Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis for FGF hormone signalling
Structural basis for FGF hormone signalling
This study reveals how Klotho and heparan sulfate glycosaminoglycan coreceptors enable FGF hormones to induce asymmetric 1:2 FGF–FGFR dimerization mandatory for FGFR kinase activation and hence signalling.
- Lingfeng Chen
- , Lili Fu
- & Moosa Mohammadi
-
Article |
 A small-molecule PI3Kα activator for cardioprotection and neuroregeneration
A small-molecule PI3Kα activator for cardioprotection and neuroregeneration
A new specific, small-molecule activator of the PI3Kα isoform (UCL-TRO-1938) identified through high-throughput screening can transiently activate PI3K signalling and biological responses in cells and tissues, with potential therapeutic applications in tissue protection and regeneration.
- Grace Q. Gong
- , Benoit Bilanges
- & Bart Vanhaesebroeck
-
Article
| Open Access An atlas of substrate specificities for the human serine/threonine kinome
An atlas of substrate specificities for the human serine/threonine kinome
Analysis of the kinase activity of 300 protein Ser/Thr kinases reveals that the substrate specificity of the kinome is substantially more diverse than expected and is driven extensively by negative selectivity
- Jared L. Johnson
- , Tomer M. Yaron
- & Lewis C. Cantley
-
Article |
 Non-canonical β-adrenergic activation of ERK at endosomes
Non-canonical β-adrenergic activation of ERK at endosomes
β2-adrenergic receptor(β2AR) signalling induces ERK activity at endosomes, but not at the plasma membrane, and this activity is dependent on active, endosome-localized Gαs and requires ligand-stimulated β2AR endocytosis.
- Yonghoon Kwon
- , Sohum Mehta
- & Jin Zhang
-
Article |
 CDK11 regulates pre-mRNA splicing by phosphorylation of SF3B1
CDK11 regulates pre-mRNA splicing by phosphorylation of SF3B1
CDK11 associates with SF3B1 and phosphorylates threonine residues at the N terminus of SF3B1 during spliceosome activation, and the inhibition of CDK11 blocks the activation and leads to widespread intron retention and the accumulation of non-functional spliceosomes on pre-mRNAs and chromatin.
- Milan Hluchý
- , Pavla Gajdušková
- & Dalibor Blazek
-
Article
| Open Access The mechanism of RNA capping by SARS-CoV-2
The mechanism of RNA capping by SARS-CoV-2
Reconstitution of the SARS-CoV-2 RNA 5′ cap reveals the unconventional mechanism by which SARS-CoV-2 caps its RNA genome, providing a new target in the development of antiviral agents to treat COVID-19.
- Gina J. Park
- , Adam Osinski
- & Vincent S. Tagliabracci
-
Article
| Open Access Core control principles of the eukaryotic cell cycle
Core control principles of the eukaryotic cell cycle
The core cell cycle is largely driven by increasing total CDK activity together with minor differences in the substrate specificity of the CDKs initiating DNA replication and mitosis.
- Souradeep Basu
- , Jessica Greenwood
- & Paul Nurse
-
Article |
 Structure determination of high-energy states in a dynamic protein ensemble
Structure determination of high-energy states in a dynamic protein ensemble
Combining NMR spectroscopy-derived pseudocontact shifts (PCSs) with Carr–Purcell–Meiboom–Gill (CPMG) relaxation dispersion enables protein structure determination of lowly populated high-energy states that are essential for macromolecular function.
- John B. Stiller
- , Renee Otten
- & Dorothee Kern
-
Article
| Open Access Structural insights into inhibitor regulation of the DNA repair protein DNA-PKcs
Structural insights into inhibitor regulation of the DNA repair protein DNA-PKcs
Cryo-electron microscopy structures of DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit bound to ATPγS and four inhibitors (wortmannin, NU7441, AZD7648 and M3814) provide molecular details and insights useful for drug design.
- Shikang Liang
- , Sherine E. Thomas
- & Tom L. Blundell
-
Article |
 Activation mechanism of PINK1
Activation mechanism of PINK1
Unphosphorylated PINK1 of Pediculus humanus corporis forms a dimerized state before undergoing trans-autophosphorylation, and phosphorylated PINK1 undergoes a conformational change in the N-lobe to produce its phosphorylated, ubiquitin-binding state.
