Featured
-
-
Article |
 A two-dimensional conjugated aromatic polymer via C–C coupling reaction
A two-dimensional conjugated aromatic polymer via C–C coupling reaction
The synthesis of well-defined planar polymers presents a significant challenge for chemists seeking to investigate their potential for use in emerging technologies. Now, a two-dimensional conjugated aromatic polymer has been synthesized via endogenous solid-state polymerization of pre-arranged monomers, and its performance as an organic anode in an ambient temperature sodium cell tested.
- Wei Liu
- , Xin Luo
- & Kian Ping Loh
-
News & Views |
 Moving into another dimension
Moving into another dimension
Molecular daisy-chain structures are typically made up of two interlocked components and can exhibit muscle-like contraction and extension in one dimension. Zinc-based multicomponent systems that can operate in two and three dimensions have now been designed and synthesized.
- Karine Fournel-Marotte
- & Frédéric Coutrot
-
Perspective |
 Interplay between defects, disorder and flexibility in metal-organic frameworks
Interplay between defects, disorder and flexibility in metal-organic frameworks
Although metal–organic frameworks are often seen as rigid crystalline structures, there is growing evidence that large-scale flexibility, the presence of defects, and long-range disorder are not the exception, but rather the norm. Here we propose that these concepts are inescapably intertwined, and the interfaces between them offer prospects for enhancement of materials' functionalities.
- Thomas D. Bennett
- , Anthony K. Cheetham
- & François-Xavier Coudert
-
Article |
 Atomically precise organomimetic cluster nanomolecules assembled via perfluoroaryl-thiol SNAr chemistry
Atomically precise organomimetic cluster nanomolecules assembled via perfluoroaryl-thiol SNAr chemistry
The operational simplicity of modifying the surfaces of thiol-capped gold nanoparticles has been a hallmark of their success in materials chemistry, despite having limited control over the surface composition. Now, SNAr chemistry on activated perfluoroaromatics has been shown to mimic this simplicity and allow for the synthesis of atomically precise nanomolecules.
- Elaine A. Qian
- , Alex I. Wixtrom
- & Alexander M. Spokoyny
-
Article |
 Surfactant-free single-layer graphene in water
Surfactant-free single-layer graphene in water
Aggregation usually prevents dissolution of graphene in water. Now, hydroxide ion adsorption has been shown to allow the stabilization of true single-layer graphene in water — with no surfactant required — so long as the liquid is degassed beforehand. The resulting aqueous dispersions can contain high concentrations of exfoliated graphene that are stable for several months.
- George Bepete
- , Eric Anglaret
- & Carlos Drummond
-
-
Article |
 From helical to planar chirality by on-surface chemistry
From helical to planar chirality by on-surface chemistry
Flat, prochiral molecules form chiral adsorbates on achiral surfaces, but such assemblies are globally racemic. Now, it is shown that this mirror symmetry can be broken through stereocontrolled on-surface synthesis. Enantiopure helicene molecules can be transformed into flat, enantiofacially adsorbed products through a cascade of reactions on Ag(111) monitored by high-resolution scanning probe microscopy.
- Oleksandr Stetsovych
- , Martin Švec
- & Ivo Starý
-
Article |
 Ionic solutions of two-dimensional materials
Ionic solutions of two-dimensional materials
Isolating nanoscale species in liquids permits their scalable manipulation, enabling numerous fundamental and applied processes. Thus, achieving true dissolution of 2D materials is particularly desirable. Now, ionic salts of a range of important layered materials have been shown to spontaneously dissolve, yielding solutions of charged, monodisperse, undamaged and easy-to-manipulate 2D nanosheets.
- Patrick L. Cullen
- , Kathleen M. Cox
- & Christopher A. Howard
-
Article |
 Self-assembly of nanoparticles into biomimetic capsid-like nanoshells
Self-assembly of nanoparticles into biomimetic capsid-like nanoshells
Biomolecular nanoscale compartments are ubiquitous in living systems. Although their formation is fairly straightforward, the same cannot be said of their inorganic counterparts. In this study, uniform nanoshells are observed self-assembling from stabilizer-free inorganic nanoparticles in water, under ambient conditions, and without the need for spherical tiling. This enables further study of inorganic prebiotic systems and compartmentalized biomimetic catalysis.
