Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article |
 Silicon-RosIndolizine fluorophores with shortwave infrared absorption and emission profiles enable in vivo fluorescence imaging
Silicon-RosIndolizine fluorophores with shortwave infrared absorption and emission profiles enable in vivo fluorescence imaging
Accessing longer-wavelength emitting organic fluorophores is critical for diagnostic imaging. Here a series of silicon-RosIndolizine fluorophores with emission maxima at 1,300 nm, 1,550 nm and 1,700 nm were synthesized. The fluorophores generate high-resolution in vivo fluorescence images in mice and establish design principles for future shortwave-infrared fluorophore designs.
- William E. Meador
- , Eric Y. Lin
- & Jared H. Delcamp
-
Article
| Open Access Porphyrin-fused graphene nanoribbons
Porphyrin-fused graphene nanoribbons
The insertion of metal atoms and heteroaromatic units provides a way to tune the optical, electronic and magnetic properties of graphene nanoribbons. Now the synthesis of a porphyrin-fused graphene nanoribbon with a narrow bandgap and high charge mobility has been achieved, and this material used to fabricate field-effect and single-electron transistors.
- Qiang Chen
- , Alessandro Lodi
- & Harry L. Anderson
-
Article |
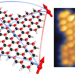 Highly entangled polyradical nanographene with coexisting strong correlation and topological frustration
Highly entangled polyradical nanographene with coexisting strong correlation and topological frustration
The design of open-shell nanographenes is commonly limited to systems featuring a single magnetic origin. Now a strategy that combines topological frustration and electron–electron interactions has been developed to generate a butterfly-shaped nanographene that hosts four highly entangled π-spins and exhibits both ferromagnetic and anti-ferromagnetic coupling.
- Shaotang Song
- , Andrés Pinar Solé
- & Jiong Lu
-
Article
| Open Access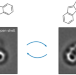 Bistability between π-diradical open-shell and closed-shell states in indeno[1,2-a]fluorene
Bistability between π-diradical open-shell and closed-shell states in indeno[1,2-a]fluorene
Switching the magnetic state of a polycyclic conjugated hydrocarbon in a reversible and controlled manner is challenging. Now, by means of single-molecule scanning probe microscopy, an indenofluorene isomer on ultrathin NaCl films has been shown to adopt both open- and closed-shell states. Furthermore, bidirectional switching between the two states is achieved by changing the adsorption site of the molecule.
- Shantanu Mishra
- , Manuel Vilas-Varela
- & Leo Gross
-
Article
| Open Access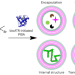 Artificial cell synthesis using biocatalytic polymerization-induced self-assembly
Artificial cell synthesis using biocatalytic polymerization-induced self-assembly
Enzyme-initiated polymerization-induced self-assembly has been used to generate various biomimetic structures. Now, myoglobin’s activity is used for biocatalytic polymerization-induced self-assembly to generate vesicular artificial cells. As various cargoes can be encapsulated during polymerization, these artificial cells are capable of protein expression and can act as microreactors for distinct enzymatic reactions.
- Andrea Belluati
- , Sètuhn Jimaja
- & Nico Bruns
-
Article |
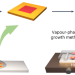 Lateral epitaxial growth of two-dimensional organic heterostructures
Lateral epitaxial growth of two-dimensional organic heterostructures
The synthesis of two-dimensional (2D) organic lateral heterostructures with desirable properties from organic single crystals remains challenging. Now, 2D organic lateral heterostructures have been produced by using a liquid-phase growth approach and vapour-phase growth method, enabling the structural inversion of organic lateral heterostructures via a two-step strategy.
- Qiang Lv
- , Xue-Dong Wang
- & Liang-Sheng Liao
-
Article |
 Optical sequencing of single synthetic polymers
Optical sequencing of single synthetic polymers
Sequences of synthetic polymers are generally heterogeneous and dictate many of their physiochemical properties, but are challenging to determine. Now an imaging method, termed CREATS (coupled reaction approach toward super-resolution imaging), can count, localize and identify each monomer of single polymer chains during (co)polymerization.
