Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Unzipped genome assemblies of polyploid root-knot nematodes reveal unusual and clade-specific telomeric repeats
Unzipped genome assemblies of polyploid root-knot nematodes reveal unusual and clade-specific telomeric repeats
Telomeres protect the extremities of linear chromosomes and are involved in ageing, senescence and genome stability. Here, the authors have identified peculiar and specific telomeric DNA repeats in the genomes of devastating plant-parasitic nematodes, opening new perspectives for their control.
- Ana Paula Zotta Mota
- , Georgios D. Koutsovoulos
- & Etienne G. J. Danchin
-
Article
| Open Access Orchestrating chromosome conformation capture analysis with Bioconductor
Orchestrating chromosome conformation capture analysis with Bioconductor
The Bioconductor project aims to develop R packages for analysis of genomic datasets. Here the authors show the HiCExperiment package suite and its companion online book (https://bioconductor.org/books/OHCA/) which present data structures, computational methods and visualization tools available in Bioconductor to investigate chromatin conformation capture (3C) data in R.
- Jacques Serizay
- , Cyril Matthey-Doret
- & Romain Koszul
-
Article
| Open Access Logical design of synthetic cis-regulatory DNA for genetic tracing of cell identities and state changes
Logical design of synthetic cis-regulatory DNA for genetic tracing of cell identities and state changes
Descriptive data in biomedical research are expanding rapidly, but functional validation methods lag behind. Here, authors present Logical Synthetic cis-regulatory DNA, a framework to design reporters that mark cellular states and pathways, showcasing its applicability to complex phenotypic states.
- Carlos Company
- , Matthias Jürgen Schmitt
- & Gaetano Gargiulo
-
Article
| Open Access The impacts of active and self-supervised learning on efficient annotation of single-cell expression data
The impacts of active and self-supervised learning on efficient annotation of single-cell expression data
Cell type annotation for single-cell data is challenging. Here, authors explore active and self-supervised learning and introduce adaptive reweighting as a tailored heuristic, demonstrating competitive performance and showing that incorporating prior knowledge enhances cell type annotation accuracy.
- Michael J. Geuenich
- , Dae-won Gong
- & Kieran R. Campbell
-
Article
| Open Access Orientation-invariant autoencoders learn robust representations for shape profiling of cells and organelles
Orientation-invariant autoencoders learn robust representations for shape profiling of cells and organelles
In image analysis, the shape properties of cells/organelles should be unaffected by image orientation. Conventional autoencoder (AE) methods can be sensitive to orientation. Here, the authors develop an unsupervised AE method that learns robust, orientation-invariant representations.
- James Burgess
- , Jeffrey J. Nirschl
- & Serena Yeung-Levy
-
Article
| Open Access Improving polygenic risk prediction in admixed populations by explicitly modeling ancestral-differential effects via GAUDI
Improving polygenic risk prediction in admixed populations by explicitly modeling ancestral-differential effects via GAUDI
Most polygenic risk score (PRS) methods focus only on individuals with distinct primary continental ancestry, without accommodating recently-admixed individuals. Here, the authors develop a novel penalized regression-based PRS method specifically designed for admixed individuals.
- Quan Sun
- , Bryce T. Rowland
- & Yun Li
-
Article
| Open Access Tigerfish designs oligonucleotide-based in situ hybridization probes targeting intervals of highly repetitive DNA at the scale of genomes
Tigerfish designs oligonucleotide-based in situ hybridization probes targeting intervals of highly repetitive DNA at the scale of genomes
Repetitive DNA intervals play important roles in the nucleus but are difficult to study due to their reiterated nature. Tigerfish introduces a novel computational platform for the design of interval-specific in situ hybridization probes.
- Robin Aguilar
- , Conor K. Camplisson
- & Brian J. Beliveau
-
Article
| Open Access Detection of senescence using machine learning algorithms based on nuclear features
Detection of senescence using machine learning algorithms based on nuclear features
Identifying senescence is complicated by a lack of universal markers. Here, Duran et al. use nuclear morphology features to devise machine-learning classifiers that detect senescence in cell lines and liver sections of patients and mouse models of aging and disease.