- Ming Yang
- , Henry Chan
- & Nicholas A. Kotov
-
-
Article |
 Multistep nucleation of nanocrystals in aqueous solution
Multistep nucleation of nanocrystals in aqueous solution
Crystals grow from nuclei. In systems where nuclei are nanometre-sized and form quickly, it is difficult to determine the mechanism of their formation. Now, through in situ TEM, the demixing of a supersaturated aqueous gold solution into metastable gold-poor and gold-rich liquid phases is observed, the latter yielding stable clusters that become nuclei for nanocrystal growth.
- N. Duane Loh
- , Soumyo Sen
- & Utkur Mirsaidov
-
Article |
 Ballbot-type motion of N-heterocyclic carbenes on gold surfaces
Ballbot-type motion of N-heterocyclic carbenes on gold surfaces
STM investigations and first principles calculations provide an understanding of the microscopic mechanism behind the mobility of N-heterocyclic carbenes (NHCs) on gold surfaces. Now, it is shown that a ballbot-type motion allows the formation of self-assembled monolayers due to the NHC extracting a gold atom from the surface, leading to a ligated gold adatom.
- Gaoqiang Wang
- , Andreas Rühling
- & Harald Fuchs
-
Article |
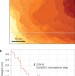 In situ observation of self-assembled hydrocarbon Fischer–Tropsch products on a cobalt catalyst
In situ observation of self-assembled hydrocarbon Fischer–Tropsch products on a cobalt catalyst
During the Fischer-Tropsch catalytic reaction, alkanes are synthesized from carbon monoxide and hydrogen at high pressure and temperature. Now it is shown using scanning tunnelling imaging of a cobalt surface during reaction that linear alkane product molecules of a specific length self-assemble on terraces, facilitating the desorption of new product molecules created at step sites.
- Violeta Navarro
- , Matthijs A. van Spronsen
- & Joost W. M. Frenken
-
Article |
 Fusing tetrapyrroles to graphene edges by surface-assisted covalent coupling
Fusing tetrapyrroles to graphene edges by surface-assisted covalent coupling
Lateral anchoring of heteromolecules to graphene paves the way for the creation of hybrid materials with tunable properties. Now, following a surface-assisted dehydrogenative coupling reaction, the edges of graphene on silver have been functionalized with porphines. This enables the assembly of well-defined multifunctional graphene-based nanostructures.
- Yuanqin He
- , Manuela Garnica
- & Johannes V. Barth
-
Article |
 Peptide tessellation yields micrometre-scale collagen triple helices
Peptide tessellation yields micrometre-scale collagen triple helices
Natural collagen contains triple helices that are approximately 1,000 residues in length and cannot be formed by chemical synthesis. Now, short collagen-mimetic peptides that self-assemble into three-stranded helices have been designed. These peptides are inspired by the mathematics of tessellations, and the triple helices formed via this approach match or exceed the length of those found in natural collagen.
- I. Caglar Tanrikulu
- , Audrey Forticaux
- & Ronald T. Raines
-
Article |
 Observation of trapped-hole diffusion on the surfaces of CdS nanorods
Observation of trapped-hole diffusion on the surfaces of CdS nanorods
Photoexcited holes in CdS nanocrystals rapidly trap to the surface and although they are integral to nanocrystal photophysics and photochemistry, their dynamics have remained elusive. Time-resolved spectroscopy and theoretical modelling have now revealed that trapped holes in CdS nanorods are mobile and undergo a random walk on the nanocrystal surface.
- James K. Utterback
- , Amanda N. Grennell
- & Gordana Dukovic
-
News & Views |
 MOF morphologies in control
MOF morphologies in control
The calcination of metal–organic framework (MOF) precursors is promising for the preparation of nanoscale carbon materials, but the resulting morphologies have remained limited. Now, controlling the growth of precursor MOFs has enabled 1D carbon nanorods to be fabricated — these can then be readily unravelled into 2D graphene nanoribbons.
