Q&A |
Featured
-
-
News & Views |
 Shaping molecular diversity
Shaping molecular diversity
Certain drug targets have been deemed undruggable because of the difficulty in finding pharmacologically useful inhibitors. Now, two teams have developed exciting technologies for the creation of diverse collections of macrocyclic molecules and have demonstrated their usefulness for discovering macrocyclic inhibitors.
- Emil S. Iqbal
- & Matthew C. T. Hartman
-
Article |
 Fragment-derived inhibitors of human N-myristoyltransferase block capsid assembly and replication of the common cold virus
Fragment-derived inhibitors of human N-myristoyltransferase block capsid assembly and replication of the common cold virus
An effective antiviral against the common cold could prevent exacerbations in asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, but the diversity and adaptability of the virus makes it a highly challenging target. Now, picomolar inhibitors of a human lipid transferase have been developed. Targeting this human lipid transferase could provide an effective and broad-spectrum approach to block viral replication in the host.
- Aurélie Mousnier
- , Andrew S. Bell
- & Edward W. Tate
-
Article |
 Cyclization of peptides with two chemical bridges affords large scaffold diversities
Cyclization of peptides with two chemical bridges affords large scaffold diversities
Crosslinking within peptides containing two pairs of cysteines to form chemical bridges has now been shown to provide rapid access to thousands of different macrocyclic scaffolds in libraries that are easy to synthesize, screen and decode. Applying this strategy to phage-encoded libraries yielded binders with remarkable affinities despite the small molecular mass.
- Sangram S. Kale
- , Camille Villequey
- & Christian Heinis
-
Article |
 Rapid phenolic O-glycosylation of small molecules and complex unprotected peptides in aqueous solvent
Rapid phenolic O-glycosylation of small molecules and complex unprotected peptides in aqueous solvent
Glycosylation is an attractive strategy to functionalize natural products and peptides for biomedical use, but non-enzymatic approaches usually require organic solvent and protecting groups. Now, an aqueous phenolic O-glycosylation reaction that uses glycosyl fluoride donors and a calcium salt has been developed for a wide range of substrates, including complex unprotected peptides.
- Tyler J. Wadzinski
- , Angela Steinauer
- & Scott J. Miller
-
Article |
 Second-generation DNA-templated macrocycle libraries for the discovery of bioactive small molecules
Second-generation DNA-templated macrocycle libraries for the discovery of bioactive small molecules
A second-generation DNA-templated library of 256,000 small-molecule macrocycles has been developed. The improved method was created by streamlining and integrating multiple aspects of DNA-encoded and DNA-templated library synthesis methodology. In vitro selection of the macrocycle library against insulin-degrading enzyme enabled the discovery of potent inhibitors.
- Dmitry L. Usanov
- , Alix I. Chan
- & David R. Liu
-
Article |
 Versatile protein recognition by the encoded display of multiple chemical elements on a constant macrocyclic scaffold
Versatile protein recognition by the encoded display of multiple chemical elements on a constant macrocyclic scaffold
Encoded display of multiple chemical elements on a constant macrocyclic scaffold could mimick antibody–antigen recognition. A chemical library constructed using this approach enabled the identification of specific binders against a variety of protein targets, including difficult targets, such as TNF.
- Yizhou Li
- , Roberto De Luca
- & Dario Neri
-
Perspective |
 Glucose-responsive insulin by molecular and physical design
Glucose-responsive insulin by molecular and physical design
Glucose-responsive insulin is a therapeutic that modulates its potency, concentration or dosing relative to a patient’s dynamic glucose concentration. This Perspective summarizes some of the recent accomplishments in this field as well as discussing new computational algorithms that may aid in the development of such therapeutics.
- Naveed A. Bakh
- , Abel B. Cortinas
- & Michael S. Strano
-
Review Article |
 The versatility of boron in biological target engagement
The versatility of boron in biological target engagement
Recent years have witnessed a surge of interest in targeted covalent inhibition of disease-associated proteins. Among the electrophiles used to interact with nucleophilic residues in protein structures, boron is unique for its chameleonic ability to display a range of coordination modes upon interaction with protein targets.