- Imanol Duran
- , Joaquim Pombo
- & Jesús Gil
-
Article
| Open Access Local structural preferences in shaping tau amyloid polymorphism
Local structural preferences in shaping tau amyloid polymorphism
In this work, using a combination of Cryo-EM, in-cell experiments and biophysical analysis, the authors decoded the aggregation propensity of tau, revealing 5 central hot spots in its primary sequence and identify PAM4 as short segment that determines both the structure, as well as the cellular propagation of tau aggregates extracted from Alzheimer’s disease, corticobasal degeneration, and progressive supranuclear palsy patients.
- Nikolaos Louros
- , Martin Wilkinson
- & Joost Schymkowitz
-
Article
| Open Access A sequence-aware merger of genomic structural variations at population scale
A sequence-aware merger of genomic structural variations at population scale
Existing tools for structural variations (SVs) calling and merging often lead to fragmented SVs and the potential of introducing unnecessary errors. Here, the authors report the PanPop pipeline to address these issues by implementing sequence-aware SV merging algorithm to efficiently merge SVs of various types.
- Zeyu Zheng
- , Mingjia Zhu
- & Yongzhi Yang
-
Matters Arising
| Open Access Reply to: Assessing the precision of morphogen gradients in neural tube development
Reply to: Assessing the precision of morphogen gradients in neural tube development
- Roman Vetter
- & Dagmar Iber
-
Article
| Open Access Congenital heart disease detection by pediatric electrocardiogram based deep learning integrated with human concepts
Congenital heart disease detection by pediatric electrocardiogram based deep learning integrated with human concepts
Congenital heart disease is life threatening, and its screening is complex and costly. Here, authors use AI to detect the disease based on pediatric electrocardiogram, suggesting superior performance over cardiologists.
- Jintai Chen
- , Shuai Huang
- & Huiying Liang
-
Article
| Open Access DeepFocus: fast focus and astigmatism correction for electron microscopy
DeepFocus: fast focus and astigmatism correction for electron microscopy
High-throughput electron microscopy demands minimal human intervention and high image quality. Here, authors introduce DeepFocus, a data-driven method for aberration correction in electron microscopy, robust for low SNR images, fast and easily adaptable to microscopes and samples. Peer Review Information: Nature Communications thanks Yang Zhang and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work. A peer review file is available.
- P. J. Schubert
- , R. Saxena
- & J. Kornfeld
-
Article
| Open Access ContScout: sensitive detection and removal of contamination from annotated genomes
ContScout: sensitive detection and removal of contamination from annotated genomes
It is unclear whether naturally evolved de novo proteins have stable, folded structures. Here, systematic identification and structural modeling of de novo genes, this study reveals that a small subset of these proteins may have well-folded structures, and were likely born with these structures.
- Balázs Bálint
- , Zsolt Merényi
- & László G. Nagy
-
Article
| Open Access Effect of aging on the human myometrium at single-cell resolution
Effect of aging on the human myometrium at single-cell resolution
Age-associated myometrial dysfunction can cause complications during pregnancy and labor. Here, the authors report that aging myometrium is characterized by diminished contractile capillary cells, altered gene expression, and disrupted cellular communication leading to impaired angiogenesis, increased fibrosis and inflammation.
- Paula Punzon-Jimenez
- , Alba Machado-Lopez
- & Aymara Mas
-
Article
| Open Access scDisInFact: disentangled learning for integration and prediction of multi-batch multi-condition single-cell RNA-sequencing data
scDisInFact: disentangled learning for integration and prediction of multi-batch multi-condition single-cell RNA-sequencing data
Here the authors propose a deep learning model that integrates multi-condition, multi-batch single-cell RNA-sequencing datasets. The model disentangles biological variation (condition effect) from technical confounders (batch effect) and overcomes some limitations of existing approaches.
- Ziqi Zhang
- , Xinye Zhao
- & Xiuwei Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Longitudinal quantification of Bifidobacterium longum subsp. infantis reveals late colonization in the infant gut independent of maternal milk HMO composition
Longitudinal quantification of Bifidobacterium longum subsp. infantis reveals late colonization in the infant gut independent of maternal milk HMO composition
Here, the authors develop a high-throughput method to quantify Bifidobacterium longum subsp. infantis (BL. infantis), a proficient HMO-utilizer, from metagenomic sequencing, and applied it to a longitudinal cohort consisting of 21 mother-infant dyads, suggesting BL. infantis colonization to start late in the breast-feeding period.
