Thesis |
Featured
-
-
Article |
 Isomerization of bioactive acylhydrazones triggered by light or thiols
Isomerization of bioactive acylhydrazones triggered by light or thiols
Acylhydrazones are often found in compounds across screening databases, and numerous bioactive acylhydrazones exist. This functional group can isomerize between E and Z in response to light or upon exposure to thiols. Now, E/Z isomerization is found to impact activities of bioactive acylhydrazones and should be routinely analysed.
- Zhiwei Zhang
- , Giang N. T. Le
- & G. Andrew Woolley
-
News & Views |
 Tipping a cell's ionic balance
Tipping a cell's ionic balance
A synthetic compound that transports chloride across membranes can kill both normal cells and cancer cells in vitro. The transporter works together with sodium channels to move NaCl into the cells, which triggers cell death.
- Jeffery T. Davis
-
Article |
 Controlling epithelial sodium channels with light using photoswitchable amilorides
Controlling epithelial sodium channels with light using photoswitchable amilorides
Amiloride is a widely used diuretic that blocks epithelial sodium channels (ENaCs); however, the functional role of the different ENaC isoforms is still poorly understood and no pharmacological tools exist to differentiate between them. Now, photoswitchable amilorides that enable the optical control of ENaCs, and can distinguish between different ENaC isoforms have been developed.
- Matthias Schönberger
- , Mike Althaus
- & Dirk Trauner
-
-
Article |
 Synthesis of 19-substituted geldanamycins with altered conformations and their binding to heat shock protein Hsp90
Synthesis of 19-substituted geldanamycins with altered conformations and their binding to heat shock protein Hsp90
The heat shock protein Hsp90 is a potential target for cancer and neurodegeneration drugs. Here, the introduction of a substituent into the 19-position of the naturally occurring inhibitor geldanamycin by chemical synthesis is shown to ameliorate toxicity, and also cause a favourable conformational switch that is required for protein binding.
- Russell R. A. Kitson
- , Chuan-Hsin Chang
- & Christopher J. Moody
-
News & Views |
 Mechanisms of potency
Mechanisms of potency
Overcoming drug resistance requires drug–protein interactions that persist in spite of mutations, but such interactions are difficult to characterize. Two-dimensional infrared spectroscopy can reveal the dynamics of how key molecular groups interact, allowing new insights into how some drugs overcome resistance.
- Christopher M. Cheatum
-
News & Views |
 A light touch to a deadly problem
A light touch to a deadly problem
Flow chemistry has grown in stature as a technique with the potential to deliver synthetic complexity with assembly-line-like efficiency. Application of flow technology to the front-line antimalarial drug artemisinin promises to revolutionalize treatment.
- Kevin Booker-Milburn
-
Article |
 Acyclic cucurbit[n]uril molecular containers enhance the solubility and bioactivity of poorly soluble pharmaceuticals
Acyclic cucurbit[n]uril molecular containers enhance the solubility and bioactivity of poorly soluble pharmaceuticals
Acyclic cucurbituril-type molecular containers have been found to increase the solubility of insoluble pharmaceutical agents in water by up to 2,750-fold. In vitro and in vivo toxicology studies suggest that the containers are well tolerated, and paclitaxel solubilized in this manner efficiently kills HeLa and SK-OV-3 cancer cells.
- Da Ma
- , Gaya Hettiarachchi
- & Lyle Isaacs
-
Article |
 Quantifying the chemical beauty of drugs
Quantifying the chemical beauty of drugs
Drug-likeness is a key consideration when selecting compounds during the early stages of drug discovery, but its evaluation in absolute terms does not adequately reflect the spectrum of compound quality. Here, an intuitive and transparent quantitative measure of drug-likeness is proposed that attempts to capture the abstract notion of aesthetics in medicinal chemistry.
- G. Richard Bickerton
- , Gaia V. Paolini
- & Andrew L. Hopkins
-
Article |
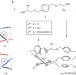 Optically pure, water-stable metallo-helical ‘flexicate’ assemblies with antibiotic activity
Optically pure, water-stable metallo-helical ‘flexicate’ assemblies with antibiotic activity
The self-assembly of monometallic moieties with organic ligands has proved to be a highly versatile approach for preparing a range of metal–ligand assemblies that are helical, optically pure and stable in aqueous solutions. One such iron(II) ‘flexicate’ system exhibits significant interactions with DNA, as well as promising antimicrobial activity properties.
- Suzanne E. Howson
- , Albert Bolhuis
- & Peter Scott
-
-
Article |
 The transcription factor FOXM1 is a cellular target of the natural product thiostrepton
The transcription factor FOXM1 is a cellular target of the natural product thiostrepton
The natural product thiostrepton is known to have anticancer properties but its mechanism of action is not known. Here, it is shown that thiostrepton binds to the protein FOXM1, preventing its interaction with several gene promoters and inhibits their expression. This illustrates the druggability of transcription factors, and provides a molecular basis for targeting FOXM1.
- Nagaratna S. Hegde
- , Deborah A. Sanders
- & Shankar Balasubramanian

 WT19F
WT19F Eliminating epitopes
Eliminating epitopes Aspirin headache solved
Aspirin headache solved