Featured
-
-
Letter |
 Singlet molecular oxygen regulates vascular tone and blood pressure in inflammation
Singlet molecular oxygen regulates vascular tone and blood pressure in inflammation
Singlet molecular oxygen, produced by indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 activity, gives rise to a signalling molecule that regulates arterial relaxation under inflammatory conditions.
- Christopher P. Stanley
- , Ghassan J. Maghzal
- & Roland Stocker
-
Letter |
 An N-nitrosating metalloenzyme constructs the pharmacophore of streptozotocin
An N-nitrosating metalloenzyme constructs the pharmacophore of streptozotocin
The metalloenzyme SznF catalyses the formation of an N–N bond in the biosynthesis of streptozotocin, providing insights into the enzymatic assembly of an N-nitroso group.
- Tai L. Ng
- , Roman Rohac
- & Emily P. Balskus
-
Letter |
 Enzymatic assembly of carbon–carbon bonds via iron-catalysed sp3 C–H functionalization
Enzymatic assembly of carbon–carbon bonds via iron-catalysed sp3 C–H functionalization
Evolved iron-containing enzymes based on cytochrome P450 achieve selective intermolecular alkylation of sp3 C–H bonds through a carbene C–H insertion strategy.
- Ruijie K. Zhang
- , Kai Chen
- & Frances H. Arnold
-
Letter |
 Metal-free ribonucleotide reduction powered by a DOPA radical in Mycoplasma pathogens
Metal-free ribonucleotide reduction powered by a DOPA radical in Mycoplasma pathogens
A subclass of ribonucleotide reductase in Mycoplasma pathogens contains a stable radical formed from a modified tyrosine residue, overturning the presumed requirement for a dinuclear metal site in aerobic ribonucleotide reductase.
- Vivek Srinivas
- , Hugo Lebrette
- & Martin Högbom
-
Letter |
 Crystal structure of a membrane-bound O-acyltransferase
Crystal structure of a membrane-bound O-acyltransferase
Crystal structures of DltB, a bacterial membrane-bound O-acyltransferase, are reported both alone and in complex with the d-alanyl donor protein DltC.
- Dan Ma
- , Zhizhi Wang
- & Wenqing Xu
-
Letter |
 OTULIN limits cell death and inflammation by deubiquitinating LUBAC
OTULIN limits cell death and inflammation by deubiquitinating LUBAC
OTULIN, which removes ubiquitin chains deposited by LUBAC, promotes LUBAC activity by preventing its auto-ubiquitination, thereby supporting normal mouse embryo development and preventing pro-inflammatory cell death in adult mice.
- Klaus Heger
- , Katherine E. Wickliffe
- & Vishva M. Dixit
-
Letter |
 Structural basis of G-quadruplex unfolding by the DEAH/RHA helicase DHX36
Structural basis of G-quadruplex unfolding by the DEAH/RHA helicase DHX36
A mechanism for the unfolding of guanine-rich DNA ‘quadruplexes’ by helicases is suggested, based on the structure of a DNA-bound helicase.
- Michael C. Chen
- , Ramreddy Tippana
- & Adrian R. Ferré-D’Amaré
-
Letter |
 Structural basis for regulation of human acetyl-CoA carboxylase
Structural basis for regulation of human acetyl-CoA carboxylase
Cryo-electron microscopy studies of distinct, catalytically active and inactive filaments of human acetyl-CoA carboxylase 1 reveal the structural basis of its regulation.
- Moritz Hunkeler
- , Anna Hagmann
- & Timm Maier
-
Letter |
 Dynamic allostery can drive cold adaptation in enzymes
Dynamic allostery can drive cold adaptation in enzymes
By engineering entropy-tuning changes into distal sites of a bacterial adenylate kinase, an allosteric tuning mechanism based on protein dynamics is revealed.
- Harry G. Saavedra
- , James O. Wrabl
- & Vincent J. Hilser
-
Letter |
 Mechanism of phosphoribosyl-ubiquitination mediated by a single Legionella effector
Mechanism of phosphoribosyl-ubiquitination mediated by a single Legionella effector
Crystal structures of the Legionella effectors SdeA and SdeD uncover the mechanism of a unique phosphoribosyl-ubiquitination reaction.