- Dena Ennis
- , Shimrit Shmorak
- & Moran Yassour
-
Article
| Open Access Single-cell analysis of psoriasis resolution demonstrates an inflammatory fibroblast state targeted by IL-23 blockade
Single-cell analysis of psoriasis resolution demonstrates an inflammatory fibroblast state targeted by IL-23 blockade
Single cell profiling of tissue from patients undergoing therapy has the potential to identify drug-induced immune changes. Here the authors show a skin scRNA-seq study of psoriasis patients treated with an IL-23 inhibitor and characterize changes in cell states during early treatment.
- Luc Francis
- , Daniel McCluskey
- & Satveer K. Mahil
-
Article
| Open Access Semi-supervised integration of single-cell transcriptomics data
Semi-supervised integration of single-cell transcriptomics data
Batch effects hinder multi-sample single-cell data analyses. Here, authors present STACAS, a scalable single-cell RNA-seq data integration tool that uses prior cell type knowledge to preserve biological variability, demonstrating robustness to noisy input cell type labels.
- Massimo Andreatta
- , Léonard Hérault
- & Santiago J. Carmona
-
Article
| Open Access Utility of long-read sequencing for All of Us
Utility of long-read sequencing for All of Us
Using All of Us pilot data, the authors compared short- and long-read performance across medically relevant genes and showcased the utility of long reads to improve variant detection and phasing in easy and hard to resolve medically relevant genes.
- M. Mahmoud
- , Y. Huang
- & F. J. Sedlazeck
-
Article
| Open Access Single-cell multiomics decodes regulatory programs for mouse secondary palate development
Single-cell multiomics decodes regulatory programs for mouse secondary palate development
Development of the secondary palate is a complex process. Here, the authors profile mouse palatogenesis through single-cell multiome sequencing, revealing dynamic gene regulation across embryonic days (E) 12.5, E13.5, E14.0, and E14.5.
- Fangfang Yan
- , Akiko Suzuki
- & Zhongming Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Trajectory inference across multiple conditions with condiments
Trajectory inference across multiple conditions with condiments
scRNA-Seq has enabled the study of dynamic systems such as response to a drug at the individual cell and gene levels. Here the authors introduce a framework to interpret differences at the trajectory, cell populations, and individual gene levels.
- Hector Roux de Bézieux
- , Koen Van den Berge
- & Sandrine Dudoit
-
Article
| Open Access SiFT: uncovering hidden biological processes by probabilistic filtering of single-cell data
SiFT: uncovering hidden biological processes by probabilistic filtering of single-cell data
Cells simultaneously encode multiple signals, some harder to recover. Here, authors introduce SiFT (Signal FilTering), a kernel-based projection method, revealing underlying biological processes in single-cell data.
- Zoe Piran
- & Mor Nitzan
-
Article
| Open Access Compositional and temporal division of labor modulates mixed sugar fermentation by an engineered yeast consortium
Compositional and temporal division of labor modulates mixed sugar fermentation by an engineered yeast consortium
Synthetic microbial communities are suitable for mixed substrates fermentation and long metabolic pathway engineering. Here, the authors combine fermentation experiments with mathematical modeling to reveal the effect of compositional and temporal changes on division of labor in cellulosic ethanol production using two yeast strains.
- Jonghyeok Shin
- , Siqi Liao
- & Yong-Su Jin
-
Article
| Open Access Anti-correlated feature selection prevents false discovery of subpopulations in scRNAseq
Anti-correlated feature selection prevents false discovery of subpopulations in scRNAseq
Typical single-cell RNAseq pipelines will subcluster homogeneous cells. Here, authors present a computational algorithm for accurately identifying cell-type marker genes in single-cell data analysis with a low false discovery rate.
- Scott R. Tyler
- , Daniel Lozano-Ojalvo
- & Eric E. Schadt
-
Article
| Open Access Emergence of periodic circumferential actin cables from the anisotropic fusion of actin nanoclusters during tubulogenesis
Emergence of periodic circumferential actin cables from the anisotropic fusion of actin nanoclusters during tubulogenesis
Periodic circumferential cytoskeletons support biological tube formation. Here, the authors show that self-assembled actin nanoclusters undergo biased fusion and develop into periodic cables in response to the membrane anisotropy of the expanding Drosophila tracheal tube.