- Zhong Yan Gan
- , Sylvie Callegari
- & David Komander
-
Article |
 Mechanism for the activation of the anaplastic lymphoma kinase receptor
Mechanism for the activation of the anaplastic lymphoma kinase receptor
Cryo-electron microscopy, nuclear magnetic resonance and X-ray crystallography are used to provide structural and mechanistic details of the activation of anaplastic lymphoma kinase by the ligands ALKAL1 and ALKAL2.
- Andrey V. Reshetnyak
- , Paolo Rossi
- & Charalampos G. Kalodimos
-
Article |
 Structural basis for ligand reception by anaplastic lymphoma kinase
Structural basis for ligand reception by anaplastic lymphoma kinase
Analysis of crystal structures of anaplastic lymphoma kinase elucidate the mechanism by which ligand binding and the glycine-rich domain regulate its activity.
- Tongqing Li
- , Steven E. Stayrook
- & Daryl E. Klein
-
Article |
 MARK4 controls ischaemic heart failure through microtubule detyrosination
MARK4 controls ischaemic heart failure through microtubule detyrosination
MARK4 regulates cardiomyocyte contractility by promoting MAP4 phosphorylation, which facilitates the access of VASH2 to microtubules for the detyrosination of α-tubulin; MARK4 deficiency after acute myocardial infarction limits the reduction in the left ventricular ejection fraction.
- Xian Yu
- , Xiao Chen
- & Xuan Li
-
Article |
 Structural basis for the action of the drug trametinib at KSR-bound MEK
Structural basis for the action of the drug trametinib at KSR-bound MEK
Crystal structures of the MEK kinase bound to the scaffold protein KSR and various MEK inhibitors, including the anti-cancer drug trametinib, reveal the molecular and functional mechanisms behind MEK inhibition.
- Zaigham M. Khan
- , Alexander M. Real
- & Arvin C. Dar
-
Article |
 Ligand-induced monoubiquitination of BIK1 regulates plant immunity
Ligand-induced monoubiquitination of BIK1 regulates plant immunity
The detection of microorganism-associated ligands by plant cells activates a signalling cascade in which the kinase BIK1 is monoubiquinated, released from the FLS2–BAK1 complex, and internalized by endocytosis.
- Xiyu Ma
- , Lucas A. N. Claus
- & Libo Shan
-
Article |
 Separase-triggered apoptosis enforces minimal length of mitosis
Separase-triggered apoptosis enforces minimal length of mitosis
If early mitosis is too short, separase induces apoptosis by cleaving MCL2 and BCL-XL, thereby eliminating cells that are prone to chromosome missegregation.
- Susanne Hellmuth
- & Olaf Stemmann
-
Article |
 The gluconeogenic enzyme PCK1 phosphorylates INSIG1/2 for lipogenesis
The gluconeogenic enzyme PCK1 phosphorylates INSIG1/2 for lipogenesis
Phosphorylation of INSIG1 and INSIG2 by PCK1 leads to a reduction in the binding of sterols, the activation of SREBP1 and SREBP2 and the downstream transcription of lipogenesis-associated genes that promote tumour growth.
- Daqian Xu
- , Zheng Wang
- & Zhimin Lu
-
Letter |
 p38γ is essential for cell cycle progression and liver tumorigenesis
p38γ is essential for cell cycle progression and liver tumorigenesis
The stress-activated kinase p38γ has a role in regulating entry into the cell cycle; in the liver, it can induce cellular proliferation during regeneration and promote the development of hepatocellular carcinoma.
- Antonia Tomás-Loba
- , Elisa Manieri
- & Guadalupe Sabio
-
Letter |
 Phosphocode-dependent functional dichotomy of a common co-receptor in plant signalling
Phosphocode-dependent functional dichotomy of a common co-receptor in plant signalling
The plant receptor kinase co-receptor BAK1 contains phosphosites that are required for immune function but not for brassinosteroid-regulated growth in Arabidopsis thaliana; an additional tyrosine phosphosite may be required for the function of many Arabidopsis receptor kinases.