- Jing Tang
- & Yusuke Yamauchi
-
Article |
 Self-organized architectures from assorted DNA-framed nanoparticles
Self-organized architectures from assorted DNA-framed nanoparticles
A broadly applicable strategy that can control the self-assembly of nanoparticles into a predefined structure has been reported. Integrating nanoparticles with DNA constructs creates individual modules that can be assembled into complex planar architectures. The approach combines nanoparticles with the selectivity and directionality of bonds provided by DNA.
- Wenyan Liu
- , Jonathan Halverson
- & Oleg Gang
-
Article |
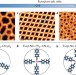 Quasicrystallinity expressed in two-dimensional coordination networks
Quasicrystallinity expressed in two-dimensional coordination networks
Quasicrystalline materials exhibit long-range order but no translational periodicity. Now, a random tiling quasicrystal has been fabricated on a Au(111) surface by coordination interactions between europium centres and linear dicarbonitrile linkers under stoichiometry control. The 2D metal–organic network exhibits the simultaneous presence of four-, five- and six-fold vertices and dodecagonal symmetry.
- José I. Urgel
- , David Écija
- & Johannes V. Barth
-
Article |
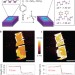 Covalent functionalization and passivation of exfoliated black phosphorus via aryl diazonium chemistry
Covalent functionalization and passivation of exfoliated black phosphorus via aryl diazonium chemistry
Few-layer black phosphorus (BP) is a promising semiconductor, but it is highly reactive and susceptible to ambient degradation. Covalent functionalization with aryl radicals has now been shown to significantly improve the stability of exfoliated BP, as well as the performance of BP-based electronic devices through a controllable p-type doping effect.
- Christopher R. Ryder
- , Joshua D. Wood
- & Mark C. Hersam
-
Article |
 Dissipative self-assembly of vesicular nanoreactors
Dissipative self-assembly of vesicular nanoreactors
Dissipative self-assembly processes are energetically uphill and require the continuous consumption of energy. Now, by using ATP as a chemical fuel, the dissipative self-assembly of vesicles has been demonstrated. These transiently formed supramolecular assemblies are able to sustain a chemical reaction and it is shown that the yield depends on the lifetime of the vesicles.
- Subhabrata Maiti
- , Ilaria Fortunati
- & Leonard J. Prins
-
News & Views |
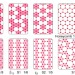 Polyphony in B flat
Polyphony in B flat
Early theories suggested the possibility of atomically thin boron layers, but electron-deficient boron favours multicentre bonds and assembles into various polymorphs, making the synthesis of such layers challenging. Now, in two independent experiments, the deposition of atomic boron has offered this long-sought material on a silver platter.
- Zhuhua Zhang
- , Evgeni S. Penev
- & Boris I. Yakobson
-
Article |
 Tuning the driving force for exciton dissociation in single-walled carbon nanotube heterojunctions
Tuning the driving force for exciton dissociation in single-walled carbon nanotube heterojunctions
The influence of the thermodynamic driving force for photoinduced electron-transfer between single-walled carbon nanotubes and fullerene derivatives has been investigated. The Marcus inverted region and small reorganization energies were observed for this model organic heterojunction. Small reorganization energies aid in minimizing energy losses for solar conversion to electricity or fuels.
- Rachelle Ihly
- , Kevin S. Mistry
- & Jeffrey L. Blackburn
-
Article |
 Experimental realization of two-dimensional boron sheets
Experimental realization of two-dimensional boron sheets
A variety of two-dimensional materials have been reported in the past few years, yet single-element systems—such as graphene and black phosphorus—have remained rare. 2D allotropes of boron have long been predicted and recently investigated. Two boron sheets have now been grown on a Ag(111) surface by molecule beam epitaxy that exhibit significant chemical stability against oxidation.