- Sayaka Sekine
- , Mitsusuke Tarama
- & Shigeo Hayashi
-
Article
| Open Access Rational strain design with minimal phenotype perturbation
Rational strain design with minimal phenotype perturbation
No consensus exists on the computationally tractable use of dynamic models for strain design. To tackle this, the authors report a framework, nonlinear-dynamic-model-assisted rational metabolic engineering design, for efficiently designing robust, artificially engineered cellular organisms.
- Bharath Narayanan
- , Daniel Weilandt
- & Vassily Hatzimanikatis
-
Article
| Open Access Human whole-exome genotype data for Alzheimer’s disease
Human whole-exome genotype data for Alzheimer’s disease
The heterogeneity of whole-exome sequencing (WES) data generation methods presents a challenge to joint analysis. Here, the authors present a bioinformatics strategy to generate high-quality data from processing diversely generated WES samples, as applied in the Alzheimer’s Disease Sequencing Project.
- Yuk Yee Leung
- , Adam C. Naj
- & Li-San Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Ultraconserved bacteriophage genome sequence identified in 1300-year-old human palaeofaeces
Ultraconserved bacteriophage genome sequence identified in 1300-year-old human palaeofaeces
Bacterial viruses (phages) are generally recognised as rapidly evolving biological entities. Here, Rozwalak et al. analyse DNA sequence datasets generated from ancient palaeofaeces and identify 298 phage genomes from the last 5300 years, including a 1300-year-old phage genome nearly identical to a present-day virus that infects human gut bacteria.
- Piotr Rozwalak
- , Jakub Barylski
- & Andrzej Zielezinski
-
Article
| Open Access MARS an improved de novo peptide candidate selection method for non-canonical antigen target discovery in cancer
MARS an improved de novo peptide candidate selection method for non-canonical antigen target discovery in cancer
Detection of neoepitopes from tumours is time consuming and requires the integration of genomic and/or RNA sequencing expression data. Here, the authors propose a machine learning method to enable direct identification of additional, tumour-specific sequences using mass spectrometry through integration of de novo peptide sequencing scores, MHC class I binding prediction, and peptide retention time prediction.
- Hanqing Liao
- , Carolina Barra
- & Nicola Ternette
-
Article
| Open Access Segment anything in medical images
Segment anything in medical images
Segmentation is an important fundamental task in medical image analysis. Here the authors show a deep learning model for efficient and accurate segmentation across a wide range of medical image modalities and anatomies.
- Jun Ma
- , Yuting He
- & Bo Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular quantitative trait loci in reproductive tissues impact male fertility in cattle
Molecular quantitative trait loci in reproductive tissues impact male fertility in cattle
Investigating the genetics of male fertility requires comprehensive genotype and phenotype data. Here, the authors characterize the transcriptional complexity of bovine male reproductive tissues to identify loci associated with male fertility.
- Xena Marie Mapel
- , Naveen Kumar Kadri
- & Hubert Pausch
-
Article
| Open Access Using big sequencing data to identify chronic SARS-Coronavirus-2 infections
Using big sequencing data to identify chronic SARS-Coronavirus-2 infections
Chronic SARS-CoV-2 infections have been hypothesised to be sources of new variants. Here, the authors use large-scale genome sequencing data to identify mutations predictive of chronic infections, which may therefore be relevant in future variants.
- Sheri Harari
- , Danielle Miller
- & Adi Stern
-
Article
| Open Access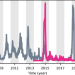 Shifting patterns of dengue three years after Zika virus emergence in Brazil
Shifting patterns of dengue three years after Zika virus emergence in Brazil
Dengue virus circulation was unusually low in Brazil in 2015-2018 following the emergence of Zika virus, but subsequently resurged causing large outbreaks with a lower mean age of infection. Here, the authors use mathematical modelling to investigate the links between dengue dynamics and prior Zika infection.
