Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Height-renderable morphable tactile display enabled by programmable modulation of local stiffness in photothermally active polymer
Height-renderable morphable tactile display enabled by programmable modulation of local stiffness in photothermally active polymer
The controllability of deformation height in reconfigurable touch displays currently limits their deliverable information. Hwang et al. present a light-triggered morphable tactile display enabling generation of refreshable, height-adjustable, and latchable 3D topologies with varying textures on a thin film surface.
- Inwook Hwang
- , Seongcheol Mun
- & Sungryul Yun
-
Article
| Open Access Electron/infrared-phonon coupling in ABC trilayer graphene
Electron/infrared-phonon coupling in ABC trilayer graphene
Via Raman and infrared spectroscopy measurements, X. Zan et al. find that rhombohedral ABC trilayer graphene has stronger electron/infrared-phonon coupling than Bernal ABA trilayer graphene.
- Xiaozhou Zan
- , Xiangdong Guo
- & Guangyu Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access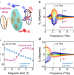 Strong transient magnetic fields induced by THz-driven plasmons in graphene disks
Strong transient magnetic fields induced by THz-driven plasmons in graphene disks
The authors provide an experimental demonstration of magnetic field generation in graphene disks via the inverse Faraday effect. When the disks are illuminated with circularly polarized radiation in resonance with the graphene plasmon frequency, the corresponding rotational motion of the charge carriers gives rise to a unipolar magnetic field.
- Jeong Woo Han
- , Pavlo Sai
- & Martin Mittendorff
-
Article
| Open Access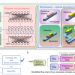 Graphene/silicon heterojunction for reconfigurable phase-relevant activation function in coherent optical neural networks
Graphene/silicon heterojunction for reconfigurable phase-relevant activation function in coherent optical neural networks
Designing an efficient activation function for optical neural networks remains a challenge. Here, the authors demonstrate a modulator-detector-in-one graphene/silicon heterojunction ring resonators enabling on-chip reconfigurable activation function devices with phase activation capability for optical neural networks.
- Chuyu Zhong
- , Kun Liao
- & Hongtao Lin
-
Article
| Open Access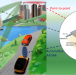 Sub-THz wireless transmission based on graphene-integrated optoelectronic mixer
Sub-THz wireless transmission based on graphene-integrated optoelectronic mixer
Here, the authors report the realization of a sub-THz wireless data link based on a graphene-integrated optoelectronic mixer with a >96 GHz bandwidth, −44 dB upconversion efficiency and <0.1 mm2 footprint, providing an alternative approach for the realization of millimeter-wave transmitters.
- Alberto Montanaro
- , Giulia Piccinini
- & Marco Romagnoli
-
Article
| Open Access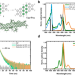 Interplay of structure and photophysics of individualized rod-shaped graphene quantum dots with up to 132 sp² carbon atoms
Interplay of structure and photophysics of individualized rod-shaped graphene quantum dots with up to 132 sp² carbon atoms
The use and characterization of graphene quantum dots is limited by their pronounced tendency to form aggregates. Here, the authors synthesize rod-shaped motifs of nanographenes with up to 132 sp2 carbon atoms that are fully individualized, which allows the precise description of their intrinsic photophysical properties.
- Daniel Medina-Lopez
- , Thomas Liu
- & Stephane Campidelli
-
Article
| Open Access In-sensor computing using a MoS2 photodetector with programmable spectral responsivity
In-sensor computing using a MoS2 photodetector with programmable spectral responsivity
Here, the authors report the design and realization of an in-sensor computing optoelectronic device with programmable spectral responsivity based on an ensemble of cavity-enhanced MoS2 photodetectors. The device can perform direct analog processing during the light detection process, without the need to computationally reconstruct the entire optical spectra.
- Dohyun Kwak
- , Dmitry K. Polyushkin
- & Thomas Mueller
-
Article
| Open Access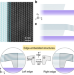 Strong bulk photovoltaic effect in engineered edge-embedded van der Waals structures
Strong bulk photovoltaic effect in engineered edge-embedded van der Waals structures
The bulk photovoltaic effect (BPVE) is a nonlinear optical effect offering a promising approach to overcome the limitations of conventional photovoltaics. Here, the authors report the observation of BPVE-induced photocurrents at the edges of 2D semiconductors embedded in various van der Waals heterostructures.