- Baojie Feng
- , Jin Zhang
- & Kehui Wu
-
News & Views |
 Mismatched lattices patched up
Mismatched lattices patched up
Controlling interfaces between transition-metal oxides and dissimilar structures is crucial for practical applications, yet has remained a quandary. Now, a coherent interface that bridges a perovskite and a fluorite structure has been formed using judiciously chosen metal cations.
- Kenneth R. Poeppelmeier
- & James M. Rondinelli
-
Article |
 Self-assembly of size-controlled liposomes on DNA nanotemplates
Self-assembly of size-controlled liposomes on DNA nanotemplates
Precise control of vesicle size is highly desirable both for basic biochemical research and biomedical applications. Now, monodispersed sub-100-nm vesicles with predefined sizes have been produced using a method based on membrane self-assembly within a DNA-nanostructure guide.
- Yang Yang
- , Jing Wang
- & Chenxiang Lin
-
Article |
 Controlled growth of high-density CdS and CdSe nanorod arrays on selective facets of two-dimensional semiconductor nanoplates
Controlled growth of high-density CdS and CdSe nanorod arrays on selective facets of two-dimensional semiconductor nanoplates
Controlling the morphology and composition of hybrid nanostructures is desirable for applications, but it has proven challenging to precisely combine different nucleation sites and growth modes. Now, three types of hierarchical 1D/2D nanostructures have been prepared by selectively growing semiconductor nanorod arrays (CdS or CdSe) on the different facets of hexagonal nanoplates.
- Xue-Jun Wu
- , Junze Chen
- & Hua Zhang
-
Article |
 Synthesis of a distinct water dimer inside fullerene C70
Synthesis of a distinct water dimer inside fullerene C70
Endohedral C70 fullerenes containing either one or two water molecules have now been prepared using a molecular-surgery approach. The structure of H2O@C70 was determined by single-crystal X-ray analysis, revealing the encapsulated water molecule to be in an off-centre position. In (H2O)2@C70, the two water molecules form a discrete dimer held together with a single hydrogen bond.
- Rui Zhang
- , Michihisa Murata
- & Yasujiro Murata
-
Article |
 Interface control by chemical and dimensional matching in an oxide heterostructure
Interface control by chemical and dimensional matching in an oxide heterostructure
The behaviour of heterostructures, crucial in nanodevices, largely depends on interfacial phenomena. These have proven difficult to control when the different materials adopt distinct crystal structures. Now, a coherent interface between perovskite and fluorite has been achieved that relies in particular on the coordination flexibility of judiciously chosen metal cations.
- Marita O'Sullivan
- , Joke Hadermann
- & Matthew J. Rosseinsky
-
Article |
 Transfer of molecular recognition information from DNA nanostructures to gold nanoparticles
Transfer of molecular recognition information from DNA nanostructures to gold nanoparticles
DNA nanostructures are typically used as molecular scaffolds. Now, it has been shown that they can also act as reusable templates for ‘molecular printing’ of DNA strands onto gold nanoparticles. The products inherit the recognition elements of the parent template: number, orientation and sequence asymmetry of DNA strands. This converts isotropic nanoparticles into complex building blocks.
- Thomas G. W. Edwardson
- , Kai Lin Lau
- & Hanadi F. Sleiman
-
News & Views |
 Molecules bearing robotic arms
Molecules bearing robotic arms
Mass production at the nanoscale requires molecular machines that can control, with high fidelity, the spatial orientation of other reactive species. The demonstration of a synthetic system in which a molecular robotic arm can be used to manipulate the position of a chemical cargo is a significant step towards achieving this goal.
- Ivan Aprahamian
-
News & Views |
 Sweet fullerenes vanquish viruses
Sweet fullerenes vanquish viruses
Fullerene-based dendritic structures coated with 120 sugars can be made in high yields in a relatively short sequence of reactions. The mannosylated compound is shown to inhibit Ebola infection in cells more efficiently than monofullerene-based glycoclusters.
