Abstract
Background:
Obesity is characterized by increased adipocyte number and size as well as white adipose tissue (WAT) inflammation, which is fundamental for the development of insulin resistance and type-2 diabetes. These processes, regulated by various endocrine, paracrine and autocrine factors, are extensively studied with the hope to interfere and to inhibit weight gain and related complications in obese patients. Recent data suggest an important role of bone morphogenic protein 4 (BMP4) in the regulation of adipogenesis and development of obesity. BMP4 is a growth factor of the transforming growth factor-β superfamily. Initially, BMPs were identified as inducers of ectopic bone formation. It is now apparent, however, that these proteins have different pleiotropic developmental actions and including playing a role in white adipogenesis.
Methods and Results:
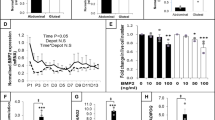
Here, we demonstrate that the expression of BMP4 in human WAT is negatively correlated to body mass index and to the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines. In vitro, BMP4 expression in cultured human adipocytes is upregulated after induction of differentiation. Cells treated with exogenous BMP4 increased peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ) expression and significantly reduced the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines including tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) and monocyte chemoattractant protein 1. TNF-α treatment of fully differentiated adipocytes resulted in downregulation of the expression of adipogenic genes and elevated expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines. Exogenous BMP4 addition significantly reduced the negative effect of TNF-α on the expression profile of adipocytes. Finally, treatment of human adipocytes with exogenous BMP4 reduced the adipocytes’ chemoattractant potential and the migration of monocytes toward adipocyte-conditioned medium.
Conclusions:
These results indicate that BMP4 is an important anti-inflammatory molecule, which may act through PPARγ and reduces TNF-α-mediated pro-inflammatory cytokine production in human adipocytes. Through its anti-inflammatory potential, BMP4 may serve as a protective factor for inflammation-related diseases such as insulin-tolerance or type-2 diabetes.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hotamisligil GS . Inflammation and metabolic disorders. Nature 2006; 444: 860–867.
Lumeng CN, Saltiel AR . Inflammatory links between obesity and metabolic disease. J Clin Invest 2011; 121: 2111–2117.
Hirsch J, Batchelor B . Adipose tissue cellularity in human obesity. Clinic Endocrinol Metab 1976; 5: 299–311.
Chawla A, Nguyen KD, Goh YP . Macrophage-mediated inflammation in metabolic disease. Nat Rev Immunol 2011; 11: 738–749.
Skurk T, Alberti-Huber C, Herder C, Hauner H . Relationship between adipocyte size and adipokine expression and secretion. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2007; 92: 1023–1033.
Ouchi N, Parker JL, Lugus JJ, Walsh K . Adipokines in inflammation and metabolic disease. Nat Rev Immunol 2011; 11: 85–97.
Kitade H, Sawamoto K, Nagashimada M, Inoue H, Yamamoto Y, Sai Y et al. CCR5 plays a critical role in obesity-induced adipose tissue inflammation and insulin resistance by regulating both macrophage recruitment and M1/M2 status. Diabetes 2012; 61: 1680–1690.
Dworacka M, Krzyzagorska E, Iskakova S, Bekmukhambetov Y, Urazayev O, Dworacki G . Increased circulating RANTES in type 2 diabetes. Eur Cytokine Netw 2014; 25: 46–51.
Shah R, Hinkle CC, Ferguson JF, Mehta NN, Li M, Qu L et al. Fractalkine is a novel human adipochemokine associated with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 2011; 60: 1512–1518.
Xueyao Y, Saifei Z, Dan Y, Qianqian P, Xuehong D, Jiaqiang Z et al. Circulating fractalkine levels predict the development of the metabolic syndrome. Int J Endocrinol 2014; 2014: 715148.
Hotamisligil GS, Shargill NS, Spiegelman BM . Adipose expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha: direct role in obesity-linked insulin resistance. Science 1993; 259: 87–91.
Kanety H, Feinstein R, Papa MZ, Hemi R, Karasik A . Tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate-1 (IRS-1). Possible mechanism for suppression of insulin-stimulated tyrosine phosphorylation of IRS-1. J Biol Chem 1995; 270: 23780–23784.
Feve B, Bastard JP . The role of interleukins in insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nat Rev Endocrinol 2009; 5: 305–311.
Xu H, Sethi JK, Hotamisligil GS . Transmembrane tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha inhibits adipocyte differentiation by selectively activating TNF receptor 1. J Biol Chem 1999; 274: 26287–26295.
Whitehead JP, Richards AA, Hickman IJ, Macdonald GA, Prins JB . Adiponectin—a key adipokine in the metabolic syndrome. Diabetes Obes Metab 2006; 8: 264–280.
Chen G, Goeddel DV . TNF-R1 signaling: a beautiful pathway. Science 2002; 296: 1634–1635.
Shi Y, Massague J . Mechanisms of TGF-beta signaling from cell membrane to the nucleus. Cell 2003; 113: 685–700.