- Zihan Liang
- , Xin Zhou
- & Xiaolong Chen
-
Article
| Open Access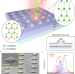 Strong second-harmonic generation by sublattice polarization in non-uniformly strained monolayer graphene
Strong second-harmonic generation by sublattice polarization in non-uniformly strained monolayer graphene
Nanostructured platforms for efficient nonlinear optics are the building block of next generation integrated photonic devices. Here the authors provide a straightforward method to engineer the lattice symmetry of monolayer graphene, boosting the SHG signal at low temperature.
- Kunze Lu
- , Manlin Luo
- & Donguk Nam
-
Article
| Open Access Quantum criticality of excitonic Mott metal-insulator transitions in black phosphorus
Quantum criticality of excitonic Mott metal-insulator transitions in black phosphorus
The exciton Mott transition refers to a transition from an insulating state of gas-like excitons to strongly correlated electron-hole plasma phases in photoexcited semiconductors. Here the authors experimentally study such a transition in black phosphorus and reveal its quantum critical properties.
- Binjie Zheng
- , Junzhuan Wang
- & Xiaomu Wang
-
Article
| Open Access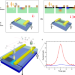 Strongly enhanced THz generation enabled by a graphene hot-carrier fast lane
Strongly enhanced THz generation enabled by a graphene hot-carrier fast lane
THz imaging and spectroscopy always request even more efficient components. Here the authors, thanks to a modified photoconductive switch that includes a graphene layer, demonstrate a high-speed photoconductive switch without sacrificing the generated power.
- Dehui Zhang
- , Zhen Xu
- & Zhaohui Zhong
-
Article
| Open Access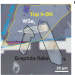 High-temperature flexible WSe2 photodetectors with ultrahigh photoresponsivity
High-temperature flexible WSe2 photodetectors with ultrahigh photoresponsivity
High-temperature photodetectors are desired for aerospace applications and harsh-environment robotics, but their responsivity is usually limited. Here, the authors report flexible hBN-encapsulated graphite/WSe2 photodetectors which can endure temperatures up to 700 °C in air with enhanced photoresponsivity.
- Yixuan Zou
- , Zekun Zhang
- & Peng Li
-
Article
| Open Access Light sources with bias tunable spectrum based on van der Waals interface transistors
Light sources with bias tunable spectrum based on van der Waals interface transistors
Here, the authors report the realization of light-emitting field-effect transistors based on van der Waals heterostructures with conduction and valence band edges at the Γ-point of the Brillouin zone, showing electrically tunable and material-dependent electroluminescence spectra at room temperature.
- Hugo Henck
- , Diego Mauro
- & Alberto F. Morpurgo
-
Article
| Open Access Waveguide-integrated mid-infrared photodetection using graphene on a scalable chalcogenide glass platform
Waveguide-integrated mid-infrared photodetection using graphene on a scalable chalcogenide glass platform
Mid-infrared photonic integrated circuits (PICs) are important for sensing and optical communications, but their operational wavelengths are usually limited below 4 μm. Here, the authors report the realization of photothermoelectric graphene photodetectors incorporated in a chalcogenide glass-on-CaF2 PIC operating at 5.2 μm, showing promising results for gas sensing applications.
- Jordan Goldstein
- , Hongtao Lin
- & Dirk Englund
-
Article
| Open Access Surface plasmons induce topological transition in graphene/α-MoO3 heterostructures
Surface plasmons induce topological transition in graphene/α-MoO3 heterostructures
Hyperbolic phonon polaritons – mixed states of photons and anisotropic lattice vibrations – offer appealing properties for nanophotonic applications. Here, the authors show that the plasmon-phonon hybridization upon electronic doping in graphene/α-MoO3 heterostructures can induce topological transitions of the polariton wavefront.
- Francesco L. Ruta
- , Brian S. Y. Kim
- & D. N. Basov
-
Article
| Open Access Berry curvature-induced local spin polarisation in gated graphene/WTe2 heterostructures
Berry curvature-induced local spin polarisation in gated graphene/WTe2 heterostructures
Spin-based electronics offers significantly improved efficiency, but a major challenge is the electric manipulation of spin. Here, Powalla et al find a large gate induced spinpolarization in graphene/WTe2 heterostructures, illustrating the potential of such heterostructures for spintronics.