- Rong Ye
- , Xiangcheng Sun
- & Peng Chen
-
Article |
 RNAs undergo phase transitions with lower critical solution temperatures
RNAs undergo phase transitions with lower critical solution temperatures
The physicochemical driving forces of protein-free, RNA-driven phase transitions were previously unclear, but it is now shown that RNAs undergo entropically driven liquid–liquid phase separation upon heating in the presence of magnesium ions. In the condensed phase, RNAs can undergo an enthalpically favourable percolation transition that leads to arrested condensates.
- Gable M. Wadsworth
- , Walter J. Zahurancik
- & Priya R. Banerjee
-
Article
| Open Access Precisely patterned nanofibres made from extendable protein multiplexes
Precisely patterned nanofibres made from extendable protein multiplexes
Molecular systems with coincident cyclic and superhelical symmetry axes have considerable advantages for materials design as they can be lengthened or shortened by changing the length of the monomers. Now a systematic approach to generate modular repeat protein oligomers with combined symmetry that can be extended by repeat propagation has been developed.
- Neville P. Bethel
- , Andrew J. Borst
- & David Baker
-
Article |
 Thickness control of organic semiconductor-incorporated perovskites
Thickness control of organic semiconductor-incorporated perovskites
Two-dimensional hybrid perovskites have gained substantial interest recently due to their controllable optoelectronic properties; however precise control over layer thickness has been synthetically challenging. Now a crystal growth method is shown to achieve high-quality single crystals of organic semiconductor-incorporated perovskites with control over their thickness and length through judicious solvent choice, affording precisely tuned optoelectronic properties.
- Jee Yung Park
- , Ruyi Song
- & Letian Dou
-
Article |
 Hybrid organic–inorganic two-dimensional metal carbide MXenes with amido- and imido-terminated surfaces
Hybrid organic–inorganic two-dimensional metal carbide MXenes with amido- and imido-terminated surfaces
Functionalizing two-dimensional transition-metal carbide (MXene) surfaces can alter their properties, but covalent functionalization has been synthetically challenging. Now, it has been shown that various organic groups can be covalently attached to MXene surfaces through amido and imido bonds. The resulting hybrid organic–inorganic structures exhibit Fano resonances and superior stability compared with traditional MXenes with a mixture of –F, –O and –OH surface terminations.
- Chenkun Zhou
- , Di Wang
- & Dmitri V. Talapin
-
Research Briefing |
 A multimodal imaging approach for interrogating energy-conversion pathways in biohybrids
A multimodal imaging approach for interrogating energy-conversion pathways in biohybrids
A multimodal imaging approach is developed to interrogate microorganism–semiconductor biohybrids at the single-cell and single-molecule level for light-driven CO2 fixation. Application to lithoautotrophic bacterium Ralstonia eutropha biohybrids reveals the roles of two hydrogenases in electron transport and bioplastic formation, the magnitude of semiconductor-to-single-cell electron transport and the associated pathways.
-
Article |
 Single-cell multimodal imaging uncovers energy conversion pathways in biohybrids
Single-cell multimodal imaging uncovers energy conversion pathways in biohybrids
Understanding interfacial and cellular electron transport is essential for guiding efficiency optimization in microbe–semiconductor biohybrids for energy conversion. A multimodal imaging platform that combines optical imaging and photocurrent mapping can now interrogate such electron-transport pathways at the single-cell level, uncovering different roles of hydrogenases and a microbe’s large electron-uptake capacity.