- Francesco Pinotti
- , Marta Giovanetti
- & José Lourenço
-
Article
| Open Access Structure-guided discovery of anti-CRISPR and anti-phage defense proteins
Structure-guided discovery of anti-CRISPR and anti-phage defense proteins
Bacteria use various defense systems to protect themselves from phage infection, and phages have evolved diverse counter-defense measures to overcome host defenses. Here, the authors use protein structural similarity and gene co-occurrence analyses for identification of new anti-phage and counter-defense systems.
- Ning Duan
- , Emily Hand
- & Akintunde Emiola
-
Article
| Open Access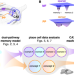 Distinguishing examples while building concepts in hippocampal and artificial networks
Distinguishing examples while building concepts in hippocampal and artificial networks
While the hippocampus is well-known to store specific memories, it can also learn common features that are shared across individual memories. Here, the authors show how this ability arises from dual input pathways and how it can inspire better machine learning methods.
- Louis Kang
- & Taro Toyoizumi
-
Article
| Open Access PROST: quantitative identification of spatially variable genes and domain detection in spatial transcriptomics
PROST: quantitative identification of spatially variable genes and domain detection in spatial transcriptomics
Understanding biological mechanisms requires a thorough exploration of spatiotemporal transcriptional patterns in complex tissues. Here, authors present PROST to quantify spatial gene expression patterns and detect spatial domains using spatial transcriptomics data of varying resolutions.
- Yuchen Liang
- , Guowei Shi
- & Zhonghui Tang
-
Article
| Open Access Clinical application of tumour-in-normal contamination assessment from whole genome sequencing
Clinical application of tumour-in-normal contamination assessment from whole genome sequencing
Assessing tumour contamination in normal samples is critical for accurate variant calling in cancer samples. Here, the authors develop TINC, a computational method to determine the level of tumour in normal contamination, and demonstrate its application in the Genomics England 100,000 Genomes Project dataset.
- Jonathan Mitchell
- , Salvatore Milite
- & Giulio Caravagna
-
Article
| Open Access Longitudinal single cell atlas identifies complex temporal relationship between type I interferon response and COVID-19 severity
Longitudinal single cell atlas identifies complex temporal relationship between type I interferon response and COVID-19 severity
Single cell transcriptomics can reveal at high resolution the body’s response to infection. Here the authors have applied this technology to a longitudinal SARS-CoV-2 infected cohort and identified gene expression changes that may predict disease severity and reveal the underlying molecular mechanisms.
- Quy Xiao Xuan Lin
- , Deepa Rajagopalan
- & Shyam Prabhakar
-
Article
| Open Access Determinants of epidemic size and the impacts of lulls in seasonal influenza virus circulation
Determinants of epidemic size and the impacts of lulls in seasonal influenza virus circulation
Seasonal influenza levels were unusually low when non-pharmaceutical interventions for COVID-19 were in place. Here, the authors analyse serological and epidemiological evidence for the hypothesis that such lulls in influenza transmission lead to reduced immunity and therefore larger epidemics in subsequent seasons.
- Simon P. J. de Jong
- , Zandra C. Felix Garza
- & Colin A. Russell
-
Article
| Open Access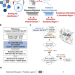 From interaction networks to interfaces, scanning intrinsically disordered regions using AlphaFold2
From interaction networks to interfaces, scanning intrinsically disordered regions using AlphaFold2
Here, the authors show that AlphaFold2 accurately predicts protein interfaces involving disordered regions. Combining different delimitations and sequence alignments increases the success rate, while scanning short overlapping fragments identifies binding sites.
- Hélène Bret
- , Jinmei Gao
- & Raphaël Guerois
-
Article
| Open Access Leveraging single-cell ATAC-seq and RNA-seq to identify disease-critical fetal and adult brain cell types
Leveraging single-cell ATAC-seq and RNA-seq to identify disease-critical fetal and adult brain cell types
This study analyzed data from human cells assayed using single-cell technologies, together with data associating genetic variants to disease, to identify fetal and brain cell types whose biologically critically influences the etiology of disease.
- Samuel S. Kim
- , Buu Truong
- & Alkes L. Price
-
Article
| Open Access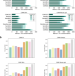 Effective binning of metagenomic contigs using contrastive multi-view representation learning
Effective binning of metagenomic contigs using contrastive multi-view representation learning
Here, the authors present COMEBin, a metagenomics binning method based on contrastive multi-view representation learning that uses data augmentation to generate multiple fragments (views) of each contig, resulting in high-quality embeddings of heterogeneous features. COMEBin outperforms state-of-the art binning methods, particularly in recovering near-complete genomes from real environmental samples.