- Lukas Powalla
- , Jonas Kiemle
- & Marko Burghard
-
Article
| Open Access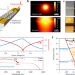 Nonlinear co-generation of graphene plasmons for optoelectronic logic operations
Nonlinear co-generation of graphene plasmons for optoelectronic logic operations
Nano-photonic devices based on 2D materials offer a potential solution for the miniaturization of optical computing technologies. Here, the authors demonstrate the implementation of high-speed logic operations via the all-optical generation and electrical control of multiple plasmon polaritons in a hybrid graphene device.
- Yiwei Li
- , Ning An
- & Baicheng Yao
-
Article
| Open Access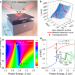 Topological phase singularities in atomically thin high-refractive-index materials
Topological phase singularities in atomically thin high-refractive-index materials
The authors combine films of two-dimensional semiconductors, which exhibit excitonic spectral features, with SiO2/Si Fabry-Perot resonators in order to realize topological phase singularities in reflection. Around these singularities, the reflection spectra demonstrate rapid phase changes while the structure behaves as a perfect absorber.
- Georgy Ermolaev
- , Kirill Voronin
- & Valentyn Volkov
-
Article
| Open Access Deep-ultraviolet electroluminescence and photocurrent generation in graphene/hBN/graphene heterostructures
Deep-ultraviolet electroluminescence and photocurrent generation in graphene/hBN/graphene heterostructures
Here, the authors report the observation of deep-ultraviolet (DUV) electroluminescence and photocurrent generation in van der Waals heterostructures based on hBN crystals, showing potential for DUV light emitting and detection devices.
- Su-Beom Song
- , Sangho Yoon
- & Jonghwan Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Multispecies and individual gas molecule detection using Stokes solitons in a graphene over-modal microresonator
Multispecies and individual gas molecule detection using Stokes solitons in a graphene over-modal microresonator
The integration of 2D materials on photonic devices provides advanced functionalities in sensing applications. The authors demonstrate a graphene functionalized microcomb sensor by exploiting spectrally trapped Stokes solitons. They obtain both multispecies gas identification and individual molecule sensitivity.
- Teng Tan
- , Zhongye Yuan
- & Baicheng Yao
-
Article
| Open Access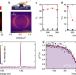 Bright single photon emitters with enhanced quantum efficiency in a two-dimensional semiconductor coupled with dielectric nano-antennas
Bright single photon emitters with enhanced quantum efficiency in a two-dimensional semiconductor coupled with dielectric nano-antennas
Single photon emitters (SPEs) in 2D semiconductors can be deterministically positioned using localized strain induced by underlying nanostructures. Here, the authors show SPE coupling in WSe2 to GaP dielectric nanoantennas, substantially increasing quantum efficiency and photoluminescence brightness.
- Luca Sortino
- , Panaiot G. Zotev
- & Alexander I. Tartakovskii
-
Article
| Open Access Structure-controllable growth of nitrogenated graphene quantum dots via solvent catalysis for selective C-N bond activation
Structure-controllable growth of nitrogenated graphene quantum dots via solvent catalysis for selective C-N bond activation
Photophysical and photochemical features of graphene quantum dots (GQDs) strongly depend on their chemical nature that remains challenging to be controlled in a systematic and uniform manner. Here the authors report an efficient solvent-catalyst-aided growth of chemically tailored N-doped GQDs.
- Byung Joon Moon
- , Sang Jin Kim
- & Sukang Bae
-
Article
| Open Access Pseudo-magnetic field-induced slow carrier dynamics in periodically strained graphene
Pseudo-magnetic field-induced slow carrier dynamics in periodically strained graphene
The effect of strain-induced pseudo-magnetic fields on the optical properties of graphene has not been experimentally explored yet. Here, pseudo-magnetic fields reaching values of 100 T are shown to increase by more than an order of magnitude the relaxation lifetime of hot carriers in periodically strained graphene.
- Dong-Ho Kang
- , Hao Sun
- & Donguk Nam
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrahigh-speed graphene-based optical coherent receiver
Ultrahigh-speed graphene-based optical coherent receiver
Graphene-based photodetectors have many advantages for applications. Here, the authors demonstrate a high-speed optical coherent receiver for optical communications based on graphene-on-plasmonic slot waveguide photodetectors.