- Anil Akturk
- , David J. Wasilko
- & Yuxin Mao
-
Letter |
 KAT2A coupled with the α-KGDH complex acts as a histone H3 succinyltransferase
KAT2A coupled with the α-KGDH complex acts as a histone H3 succinyltransferase
The histone acetyl transferase KAT2A (also known as GCN5) can also catalyse histone succinylation, with the α-KGDH complex providing a local source of succinyl-CoA.
- Yugang Wang
- , Yusong R. Guo
- & Zhimin Lu
-
Article |
 Structures of transcription pre-initiation complex with TFIIH and Mediator
Structures of transcription pre-initiation complex with TFIIH and Mediator
Cryo-electron microscopy structures of the yeast pre-initiation complex (PIC) and its complex with core Mediator provide insights into the opening of promoter DNA and the initiation of transcription.
- S. Schilbach
- , M. Hantsche
- & P. Cramer
-
Letter |
 ISWI chromatin remodellers sense nucleosome modifications to determine substrate preference
ISWI chromatin remodellers sense nucleosome modifications to determine substrate preference
A high-throughput approach using a DNA-barcoded nucleosome library shows that ISWI chromatin remodellers can distinguish between differently modified nucleosomes.
- Geoffrey P. Dann
- , Glen P. Liszczak
- & Tom W. Muir
-
Letter |
 Unique roles for histone H3K9me states in RNAi and heritable silencing of transcription
Unique roles for histone H3K9me states in RNAi and heritable silencing of transcription
Heterochromatin formation involves histone H3 methylation, with H3K9me2 defining a distinct heterochromatin state that is transcriptionally permissive and can couple with RNAi, and the transition to non-permissive H3K9me3 required for the epigenetic heritability of heterochromatin.
- Gloria Jih
- , Nahid Iglesias
- & Danesh Moazed
-
Article |
 A B12-dependent radical SAM enzyme involved in oxetanocin A biosynthesis
A B12-dependent radical SAM enzyme involved in oxetanocin A biosynthesis
The biosynthesis of oxetanocin A involves OxsB, a B12-dependent S-adenosylmethionine radical enzyme, which catalyses an unusual ring contraction of a 2′-deoxyadenosine phosphate.
- Jennifer Bridwell-Rabb
- , Aoshu Zhong
- & Hung-wen Liu
-
Letter |
 Structural insights into adiponectin receptors suggest ceramidase activity
Structural insights into adiponectin receptors suggest ceramidase activity
Structures of the adiponectin receptors ADIPOR1 and ADIPOR2 combined with molecular dynamics simulations and enzymatic assays suggest that both receptors have intrinsic ceramidase activity.
- Ieva Vasiliauskaité-Brooks
- , Remy Sounier
- & Sébastien Granier
-
Article |
 Elucidation of the biosynthesis of the methane catalyst coenzyme F430
Elucidation of the biosynthesis of the methane catalyst coenzyme F430
The enzymes and pathway involved in the biosynthesis of coenzyme F430 are identified, completing our understanding of how members of the cyclic modified tetrapyrrole family are constructed.
- Simon J. Moore
- , Sven T. Sowa
- & Martin J. Warren
-
Letter |
 Two distinct RNase activities of CRISPR-C2c2 enable guide-RNA processing and RNA detection
Two distinct RNase activities of CRISPR-C2c2 enable guide-RNA processing and RNA detection
The CRISPR-associated bacterial enzyme C2c2 is shown to contain two separable, distinct sites for the highly sensitive detection and cleavage of single-stranded RNA.
- Alexandra East-Seletsky
- , Mitchell R. O’Connell
- & Jennifer A. Doudna
-
Letter |
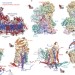 Structure of mammalian respiratory complex I
Structure of mammalian respiratory complex I
Electron cryomicroscopy structures are provided for all core and supernumerary protein subunits of mammalian complex I, a 45-subunit enzyme that powers eukaryotic respiration.
- Jiapeng Zhu
- , Kutti R. Vinothkumar
- & Judy Hirst
-
Letter |
 Structural insights into inhibition of lipid I production in bacterial cell wall synthesis
Structural insights into inhibition of lipid I production in bacterial cell wall synthesis
The crystal structure of the MraY enzyme from Aquifex aeolicus in complex with the naturally occurring nucleoside inhibitor muraymycin D2 (MD2) reveals that MraY undergoes a large conformational rearrangement near the active site after the binding of MD2, leading to the generation of a nucleoside-binding pocket and a peptide-binding site.
