Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Circumventing the stability problems of graphene nanoribbon zigzag edges
Circumventing the stability problems of graphene nanoribbon zigzag edges
On-surface synthesis enables highly reactive structures to be produced under vacuum, but they need to be passivated to be incorporated into practical devices. Here, the facile protection of air-sensitive chiral graphene nanoribbons has been shown, by either hydrogenation or synthesis of an oxidized form. The chemically stable forms can subsequently be deprotected.
- James Lawrence
- , Alejandro Berdonces-Layunta
- & Dimas G. de Oteyza
-
Article |
 General synthesis of single-atom catalysts with high metal loading using graphene quantum dots
General synthesis of single-atom catalysts with high metal loading using graphene quantum dots
Transition-metal single-atom catalysts display excellent activity per metal atom site, but suffer from low metal atom densities (typically less than 5 wt% or 1 at.%), which limits their overall catalytic performance. Now, the use of a graphene-quantum-dot primary support, later interweaved into a carbon matrix, has enabled the synthesis of single-atom catalysts with high transition-metal atom loadings of up to 40 wt% or 3.84 at.%.
- Chuan Xia
- , Yunrui Qiu
- & Haotian Wang
-
News & Views |
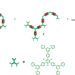 Mesoscale coordination constructs
Mesoscale coordination constructs
A series of mesoscale supramolecular hexagonal grids have been constructed in solution through stepwise intra- then intermolecular coordination-driven self-assembly, and characterized with atomic resolution by scanning tunnelling microscopy and spectroscopy.
- Ruoning Li
- & Yongfeng Wang
-
Article |
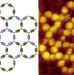 Intra- and intermolecular self-assembly of a 20-nm-wide supramolecular hexagonal grid
Intra- and intermolecular self-assembly of a 20-nm-wide supramolecular hexagonal grid
Metal-mediated self-assembly in solution typically leads to small two- and three-dimensional architectures on scales smaller than 10 nm, but now a series of large, discrete, two-dimensional supramolecular hexagonal grids have been prepared through a combination of intra- and intermolecular coordination interactions. These 20-nm-wide grids have been imaged at submolecular resolution using scanning tunnelling microscopy.
- Zhe Zhang
- , Yiming Li
- & Xiaopeng Li
-
News & Views |
 Precipitates shape up
Precipitates shape up
Precipitation processes enable the fast preparation of a variety of inorganic materials, although typically with little control over their morphology. Now, their one-, two- or three-dimensional growth has been promoted simply by tuning the electrolytic dissociation of the reactants and the supersaturation of the solution.
- Mihui Park
- , Gi-Hyeok Lee
- & Yong-Mook Kang
-
Article |
 Morphology tuning of inorganic nanomaterials grown by precipitation through control of electrolytic dissociation and supersaturation
Morphology tuning of inorganic nanomaterials grown by precipitation through control of electrolytic dissociation and supersaturation
Precipitation enables the straightforward production of a variety of inorganic materials, but the rapid reaction rates involved typically make controlling their morphologies difficult. Now, the growth of either one-, two- or three-dimensional materials has been promoted by tuning of the reactants’ electrolytic dissociation and solution supersaturation, without the need for capping agents and templates.
- Wei-Hong Lai
- , Yun-Xiao Wang
- & Shi-Xue Dou
-
Article |
 Acceleration of a ground-state reaction by selective femtosecond-infrared-laser-pulse excitation
Acceleration of a ground-state reaction by selective femtosecond-infrared-laser-pulse excitation
A practical realization of selective IR-driven reaction-rate control has been hampered by competing processes leading to sample heating. Now, the acceleration of a bimolecular ground-state reaction in solution using the IR excitation of a vibration connected to the reaction coordinate is demonstrated. The behaviour is monitored and understood using a combination of femtosecond IR-pump IR-probe spectroscopy and theoretical calculations.
- Till Stensitzki
- , Yang Yang
- & Karsten Heyne
-
Article |
 Scalable and uniform 1D nanoparticles by synchronous polymerization, crystallization and self-assembly
Scalable and uniform 1D nanoparticles by synchronous polymerization, crystallization and self-assembly
A scalable, one-pot, solution-based protocol for the controlled synthesis of uniform non-spherical block copolymer micelles is a desirable but challenging target. Now, a polymerization-induced crystallization-driven self-assembly process has been developed that offers facile access to 1D and platelet micelle morphologies and to near monodisperse cylinders of controlled length.
- Charlotte E. Boott
- , Jessica Gwyther
- & Ian Manners
-
Article |
 Surfactant-free single-layer graphene in water
Surfactant-free single-layer graphene in water
Aggregation usually prevents dissolution of graphene in water. Now, hydroxide ion adsorption has been shown to allow the stabilization of true single-layer graphene in water — with no surfactant required — so long as the liquid is degassed beforehand. The resulting aqueous dispersions can contain high concentrations of exfoliated graphene that are stable for several months.
- George Bepete
- , Eric Anglaret
- & Carlos Drummond
-
-
Article |
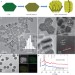 Controlled growth of high-density CdS and CdSe nanorod arrays on selective facets of two-dimensional semiconductor nanoplates
Controlled growth of high-density CdS and CdSe nanorod arrays on selective facets of two-dimensional semiconductor nanoplates
Controlling the morphology and composition of hybrid nanostructures is desirable for applications, but it has proven challenging to precisely combine different nucleation sites and growth modes. Now, three types of hierarchical 1D/2D nanostructures have been prepared by selectively growing semiconductor nanorod arrays (CdS or CdSe) on the different facets of hexagonal nanoplates.
