes.
- Muchun Liu
- , Paula J. Weston
- & Robert H. Hurt
-
Article
| Open Access Catalytic activity of graphene-covered non-noble metals governed by proton penetration in electrochemical hydrogen evolution reaction
Catalytic activity of graphene-covered non-noble metals governed by proton penetration in electrochemical hydrogen evolution reaction
Graphene-covering technology provides a promising approach for achieving a non-noble-metal-catalyst with corrosion protection and catalytic activity under acidic media. Here, the authors unveil that the electrochemical hydrogen evolution mechanism is governed by the proton penetration phenomenon.
- Kailong Hu
- , Tatsuhiko Ohto
- & Yoshikazu Ito
-
Article
| Open Access High-frequency gas effusion through nanopores in suspended graphene
High-frequency gas effusion through nanopores in suspended graphene
Atomically thin porous graphene is promising for filtration and sieving applications. Here the authors, using a laser-actuated micro-drum device of bilayer graphene with controlled number of nanopores, and measuring the permeation rate of different gases, show that it can also be used for permeation-based sensing.
- I. E. Rosłoń
- , R. J. Dolleman
- & P. G. Steeneken
-
Article
| Open Access Direct measurements of interfacial adhesion in 2D materials and van der Waals heterostructures in ambient air
Direct measurements of interfacial adhesion in 2D materials and van der Waals heterostructures in ambient air
Here, the authors devise an experimental method based on atomic force microscopy to precisely measure the interfacial adhesion energy of layered materials, van der Waals heterostructures and two-dimensional materials on SiO2 substrates.
- Hossein Rokni
- & Wei Lu
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamically-enhanced strain in atomically thin resonators
Dynamically-enhanced strain in atomically thin resonators
Here, the authors use Raman spectroscopy on circular graphene drums to demonstrate dynamical softening of optical phonons induced by the macroscopic flexural motion of graphene, and find evidence that the strain in graphene is enhanced under non-linear driving.
- Xin Zhang
- , Kevin Makles
- & Stéphane Berciaud
-
Article
| Open Access Ultralight covalent organic framework/graphene aerogels with hierarchical porosity
Ultralight covalent organic framework/graphene aerogels with hierarchical porosity
Macroscopic architectures of covalent organic frameworks (COF) allow to fully exploit their chemical functionality and porosity but achieving three-dimensional hierarchical porous COF architectures remains challenging. Here, the authors present a COF/reduced graphene oxide aerogel which is synthesized by growing COF during a hydrothermal process along the surface of graphene sheets.
- Changxia Li
- , Jin Yang
- & Arne Thomas
-
Article
| Open Access Continuous crystalline graphene papers with gigapascal strength by intercalation modulated plasticization
Continuous crystalline graphene papers with gigapascal strength by intercalation modulated plasticization
Strong but flexible graphene tends to wrinkle, which compromises some properties. Here the authors report a solid plasticization method to prepare continuous graphene papers with high crystalline order, achieving high strength, stiffness, electrical and thermal conductivities.
- Peng Li
- , Mincheng Yang
- & Chao Gao
-
Article
| Open Access Super-tough MXene-functionalized graphene sheets
Super-tough MXene-functionalized graphene sheets
Poor mechanical properties of reduced graphene oxide sheets hinder development of flexible energy storage systems. MXene functionalised graphene oxide with Ti-O-C bonding and additional crosslinking is here reported to dramatically increase toughness for flexible supercapacitors.
- Tianzhu Zhou
- , Chao Wu
- & Qunfeng Cheng
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanical cleaning of graphene using in situ electron microscopy
Mechanical cleaning of graphene using in situ electron microscopy
Contamination of 2D materials adversely impacts device performance and calls for cleaning methods down to the atomic scale and over large areas. Here, the authors present a site-specific mechanical cleaning approach capable of cleaning both sides of suspended 2D membranes and achieving atomically clean areas of several μm2 within minutes.
- Peter Schweizer
- , Christian Dolle
- & Erdmann Spiecker
-
Article
| Open Access Tunable macroscale structural superlubricity in two-layer graphene via strain engineering
Tunable macroscale structural superlubricity in two-layer graphene via strain engineering
Superlubricity in macro-scale graphitic samples is hampered by commensurate stacking domains that prevent facile sliding between adjacent graphene layers. Here, the authors show the presence of macroscale structural superlubricity between two randomly stacked graphene layers produced by both mechanical exfoliation and CVD upon the imposition of a tensile stress.