- Bing Fu
- , Xianwen Mao
- & Peng Chen
-
Article |
 Time-resolved imaging and analysis of the electron beam-induced formation of an open-cage metallo-azafullerene
Time-resolved imaging and analysis of the electron beam-induced formation of an open-cage metallo-azafullerene
Visualizing single-molecule reactions using electron microscopy can be difficult because of potential radiation damage from the electron beam. Now, however, it has been shown that a high-energy electron beam can be used to synthesize metallo-azafullerenes. Atomic-resolution, time-resolved transmission electron microscopy, with the help of computational calculations, is used to monitor the metal-encapsulation dynamics.
- Helen Hoelzel
- , Sol Lee
- & Dominik Lungerich
-
Article |
 Efficient photon upconversion enabled by strong coupling between silicon quantum dots and anthracene
Efficient photon upconversion enabled by strong coupling between silicon quantum dots and anthracene
Hybrid structures made up of quantum dots functionalized with molecules are highly tunable platforms for light-driven applications; however, the interaction between their components is often weak. Now it has been shown that by connecting molecules to silicon quantum dots via p-conjugated tethers, strongly coupled exciton states can be generated that prove advantageous for photon upconversion.
- Kefu Wang
- , R. Peyton Cline
- & Ming Lee Tang
-
Research Briefing |
 Route to complex colloidal crystals through entropy compartmentalization
Route to complex colloidal crystals through entropy compartmentalization
Colloidal clathrate crystals self-assembled from hard polyhedral shapes in computer simulations are stabilized by entropy compartmentalization, whereby hosts and guests contribute unequally to the entropy. This creative solution to satisfying the laws of thermodynamics suggests new ways to make colloidal crystals with open cages and hierarchical host–guest structures.
-
Article |
 Entropy compartmentalization stabilizes open host–guest colloidal clathrates
Entropy compartmentalization stabilizes open host–guest colloidal clathrates
Clathrates—open crystals with a hierarchy of polyhedral cages—are mostly found in atomic and molecular systems. Now, it has been shown through Monte Carlo simulations that the formation of colloidal host–guest clathrates can be driven by entropy alone, through entropy compartmentalization.
- Sangmin Lee
- , Thi Vo
- & Sharon C. Glotzer
-
Article |
 Real-time monitoring of reaction stereochemistry through single-molecule observations of chirality-induced spin selectivity
Real-time monitoring of reaction stereochemistry through single-molecule observations of chirality-induced spin selectivity
In situ chirality identification for single-molecule systems is not a straightforward task. Now, real-time chirality identification during a Michael addition reaction has been realized by continuous measurements of spin-polarized currents through a single-molecule junction, providing a promising method for studying symmetry-breaking reactions.
- Chen Yang
- , Yanwei Li
- & Xuefeng Guo
-
Article
| Open Access In vivo metallophilic self-assembly of a light-activated anticancer drug
In vivo metallophilic self-assembly of a light-activated anticancer drug
The metallophilic interaction between cyclometalated palladium complexes can facilitate supramolecular nanostructure formation in living mice, providing a phototoxic prodrug with a long circulation time and high tumour-targeting efficiency. Upon green light irradiation, this palladium-based drug destroys solid tumours, leaving non-irradiated organs intact.
- Xue-Quan Zhou
- , Peiyuan Wang
- & Sylvestre Bonnet
-
Review Article |
 Advances in single-molecule junctions as tools for chemical and biochemical analysis
Advances in single-molecule junctions as tools for chemical and biochemical analysis
The ability to detect and quantify a given analyte at the molecular level is a long-lasting goal for analytical and bioanalytical chemistry. This Review highlights how single-molecule junctions (SMJs) have been used for analytical purposes, from the detection of isomers and reaction intermediates to the detection of proteins and nucleic acids. Different SMJ approaches are discussed, along with their advantages and limitations over bulk analytical techniques.
- Essam M. Dief
- , Paul J. Low
- & Nadim Darwish
-
Article
| Open Access Accurate structure models and absolute configuration determination using dynamical effects in continuous-rotation 3D electron diffraction data
Accurate structure models and absolute configuration determination using dynamical effects in continuous-rotation 3D electron diffraction data
Continuous-rotation 3D electron diffraction is a powerful technique to determine structures from nanocrystals. A data treatment method that takes into account dynamical diffraction effects has now been shown to lead to more accurate structure models, better sensitivity to weak signals and a reliable determination of absolute configuration—even for materials containing only light atoms.