- Yilun Wang
- , Xiang Li
- & Xinliang Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access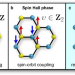 Optical N-invariant of graphene’s topological viscous Hall fluid
Optical N-invariant of graphene’s topological viscous Hall fluid
Graphene is the archetype for realizing two-dimensional topological phases of matter. Here, the authors introduce a new topological classification connected to polarization transport, where the topological number is revealed in the spatiotemporal dispersion of the susceptibility tensor.
- Todd Van Mechelen
- , Wenbo Sun
- & Zubin Jacob
-
Review Article
| Open Access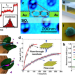 Nanophotonic biosensors harnessing van der Waals materials
Nanophotonic biosensors harnessing van der Waals materials
This review presents an overview of scenarios where van der Waals (vdW) materials provide unique advantages for nanophotonic biosensing applications. The authors discuss basic sensing principles based on vdW materials, advantages of the reduced dimensionality as well as technological challenges.
- Sang-Hyun Oh
- , Hatice Altug
- & Michael S. Strano
-
Article
| Open Access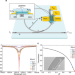 High-responsivity graphene photodetectors integrated on silicon microring resonators
High-responsivity graphene photodetectors integrated on silicon microring resonators
Optical receivers based on graphene still suffer from low responsivity. Here, the authors integrate a photo-thermoelectric graphene photodetector with a Si micro-ring resonator, and obtain a voltage responsivity ~ 90 V/W and a reduction of energy-per-bit consumption, enabling performance on par with mature semiconductor technology.
- S. Schuler
- , J. E. Muench
- & T. Mueller
-
Article
| Open Access Quantum surface-response of metals revealed by acoustic graphene plasmons
Quantum surface-response of metals revealed by acoustic graphene plasmons
Knowledge of the quantum response of materials is essential for designing light–matter interactions at the nanoscale. Here, the authors report a theory for understanding the impact of metallic quantum response on acoustic graphene plasmons and how such response could be inferred from measurements.
- P. A. D. Gonçalves
- , Thomas Christensen
- & N. Asger Mortensen
-
Article
| Open Access The limits of near field immersion microwave microscopy evaluated by imaging bilayer graphene moiré patterns
The limits of near field immersion microwave microscopy evaluated by imaging bilayer graphene moiré patterns
Here, the authors image twisted bilayer graphene using scanning microwave imaging microscopy, revealing structures with sizes down to 1 nm. They show that is possible by using spontaneously forming nanoscale water menisci that concentrates the microwave fields in small regions.
- Douglas A. A. Ohlberg
- , Diego Tami
- & Gilberto Medeiros-Ribeiro
-
Article
| Open Access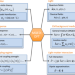 Combining density functional theory with macroscopic QED for quantum light-matter interactions in 2D materials
Combining density functional theory with macroscopic QED for quantum light-matter interactions in 2D materials
The development of a quantitative and predictive theory of quantum light-matter interactions in ultrathin materials is both a conceptual and computational challenge. Here, the authors develop such a framework by combining density functional theory with macroscopic quantum electrodynamics, and use it to quantify the Purcell effect in van der Waals heterostructures.
- Mark Kamper Svendsen
- , Yaniv Kurman
- & Kristian S. Thygesen
-
Article
| Open Access Optoelectronic mixing with high-frequency graphene transistors
Optoelectronic mixing with high-frequency graphene transistors
Here, the authors report optoelectronic mixing up to 67 GHz using high-frequency back-gated graphene field effect transistors (GFETs). These devices mix an electrical signal injected into the GFET gate and a modulated optical signal onto a single layer graphene channel.
- A. Montanaro
- , W. Wei
- & E. Pallecchi
-
Article
| Open Access Neural network based 3D tracking with a graphene transparent focal stack imaging system
Neural network based 3D tracking with a graphene transparent focal stack imaging system
Transparent photodetectors based on graphene stacked vertically along the optical axis have shown promising potential for light field reconstruction. Here, the authors develop transparent photodetector arrays and implement a neural network for real-time 3D optical imaging and object tracking.
- Dehui Zhang
- , Zhen Xu
- & Theodore B. Norris
-
Article
| Open Access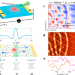 Hyperbolic enhancement of photocurrent patterns in minimally twisted bilayer graphene
Hyperbolic enhancement of photocurrent patterns in minimally twisted bilayer graphene
Here, the authors use scanning probe photocurrent imaging to resolve nanoscale variations of the Seebeck coefficient occurring at domain walls separating micron-scale AB and BA stacking regions in twisted bilayer graphene, and observe hyperbolic enhancement of the photocurrent pattern.