- Ben C. Chung
- , Ellene H. Mashalidis
- & Seok-Yong Lee
-
Letter |
 Ubiquitination independent of E1 and E2 enzymes by bacterial effectors
Ubiquitination independent of E1 and E2 enzymes by bacterial effectors
An unprecedented mechanism of ubiquitination that is independent of E1 and E2 enzymes, instead relying on activation of ubiquitin by ADP-ribosylation, and which is mediated by members of the SidE effector family encoded by the bacterial pathogen Legionella pneumophila, establishes that ubiquitination can be carried out by a single enzyme.
- Jiazhang Qiu
- , Michael J. Sheedlo
- & Zhao-Qing Luo
-
Letter |
 Repairing oxidized proteins in the bacterial envelope using respiratory chain electrons
Repairing oxidized proteins in the bacterial envelope using respiratory chain electrons
The identification of an enzymatic system repairing proteins containing oxidized methionine in the bacterial cell envelope, a compartment particularly susceptible to oxidative damage by host defence mechanisms.
- Alexandra Gennaris
- , Benjamin Ezraty
- & Frédéric Barras
-
Letter |
 CMT2D neuropathy is linked to the neomorphic binding activity of glycyl-tRNA synthetase
CMT2D neuropathy is linked to the neomorphic binding activity of glycyl-tRNA synthetase
Charcot–Marie–Tooth diseases are hereditary peripheral neuropathies for which there are currently no effective therapies; here the type 2D subtype of these diseases is shown to be caused by mutations impeding a signalling pathway necessary for motor neuron survival.
- Weiwei He
- , Ge Bai
- & Xiang-Lei Yang
-
Article |
 The mechanism of DNA replication termination in vertebrates
The mechanism of DNA replication termination in vertebrates
This study describes a new model of eukaryotic replication termination in which converging leading strands pass each other unhindered and the replicative DNA helicase is unloaded late, after all strands have been ligated.
- James M. Dewar
- , Magda Budzowska
- & Johannes C. Walter
-
Letter |
 X-ray structure of a mammalian stearoyl-CoA desaturase
X-ray structure of a mammalian stearoyl-CoA desaturase
The crystal structure of mouse SCD1 bound to fatty acid stearoyl-CoA is solved at 2.6 Å resolution; the structure reveals a novel geometry for the dimetal centre, and the acyl chain of the bound fatty acid is shown to be shielded and shaped to a particular conformation by the enzyme, providing a structural basis for the selectivity of fatty acid metabolism.
- Yonghong Bai
- , Jason G. McCoy
- & Ming Zhou
-
Letter |
 Structure of the key species in the enzymatic oxidation of methane to methanol
Structure of the key species in the enzymatic oxidation of methane to methanol
Time-resolved resonance Raman vibrational spectroscopy was used to study the mechanism of soluble methane monooxygenase and obtain structural information on the key reaction cycle intermediate, compound Q, which contains a unique dinuclear FeIV cluster that breaks the strong C-H bond of methane and inserts an oxygen atom (from O2) to form methanol.
- Rahul Banerjee
- , Yegor Proshlyakov
- & Denis A. Proshlyakov
-
Letter |
 Catalysts from synthetic genetic polymers
Catalysts from synthetic genetic polymers
Four different XNAs — polymers with backbone chemistries not found in nature, namely, arabino nucleic acids, 2′-fluoroarabino nucleic acids, hexitol nucleic acids and cyclohexene nucleic acids — are found to be able to support the evolution of synthetic enzymes (XNAzymes) that catalyse several chemical reactions.
- Alexander I. Taylor
- , Vitor B. Pinheiro
- & Philipp Holliger
-
Letter |
 A cross-chiral RNA polymerase ribozyme
A cross-chiral RNA polymerase ribozyme
Here, a cross-chiral RNA polymerase is developed—an RNA enzyme that can catalyse the templated polymerization of activated mononucleotides that are of the opposite handedness—shedding light on how RNA-based life could have emerged.