- Paul B. Klar
- , Yaşar Krysiak
- & Lukas Palatinus
-
Article
| Open Access Uniform segmented platelet micelles with compositionally distinct and selectively degradable cores
Uniform segmented platelet micelles with compositionally distinct and selectively degradable cores
The synthesis of two-dimensional nanostructures with controlled dimensions from polymeric precursors remains challenging. Now, two-dimensional nanoparticles with chemically different spatially defined cores have been fabricated through seeded growth and are shown to undergo a programmable degradation process.
- Zaizai Tong
- , Yujie Xie
- & Andrew P. Dove
-
News & Views |
 A liquid quasicrystal of columns
A liquid quasicrystal of columns
Systems that feature long-range order but no translational periodicity are intriguing. Now, a T-shaped molecule consisting of three non-miscible components has been devised that self-assembles into a columnar liquid quasicrystal.
- Marianne Impéror-Clerc
-
Article |
 Emulsion-oriented assembly for Janus double-spherical mesoporous nanoparticles as biological logic gates
Emulsion-oriented assembly for Janus double-spherical mesoporous nanoparticles as biological logic gates
Large biomolecules cannot be loaded into conventional Janus nanoparticles with small mesopores, preventing the establishment of efficient logic-gate systems in single Janus nanoparticles. Now, an emulsion-oriented assembly approach has been shown to fabricate Janus double-spherical nanoparticles with dual-tunable mesopores, enabling the design of various single-particle-level logic systems.
- Tiancong Zhao
- , Liang Chen
- & Dongyuan Zhao
-
Article |
 Growth of single-crystal imine-linked covalent organic frameworks using amphiphilic amino-acid derivatives in water
Growth of single-crystal imine-linked covalent organic frameworks using amphiphilic amino-acid derivatives in water
Covalent organic frameworks (COFs) have remained difficult to grow as single crystals. Now, amphiphilic amino-acid derivatives that assemble in micelles in aqueous solutions have been shown to promote the growth of a variety of imine-bridged COFs into single crystals, in a step-by-step fashion, within their hydrophobic compartment.
- Zhipeng Zhou
- , Lei Zhang
- & Zhikun Zheng
-
Article |
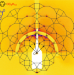 A columnar liquid quasicrystal with a honeycomb structure that consists of triangular, square and trapezoidal cells
A columnar liquid quasicrystal with a honeycomb structure that consists of triangular, square and trapezoidal cells
Quasicrystals are intriguing structures that exhibit long-range positional correlations but no periodicity in real space. Now, T-shaped amphiphilic molecules featuring rigid cores have been found to self-assemble into a columnar liquid quasicrystal with dodecagonal symmetry. The honeycomb structure observed arises from a strictly quasiperiodic tessellation of square, triangular and trapezoidal tiles, rather than from random tiling.
- Xiangbing Zeng
- , Benjamin Glettner
- & Carsten Tschierske
-
Article
| Open Access Structural resolution of a small organic molecule by serial X-ray free-electron laser and electron crystallography
Structural resolution of a small organic molecule by serial X-ray free-electron laser and electron crystallography
The structural analysis of small crystals has remained challenging. Now, the structure of a small organic molecule, rhodamine-6G, has been resolved from microcrystals using an X-ray free-electron laser and electron diffraction. The former showed better reliability for atomic coordinates, whereas the latter was more sensitive to charges; both techniques accurately determined the position of hydrogen atoms.
- Kiyofumi Takaba
- , Saori Maki-Yonekura
- & Koji Yonekura
-
News & Views |
 Colouring by force
Colouring by force
Mechanical force has recently become a new tool for chemists to create colours, trigger reactions, and develop advanced fabrication techniques not possible using other methods. Force-induced multiple colouring has now been developed as a printing technique in soft lithography, enabling the colouring of polymeric materials without inks.
