News & Views |
Featured
-
-
News & Views |
 Magnetic proximity boosts chiral quantum emission
Magnetic proximity boosts chiral quantum emission
Chiral single-photon emitters are desirable, versatile tools for quantum information processing. Exploiting proximity to a strain-induced local magnetic field in the van der Waals antiferromagnet NiPS3 enables the emission of high-purity chiral single photons from monolayer WSe2 at zero external magnetic field.
- Jing Tang
- & Xi Ling
-
Article |
 Electrical switching of the edge current chirality in quantum anomalous Hall insulators
Electrical switching of the edge current chirality in quantum anomalous Hall insulators
Thermally assisted spin–orbit torque is used to switch the edge current chirality in mesoscopic quantum anomalous Hall devices.
- Wei Yuan
- , Ling-Jie Zhou
- & Cui-Zu Chang
-
Article |
 Quadrupolar–dipolar excitonic transition in a tunnel-coupled van der Waals heterotrilayer
Quadrupolar–dipolar excitonic transition in a tunnel-coupled van der Waals heterotrilayer
The authors report the emergence of quadrupolar excitons in WS2/WSe2/WS2 trilayer heterostructures where the electron is layer-hybridized in WS2 layers and the hole localizes in WSe2. Quadrupolar excitons exhibit distinct behaviour under electric fields, enriching exciton–exciton interactions.
- Weijie Li
- , Zach Hadjri
- & Ajit Srivastava
-
Article |
 Thermally induced atomic reconstruction into fully commensurate structures of transition metal dichalcogenide layers
Thermally induced atomic reconstruction into fully commensurate structures of transition metal dichalcogenide layers
Encapsulation annealing leads to atomic reconstruction of transition metal dichalcogenide layers into fully commensurate structures with zero twist angle, enabling control over interfacial properties.
- Ji-Hwan Baek
- , Hyoung Gyun Kim
- & Gwan-Hyoung Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Defeating depolarizing fields with artificial flux closure in ultrathin ferroelectrics
Defeating depolarizing fields with artificial flux closure in ultrathin ferroelectrics
Ferroelectric dead layers can form at perovskite interfaces—a major challenge in integrating oxide thin films into devices. Here, by depositing an in-plane-polarized epitaxial buffer layer of Bi5FeTi3O15, out-of-plane polarization is demonstrated in ultrathin films down to the single-unit-cell level.
- Elzbieta Gradauskaite
- , Quintin N. Meier
- & Morgan Trassin
-
Article |
 Long-term stability of aerophilic metallic surfaces underwater
Long-term stability of aerophilic metallic surfaces underwater
Trapped films of air known as plastrons are promising for underwater engineering but typically have short lifetimes. Here, aerophilic titanium alloy surfaces are developed with thermodynamically stabilized plastrons for antifouling applications.
- Alexander B. Tesler
- , Stefan Kolle
- & Wolfgang H. Goldmann
-
News & Views |
 A handy way to rotate chiral spins
A handy way to rotate chiral spins
In a non-collinear antiferromagnet, elementary spins rotate with opposite handedness with respect to the collective octupole magnetic moment when stirred by spin currents.
- Enrique del Barco
- & Andrew D. Kent
-
News & Views |
 The hole truth
The hole truth
By tracking the electrochromic doping front, a hole-limited electrochemical doping mechanism is discovered in organic mixed ionic–electronic conductors.
- Ruiheng Wu
- , Dilara Meli
- & Jonathan Rivnay
-
Article |
 Superconductivity in twisted double bilayer graphene stabilized by WSe2
Superconductivity in twisted double bilayer graphene stabilized by WSe2
The authors use low-temperature transport measurements to report superconductivity in a twisted double bilayer graphene system.
- Ruiheng Su
- , Manabendra Kuiri
- & Joshua Folk
-
-
News & Views |
 A double-helix dislocation in graphene
A double-helix dislocation in graphene
By means of a precise folding–tearing process, screw dislocations with helical cores — appearing in pairs and taking on a DNA-like double-helix structure — are engineered to control the growth of twisted bilayer graphene.