- Charalampos Androulidakis
- , Emmanuel N. Koukaras
- & Costas Galiotis
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrasensitive detection of nucleic acids using deformed graphene channel field effect biosensors
Ultrasensitive detection of nucleic acids using deformed graphene channel field effect biosensors
Field effect transistors based on graphene hold promise for sensing applications. Here, the authors report a millimeter-sized transistor based on deformed graphene as a biosensor that can detect nucleic acid molecules having detection limit of ~18 molecules of DNA in physiological buffer solution and ~600 molecules in human serum.
- Michael Taeyoung Hwang
- , Mohammad Heiranian
- & Rashid Bashir
-
Article
| Open Access Disordered protein-graphene oxide co-assembly and supramolecular biofabrication of functional fluidic devices
Disordered protein-graphene oxide co-assembly and supramolecular biofabrication of functional fluidic devices
Self-organising systems have huge potential in device design and fabrication; however, demonstrations of this are limited. Here, the authors report on a combination of disordered proteins and graphene oxide which allows spatio-temporal patterning and demonstrate the fabrication of microfluidic devices.
- Yuanhao Wu
- , Babatunde O. Okesola
- & Alvaro Mata
-
Article
| Open Access Liquids relax and unify strain in graphene
Liquids relax and unify strain in graphene
Here, the authors report water as a superior platform to suspend graphene compared to solid substrates that induce non-uniformity and do not provide structural flexibility. They utilize confocal Raman spectroscopy to study graphene floating freely on the surface of water to show that a liquid support relieves the pre-existing strain.
- Liubov A. Belyaeva
- , Lin Jiang
- & Grégory F. Schneider
-
Article
| Open Access Strong graphene oxide nanocomposites from aqueous hybrid liquid crystals
Strong graphene oxide nanocomposites from aqueous hybrid liquid crystals
Reinforcing polymers with carbon-based nanofillers is non-trivial due to incompatibilities between matrix and filler. Here, the authors report highly reinforced graphene oxide–aramid nanocomposites utilizing a water-based hybrid biaxial nematic mixture.
- Maruti Hegde
- , Lin Yang
- & Theo J. Dingemans
-
Article
| Open Access Elastic straining of free-standing monolayer graphene
Elastic straining of free-standing monolayer graphene
The extraordinary mechanical properties of graphene are usually measured on very small or supported samples. Here, the authors develop a method to test a large area of graphene and show that even with edge defects it displays near-ideal mechanical performance.
- Ke Cao
- , Shizhe Feng
- & Yang Lu
-
Article
| Open Access A fast and sensitive room-temperature graphene nanomechanical bolometer
A fast and sensitive room-temperature graphene nanomechanical bolometer
Bolometers are highly sensitive instruments that can detect radiant energy. Here, authors report micro-bolometers based on suspended graphene nano-electromechanical membranes that can detect light at room-temperature with a NEP coefficient of 2 pW/Hz^1/2 and bandwidth up to 1.3 MHz.
- Andrew Blaikie
- , David Miller
- & Benjamín J. Alemán
-
Article
| Open Access Direct imaging of light-element impurities in graphene reveals
triple-coordinated oxygen
Direct imaging of light-element impurities in graphene reveals
triple-coordinated oxygen
Annular dark field scanning transmission electron microscopy is able to distinguish the contrasts between light elements. Here, the authors directly image the bonding configurations of oxygen and nitrogen atoms in defective graphene, and surprisingly identify instances of unusual triple-coordinated oxygen with three carbon neighbors.
- Christoph Hofer
- , Viera Skákalová
- & Jannik C. Meyer
-
Article
| Open Access Force-driven reversible liquid–gas phase transition mediated by elastic nanosponges
Force-driven reversible liquid–gas phase transition mediated by elastic nanosponges
Conventional cooling systems rely on environmentally harmful halocarbons, while alternatives based on solid–solid transitions do not reach the required performance. Here the authors demonstrate using water and alcohol as refrigerants, through their confinement in nanosponges and their release by mechanical pressure.
- Keita Nomura
- , Hirotomo Nishihara
- & Takashi Kyotani
-
Article
| Open Access Chemically modified graphene films with tunable negative Poisson’s ratios
Chemically modified graphene films with tunable negative Poisson’s ratios
Negative Poisson’s ratio, offering unusual properties, is displayed by several materials and predicted for graphene. This work demonstrates such behaviors in monolithic films with interconnected networks of close-packed graphene laminates, and tunability through the chemistry and microstructures.