- Xiaocun Lu
-
Article |
 Functional advantages of building nanosystems using multiple molecular components
Functional advantages of building nanosystems using multiple molecular components
The advantages and disadvantages of building a nanosystem using one, two or more molecular components are poorly understood. Now, using structural and catalytic DNA-based nanosystems and theoretical simulations, it has been shown that the assembly of trimeric nanosystems displays much higher levels of programmability and functionality than the monomeric or dimeric counterparts.
- D. Lauzon
- & A. Vallée-Bélisle
-
Article |
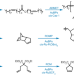 Plasmonic visible–near infrared photothermal activation of olefin metathesis enabling photoresponsive materials
Plasmonic visible–near infrared photothermal activation of olefin metathesis enabling photoresponsive materials
Current strategies for photoinduced olefin metathesis lack wavelength tunability. Now, plasmonic nanoparticles have been used to activate latent ruthenium catalysts, enabling light-induced olefin metathesis in the infrared range with several advantages when compared with conventional heating. Implementing this approach in ring-opening metathesis polymerization resulted in photoresponsive polymer–nanoparticle composites with enhanced mechanical properties.
- Nir Lemcoff
- , Noy B. Nechmad
- & Yossi Weizmann
-
News & Views |
 Non-complementary computation
Non-complementary computation
Molecular computing programmed with complementary nucleic acid strands allows the construction of sophisticated biomolecular circuits. Now, systems with partially complementary strands have been shown to enable more compact and faster molecular circuits, and may illuminate biological processes.
- Philip Petersen
- & Grigory Tikhomirov
-
News & Views |
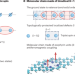 Quantum spin chains go organic
Quantum spin chains go organic
An organic quantum magnet has been prepared in short chains of porphyrin derivatives through a combination of on-surface synthesis and atom manipulation using the tip of a scanning probe microscope.
- P. Jelínek
-
Article
| Open Access Adaptive insertion of a hydrophobic anchor into a poly(ethylene glycol) host for programmable surface functionalization
Adaptive insertion of a hydrophobic anchor into a poly(ethylene glycol) host for programmable surface functionalization
Modulation of surface properties and functions can be achieved through covalent and non-covalent molecular binding, but the lack of responsiveness and requirement for specific binding groups makes spatiotemporal control challenging. Now, it has been shown that adaptive insertion of a hydrophobic anchor into a poly(ethylene glycol) host is an effective non-covalent binding strategy for programmable surface functionalization.
- Shaohua Zhang
- , Wei Li
- & Daniela A. Wilson
-
Article |
 Supercrystal engineering of atomically precise gold nanoparticles promoted by surface dynamics
Supercrystal engineering of atomically precise gold nanoparticles promoted by surface dynamics
Gold nanoparticles typically exhibit hard-sphere-like assembly behaviour, but now the size, morphology and symmetry of crystals of Au25 nanoparticles have been tuned. The presence of excess tetraethylammonium cations has been shown to promote the one-dimensional assembly of the nanoparticles, which in turn form rod-like crystals, by stabilizing dynamically detached ligands from adjacent particles into interparticle linkers through CH⋯π and ion-pairing interactions.
- Qiaofeng Yao
- , Lingmei Liu
- & Jianping Xie
-
Article
| Open Access On-surface synthesis of disilabenzene-bridged covalent organic frameworks
On-surface synthesis of disilabenzene-bridged covalent organic frameworks
Incorporating silicon into organic molecules and materials leads to interesting changes in electronic structure and properties; silabenzenes are attractive species for this purpose, but their high reactivity in solution poses challenges. Now, 1D and 2D covalent organic frameworks featuring disilabenzene rings (C4Si2) as linkers have been prepared by reacting silicon atoms and polyaromatic hydrocarbon precursors on a Au(111) surface.
