News & Views |
Featured
-
-
Article |
 Efficient photon upconversion enabled by strong coupling between silicon quantum dots and anthracene
Efficient photon upconversion enabled by strong coupling between silicon quantum dots and anthracene
Hybrid structures made up of quantum dots functionalized with molecules are highly tunable platforms for light-driven applications; however, the interaction between their components is often weak. Now it has been shown that by connecting molecules to silicon quantum dots via p-conjugated tethers, strongly coupled exciton states can be generated that prove advantageous for photon upconversion.
- Kefu Wang
- , R. Peyton Cline
- & Ming Lee Tang
-
Article |
 Achieving spin-triplet exciton transfer between silicon and molecular acceptors for photon upconversion
Achieving spin-triplet exciton transfer between silicon and molecular acceptors for photon upconversion
Quantum dots functionalized with energy-accepting dyes hold promise for converting low-energy photons into higher-energy visible light for bioimaging, catalysis and solar energy harvesting. Now, it has been shown that non-toxic silicon quantum dots can be used in these systems; the transfer of spin-triplet excitons to molecules at their surface has been observed.
- Pan Xia
- , Emily K. Raulerson
- & Sean T. Roberts
-
Article |
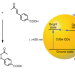 Regio- and diastereoselective intermolecular [2+2] cycloadditions photocatalysed by quantum dots
Regio- and diastereoselective intermolecular [2+2] cycloadditions photocatalysed by quantum dots
Tuning the selectivity for [2+2] photocycloadditions remains challenging. Now, triplet–triplet energy transfer from CdSe quantum dots enables the homo- and heterocouplings of 4-vinylbenzoic acid derivatives via [2+2] photocycloaddition. Preorganization of substrates on the quantum dots reverses intrinsic stereoelectronic preferences to yield cyclobutane products with unprecedented diastereo- and regioselectivity.
- Yishu Jiang
- , Chen Wang
- & Emily A. Weiss
-
Article |
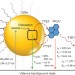 Thermally activated delayed photoluminescence from pyrenyl-functionalized CdSe quantum dots
Thermally activated delayed photoluminescence from pyrenyl-functionalized CdSe quantum dots
The ability to merge the photophysical properties of semiconductor quantum dots with those of well-understood and inexpensive molecular chromophores is important for the development of various emerging photonic and optoelectronic technologies. Now, 1-pyrenecarboxylic acid-functionalized CdSe quantum dots have been shown to undergo thermally activated delayed photoluminescence and display tunable photophysical properties.
- Cédric Mongin
- , Pavel Moroz
- & Felix N. Castellano
-
Article |
 Stability of quantum dots in live cells
Stability of quantum dots in live cells
Intracellular biothiols can degrade nanoparticle monolayers, compromising the function of these potentially promising tools. Here, we describe a label-free method for quantifying the intracellular stability of quantum dot monolayers, using laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry coupled with inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry.
- Zheng-Jiang Zhu
- , Yi-Cheun Yeh
- & Vincent M. Rotello
-

 The year dot
The year dot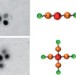 Quantum dot bricks and DNA mortar
Quantum dot bricks and DNA mortar