- Pascal Pochet
- & Harley T. Johnson
-
News & Views |
 Ferroelectric hafnia surface in action
Ferroelectric hafnia surface in action
Piezoresponse microscopy and spectroscopy reveal the inextricable role of surface electrochemistry in stabilizing and controlling ferroelectricity in doped hafnia.
- Xia Hong
-
Article |
 Ferroelectricity in hafnia controlled via surface electrochemical state
Ferroelectricity in hafnia controlled via surface electrochemical state
Ferroelectricity in hafnia-based systems seems to be correlated with oxygen vacancy dynamics, but the coupling of this and ferroelectric response is rarely studied. Here it is shown that Hf0.5Zr0.5O2 can be antiferroionic, with antiferroelectric behaviour coupled to surface electrochemistry.
- Kyle P. Kelley
- , Anna N. Morozovska
- & Sergei V. Kalinin
-
Article |
 Handedness anomaly in a non-collinear antiferromagnet under spin–orbit torque
Handedness anomaly in a non-collinear antiferromagnet under spin–orbit torque
In the non-collinear antiferromagnet Mn3Sn, a spin–orbit torque makes the collective octupole moment and individual moments rotate in opposite directions, leading to a sign-reversed switching polarity compared with collinear magnets.
- Ju-Young Yoon
- , Pengxiang Zhang
- & Luqiao Liu
-
Article |
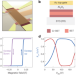 Direct visualization of electronic transport in a quantum anomalous Hall insulator
Direct visualization of electronic transport in a quantum anomalous Hall insulator
Magnetic imaging reveals that a transport current flows in the interior of Cr-(Bi,Sb)2Te3 samples within the quantum anomalous Hall regime, contrary to the common assumption of current flow along the sample edge.
- G. M. Ferguson
- , Run Xiao
- & Katja C. Nowack
-
News & Views |
 Capturing polarizability in sliding ferroelectrics
Capturing polarizability in sliding ferroelectrics
Detailed transmission electron microscopy imaging of the dynamics of domain walls in twisted van der Waals ferroelectrics is obtained, capturing the transition to a hysteretic response.
- Moshe Ben Shalom
-
News & Views |
 Optical control of spin-galvanic currents
Optical control of spin-galvanic currents
Circularly polarized photoexcitation initiates spin domain formation in polycrystalline halide perovskite films with strong spin–orbit coupling and local inversion symmetry breaking, as revealed by ultrafast optical microscopy.
- Richard D. Averitt
-
News & Views |
 A deeper look into argyrodite phonons
A deeper look into argyrodite phonons
By monitoring the lattice dynamics of single-crystal argyrodite Ag8SnSe6 through the superionic transition, low thermal conductivity and ionic transport are found to arise from extreme phonon anharmonicity.
- M. de Boissieu
-
Article
| Open Access Li iontronics in single-crystalline T-Nb2O5 thin films with vertical ionic transport channels
Li iontronics in single-crystalline T-Nb2O5 thin films with vertical ionic transport channels
The two-dimensional layered crystal structure of niobium oxide polymorph T-Nb2O5 exhibits fast Li-ion diffusion that is promising for energy storage applications. Epitaxial growth of single-crystalline T-Nb2O5 thin films with ionic transport channels oriented perpendicular to the surface are now demonstrated.
- Hyeon Han
- , Quentin Jacquet
- & Stuart S. P. Parkin
-
News & Views |
 A new spin on impact ionization
A new spin on impact ionization
Quantum dots are engineered to use dopant states to achieve substantially enhanced impact ionization, which is potentially useful for light-harvesting applications.
- Miri Kazes
- & Dan Oron
-
Article
| Open Access Spin-exchange carrier multiplication in manganese-doped colloidal quantum dots
Spin-exchange carrier multiplication in manganese-doped colloidal quantum dots
Carrier multiplication generates multiple excitons for each absorbed photon but is normally limited by fast phonon-assisted relaxation. Here the authors achieve a threefold enhancement in multiexciton yields in Mn-doped PbSe/CdSe quantum dots, due to very fast spin-exchange interactions between Mn ions and the quantum dots that outpace energy losses arising from phonon emission.