- Diego B. Diaz
- & Andrei K. Yudin
-
Article |
 Synthesis facilitates an understanding of the structural basis for translation inhibition by the lissoclimides
Synthesis facilitates an understanding of the structural basis for translation inhibition by the lissoclimides
Several natural and unnatural lissoclimide cytotoxins have been prepared via semi-synthesis and total synthesis. An X-ray co-crystal structure of chlorolissoclimide with the ribosome and evaluation of cytotoxicity and translation inhibition of new compounds in the series improves our understanding of the molecular basis for cytotoxicity.
- Zef A. Könst
- , Anne R. Szklarski
- & Christopher D. Vanderwal
-
Article |
 A synthetic ion transporter that disrupts autophagy and induces apoptosis by perturbing cellular chloride concentrations
A synthetic ion transporter that disrupts autophagy and induces apoptosis by perturbing cellular chloride concentrations
A squaramide-based anion transporter has now been shown to cause changes in the lysosomal pH leading to impairment of lysosomal enzyme activity and disruption of autophagic processes. The study provides the first experimental evidence that synthetic ion transporters can both disrupt autophagy and induce apoptosis.
- Nathalie Busschaert
- , Seong-Hyun Park
- & Injae Shin
-
News & Views |
 The missing link
The missing link
The targeted release of bioactive molecules to diseased tissues has the potential to improve therapeutic efficacy, but not all drugs contain a free functional group that can be easily attached to an antibody. Now, a linker technology has been developed to enable the traceless release of tertiary and heteroaryl amine-containing drugs.
- Tiago Rodrigues
- & Gonçalo J. L. Bernardes
-
Article |
 Dynamic undocking and the quasi-bound state as tools for drug discovery
Dynamic undocking and the quasi-bound state as tools for drug discovery
Structure-based drug design has generally focused on calculating binding free energies of protein–ligand complexes. It has now been shown that structural, rather than thermodynamic, stability — specifically, the work necessary to reach a quasi-bound state in which the ligand has just broken the most important contact with the receptor — can be calculated and used as a tool in virtual screening.
- Sergio Ruiz-Carmona
- , Peter Schmidtke
- & Xavier Barril
-
Article |
 Oxadiazole grafts in peptide macrocycles
Oxadiazole grafts in peptide macrocycles
Controlling macrocycle conformation represents a powerful tool for the construction of new bioactive molecules. Now, peptide-based macrocycles bearing a 1,3,4-oxadiazole moiety grafted into their backbone have been synthesized via a new cyclization approach. The resulting cyclic products exhibit conformationally rigid turn structures (stabilized through intramolecular hydrogen bonding) that can display passive membrane permeability.
- John R. Frost
- , Conor C. G. Scully
- & Andrei K. Yudin
-
Review Article |
 Materials and methods for delivery of biological drugs
Materials and methods for delivery of biological drugs
Biological drugs can offer high potency and selectivity; however, this class of therapeutics often shows poor stability upon oral administration and during subsequent circulation. This Review highlights the materials and methods used to deliver biological drugs, and discusses how these approaches can improve their pharmacokinetics.
- Alexander N. Zelikin
- , Carsten Ehrhardt
- & Anne Marie Healy
-
Article |
 Targeted drug delivery through the traceless release of tertiary and heteroaryl amines from antibody–drug conjugates
Targeted drug delivery through the traceless release of tertiary and heteroaryl amines from antibody–drug conjugates
Many drugs contain tertiary and heteroaryl amines; however, these functional groups are difficult to reversibly crosslink to a carrier protein. Now, a method for conjugating anticancer and antibiotic drugs to antibodies via a quaternary ammonium salt has been developed. Cleavage of the linker results in the traceless release of the free drug and subsequent therapeutic activity.