- Artemis Perraki
- , Thomas A. DeFalco
- & Cyril Zipfel
-
Article |
 Kinase-controlled phase transition of membraneless organelles in mitosis
Kinase-controlled phase transition of membraneless organelles in mitosis
The dual-specificity kinase DYRK3 acts as a central ‘dissolvase’, mediating the phase transitions of several types of membraneless organelles during mitosis.
- Arpan Kumar Rai
- , Jia-Xuan Chen
- & Lucas Pelkmans
-
Letter |
 A Cdk9–PP1 switch regulates the elongation–termination transition of RNA polymerase II
A Cdk9–PP1 switch regulates the elongation–termination transition of RNA polymerase II
The kinase Cdk9 and the phosphatase Dis2 regulate the termination of transcription in fission yeast in part by controlling the phosphorylation state of the elongation factor Spt5.
- Pabitra K. Parua
- , Gregory T. Booth
- & Robert P. Fisher
-
Letter |
 Phase-separation mechanism for C-terminal hyperphosphorylation of RNA polymerase II
Phase-separation mechanism for C-terminal hyperphosphorylation of RNA polymerase II
The histidine-rich domain of cyclin T1 promotes phase separation into liquid droplets, which facilitates the hyperphosphorylation of the C-terminal domain repeats of RNA polymerase II.
- Huasong Lu
- , Dan Yu
- & Qiang Zhou
-
Article |
 Mechanisms of mTORC1 activation by RHEB and inhibition by PRAS40
Mechanisms of mTORC1 activation by RHEB and inhibition by PRAS40
The cryo-electron microscopy and crystal structures of several mTORC1 complexes, and accompanying biochemical analyses, shed light on how mTORC1 is regulated and how cancer mutations lead to its hyperactivation.
- Haijuan Yang
- , Xiaolu Jiang
- & Nikola P. Pavletich
-
Letter |
 Cyclin D–CDK4 kinase destabilizes PD-L1 via cullin 3–SPOP to control cancer immune surveillance
Cyclin D–CDK4 kinase destabilizes PD-L1 via cullin 3–SPOP to control cancer immune surveillance
Abundance of PD-L1, the ligand of the anti-cancer immunotherapy target PD-1, is negatively regulated by poly-ubiquitination via the cyclin D–CDK4/cullin 3–SPOP axis and PD-1 blockade treatment in mice improved survival when combined with CDK4/6 inhibitors.
- Jinfang Zhang
- , Xia Bu
- & Wenyi Wei
-
Letter |
 TORC1 organized in inhibited domains (TOROIDs) regulate TORC1 activity
TORC1 organized in inhibited domains (TOROIDs) regulate TORC1 activity
In budding yeast, glucose withdrawal, via the Rag GTPases, leads to TORC1 inhibition through its re-organization into a giant, vacuole-associated helix named a TOROID (TORC1 organized in inhibited domain).
- Manoël Prouteau
- , Ambroise Desfosses
- & Robbie Loewith
-
Letter |
 Tumours with class 3 BRAF mutants are sensitive to the inhibition of activated RAS
Tumours with class 3 BRAF mutants are sensitive to the inhibition of activated RAS
Hypoactive BRAF mutants bind more tightly than wild type to the upstream regulator RAS, thus amplifying to amplify ERK signalling; tumours expressing these mutants require coexistent mechanisms for RAS activation to grow and are sensitive to their inhibition.
- Zhan Yao
- , Rona Yaeger
- & Neal Rosen
-
Letter |
 TRAF2 and OTUD7B govern a ubiquitin-dependent switch that regulates mTORC2 signalling
TRAF2 and OTUD7B govern a ubiquitin-dependent switch that regulates mTORC2 signalling
Ubiquitination of the GβL subunit, a component of both mTORC1 and mTORC2, acts as a regulatory switching mechanism to balance levels of mTORC1 and mTORC2; the failure of this mechanism in some cancers leads to elevated mTORC2 formation and tumorigenesis.
- Bin Wang
- , Zuliang Jie
- & Wenyi Wei
-
Letter |
 EPRS is a critical mTORC1–S6K1 effector that influences adiposity in mice
EPRS is a critical mTORC1–S6K1 effector that influences adiposity in mice
Glutamyl-prolyl tRNA synthetase (EPRS) is a downstream effector of the mTORC1–S6K1 signalling axis and contributes to adiposity and ageing in mice.