- Xue-Jun Wu
- , Junze Chen
- & Hua Zhang
-
Article |
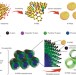 Incorporation of well-dispersed sub-5-nm graphitic pencil nanodots into ordered mesoporous frameworks
Incorporation of well-dispersed sub-5-nm graphitic pencil nanodots into ordered mesoporous frameworks
Doping mesoporous materials is an attractive way to tune their properties, but typically disrupts the host materials’ structures. Ultrasmall graphitic pencil nanodots have now been prepared, doped with heteroatoms, and inserted in a well-dispersed manner within the ordered structure of mesoporous materials including TiO2, carbon and silica, by a co-assembly approach.
- Biao Kong
- , Jing Tang
- & Dongyuan Zhao
-
Article |
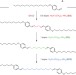 Dynamic covalent chemistry of bisimines at the solid/liquid interface monitored by scanning tunnelling microscopy
Dynamic covalent chemistry of bisimines at the solid/liquid interface monitored by scanning tunnelling microscopy
Constructing molecular architectures using dynamic covalent chemistry combines the robustness of covalent bonds with the reversibility of supramolecular chemistry. Now, a surface-mediated approach has been used to control the thermodynamic and kinetic features of dynamic processes at a surface, leading to constituent selection and selective pattern formation.
- Artur Ciesielski
- , Mohamed El Garah
- & Paolo Samorì
-
Article |
 Tailored hierarchical micelle architectures using living crystallization-driven self-assembly in two dimensions
Tailored hierarchical micelle architectures using living crystallization-driven self-assembly in two dimensions
Self-assembly is commonly used to construct complex nanostructures from soft matter. Now, using the living crystallization-driven self-assembly approach, controlled nanostructure growth in both one and two dimensions has been achieved. Uniform lenticular multiblock platelets, as well as hierarchical structures analogous to nanoscale single- and double-headed arrows and spears have been prepared with controlled sizes in two dimensions.
- Zachary M. Hudson
- , Charlotte E. Boott
- & Ian Manners
-
Article |
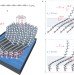 Functional carbon nanosheets prepared from hexayne amphiphile monolayers at room temperature
Functional carbon nanosheets prepared from hexayne amphiphile monolayers at room temperature
Carbonization of a self-assembled monolayer of a hexayne amphiphile at the air/water interface at room temperature results in the formation of functional carbon nanosheets. The nanosheets exhibit a molecularly defined thickness, are mechanically self-supporting over several micrometres, and have macroscopic lateral dimensions on the order of centimetres.
- Stephen Schrettl
- , Cristina Stefaniu
- & Holger Frauenrath
-
Article |
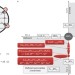 In situ growth of nanoparticles through control of non-stoichiometry
In situ growth of nanoparticles through control of non-stoichiometry
Surfaces decorated with nanoparticles are typically prepared by depositing particles on the substrate. Instead, particles have now been grown in situ directly from perovskites, by exsolution through judicious tuning of the materials’ compositions, particularly their nonstoichiometry. This approach enables control over particle composition, size, surface coverage and anchorage.
- Dragos Neagu
- , George Tsekouras
- & John T. S. Irvine
-
Article |
 Initiation of carbon nanotube growth by well-defined carbon nanorings
Initiation of carbon nanotube growth by well-defined carbon nanorings
Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are typically produced as a mixture of tubes with different diameters and sidewall structures — parameters that determine the optical and electronic properties of these materials. Now, it has been shown that discrete carbon nanorings can be used as templates to control the bottom-up growth of CNTs with a narrow distribution of diameters.
- Haruka Omachi
- , Takuya Nakayama
- & Kenichiro Itami
-
Article |
 A spray-drying strategy for synthesis of nanoscale metal–organic frameworks and their assembly into hollow superstructures
A spray-drying strategy for synthesis of nanoscale metal–organic frameworks and their assembly into hollow superstructures
Metal–organic framework (MOF) nanoparticles and their assembly into three-dimensional superstructures are attracting attention in various fields. Now, a general spray-drying method has been developed to create more complex hollow spherical MOF superstructures and entrap guest species within them, thereby providing new routes to capsules, reactors and composite materials.
- Arnau Carné-Sánchez
- , Inhar Imaz
- & Daniel Maspoch
-
Article |
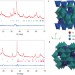 Rapid room-temperature synthesis of nanocrystalline spinels as oxygen reduction and evolution electrocatalysts
Rapid room-temperature synthesis of nanocrystalline spinels as oxygen reduction and evolution electrocatalysts
Ceramic preparation of spinels — materials useful for a wide range of applications — requires complicated procedures and heat treatment over long periods. Now, it is shown that rapid synthesis of nanocrystalline Co–Mn–O spinels can be achieved under ambient conditions, and the resulting nanoparticles exhibit considerable catalytic activity towards the electrochemical oxygen reduction/evolution reactions.
- Fangyi Cheng
- , Jian Shen
- & Jun Chen

 Emulsion-oriented assembly for Janus double-spherical mesoporous nanoparticles as biological logic gates
Emulsion-oriented assembly for Janus double-spherical mesoporous nanoparticles as biological logic gates Two sides to every particle
Two sides to every particle