Featured
-
-
News & Views |
 Defogging the view through a milling jar
Defogging the view through a milling jar
Innovations in instrumentation together with new strategies of data collection and processing have been shown to solve the problem of data quality for time-resolved in situ X-ray diffraction studies on ball milling, opening new horizons in mechanochemistry.
- Elena Boldyreva
-
News & Views |
 A step beyond flatland
A step beyond flatland
Non-covalent interactions can organize planar molecules into two-dimensional arrays. It has now been shown that such arrays can be combined at the solid–liquid interface into bilayered heterostructures.
- Manfred Buck
-
Article |
 Supramolecular heterostructures formed by sequential epitaxial deposition of two-dimensional hydrogen-bonded arrays
Supramolecular heterostructures formed by sequential epitaxial deposition of two-dimensional hydrogen-bonded arrays
Supramolecular heterostructures have been formed by the sequential deposition of two molecular layers with different symmetries and lattice constants — one consisting of carboxylic acid, the other of cyanuric acid and melamine — on a hexagonal boron nitride substrate. Characterization by atomic force microscopy and molecular dynamics simulations shows epitaxial arrangements between the layers.
- Vladimir V. Korolkov
- , Matteo Baldoni
- & Peter H. Beton
-
Article |
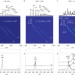 Infrared spectrum and structure of the homochiral serine octamer–dichloride complex
Infrared spectrum and structure of the homochiral serine octamer–dichloride complex
Octameric complexes of serine are long known for their special properties, such as their enhanced stability and preference for homochirality. Yet, there is no consensus on their structures. Now, experimental data on the serine octamer–dichloride complex is presented that supports a highly symmetrical, highly stable structure.
- Jongcheol Seo
- , Stephan Warnke
- & Gert von Helden
-
Perspective |
 Interplay between defects, disorder and flexibility in metal-organic frameworks
Interplay between defects, disorder and flexibility in metal-organic frameworks
Although metal–organic frameworks are often seen as rigid crystalline structures, there is growing evidence that large-scale flexibility, the presence of defects, and long-range disorder are not the exception, but rather the norm. Here we propose that these concepts are inescapably intertwined, and the interfaces between them offer prospects for enhancement of materials' functionalities.
- Thomas D. Bennett
- , Anthony K. Cheetham
- & François-Xavier Coudert
-
-
News & Views |
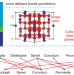 Mismatched lattices patched up
Mismatched lattices patched up
Controlling interfaces between transition-metal oxides and dissimilar structures is crucial for practical applications, yet has remained a quandary. Now, a coherent interface that bridges a perovskite and a fluorite structure has been formed using judiciously chosen metal cations.
- Kenneth R. Poeppelmeier
- & James M. Rondinelli
-
Article |
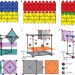 Interface control by chemical and dimensional matching in an oxide heterostructure
Interface control by chemical and dimensional matching in an oxide heterostructure
The behaviour of heterostructures, crucial in nanodevices, largely depends on interfacial phenomena. These have proven difficult to control when the different materials adopt distinct crystal structures. Now, a coherent interface between perovskite and fluorite has been achieved that relies in particular on the coordination flexibility of judiciously chosen metal cations.
- Marita O'Sullivan
- , Joke Hadermann
- & Matthew J. Rosseinsky
-
Article |
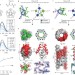 Shaping quaternary assemblies of water-soluble non-peptide helical foldamers by sequence manipulation
Shaping quaternary assemblies of water-soluble non-peptide helical foldamers by sequence manipulation
The self-assembly of short amphiphilic α-helicomimetic foldamers bearing proteinaceous side-chains can be controlled by manipulating the side-chain sequence. This enables the foldamers to be programmed to form either discrete helical bundles containing isolated cavities, or pH-responsive water-filled channels with controllable pore diameters.
- Gavin W. Collie
- , Karolina Pulka-Ziach
- & Gilles Guichard
-
Article |
 Photoinduced reversible switching of porosity in molecular crystals based on star-shaped azobenzene tetramers
Photoinduced reversible switching of porosity in molecular crystals based on star-shaped azobenzene tetramers
Rigid star-shaped azobenzene tetramers form a porous molecular crystal when the azobenzene moieties are in the trans configuration, and a non-porous amorphous material on their isomerization to the cis configuration. These two forms are reversibly interconverted in the solid state by light irradiation, thus enabling the photoswitching of optical and gas-capture properties.
- Massimo Baroncini
- , Simone d'Agostino
- & Alberto Credi
-
Article |
 Irreversible xenon insertion into a small-pore zeolite at moderate pressures and temperatures
Irreversible xenon insertion into a small-pore zeolite at moderate pressures and temperatures
Several solutions to the ‘missing xenon’ problem have been proposed that involve the selective sorption of Xe in minerals found in the Earth. It is now shown that a zeolite, Ag-natrolite, absorbs and retains 28 wt% Xe at 1.7 GPa and 250 °C, conditions found in subsurface Earth, through expulsion of metallic Ag(0).
- Donghoon Seoung
- , Yongmoon Lee
- & Yongjae Lee
-
Research Highlights |
 Flexible magnetic aerogels
Flexible magnetic aerogels
A nanocomposite of bacterial cellulose nanofibrils and cobalt ferrite nanoparticles combines the flexibility of the former with the magnetic properties of the latter.
- Neil Withers
-
Article |
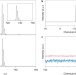 A layered ionic crystal of polar Li@C60 superatoms
A layered ionic crystal of polar Li@C60 superatoms
Metal-containing fullerene cages are widely known, but hard to characterize because of their reactivity towards empty cages. Now the molecular and crystal structures of lithium-containing C60 molecules have been determined.
- Shinobu Aoyagi
- , Eiji Nishibori
- & Hiromi Tobita
-
Research Highlights |
 Surfactant sheets
Surfactant sheets
The hydrophilic edges and hydrophobic centres of graphene oxide sheets mean they act as surfactants.
- Neil Withers

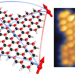 Highly entangled polyradical nanographene with coexisting strong correlation and topological frustration
Highly entangled polyradical nanographene with coexisting strong correlation and topological frustration Two sides to every particle
Two sides to every particle