Featured
-
-
News & Views |
 A hydroxide lock for metallo-β-lactamases
A hydroxide lock for metallo-β-lactamases
It is extremely difficult to design a broad-spectrum inhibitor for metallo-β-lactamases (MBLs) due to the diversity in the active site. Now, indole-2-carboxylates have been developed as broad-spectrum inhibitors for MBLs. These inhibitors take advantage of key elements of both MBL substrates and products and work by locking a hydroxide.
- Hongyan Li
- & Hongzhe Sun
-
Article |
 Inhibiting amyloid-β cytotoxicity through its interaction with the cell surface receptor LilrB2 by structure-based design
Inhibiting amyloid-β cytotoxicity through its interaction with the cell surface receptor LilrB2 by structure-based design
Inhibiting the interaction between amyloid-β (Aβ) and a neuronal cell surface receptor, LilrB2, could offer a potential route for treating Alzheimer’s disease. Now, binding sites between Aβ and LilrB2 have been discovered and computational selection has identified inhibitors that block this binding site. Cell-penetrating inhibitors were found to block the Aβ–LilrB2 interaction and limit Aβ-induced cytotoxicity.
- Qin Cao
- , Woo Shik Shin
- & Lin Jiang
-
News & Views |
 A positive positive to negative
A positive positive to negative
The structure of an antibiotic that is effective against Gram-positive bacteria, but not against Gram-negative bacteria, has now been modified to improve its effectiveness against Gram-negative bacteria. The approach could help broaden the spectrum of activity of other antibiotics.
- Jed F. Fisher
- & Shahriar Mobashery
-
Article |
 Synthesis facilitates an understanding of the structural basis for translation inhibition by the lissoclimides
Synthesis facilitates an understanding of the structural basis for translation inhibition by the lissoclimides
Several natural and unnatural lissoclimide cytotoxins have been prepared via semi-synthesis and total synthesis. An X-ray co-crystal structure of chlorolissoclimide with the ribosome and evaluation of cytotoxicity and translation inhibition of new compounds in the series improves our understanding of the molecular basis for cytotoxicity.
- Zef A. Könst
- , Anne R. Szklarski
- & Christopher D. Vanderwal
-
Article |
 Dynamic undocking and the quasi-bound state as tools for drug discovery
Dynamic undocking and the quasi-bound state as tools for drug discovery
Structure-based drug design has generally focused on calculating binding free energies of protein–ligand complexes. It has now been shown that structural, rather than thermodynamic, stability — specifically, the work necessary to reach a quasi-bound state in which the ligand has just broken the most important contact with the receptor — can be calculated and used as a tool in virtual screening.
- Sergio Ruiz-Carmona
- , Peter Schmidtke
- & Xavier Barril
-
News & Views |
 Bicycling into cells
Bicycling into cells
Bicyclic peptides that are cell-permeable and can inhibit an intracellular target have been developed. These peptides consist of two rings: one enables the peptide to pass through the membrane, the other can inhibit the target.
- Rob M. J. Liskamp
-
Article |
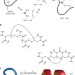 Dithiol amino acids can structurally shape and enhance the ligand-binding properties of polypeptides
Dithiol amino acids can structurally shape and enhance the ligand-binding properties of polypeptides
Disulfide bonds formed between two cysteine residues are important in the folding and stability of proteins. Now, unnatural amino acids with side-chains that contain two thiol groups are described. Incorporation of these dithiol amino acids into a serine protease inhibitor and a nicotinic acetyl choline receptor antagonist is shown to increase their inhibitory activity.
- Shiyu Chen
- , Ranganath Gopalakrishnan
- & Christian Heinis
-
Article |
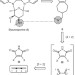 Structural complexity through multicomponent cycloaddition cascades enabled by dual-purpose, reactivity regenerating 1,2,3-triene equivalents
Structural complexity through multicomponent cycloaddition cascades enabled by dual-purpose, reactivity regenerating 1,2,3-triene equivalents
Cascade reactions allow step-economical generation of molecular complexity. Now, a butatriene equivalent, TMSCH2C ≡ CCH2OH, is used to couple two powerful and convergent cycloadditions — the homologous Diels–Alder ([5 + 2]) and the Diels–Alder ([4 + 2]) reactions –– through a vinylogous Peterson elimination, en route to a series of kinase inhibitors inspired by staurosporine.
- Paul A. Wender
- , Dennis N. Fournogerakis
- & Magnus Pfaffenbach
-
Article |
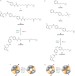 Optochemical control of genetically engineered neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors
Optochemical control of genetically engineered neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors
Light-sensitive ligands can be used to regulate neurobiological receptors with high spatiotemporal precision. Here, the optochemical control of neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors, using both photoswitchable tethered agonists and antagonists, is described. These rationally designed hybrid photoreceptors will facilitate the investigation of the physiological and pathological functions of nicotinic receptors in the brain.
- Ivan Tochitsky
- , Matthew R. Banghart
- & Dirk Trauner
-
News & Views |
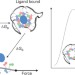 Untying a nanoscale knot
Untying a nanoscale knot
Mechanical unfolding of a single DNA G-quadruplex structure with and without a stabilizing ligand can be used to calculate the binding strength of the ligand and could help to identify drugs to target these important biological assemblies.
- Micah J. McCauley
- & Mark C. Williams

 Molecular jackhammers eradicate cancer cells by vibronic-driven action
Molecular jackhammers eradicate cancer cells by vibronic-driven action