- Sébastien Vidal
-
Article |
 Incorporation of well-dispersed sub-5-nm graphitic pencil nanodots into ordered mesoporous frameworks
Incorporation of well-dispersed sub-5-nm graphitic pencil nanodots into ordered mesoporous frameworks
Doping mesoporous materials is an attractive way to tune their properties, but typically disrupts the host materials’ structures. Ultrasmall graphitic pencil nanodots have now been prepared, doped with heteroatoms, and inserted in a well-dispersed manner within the ordered structure of mesoporous materials including TiO2, carbon and silica, by a co-assembly approach.
- Biao Kong
- , Jing Tang
- & Dongyuan Zhao
-
Article |
 Real-time observation of multiexcitonic states in ultrafast singlet fission using coherent 2D electronic spectroscopy
Real-time observation of multiexcitonic states in ultrafast singlet fission using coherent 2D electronic spectroscopy
Singlet fission, a spin-allowed conversion of a spin-singlet state into a pair of spin-triplet excitons, may be useful for the development of next-generation photovoltaics. Ultrafast coherence measurements now show that vibrational motions play a critical role in fission as they facilitate the mixing of triplet-pair states with singlet excitons.
- Artem A. Bakulin
- , Sarah E. Morgan
- & Akshay Rao
-
News & Views |
 One rule for the electron-rich...
One rule for the electron-rich...
A vast number of possible isomers exist for each fullerene, yet few are observed experimentally. Neutral fullerenes typically minimize adjacent pentagons, but charged ones often tolerate them. Now, a simple model taking into account structural strain and π electronic aspects predicts the asymmetric relative stabilities of charged isomers.
- Patrick Fowler
-
Article |
 Cage connectivity and frontier π orbitals govern the relative stability of charged fullerene isomers
Cage connectivity and frontier π orbitals govern the relative stability of charged fullerene isomers
The stability of charged fullerenes is not as well understood as that of their neutral counterparts, with, for example, more frequent violations of the isolated-pentagon and pentagon-adjacency penalty rules. Now, a simple model based on the concepts of cage connectivity and frontier π orbitals predicts the relative stability of cationic and anionic fullerene isomers.
- Yang Wang
- , Sergio Díaz-Tendero
- & Fernando Martín
-
Article |
 Co-assembly, spatiotemporal control and morphogenesis of a hybrid protein–peptide system
Co-assembly, spatiotemporal control and morphogenesis of a hybrid protein–peptide system
Amphiphilic-peptide-driven opening of elastin-like protein molecules triggers the self-assembly of a multilayered membrane. This dynamic system can undergo morphogenesis into hierarchically ordered tubular structures that can be used to create complex scaffolds for tissue engineering.
- Karla E. Inostroza-Brito
- , Estelle Collin
- & Alvaro Mata
-
Article |
 Shaping quaternary assemblies of water-soluble non-peptide helical foldamers by sequence manipulation
Shaping quaternary assemblies of water-soluble non-peptide helical foldamers by sequence manipulation
The self-assembly of short amphiphilic α-helicomimetic foldamers bearing proteinaceous side-chains can be controlled by manipulating the side-chain sequence. This enables the foldamers to be programmed to form either discrete helical bundles containing isolated cavities, or pH-responsive water-filled channels with controllable pore diameters.
- Gavin W. Collie
- , Karolina Pulka-Ziach
- & Gilles Guichard
-
News & Views |
 Nanocrystals by design
Nanocrystals by design
Nanocrystals with precisely defined structures offer promise as components of advanced materials yet they are challenging to create. Now, a nanocrystal made up of seven cadmium and twelve chloride ions has been synthesized via a biotemplating approach that uses a de novo designed protein.
- Li Shang
- & Gerd Ulrich Nienhaus
-
Article |
 Efficient green methanol synthesis from glycerol
Efficient green methanol synthesis from glycerol
Impure glycerol is obtained as a significant by-product of biodiesel production. Now it is shown that this crude glycerol can be reacted with water over very simple basic or redox oxide catalysts to produce methanol in high yields, together with other useful chemicals, in a one-step low pressure process.