- Kewei Sun
- , Orlando J. Silveira
- & Shigeki Kawai
-
Article |
 Digital micelles of encoded polymeric amphiphiles for direct sequence reading and ex vivo label-free quantification
Digital micelles of encoded polymeric amphiphiles for direct sequence reading and ex vivo label-free quantification
Identifying and quantifying the biodistribution of synthetic polymeric nanoparticles in biological milieu is crucial for biomedical applications. Now, it has been shown that encoded polymeric amphiphiles with discrete molar masses undergo sequence- and length-dependent self-assembly into precise digital micelles that can be used in direct sequence reading and ex vivo label-free quantification assays.
- Qiangqiang Shi
- , Hao Yin
- & Shiyong Liu
-
Article |
 Machine learning overcomes human bias in the discovery of self-assembling peptides
Machine learning overcomes human bias in the discovery of self-assembling peptides
Peptide design remains a challenge owing to the large library of amino acids. Rational design approaches, although successful, result in a peptide design bias. Now it has been shown that AI techniques can be used to overcome such bias and discover unusual peptides as efficiently as humans.
- Rohit Batra
- , Troy D. Loeffler
- & Subramanian K. R. S. Sankaranarayanan
-
Article |
 Controlling anisotropic properties by manipulating the orientation of chiral small molecules
Controlling anisotropic properties by manipulating the orientation of chiral small molecules
The properties of chiral conjugated molecules, such as the absorption and/or emission of circularly polarized light or electron transport, are highly anisotropic. Now it has been shown that templating layers can control the orientation and anisotropic properties of small chiral molecules in bulk thin films useful for a range of emerging technologies.
- Jessica Wade
- , Francesco Salerno
- & Matthew J. Fuchter
-
Article |
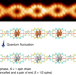 Quantum nanomagnets in on-surface metal-free porphyrin chains
Quantum nanomagnets in on-surface metal-free porphyrin chains
Quantum nanomagnets, which display collective quantum behaviours, serve as important components in modern quantum technologies, but their fabrication has remained challenging. Quantum nanomagnets have now been constructed spin by spin in metal-free porphyrin chains, using on-surface synthesis and hydrogen manipulation using a scanning tunnelling microscope, and their collective quantum behaviours have been clearly resolved.
- Yan Zhao
- , Kaiyue Jiang
- & Shiyong Wang
-
Article |
 A soil-inspired dynamically responsive chemical system for microbial modulation
A soil-inspired dynamically responsive chemical system for microbial modulation
Creating hierarchical synthetic materials that can modulate microbial communities remains a great challenge due to the complex interactions between microbiota and their colonized environments. Now, a soil-inspired chemical system that responds to chemical, optical and mechanical stimuli has been developed. The soil-inspired chemical system can enhance microbial cultures and biofuel production, enrich gut bacterial diversity and alleviate ulcerative colitis symptoms.
- Yiliang Lin
- , Xiang Gao
- & Bozhi Tian
-
Article
| Open Access Circumventing the stability problems of graphene nanoribbon zigzag edges
Circumventing the stability problems of graphene nanoribbon zigzag edges
On-surface synthesis enables highly reactive structures to be produced under vacuum, but they need to be passivated to be incorporated into practical devices. Here, the facile protection of air-sensitive chiral graphene nanoribbons has been shown, by either hydrogenation or synthesis of an oxidized form. The chemically stable forms can subsequently be deprotected.
- James Lawrence
- , Alejandro Berdonces-Layunta
- & Dimas G. de Oteyza
-
Article |
 Nanopore microscope identifies RNA isoforms with structural colours
Nanopore microscope identifies RNA isoforms with structural colours
A method has been developed to identify RNA transcript isoforms at the single-molecule level using solid-state nanopore microscopy. In this method, target RNA is refolded into RNA identifiers with designed sets of complementary DNA strands. Each reshaped molecule carries a unique sequence of structural (pseudo)colours that enables identification and quantification using solid-state nanopore microscopy.