- Ho Jin
- , Clément Livache
- & Victor I. Klimov
-
Article
| Open Access Light-induced hexatic state in a layered quantum material
Light-induced hexatic state in a layered quantum material
The authors report the emergence of a transient hexatic state during laser-induced transformation between two charge-density wave (CDW) phases in a thin film of the CDW material 1T-TaS2.
- Till Domröse
- , Thomas Danz
- & Claus Ropers
-
Article
| Open Access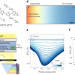 Hole-limited electrochemical doping in conjugated polymers
Hole-limited electrochemical doping in conjugated polymers
Electrochemical doping is assumed to be limited by ion motion due to large mass in mixed ionic-electronic conductors. Here, the authors reveal in a typical polythiophene that electrochemical doping speeds are limited by poor hole transport at low doping levels, leading to much slower switching speeds than expected.
- Scott T. Keene
- , Joonatan E. M. Laulainen
- & George G. Malliaras
-
Editorial |
 A mixed legacy
A mixed legacy
After a decade of intense activity, the Graphene Flagship has helped to establish an incipient European graphene industry, yet mainstream commercialization of graphene products continues to be hindered by limited market readiness and industry acceptance.
-
Comment |
 Revisiting point defects in ionic solids and semiconductors
Revisiting point defects in ionic solids and semiconductors
The study of point defects in non-metallic crystals has become relevant for an increasing number of materials applications. Progress requires a foundation of consistent definitions and terminology. This Comment clarifies the underlying definitions of point defects, encourages the correct use of relative charge for their description and emphasizes their recognition as quasiparticles.
- Roger De Souza
- & George Harrington
-
Article |
 Operando electron microscopy investigation of polar domain dynamics in twisted van der Waals homobilayers
Operando electron microscopy investigation of polar domain dynamics in twisted van der Waals homobilayers
Polar domains have been observed in twist-stacked van der Waals layers, but their dynamics are unexplored. Here, using operando electron microscopy, it is found that polar domains in an antiferroelectric arrangement cannot transition to a ferroelectric state due to topological protection of the domain wall network.
- Kahyun Ko
- , Ayoung Yuk
- & Hyobin Yoo
-
Article |
 Spontaneous orbital polarization in the nematic phase of FeSe
Spontaneous orbital polarization in the nematic phase of FeSe
FeSe does not exhibit magnetic order and lacks a nematic quantum critical point coinciding with optimal superconductivity, suggesting that an orbital mechanism drives nematicity, but direct evidence is lacking. Here, combining X-ray linear dichroism with in situ uniaxial stress, the role of spontaneous orbital polarization in nematic-phase FeSe is determined.
- Connor A. Occhialini
- , Joshua J. Sanchez
- & Riccardo Comin
-
Article |
 Harnessing dislocation motion using an electric field
Harnessing dislocation motion using an electric field
A method to manipulate the dislocation motion via a non-mechanical field alone has remained elusive. Here, using in situ TEM, it is directly observed that dislocation motion can be controlled solely by an external electric field.
- Mingqiang Li
- , Yidi Shen
- & Yu Zou
-
Article |
 Local symmetry breaking drives picosecond spin domain formation in polycrystalline halide perovskite films
Local symmetry breaking drives picosecond spin domain formation in polycrystalline halide perovskite films
The authors apply several advanced methods to probe spin dynamics in polycrystalline halide pervoskites.
- Arjun Ashoka
- , Satyawan Nagane
- & Akshay Rao
-
News & Views |
 Ultrafast push for counterintuitive spintronics
Ultrafast push for counterintuitive spintronics
Current-inducing switching of magnetization is crucial for future magnetic data processing technologies, but switching it with speed and energy efficiency remains challenging. Using femtosecond optical pulses, instead of conventional charge currents, is found to make spintronics not only ultrafast but also counterintuitive.
- Dmytro Afanasiev
- & Alexey V. Kimel
-
Research Briefing |
 Polymer actuation using a Joule-heating-induced ferroelectric phase transition
Polymer actuation using a Joule-heating-induced ferroelectric phase transition
The output mechanical energy densities of ferroelectric polymers remain orders of magnitude smaller than those of piezoelectric ceramics and crystals, limiting their applications in soft actuators. But polymer composites subject to an electro-thermally driven ferroelectric phase transition under low electric fields are now shown to have giant actuation strains and large energy densities.