- Leanna R. Staben
- , Stefan G. Koenig
- & Thomas H. Pillow
-
Article |
 New ligands for nickel catalysis from diverse pharmaceutical heterocycle libraries
New ligands for nickel catalysis from diverse pharmaceutical heterocycle libraries
Pharmaceutical compound libraries are an essential part of drug discovery and the screening of libraries for new drug leads is routine. It has now been shown that these heterocycle-rich, diverse libraries can also be used for ligand discovery. The discovery and application of several new ligands to nickel-catalysed cross-electrophile coupling is demonstrated.
- Eric C. Hansen
- , Dylan J. Pedro
- & Daniel J. Weix
-
Review Article |
 Counting on natural products for drug design
Counting on natural products for drug design
Natural products are a prime source of innovative molecular fragments and privileged scaffolds for drug discovery and chemical biology. Advanced machine-learning approaches can help analyse and design synthetically accessible, natural-product-derived, compound libraries and provide insight into the high selectivity of such compounds.
- Tiago Rodrigues
- , Daniel Reker
- & Gisbert Schneider
-
News & Views |
 Straining to react
Straining to react
A new click-style reaction based on a strain-release amination strategy has been developed. This approach can be used to append small, strained ring systems onto a core scaffold.
- John A. Milligan
- & Peter Wipf
-
News & Views |
 Standing out from the crowd
Standing out from the crowd
The discovery of a tetrapeptide containing a reactive cysteine provides a method to site-selectively modify peptides and proteins, even if other cysteine residues are present in the polypeptide chain.
- Yichao Huang
- & Lei Liu
-
Perspective |
 Recent advances in the construction of antibody–drug conjugates
Recent advances in the construction of antibody–drug conjugates
Antibody–drug conjugates have shown considerable promise for treating disease. However, in order to deliver their full potential, sophisticated site-specific conjugation technologies are needed. This Perspective provides an overview of the different methods used for the site-specific attachment of cytotoxic agents to antibodies.
- Vijay Chudasama
- , Antoine Maruani
- & Stephen Caddick
-
In Your Element |
 Rhodium roles
Rhodium roles
Lars Öhrström relates the various roles played by rhodium in our daily lives, ranging from car components to drugs.
- Lars Öhrström
-
Perspective |
 Recent advances in the molecular design of synthetic vaccines
Recent advances in the molecular design of synthetic vaccines
Synthetic vaccines offer one method to avoid the drawbacks associated with vaccines derived from whole organisms. This Perspective highlights the improvements and significant recent progress that has been achieved in developing well-defined synthetic vaccines using a variety of molecular antigens.
- Lyn H. Jones
-
Article |
 Synthesis of giant globular multivalent glycofullerenes as potent inhibitors in a model of Ebola virus infection
Synthesis of giant globular multivalent glycofullerenes as potent inhibitors in a model of Ebola virus infection
Tridecafullerenes with 120 peripheral carbohydrate groups have been made in one step from hexakis-adducts of [60]fullerene by using azide–alkyne click chemistry. This synthetic approach offers control over the size and multivalency of these ‘sugar superballs', which are shown to be potent inhibitors of cell infection by an artificial Ebola virus, with IC50 values in the sub-nanomolar range.
- Antonio Muñoz
- , David Sigwalt
- & Nazario Martín
-
Article |
 Efficient, non-toxic anion transport by synthetic carriers in cells and epithelia
Efficient, non-toxic anion transport by synthetic carriers in cells and epithelia
Synthetic anion transporters that replace the activity of defective anion channels have been proposed as treatments for cystic fibrosis; however, it remains uncertain whether such molecules are fundamentally toxic. A series of bis- and tris-(thio)ureas capable of transporting anions have now been tested in cells expressing halide-sensitive yellow fluorescent protein. One bis-urea compound proved especially effective while showing almost no toxicity.