- S. S. Sunku
- , D. Halbertal
- & D. N. Basov
-
Article
| Open Access Nano-imaging photoresponse in a moiré unit cell of minimally twisted bilayer graphene
Nano-imaging photoresponse in a moiré unit cell of minimally twisted bilayer graphene
Here, the authors use a nanoscale probe to study the photoresponse within a single moiré unit cell of minimally twisted bilayer graphene, and observe an intricate photo-thermoelectric response attributed to the Seebeck coefficient variation at AB-BA domain boundaries.
- Niels C. H. Hesp
- , Iacopo Torre
- & Frank H. L. Koppens
-
Article
| Open Access Real-space imaging of acoustic plasmons in large-area graphene grown by chemical vapor deposition
Real-space imaging of acoustic plasmons in large-area graphene grown by chemical vapor deposition
Acoustic graphene plasmons are superior to the graphene surface plasmons in field confinement and normalized propagation length, thus promising for applications. Here, the authors report near-field imaging of acoustic plasmons in high-quality CVD graphene, measure the AGP dispersion and propagation loss, and investigate their behavior in a periodic structure.
- Sergey G. Menabde
- , In-Ho Lee
- & Min Seok Jang
-
Article
| Open Access Interfacial jamming reinforced Pickering emulgel for arbitrary architected nanocomposite with connected nanomaterial matrix
Interfacial jamming reinforced Pickering emulgel for arbitrary architected nanocomposite with connected nanomaterial matrix
Nanocomposite (NC) printing emerged as a major approach to translate nanomaterial properties to 3D geometries but printing of conventional NCs lacks control over nanomaterial connection. Here, the authors develop viscoelastic Pickering emulgels as NC inks through jamming nanomaterials on interfaces and in continuous phase
- Yuanyuan Zhang
- , Guangming Zhu
- & Feng Xing
-
Article
| Open Access Zero-bias mid-infrared graphene photodetectors with bulk photoresponse and calibration-free polarization detection
Zero-bias mid-infrared graphene photodetectors with bulk photoresponse and calibration-free polarization detection
Here, graphene-based plasmonic metamaterials are used to generate an artificial bulk photovoltaic effect, enabling the realization of mid-infrared photodetectors with enhanced responsivity and calibration-free polarization detection at room temperature.
- Jingxuan Wei
- , Ying Li
- & Chengkuo Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamically-enhanced strain in atomically thin resonators
Dynamically-enhanced strain in atomically thin resonators
Here, the authors use Raman spectroscopy on circular graphene drums to demonstrate dynamical softening of optical phonons induced by the macroscopic flexural motion of graphene, and find evidence that the strain in graphene is enhanced under non-linear driving.
- Xin Zhang
- , Kevin Makles
- & Stéphane Berciaud
-
Article
| Open Access Blue emission at atomically sharp 1D heterojunctions between graphene and h-BN
Blue emission at atomically sharp 1D heterojunctions between graphene and h-BN
Here, the authors explore the blue photoluminescence signal arising from the interface between graphene and h-BN arranged in in-plane heterostructures, and fabricate a blue light emitting device utilizing the heterojunction as the emitting layer.
- Gwangwoo Kim
- , Kyung Yeol Ma
- & Hyeon Suk Shin
-
Article
| Open Access Plasmonic antenna coupling to hyperbolic phonon-polaritons for sensitive and fast mid-infrared photodetection with graphene
Plasmonic antenna coupling to hyperbolic phonon-polaritons for sensitive and fast mid-infrared photodetection with graphene
A significant challenge of infrared (IR) photodetectors is to funnel light into a small nanoscale active area and efficiently convert it into an electrical signal. Here, the authors couple a plasmonic antenna to hyperbolic phonon-polaritons in hexagonal-BN to highly concentrate mid-IR light into a graphene pn-junction.
- Sebastián Castilla
- , Ioannis Vangelidis
- & Frank H. L. Koppens
-
Article
| Open Access Stimulated plasmon polariton scattering
Stimulated plasmon polariton scattering
Here, the authors propose an approach for harnessing nonlinear resonant scattering called stimulated plasmon polariton scattering. The proposal allows the excitation, amplification and detection 2D plasmon and phonon polaritons all across the THz-range while requiring optical components in the near-IR or visible range.