-
Article |
 Electro-thermal actuation in percolative ferroelectric polymer nanocomposites
Electro-thermal actuation in percolative ferroelectric polymer nanocomposites
Piezoelectric actuators play a critical role in precision positioning devices; however, materials with high actuation strain and mechanical energy density are rare. Here a composite of poly(vinylidene fluoride) and TiO2 demonstrates superior performance in these metrics, with the ferroelectric transition driven by Joule heating.
- Yang Liu
- , Yao Zhou
- & Qing Wang
-
Article |
 Strongly enhanced light–matter coupling of monolayer WS2 from a bound state in the continuum
Strongly enhanced light–matter coupling of monolayer WS2 from a bound state in the continuum
Combining a tungsten disulfide monolayer and a topologically protected bound state in the continuum formed by a one-dimensional photonic crystal, strong light–matter interaction enhancement and large exciton–polariton nonlinearities at room temperature are demonstrated.
- Eugenio Maggiolini
- , Laura Polimeno
- & Dario Ballarini
-
Article |
 Extreme phonon anharmonicity underpins superionic diffusion and ultralow thermal conductivity in argyrodite Ag8SnSe6
Extreme phonon anharmonicity underpins superionic diffusion and ultralow thermal conductivity in argyrodite Ag8SnSe6
Superionic materials are of interest for solid-state batteries or thermoelectrics, yet a clear understanding of the atomistic mechanisms is lacking. Here it is shown that transverse acoustic phonons persist above the superionic transition in argyrodite Ag8SnSe6, and that the free-Se sublattice controls fast Ag cation diffusion.
- Qingyong Ren
- , Mayanak K. Gupta
- & Jie Ma
-
News & Views |
 High-temperature superconductivity survives
High-temperature superconductivity survives
In heavily hole-doped cuprates, superconductivity does not die by simply dissolving into a uniform metal due to the lack of pairing, but rather survives by shattering into nanoscale superconducting puddles.
- Yu He
-
Editorial |
 Ferroelectrics forge forward
Ferroelectrics forge forward
Ferroelectrics have already impacted scientific research and commercial applications, but they still show plenty of potential to surprise.
-
News & Views |
 Flipping antiferromagnetism by light
Flipping antiferromagnetism by light
Antiferromagnetism has a vanishing total magnetization and thus is extremely challenging to manipulate. Now, circularly polarized light is shown to efficiently detect, induce and switch a unique class of antiferromagnets.
- Youngjun Ahn
- & Liuyan Zhao
-
Perspective |
 Spherical ferroelectric solitons
Spherical ferroelectric solitons
Nanoscale ferroelectric topological solitons, such as polar bubbles, polar bubble skyrmions and hopfions, have garnered immense interest due to their emergent properties. This Perspective discusses how these structures form, advances in their study and how they can enable new devices and physics.
- Vivasha Govinden
- , Sergei Prokhorenko
- & Nagarajan Valanoor
-
News & Views |
 Correlated states shine brighter
Correlated states shine brighter
An optical spectroscopy approach unravels different layer-dependent correlated electron phases in a two-dimensional semiconductor heterobilayer.
- Mauro Brotons-Gisbert
- & Brian D. Gerardot
-
Article |
 Layer-dependent correlated phases in WSe2/MoS2 moiré superlattice
Layer-dependent correlated phases in WSe2/MoS2 moiré superlattice
The authors demonstrate electrical on/off switching of interlayer interactions in tungsten diselenide/molybdenum disulfide heterobilayers, the phase diagram of which contains layer-dependent correlated regions that reveal the role of strong correlations in interlayer exciton dynamics.
- Qinghai Tan
- , Abdullah Rasmita
- & Weibo Gao
-
Article |
 Tunable spin and valley excitations of correlated insulators in Γ-valley moiré bands
Tunable spin and valley excitations of correlated insulators in Γ-valley moiré bands
Electronic compressibility measurements of twisted double-bilayer WSe2 reveal correlated insulators with spin-polaron charged excitations, as well as close competition between moiré bands at Γ and K valleys.