- Ziye Wang
- , Ronghui You
- & Shanfeng Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access Haplotype-aware modeling of cis-regulatory effects highlights the gaps remaining in eQTL data
Haplotype-aware modeling of cis-regulatory effects highlights the gaps remaining in eQTL data
Genetic variants that influence gene expression play a major role in human phenotypic variability and disease susceptibility. Here, the authors introduce a computational method to estimate the regulatory effect size in genes with multiple conditionally independent regulatory variants.
- Nava Ehsan
- , Bence M. Kotis
- & Pejman Mohammadi
-
Article
| Open Access Systematic detection of co-infection and intra-host recombination in more than 2 million global SARS-CoV-2 samples
Systematic detection of co-infection and intra-host recombination in more than 2 million global SARS-CoV-2 samples
SARS-CoV-2 coinfections may lead to recombination events which could be important in the emergence of new variants. Here, the authors develop an automated bioinformatics pipeline to identify coinfections in genomic data and test it on >2 million publicly available raw read data sets collected globally.
- Orsolya Anna Pipek
- , Anna Medgyes-Horváth
- & István Csabai
-
Article
| Open Access BIDCell: Biologically-informed self-supervised learning for segmentation of subcellular spatial transcriptomics data
BIDCell: Biologically-informed self-supervised learning for segmentation of subcellular spatial transcriptomics data
Subcellular in situ spatial transcriptomics offers the promise to address biological problems that were previously inaccessible but requires accurate cell segmentation to uncover insights. Here, authors present BIDCell, a biologically informed, deep learning-based cell segmentation framework.
- Xiaohang Fu
- , Yingxin Lin
- & Jean Y. H. Yang
-
Article
| Open Access DiffDomain enables identification of structurally reorganized topologically associating domains
DiffDomain enables identification of structurally reorganized topologically associating domains
Topologically associating domains (TADs) are critical structural units in 3D genome organization, and their reorganization between health and disease states is associated with essential genome functions. However, computational methods for identifying reorganized TADs are still in the early stages of development. Here, the authors present an algorithm leveraging random matrix theory to identify reorganized TADs.
- Dunming Hua
- , Ming Gu
- & Dechao Tian
-
Article
| Open Access Cryo-EM structure and B-factor refinement with ensemble representation
Cryo-EM structure and B-factor refinement with ensemble representation
Cryo-EM is the go-to method for visualizing large, flexible biomolecules. Here, authors introduce a new Gaussian mixture modelling method for cryo-EM modelling tasks, including refinement, composite map generation and ensemble representation.
- Joseph G. Beton
- , Thomas Mulvaney
- & Maya Topf
-
Article
| Open Access Ligand coupling mechanism of the human serotonin transporter differentiates substrates from inhibitors
Ligand coupling mechanism of the human serotonin transporter differentiates substrates from inhibitors
The serotonin transporter, targeted by several medications, terminates neurotransmission by clearing serotonin from the synaptic cleft. Combining biochemical results with in silico data, the authors show the key interactions that initiate substrate transport.
- Ralph Gradisch
- , Katharina Schlögl
- & Thomas Stockner
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Biochemical reaction networks
- Cellular signalling networks
- Classification and taxonomy
- Communication and replication
- Computational models
- Computational neuroscience
- Computational platforms and environments
- Data acquisition
- Data integration
- Data mining
- Data processing
- Data publication and archiving
- Databases
- Functional clustering
- Gene ontology
- Gene regulatory networks
- Genome informatics
- Hardware and infrastructure
- High-throughput screening
- Image processing
- Literature mining
- Machine learning
- Microarrays
- Network topology
- Phylogeny
- Power law
- Predictive medicine
- Probabilistic data networks
- Programming language
- Protein analysis
- Protein design
- Protein folding
- Protein function predictions
- Protein structure predictions
- Proteome informatics
- Quality control
- Scale invariance
- Sequence annotation
- Software
- Standards
- Statistical methods
- Virtual drug screening

 Protein structure generation via folding diffusion
Protein structure generation via folding diffusion