- C. Wolff
- & N. A. Mortensen
-
Article
| Open Access Structured graphene metamaterial selective absorbers for high efficiency and omnidirectional solar thermal energy conversion
Structured graphene metamaterial selective absorbers for high efficiency and omnidirectional solar thermal energy conversion
Here, the authors demonstrate a selective solar thermal absorber with wavelength selectivity, arising from metallic trench-like structures, using broadband dispersionless ultrathin graphene metamaterial film, with excellent thermal conductivity.
- Keng-Te Lin
- , Han Lin
- & Baohua Jia
-
Article
| Open Access Liquids relax and unify strain in graphene
Liquids relax and unify strain in graphene
Here, the authors report water as a superior platform to suspend graphene compared to solid substrates that induce non-uniformity and do not provide structural flexibility. They utilize confocal Raman spectroscopy to study graphene floating freely on the surface of water to show that a liquid support relieves the pre-existing strain.
- Liubov A. Belyaeva
- , Lin Jiang
- & Grégory F. Schneider
-
Article
| Open Access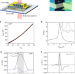 Ultra-long carrier lifetime in neutral graphene-hBN van der Waals heterostructures under mid-infrared illumination
Ultra-long carrier lifetime in neutral graphene-hBN van der Waals heterostructures under mid-infrared illumination
Long carrier lifetimes are beneficial for graphene-based optoelectronics, but carrier recombination processes in graphene possess sub-picosecond characteristic times. Here, the authors report carrier lifetimes ~30 ps at low energy in graphene/hBN Zener-Klein transistors, attributed to interband Auger processes.
- P. Huang
- , E. Riccardi
- & J. Mangeney
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrasensitive negative capacitance phototransistors
Ultrasensitive negative capacitance phototransistors
Here, the authors report ultrasensitive negative capacitance phototransistors based on MoS2 regulated by a layer of ferroelectric hafnium zirconium oxide film to demonstrate a hysteresis-free ultra-steep subthreshold slope of 17.64 mV/dec and specific detectivity of 4.75 × 1014 cm Hz1/2 W−1 at room temperature.
- Luqi Tu
- , Rongrong Cao
- & Junhao Chu
-
Article
| Open Access Redox-governed charge doping dictated by interfacial diffusion in two-dimensional materials
Redox-governed charge doping dictated by interfacial diffusion in two-dimensional materials
Manipulation of charge carriers is promising for tuning electronic, optical and magnetic properties in two-dimensional materials, but mechanistic details are not fully understood. Here, the authors report that ambient redox reactions govern charge transfer doping in graphene and tungsten disulfide.
- Kwanghee Park
- , Haneul Kang
- & Sunmin Ryu
-
Article
| Open Access Photonic crystal for graphene plasmons
Photonic crystal for graphene plasmons
Traditional photonic crystals consist of periodic media with a pre-defined optical response. Here, the authors combine nanostructured back-gate insulators with a continuous layer of graphene to demonstrate an electrically tunable two-dimensional photonic crystal suitable for controlling the propagation of surface plasmon polaritons.
- L. Xiong
- , C. Forsythe
- & D. N. Basov
-
Article
| Open Access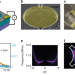 A fast and sensitive room-temperature graphene nanomechanical bolometer
A fast and sensitive room-temperature graphene nanomechanical bolometer
Bolometers are highly sensitive instruments that can detect radiant energy. Here, authors report micro-bolometers based on suspended graphene nano-electromechanical membranes that can detect light at room-temperature with a NEP coefficient of 2 pW/Hz^1/2 and bandwidth up to 1.3 MHz.
- Andrew Blaikie
- , David Miller
- & Benjamín J. Alemán
-
Article
| Open Access Fermi level-tuned optics of graphene for attocoulomb-scale quantification of electron transfer at single gold nanoparticles
Fermi level-tuned optics of graphene for attocoulomb-scale quantification of electron transfer at single gold nanoparticles
Measurement of single-molecule level electron transfer is restricted by detection limits in nanoampere to picoampere ranges. Here the authors develop graphene-based electrochemical microscopy to attain an attoampere-level detection limit for faraday current at single nanoparticles.
- Qing Xia
- , Zixuan Chen
- & Jun-Jie Zhu

 Hyperbolic metamaterial empowered controllable photonic Weyl nodal line semimetals
Hyperbolic metamaterial empowered controllable photonic Weyl nodal line semimetals