- Yeye Wen
- , Enlai Gao
- & Chun Li
-
Article
| Open Access Mosaic pattern formation in exfoliated graphene by mechanical deformation
Mosaic pattern formation in exfoliated graphene by mechanical deformation
Owing to its atomic thinness, graphene is susceptible to wrinkles and folds. Here, the authors demonstrate controlled wrinkle formation in graphene under uniaxial tension and show that the obtained mosaic patterns can be used as channels for trapping or administering water and other fluids.
- Maria Giovanna Pastore Carbone
- , Anastasios C. Manikas
- & Costas Galiotis
-
Article
| Open Access Controllable ion transport by surface-charged graphene oxide membrane
Controllable ion transport by surface-charged graphene oxide membrane
Graphene oxide membranes have great potential in separation processes, but small ions rejection needs improvement for large scale applications. Here the authors manipulate the membrane’s surface charge to control selective ion transport, achieving high rejection for A2B and AB2 type salts and maintaining high water permeance.
- Mengchen Zhang
- , Kecheng Guan
- & Nanping Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Binder-free graphene oxide doughs
Binder-free graphene oxide doughs
Graphene oxide (GO) dispersions may be used as starting materials for graphene-based architectures. Here, a malleable and versatile dough state of GO is discovered, completing the GO–water continuum, which can be diluted or converted to glassy GO or graphene solids without long-range stacking order with enhanced mechanical and electrochemical properties
- Che-Ning Yeh
- , Haiyue Huang
- & Jiaxing Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Lithium intercalation into bilayer graphene
Lithium intercalation into bilayer graphene
The mechanism of lithium storage in graphenic carbon remains a fundamental question to be addressed. Here the authors employ suitable bilayer graphene foam to investigate various physiochemical phenomena of lithium intercalation and propose a storage model.
- Kemeng Ji
- , Jiuhui Han
- & Yutaka Oyama
-
Article
| Open Access Silicon as a ubiquitous contaminant in graphene derivatives with significant impact on device performance
Silicon as a ubiquitous contaminant in graphene derivatives with significant impact on device performance
Silicon-based contaminants are ubiquitous in natural graphite, and they are thus expected to be present in exfoliated graphene. Here, the authors show that such impurities play a non-negligible role in graphene-based devices, and use high-purity parent graphite to boost the performance of graphene sensors and supercapacitor microelectrodes.
- Rouhollah Jalili
- , Dorna Esrafilzadeh
- & Gordon G. Wallace
-
Article
| Open Access Graphene mechanical pixels for Interferometric Modulator Displays
Graphene mechanical pixels for Interferometric Modulator Displays
The electro-optical response of suspended graphene membranes measured by change in wavelength-dependent reflectance can enable interferometric modulation display (IMOD) technology. Here, the authors report suspended double layer graphene based IMOD drums with 2500 pixels per inch.
- Santiago J. Cartamil-Bueno
- , Dejan Davidovikj
- & Samer Houri
-
Article
| Open Access Anomalous twin boundaries in two dimensional materials
Anomalous twin boundaries in two dimensional materials
All materials subjected to mechanical deformation form low energy interfaces known as twin boundaries. Here, the authors investigate a variety of structural features that form upon bending atomically thin 2D-crystals, and predict distinct classes of post deformation microstructure based on their atomic arrangement, bend angle and flake thickness.
- A. P. Rooney
- , Z. Li
- & S. J. Haigh
-
Article
| Open Access Highly stretchable carbon aerogels
Highly stretchable carbon aerogels
Improved compressive elasticity was lately demonstrated for carbon aerogels but the problem of reversible stretchability remained a challenge. Here the authors use a hierarchical structure design and synergistic effects between carbon nanotubes and graphene to achieve high stretchability in carbon aerogels.
- Fan Guo
- , Yanqiu Jiang
- & Chao Gao
-
Article
| Open Access Anti-fouling graphene-based membranes for effective water desalination
Anti-fouling graphene-based membranes for effective water desalination
Intrinsic limitations of nanoporous graphene limit its applications in water treatment. Here the authors produce post-treatment-free, low-cost graphene-based membranes from renewable biomass and demonstrate their high water permeance and antifouling properties using real seawater.
- Dong Han Seo
- , Shafique Pineda
- & Kostya (Ken) Ostrikov

 Universal Murray’s law for optimised fluid transport in synthetic structures
Universal Murray’s law for optimised fluid transport in synthetic structures