- Muhammad H. Haider
- , Nicholas F. Dummer
- & Graham J. Hutchings
-
Article |
 Improved performance and stability of perovskite solar cells by crystal crosslinking with alkylphosphonic acid ω-ammonium chlorides
Improved performance and stability of perovskite solar cells by crystal crosslinking with alkylphosphonic acid ω-ammonium chlorides
Perovskite materials show great promise for solar cell devices, owing in particular to their high power conversion efficiency. Now, the addition of butylphosphonic acid 4-ammonium cations during a one-step process has been shown to improve both the efficiency and moisture stability of perovskite photovoltaics, through the formation of hydrogen-bonding crosslinks between neighbouring grains.
- Xiong Li
- , M. Ibrahim Dar
- & Michael Grätzel
-
Article |
 Light-controlled self-assembly of non-photoresponsive nanoparticles
Light-controlled self-assembly of non-photoresponsive nanoparticles
Controlling the self-assembly of nanoparticles using light has been demonstrated in many systems where the particle surfaces are functionalized with photoswitchable ligands. Now, it has been shown that the light-controlled self-assembly of non-photoresponsive nanoparticles can be achieved in a quantitative and reversible fashion by placing them in a photoresponsive medium.
- Pintu K. Kundu
- , Dipak Samanta
- & Rafal Klajn
-
Article |
 Photoinduced reversible switching of porosity in molecular crystals based on star-shaped azobenzene tetramers
Photoinduced reversible switching of porosity in molecular crystals based on star-shaped azobenzene tetramers
Rigid star-shaped azobenzene tetramers form a porous molecular crystal when the azobenzene moieties are in the trans configuration, and a non-porous amorphous material on their isomerization to the cis configuration. These two forms are reversibly interconverted in the solid state by light irradiation, thus enabling the photoswitching of optical and gas-capture properties.
- Massimo Baroncini
- , Simone d'Agostino
- & Alberto Credi
-
-
-
News & Views |
 Rise of the nanobots
Rise of the nanobots
Bioorthogonal catalysis provides new ways of mediating artificial transformations in living environs. Now, researchers have developed a nanodevice whose catalytic activity can be regulated by host–guest chemistry.
- Asier Unciti-Broceta
-
Article |
 Supramolecular regulation of bioorthogonal catalysis in cells using nanoparticle-embedded transition metal catalysts
Supramolecular regulation of bioorthogonal catalysis in cells using nanoparticle-embedded transition metal catalysts
Regulation of bioorthogonal catalysis in living systems is challenging because of the complex intracellular environment. Now, the activity of protein-sized bioorthogonal nanozymes has been regulated by binding a supramolecular cucurbit[7]uril ‘gate-keeper’ onto the monolayer surface. This arrangement enables the controlled activation of profluorophores and prodrugs inside living cells for imaging and therapeutic applications.
- Gulen Yesilbag Tonga
- , Youngdo Jeong
- & Vincent M. Rotello
-
-
Article |
 Supramolecular nesting of cyclic polymers
Supramolecular nesting of cyclic polymers
Biopolymers adopt functional tertiary structures through folding and multiplex formation. Synthetic molecules with protein-like dimensions — monodisperse cyclic porphyrin polymers with diameters of 13–21 nm — have now been shown to exhibit biomimetic self-organization by forming nested structures on a gold surface. These assemblies are formed both under vacuum and during deposition from solution.
- Dmitry V. Kondratuk
- , Luís M. A. Perdigão
- & Harry L. Anderson
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Carbon nanotubes and fullerenes
- Electronic properties and materials
- Graphene
- Magnetic properties and materials
- Metamaterials
- Molecular machines and motors
- Molecular self-assembly
- Nanoparticles
- Nanowires
- Organic–inorganic nanostructures
- Quantum dots
- Structural properties
- Synthesis and processing
- Two-dimensional materials

 Scalable and uniform 1D nanoparticles by synchronous polymerization, crystallization and self-assembly
Scalable and uniform 1D nanoparticles by synchronous polymerization, crystallization and self-assembly Molecular machines
Molecular machines Two sides to every particle
Two sides to every particle Tales from the cryptates
Tales from the cryptates A right tangle
A right tangle Spoiler alert
Spoiler alert