- Filip Bošković
- & Ulrich Felix Keyser
-
Article |
 Standardized excitable elements for scalable engineering of far-from-equilibrium chemical networks
Standardized excitable elements for scalable engineering of far-from-equilibrium chemical networks
Synthetic chemical networks with far-from-equilibrium dynamics akin to genetic regulatory networks in living cells could precisely regulate the kinetics of chemical synthesis or self-assembly. Now standardized excitable chemical regulatory elements, termed genelets, that enable predictive bottom-up construction of in vitro networks with designed temporal and multistable behaviour have been developed.
- Samuel W. Schaffter
- , Kuan-Lin Chen
- & Rebecca Schulman
-
Article |
 σ–σ Stacked supramolecular junctions
σ–σ Stacked supramolecular junctions
Supramolecular interactions play an essential role in organic electronic materials and biological systems. Now, it has been demonstrated that the σ–σ stacking interactions between neighbouring non-conjugated molecules can offer an efficient pathway for charge transport through supramolecular junctions, which provides a new guideline for the design and fabrication of organic materials and devices.
- Anni Feng
- , Yu Zhou
- & Wenjing Hong
-
Article |
 Highly conducting single-molecule topological insulators based on mono- and di-radical cations
Highly conducting single-molecule topological insulators based on mono- and di-radical cations
Designing long and highly conducting molecular wires has been a great challenge for decades. It has now been shown that a singly oxidized 2.6-nm-long oligophenylene-bridged bis(triarylamine) can show a single-molecule junction conductance over 0.1G0.
- Liang Li
- , Jonathan Z. Low
- & Latha Venkataraman
-
In Your Element |
 Ionic liquids charge ahead
Ionic liquids charge ahead
Choline 2-hexenoate is an ionic compound that is a liquid at room temperature, and is just one of a class of compounds that have huge potential in biomedical research and clinical applications, explains Eden E. L. Tanner.
- Eden E. L. Tanner
-
Review Article |
 Chemical fuels for molecular machinery
Chemical fuels for molecular machinery
Chemically fuelled synthetic molecular machines are capable of driving and sustaining non-equilibrium motion, analogous to the biomachinery that underpins life. This Review discusses the chemical and physical features of biological and synthetic chemical fuels and highlights potential challenges and opportunities for the development of synthetic chemically fuelled machinery.
- Stefan Borsley
- , David A. Leigh
- & Benjamin M. W. Roberts
-
Article |
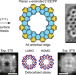 Planar π-extended cycloparaphenylenes featuring an all-armchair edge topology
Planar π-extended cycloparaphenylenes featuring an all-armchair edge topology
The strained topology of [n]paracyclophenylenes ([n]CPPs) typically prevents their π sysytem from being extended, but now the formation of a planar π-extended CPP has been achieved through a bottom-up on-surface synthesis approach. The planar π-extended [12]CPP produced by this method is a nanographene featuring an all-armchair edge, which leads to delocalized electronic states around the entire ring.
- Feifei Xiang
- , Sven Maisel
- & Sabine Maier
-
Article
| Open Access Functional DNA-based cytoskeletons for synthetic cells
Functional DNA-based cytoskeletons for synthetic cells
Cytoskeletons are essential components of cells that perform a variety of tasks, and artificial cytoskeletons that perform these functions are required for the bottom-up assembly of synthetic cells. Now, a multi-functional cytoskeleton mimic has been engineered from DNA, consisting of confined DNA filaments that are capable of reversible self-assembly and transport of gold nanoparticles and vesicular cargo.
- Pengfei Zhan
- , Kevin Jahnke
- & Kerstin Göpfrich

 Designer peptide–DNA cytoskeletons regulate the function of synthetic cells
Designer peptide–DNA cytoskeletons regulate the function of synthetic cells