- Abul Arif
- , Fulvia Terenzi
- & Paul L. Fox
-
Letter |
 Small molecule stabilization of the KSR inactive state antagonizes oncogenic Ras signalling
Small molecule stabilization of the KSR inactive state antagonizes oncogenic Ras signalling
A class of small molecules that stabilize a previously unrecognized inactive state of KSR is reported; the agonists synergize with MEK inhibitors to prevent growth of Ras mutant cell lines.
- Neil S. Dhawan
- , Alex P. Scopton
- & Arvin C. Dar
-
Letter |
 Overcoming EGFR(T790M) and EGFR(C797S) resistance with mutant-selective allosteric inhibitors
Overcoming EGFR(T790M) and EGFR(C797S) resistance with mutant-selective allosteric inhibitors
An allosteric inhibitor, EAI045, is reported that is selective for certain drug-resistant EGFR mutants, but spares the wild-type receptor; combination therapy of EAI045 with EGFR-dimerization-blocking antibodies is effective in mouse models of lung cancer driven by mutant versions of EGFR that are resistant to all previously developed inhibitors.
- Yong Jia
- , Cai-Hong Yun
- & Michael J. Eck
-
Letter |
 Targeting transcription regulation in cancer with a covalent CDK7 inhibitor
Targeting transcription regulation in cancer with a covalent CDK7 inhibitor
Here, a covalent inhibitor targeting cyclin-dependent kinase 7 (CDK7) demonstrates in vitro and in vivo efficacy against T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukaemia by downregulating oncogenic transcriptional programs.
- Nicholas Kwiatkowski
- , Tinghu Zhang
- & Nathanael S. Gray
-
Letter |
 Cell-cycle-regulated activation of Akt kinase by phosphorylation at its carboxyl terminus
Cell-cycle-regulated activation of Akt kinase by phosphorylation at its carboxyl terminus
Phosphorylation of Akt at its carboxy-terminal tail is an essential layer of Akt activation to regulate its physiological functions.
- Pengda Liu
- , Michael Begley
- & Wenyi Wei
-
Letter |
 Mechanism of MEK inhibition determines efficacy in mutant KRAS- versus BRAF-driven cancers
Mechanism of MEK inhibition determines efficacy in mutant KRAS- versus BRAF-driven cancers
The mechanism of action of three different allosteric MEK inhibitors that target the MAP kinase pathway is investigated, and their efficacy is shown to be explained by the distinct mechanisms regulating MEK activation in KRAS- versus BRAF-driven tumours; this work provides a rationale for designing more effective cancer therapies for these common genetic subtypes of cancer.
- Georgia Hatzivassiliou
- , Jacob R. Haling
- & Marcia Belvin
-
Article |
 KAT5 tyrosine phosphorylation couples chromatin sensing to ATM signalling
KAT5 tyrosine phosphorylation couples chromatin sensing to ATM signalling
KAT5 tyrosine phosphorylation, mediated by the tyrosine kinase c-Abl, increases after DNA damage, promoting KAT5 binding to histone H3K9me3, which triggers KAT5-mediated acetylation of the ATM kinase; this promotes the activation of the DNA damage checkpoint and cell survival.
- Abderrahmane Kaidi
- & Stephen P. Jackson
-
Letter |
 Crystal structure of the integral membrane diacylglycerol kinase
Crystal structure of the integral membrane diacylglycerol kinase
This study presents the crystal structures of three functional forms of diacylglycerol kinase, an integral membrane protein that catalyses a crucial step in oligosaccharide and lipopolysaccharide synthesis and assembly; these X-ray structures are markedly different from the only other structure available for this unique kinase that was solved using solution NMR.
- Dianfan Li
- , Joseph A. Lyons
- & Martin Caffrey
-
Article |
 mTOR kinase structure, mechanism and regulation
mTOR kinase structure, mechanism and regulation
Co-crystal structures of a number of complexes involving truncated mammalian target of rapamycin, a phosphoinositide 3-kinase-related protein kinase, reveal an intrinsically active kinase conformation and show how rapamycin–FKBP12 directly blocks substrate recruitment to the kinase domain.