- Hongyu Li
- , Hennie Valkenier
- & Anthony P. Davis
-
-
News & Views |
 Rise of the nanobots
Rise of the nanobots
Bioorthogonal catalysis provides new ways of mediating artificial transformations in living environs. Now, researchers have developed a nanodevice whose catalytic activity can be regulated by host–guest chemistry.
- Asier Unciti-Broceta
-
-
-
Article |
 Dual-display of small molecules enables the discovery of ligand pairs and facilitates affinity maturation
Dual-display of small molecules enables the discovery of ligand pairs and facilitates affinity maturation
A method to identify pairs of ligands that simultaneously bind to a target protein has been developed. The method uses two DNA-encoded chemical sub-libraries that self-assemble to form stable dual-display structures, and an encoding system that can be decoded by DNA sequencing and enables both ligands to be identified.
- Moreno Wichert
- , Nikolaus Krall
- & Jörg Scheuermann
-
Article |
 Screening and classifying small-molecule inhibitors of amyloid formation using ion mobility spectrometry–mass spectrometry
Screening and classifying small-molecule inhibitors of amyloid formation using ion mobility spectrometry–mass spectrometry
A method for rapidly screening small-molecule inhibitors of amyloid assembly has been developed. This method uses electrospray ionization–ion mobility spectrometry–mass spectrometry to detect and identify the type of inhibition. A screen of this nature could help in the discovery of therapeutics for numerous diseases associated with aberrant protein aggregation.
- Lydia M. Young
- , Janet C. Saunders
- & Alison E. Ashcroft
-
Article |
 Rhodanine hydrolysis leads to potent thioenolate mediated metallo-β-lactamase inhibition
Rhodanine hydrolysis leads to potent thioenolate mediated metallo-β-lactamase inhibition
The use of β-lactam antibiotics is severely threatened by metallo-β-lactamases (MBLs), which contribute to the development of resistance. Now, crystallographic and solution studies reveal that recently reported MBL inhibition with a rhodanine can be attributed to fragmentation and complex formation with the resulting thioenolate.
- Jürgen Brem
- , Sander S. van Berkel
- & Christopher J. Schofield
-
Article |
 Revealing the macromolecular targets of complex natural products
Revealing the macromolecular targets of complex natural products
Natural products provide a rich source of leads for drug discovery. Now, a computational method is available that can be used to identify the macromolecular targets of these compounds. Much like medicinal chemists' reasoning, the software infers target information by comparing the substructures with those of drugs and other natural products with known targets.
- Daniel Reker
- , Anna M. Perna
- & Gisbert Schneider
-
-
Interview |
 Public libraries
Public libraries
Jeffrey Bode from ETH Zürich talks with Nature Chemistry about his group's work on synthetic fermentation, and how he hopes it could bring the power of chemical synthesis into the hands of citizen scientists.
- Stephen Davey
-
News & Views |
 Bicycling into cells
Bicycling into cells
Bicyclic peptides that are cell-permeable and can inhibit an intracellular target have been developed. These peptides consist of two rings: one enables the peptide to pass through the membrane, the other can inhibit the target.
- Rob M. J. Liskamp
-
Editorial |
Inspiration comes naturally
A collection of articles in this issue focuses on attempts to mimic aspects of natural-product biosynthesis for the identification of new drugs.
-
News & Views |
 Tipping a cell's ionic balance
Tipping a cell's ionic balance
A synthetic compound that transports chloride across membranes can kill both normal cells and cancer cells in vitro. The transporter works together with sodium channels to move NaCl into the cells, which triggers cell death.
- Jeffery T. Davis
-
News & Views |
 Combichem all over again
Combichem all over again
The generation of chemical libraries for screening is a key part of the drug discovery process. Now, two studies describe attempts to combine features of natural product biosynthesis into the creation of libraries with the aim of mimicking nature's success at the production of bioactive molecules.