- Jonathan T. Sczepanski
- & Gerald F. Joyce
-
Article |
 Crystal structure of the human COP9 signalosome
Crystal structure of the human COP9 signalosome
The COP9 signalosome (CSN) complex regulates cullin–RING E3 ubiquitin ligases—the largest class of ubiquitin ligase enzymes, which are involved in a multitude of regulatory processes; here, the crystal structure of the entire human CSN holoenzyme is presented.
- Gondichatnahalli M. Lingaraju
- , Richard D. Bunker
- & Nicolas H. Thomä
-
Article |
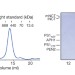 Three-dimensional structure of human γ-secretase
Three-dimensional structure of human γ-secretase
The three-dimensional structure of intact human γ-secretase complex at 4.5 Å resolution is revealed by cryo-electron-microscopy single-particle analysis; the complex comprises a horseshoe-shaped transmembrane domain containing 19 transmembrane segments, and a large extracellular domain from nicastrin, which sits immediately above the hollow space formed by the horseshoe.
- Peilong Lu
- , Xiao-chen Bai
- & Yigong Shi
-
Letter |
 Trace-gas metabolic versatility of the facultative methanotroph Methylocella silvestris
Trace-gas metabolic versatility of the facultative methanotroph Methylocella silvestris
Distinct groups of microorganisms have been thought to grow on methane and on short-chain alkanes; now, the methanotroph Methylocella silvestris is shown to express two distinct soluble di-iron centre monooxygenases that allow it to use either methane or propane as a carbon and energy source.
- Andrew T. Crombie
- & J. Colin Murrell
-
Letter |
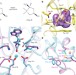 Discovery of new enzymes and metabolic pathways by using structure and genome context
Discovery of new enzymes and metabolic pathways by using structure and genome context
Pathway docking (in silico docking of metabolites to several enzymes and binding proteins in a metabolic pathway) enables the discovery of a catabolic pathway for the osmolyte trans-4-hydroxy-l-proline betaine.
- Suwen Zhao
- , Ritesh Kumar
- & Matthew P. Jacobson
-
Letter |
 The catalytic mechanism for aerobic formation of methane by bacteria
The catalytic mechanism for aerobic formation of methane by bacteria
A mechanism is proposed for the formation of methane by bacteria, through the cleavage of a highly unreactive carbon–phosphorus bond in methyl phosphonate by PhnJ in the bacterial C–P lyase complex.
- Siddhesh S. Kamat
- , Howard J. Williams
- & Frank M. Raushel
-
Letter |
 Diverse type VI secretion phospholipases are functionally plastic antibacterial effectors
Diverse type VI secretion phospholipases are functionally plastic antibacterial effectors
A functionally diverse superfamily of bacterial phospholipase enzymes that mediate antagonisitc interactions as effectors of the type VI secretion system is uncovered; these enzymes degrade the bacterial membrane, representing a novel mechanism of bacterial competition.
- Alistair B. Russell
- , Michele LeRoux
- & Joseph D. Mougous
-
Letter |
 SIRT6 regulates TNF-α secretion through hydrolysis of long-chain fatty acyl lysine
SIRT6 regulates TNF-α secretion through hydrolysis of long-chain fatty acyl lysine
The sirtuin family of enzymes are known as NAD-dependent deacetylases, although some of them have very weak deacetylase activity; here human SIRT6, an enzyme important for DNA repair and transcription, is shown to remove long-chain fatty acyl groups from protein lysine residues, and to have a function in promoting tumour necrosis factor alpha secretion.
- Hong Jiang
- , Saba Khan
- & Hening Lin
-
Letter |
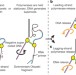 A solution to release twisted DNA during chromosome replication by coupled DNA polymerases
A solution to release twisted DNA during chromosome replication by coupled DNA polymerases
During chromosome replication, coupled polymerases introduce topological changes that cause lower processivity and transient lagging-strand polymerase dissociation from DNA.
- Isabel Kurth
- , Roxana E. Georgescu
- & Mike E. O'Donnell
-
Article |
 Crystal structure of the entire respiratory complex I
Crystal structure of the entire respiratory complex I
The atomic-resolution structure of the entire respiratory complex I is reported, with the resolution high enough to map out the locations and orientations of nearly all amino-acid side chains—some of which link to human neurodegenerative diseases—and reveals which amino-acid interactions take place at the hydrophilic domain–membrane domain interface.