- Haijuan Yang
- , Derek G. Rudge
- & Nikola P. Pavletich
-
Letter |
 Structural basis for RNA-duplex recognition and unwinding by the DEAD-box helicase Mss116p
Structural basis for RNA-duplex recognition and unwinding by the DEAD-box helicase Mss116p
Analysis of the yeast DEAD-box nucleic acid helicase Mss116p provides a structural model for how DEAD-box proteins recognize and unwind RNA duplexes.
- Anna L. Mallam
- , Mark Del Campo
- & Alan M. Lambowitz
-
News & Views |
 A division duet
A division duet
The orchestration of cell division requires a programme of events choreographed by protein modification. A study shows that the relative activity of a phosphatase enzyme towards its substrates imposes order during the final act of division.
- Curt Wittenberg
-
Letter |
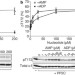 Structure of mammalian AMPK and its regulation by ADP
Structure of mammalian AMPK and its regulation by ADP
- Bing Xiao
- , Matthew J. Sanders
- & Steven J. Gamblin
-
-
Research Highlights |
Neuroscience: Enzyme helps pain persist
-
Letter |
 Lkb1 regulates quiescence and metabolic homeostasis of haematopoietic stem cells
Lkb1 regulates quiescence and metabolic homeostasis of haematopoietic stem cells
Haematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) are very sensitive to energetic and oxidative stress, and modulation of the balance between their quiescence and proliferation is needed to respond to metabolic stress while preserving HSCs' long-term regenerative capacity. Here, and in two accompanying studies, it is shown that the tumour suppressor Lkb1 has a crucial role in maintaining energy homeostasis in haematopoietic cells.
- Boyi Gan
- , Jian Hu
- & Ronald A. DePinho
-
News |
 High hopes for arthritis drugs
High hopes for arthritis drugs
Race is on to develop treatments that inhibit signalling proteins.
- Heidi Ledford
-
Letter |
 Calcium-dependent protein kinase 1 is an essential regulator of exocytosis in Toxoplasma
Calcium-dependent protein kinase 1 is an essential regulator of exocytosis in Toxoplasma
Toxoplasma gondii is an opportunistic human pathogen that secretes organelles called micronemes during infection. This is important for parasite motility, host-cell invasion and egress. It is now shown that the secretion of micronemes is dependent on the T. gondii calcium-dependent protein kinase 1. This kinase is not found in the parasite's mammalian hosts, and might represent a valid drug target.
- Sebastian Lourido
- , Joel Shuman
- & L. David Sibley
-
Letter |
 Phosphorylation of histone H3T6 by PKCβI controls demethylation at histone H3K4
Phosphorylation of histone H3T6 by PKCβI controls demethylation at histone H3K4
The amino-terminal tails of histone proteins are subject to a variety of post-translational modifications; addition or removal of these 'marks' facilitates gene activation or silencing. Here, a mechanism is defined that modulates the activity of the dual-specificity histone demethylase LSD1 during androgen-dependent transcription. Androgen-dependent signalling through protein kinase C beta I leads to phosphorylation of a histone amino acid, which prevents demethylation of an adjacent amino acid by LSD1.
- Eric Metzger
- , Axel Imhof
- & Roland Schüle
-
Letter |
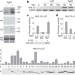 Differential innate immune signalling via Ca2+ sensor protein kinases
Differential innate immune signalling via Ca2+ sensor protein kinases
Plants and animals sense intruding pathogens by using proteins that recognize diverse microbe-associated molecular patterns (MAMPs) and initiate innate immune responses. Early signalling responses in the host include calcium influx, an oxidative burst and transcriptional reprogramming. Here, four calcium-dependent protein kinases are described that function as calcium sensors, act as convergence points for various MAMPs, and are crucial for transcriptional reprogramming and oxidative burst in plants.
- Marie Boudsocq
- , Matthew R. Willmann
- & Jen Sheen

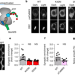 LTP induction by structural rather than enzymatic functions of CaMKII
LTP induction by structural rather than enzymatic functions of CaMKII Enzyme can strengthen memories
Enzyme can strengthen memories