- Derek B. Lowe
-
Article |
 Synthetic fermentation of bioactive non-ribosomal peptides without organisms, enzymes or reagents
Synthetic fermentation of bioactive non-ribosomal peptides without organisms, enzymes or reagents
The production of biologically active compounds by microbial fermentation has proved highly successful in drug discovery. Now, a method that mimics this process has been used to prepare unnatural peptides from small building blocks without the need for additional reagents, and in a fashion that is immediately compatible with biological screening.
- Yi-Lin Huang
- & Jeffrey W. Bode
-
Article |
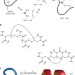 Dithiol amino acids can structurally shape and enhance the ligand-binding properties of polypeptides
Dithiol amino acids can structurally shape and enhance the ligand-binding properties of polypeptides
Disulfide bonds formed between two cysteine residues are important in the folding and stability of proteins. Now, unnatural amino acids with side-chains that contain two thiol groups are described. Incorporation of these dithiol amino acids into a serine protease inhibitor and a nicotinic acetyl choline receptor antagonist is shown to increase their inhibitory activity.
- Shiyu Chen
- , Ranganath Gopalakrishnan
- & Christian Heinis
-
-
News & Views |
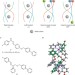 Making head–head–tails of it
Making head–head–tails of it
Enantiomerically pure head-to-head-to-tail triple-stranded helicates synthesized using a subcomponent self-assembly approach possess high anticancer activities against cancer cell lines without significant damage to DNA and with low toxicity to bacteria.
- Markus Albrecht
-
-
Article |
 Controlling epithelial sodium channels with light using photoswitchable amilorides
Controlling epithelial sodium channels with light using photoswitchable amilorides
Amiloride is a widely used diuretic that blocks epithelial sodium channels (ENaCs); however, the functional role of the different ENaC isoforms is still poorly understood and no pharmacological tools exist to differentiate between them. Now, photoswitchable amilorides that enable the optical control of ENaCs, and can distinguish between different ENaC isoforms have been developed.
- Matthias Schönberger
- , Mike Althaus
- & Dirk Trauner
-
News & Views |
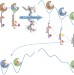 Docking points
Docking points
The flexibility and structural dynamics of proteins pose a big challenge for those trying to discover new bioactive compounds. Now, by using guiding crystallographic data, a method that uses the energetic balance between protein conformers to weight docking scores is shown to aid the hunt for new ligands.
- Xavier Barril
-
Article |
 Incorporation of protein flexibility and conformational energy penalties in docking screens to improve ligand discovery
Incorporation of protein flexibility and conformational energy penalties in docking screens to improve ligand discovery
The adoption of multiple conformations by proteins presents a challenge for ligand discovery using docking simulations. Now, a method for representing the conformational behaviour of a flexible protein in docking screens, which is guided by experimental crystallography data, is shown to predict protein conformation, ligand pose and aid the discovery of new ligands.
- Marcus Fischer
- , Ryan G. Coleman
- & Brian K. Shoichet
-
-
-
Article |
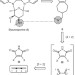 Structural complexity through multicomponent cycloaddition cascades enabled by dual-purpose, reactivity regenerating 1,2,3-triene equivalents
Structural complexity through multicomponent cycloaddition cascades enabled by dual-purpose, reactivity regenerating 1,2,3-triene equivalents
Cascade reactions allow step-economical generation of molecular complexity. Now, a butatriene equivalent, TMSCH2C ≡ CCH2OH, is used to couple two powerful and convergent cycloadditions — the homologous Diels–Alder ([5 + 2]) and the Diels–Alder ([4 + 2]) reactions –– through a vinylogous Peterson elimination, en route to a series of kinase inhibitors inspired by staurosporine.
- Paul A. Wender
- , Dennis N. Fournogerakis
- & Magnus Pfaffenbach

 Looking in the library
Looking in the library Relief from racemization
Relief from racemization An interfering delivery
An interfering delivery Sensitive after a knockdown
Sensitive after a knockdown