- Rozbeh Baradaran
- , John M. Berrisford
- & Leonid A. Sazanov
-
Letter |
 Control of substrate access to the active site in methane monooxygenase
Control of substrate access to the active site in methane monooxygenase
The crystal structure of the complex between the hydroxylase and regulatory component of soluble methane monooxygenase is presented, revealing how the latter component controls substrate access to the hydroxylase active site.
- Seung Jae Lee
- , Michael S. McCormick
- & Uhn-Soo Cho
-
News & Views |
 Another aspect of nature's ingenuity
Another aspect of nature's ingenuity
Eyewitnesses are sometimes asked to identify a culprit from a line-up of people associated with a crime scene. An enzyme — iridoid synthase — that catalyses an unusual reaction has been identified by a similar approach. See Letter p.138
- Joe Chappell
-
Letter |
 An alternative route to cyclic terpenes by reductive cyclization in iridoid biosynthesis
An alternative route to cyclic terpenes by reductive cyclization in iridoid biosynthesis
Iridoids are a large family of bicyclic natural products that possess anticancer, anti-inflammatory, antifungal and antibacterial activities; here the essential cyclization step in their biosynthesis is identified, opening up the possibility of production of naturally occurring and synthetic variants of iridoids for use in pharmacy or agriculture.
- Fernando Geu-Flores
- , Nathaniel H. Sherden
- & Sarah E. O’Connor
-
News & Views |
 A glimpse of molecular competition
A glimpse of molecular competition
Single-molecule studies reveal how the DNA-repair protein RecA overcomes competition from another protein to bind to single-stranded DNA, and how other mediator proteins assist in this process. See Letter p.274
- Susan T. Lovett
-
Letter |
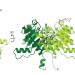 Structure and function of Zucchini endoribonuclease in piRNA biogenesis
Structure and function of Zucchini endoribonuclease in piRNA biogenesis
Zucchini has been identified as an endoribonuclease responsible for the maturation of small RNA molecules that protect the genome from the damaging effects of unrestrained expression of mobile elements.
- Hiroshi Nishimasu
- , Hirotsugu Ishizu
- & Osamu Nureki
-
Research Highlights |
Enzyme design inspired by cancer
-
Letter |
 The yeast Fun30 and human SMARCAD1 chromatin remodellers promote DNA end resection
The yeast Fun30 and human SMARCAD1 chromatin remodellers promote DNA end resection
Fun30 and SMARCAD1 are identified as chromatin remodellers that promote DNA end resection during DNA repair and preserve genome stability in yeast and humans, respectively.
- Thomas Costelloe
- , Raphaël Louge
- & Bertrand Llorente
-
Letter |
 Structural basis for RNA-duplex recognition and unwinding by the DEAD-box helicase Mss116p
Structural basis for RNA-duplex recognition and unwinding by the DEAD-box helicase Mss116p
Analysis of the yeast DEAD-box nucleic acid helicase Mss116p provides a structural model for how DEAD-box proteins recognize and unwind RNA duplexes.
- Anna L. Mallam
- , Mark Del Campo
- & Alan M. Lambowitz
-
News & Views |
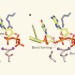 DNA replication caught in the act
DNA replication caught in the act
By freezing a DNA polymerase enzyme at several points along its reaction pathway, a sequence of X-ray crystal structures has been obtained, showing how the enzyme replicates DNA and revealing surprising mechanistic details. See Article p.196
- Kenneth A. Johnson
-
Research Highlights |
Bacterial border defence
-
Article |
 Rab5 is necessary for the biogenesis of the endolysosomal system in vivo
Rab5 is necessary for the biogenesis of the endolysosomal system in vivo
The small GTPase Rab5 has been proposed to be a master regulator of endosome biogenesis; using in vivo RNA interference and mathematical modelling it is shown here that the endolysosomal system is resilient to loss of Rab5 until its concentration drops below a critical level, at which point endosomes are lost, leading to increased serum low-density lipoprotein levels, alterations in metabolism and hepatocellular polarity.
- Anja Zeigerer
- , Jerome Gilleron
- & Marino Zerial
-
News |
 A biological clock to wind them all
A biological clock to wind them all
Enzymes that mop up toxic hydrogen peroxide may have formed life's first circadian clock.
- Ewen Callaway

 An allosteric mechanism for potent inhibition of human ATP-citrate lyase
An allosteric mechanism for potent inhibition of human ATP-citrate lyase