- Benjamin A. Foutty
- , Jiachen Yu
- & Benjamin E. Feldman
-
Article |
 Covalent organic framework atropisomers with multiple gas-triggered structural flexibilities
Covalent organic framework atropisomers with multiple gas-triggered structural flexibilities
Soft porous crystals combine high crystallinity with structural transformability, potentially enabling applications. Here, an atropisomeric covalent organic framework is reported, which demonstrates different structural transformations upon exposure to different gases.
- Chengjun Kang
- , Zhaoqiang Zhang
- & Dan Zhao
-
News & Views |
 Atomic heteroepitaxy for topological superconductivity
Atomic heteroepitaxy for topological superconductivity
Epitaxial topological heterostructures of (Bi,Sb)2Te3/graphene/gallium have been achieved using molecular-beam epitaxy, providing the opportunity to access Majorana zero modes in electrical transport when combined with van der Waals tunnel junctions.
- Faxian Xiu
-
Article |
 Observation of anti-damping spin–orbit torques generated by in-plane and out-of-plane spin polarizations in MnPd3
Observation of anti-damping spin–orbit torques generated by in-plane and out-of-plane spin polarizations in MnPd3
The authors address spin–orbit torques and magnetization switching in MnPd3/CoFeB hetrostructures.
- Mahendra DC
- , Ding-Fu Shao
- & Shan X. Wang
-
News & Views |
 A magnetic field for each electron
A magnetic field for each electron
The arrangement of magnetic ions between layers of NbS2 affects it as though a giant magnetic field is applied in different directions for electrons moving with opposite velocities. This discovery goes beyond the reach of conventional magnets, and opens up the way to custom-made effective fields engineered to guide materials into new territory.
- Jasper van Wezel
-
News & Views |
 A new way to Weyl
A new way to Weyl
Scientists have realized Weyl modes by exposing a topological insulator to large magnetic fields. Their effort enriches the toolbox to design, engineer and manipulate topological materials for physics research and materials applications.
- Zhengguang Lu
- & Long Ju
-
News & Views |
 Tunnelling electrons locally ignite excitons
Tunnelling electrons locally ignite excitons
Using low-temperature scanning tunnelling microscopy on a MoSe2/few-layer graphene heterostructure enables localized exciton generation and mapping with atomic-scale spatial resolution.
- Libai Huang
-
Article |
 Resolving the polar interface of infinite-layer nickelate thin films
Resolving the polar interface of infinite-layer nickelate thin films
Nickelate superconductivity has so far been limited to thin films, raising questions about the role of the polar substrate–film interface. Here the authors utilize advanced characterization techniques to reveal the interfacial atomic structure and its relevance for superconductivity.
- Berit H. Goodge
- , Benjamin Geisler
- & Lena F. Kourkoutis
-
Article |
 Magnetic detection under high pressures using designed silicon vacancy centres in silicon carbide
Magnetic detection under high pressures using designed silicon vacancy centres in silicon carbide
Optically detected magnetic resonance of nitrogen vacancy centres in diamond enables the detection of pressure-induced phase transitions, but interpreting their magnetic resonance spectra remains challenging. Here the authors propose implanted silicon vacancy defects in 4H-SiC for in situ magnetic phase detection at high pressures.
- Jun-Feng Wang
- , Lin Liu
- & Guang-Can Guo
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Bose–Einstein condensates
- Electronic properties and materials
- Ferroelectrics and multiferroics
- Ferromagnetism
- Magnetic properties and materials
- Molecular electronics
- Phase transitions and critical phenomena
- Quantum fluids and solids
- Quantum Hall
- Semiconductors
- Spintronics
- Structure of solids and liquids
- Superconducting properties and materials
- Surfaces, interfaces and thin films
- Topological matter

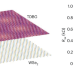 Revived superconductivity in twisted double bilayer graphene
Revived superconductivity in twisted double bilayer graphene Seeing polarization reverse
Seeing polarization reverse