Gustafson B, Smith U . The WNT inhibitor Dickkopf 1 and bone morphogenetic protein 4 rescue adipogenesis in hypertrophic obesity in humans. Diabetes 2012; 61: 1217–1224.
Bowers RR, Kim JW, Otto TC, Lane MD . Stable stem cell commitment to the adipocyte lineage by inhibition of DNA methylation: role of the BMP-4 gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2006; 103: 13022–13027.
Wabitsch M, Brenner RE, Melzner I, Braun M, Moller P, Heinze E et al. Characterization of a human preadipocyte cell strain with high capacity for adipose differentiation. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 2001; 25: 8–15.
Schlottmann I, Ehrhart-Bornstein M, Wabitsch M, Bornstein SR, Lamounier-Zepter V . Calcium-dependent release of adipocyte fatty acid binding protein from human adipocytes. Int J Obes (Lond) 2014; 38: 1221–1227.
Hotamisligil GS, Spiegelman BM . Tumor necrosis factor alpha: a key component of the obesity-diabetes link. Diabetes 1994; 43: 1271–1278.
Kanda H, Tateya S, Tamori Y, Kotani K, Hiasa K, Kitazawa R et al. MCP-1 contributes to macrophage infiltration into adipose tissue, insulin resistance, and hepatic steatosis in obesity. J Clin Invest 2006; 116: 1494–1505.
Kamei N, Tobe K, Suzuki R, Ohsugi M, Watanabe T, Kubota N et al. Overexpression of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in adipose tissues causes macrophage recruitment and insulin resistance. J Biol Chem 2006; 281: 26602–26614.
Qian SW, Tang Y, Li X, Liu Y, Zhang YY, Huang HY et al. BMP4-mediated brown fat-like changes in white adipose tissue alter glucose and energy homeostasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2013; 110: E798–E807.
Gustafson B, Hammarstedt A, Hedjazifar S, Smith U . Restricted adipogenesis in hypertrophic obesity: the role of WISP2, WNT, and BMP4. Diabetes 2013; 62: 2997–3004.
Jansson PA, Pellme F, Hammarstedt A, Sandqvist M, Brekke H, Caidahl K et al. A novel cellular marker of insulin resistance and early atherosclerosis in humans is related to impaired fat cell differentiation and low adiponectin. FASEB J 2003; 17: 1434–1440.
Neeland IJ, Turer AT, Ayers CR, Powell-Wiley TM, Vega GL, Farzaneh-Far R et al. Dysfunctional adiposity and the risk of prediabetes and type 2 diabetes in obese adults. JAMA 2012; 308: 1150–1159.
Weisberg SP, McCann D, Desai M, Rosenbaum M, Leibel RL, Ferrante AW Jr . Obesity is associated with macrophage accumulation in adipose tissue. J Clin Invest 2003; 112: 1796–1808.
McQuaid SE, Hodson L, Neville MJ, Dennis AL, Cheeseman J, Humphreys SM et al. Downregulation of adipose tissue fatty acid trafficking in obesity: a driver for ectopic fat deposition? Diabetes 2011; 60: 47–55.
Kim JY, van de Wall E, Laplante M, Azzara A, Trujillo ME, Hofmann SM et al. Obesity-associated improvements in metabolic profile through expansion of adipose tissue. J Clin Invest 2007; 117: 2621–2637.
Huang H, Song TJ, Li X, Hu L, He Q, Liu M et al. BMP signaling pathway is required for commitment of C3H10T1/2 pluripotent stem cells to the adipocyte lineage. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2009; 106: 12670–12675.
Gustafson B, Hammarstedt A, Hedjazifar S, Hoffmann JM, Svensson PA, Grimsby J et al. BMP4 and BMP antagonists regulate human white and beige adipogenesis. Diabetes 2015; 64: 1670–1681.
Cho N, Momose Y . Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma agonists as insulin sensitizers: from the discovery to recent progress. Cur Top Med Chem 2008; 8: 1483–1507.
Xu H, Barnes GT, Yang Q, Tan G, Yang D, Chou CJ et al. Chronic inflammation in fat plays a crucial role in the development of obesity-related insulin resistance. J Clin Invest 2003; 112: 1821–1830.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr med. Holger Pult, Dresden, for his help in obtaining human WAT.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
Dr BS Hamilton is employed by Boehringer Ingelheim Pharma GmbH & Co. KG. This study was supported by a research grant from Boehringer Ingelheim GmbH & Co. (da steht and, muss geändert werden) KG. The remaining authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on International Journal of Obesity website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baraban, E., Chavakis, T., Hamilton, B. et al. Anti-inflammatory properties of bone morphogenetic protein 4 in human adipocytes. Int J Obes 40, 319–327 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2015.141
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2015.141
This article is cited by
-
The Role of Bone Morphogenetic Protein 4 in Ovarian Function and Diseases
Reproductive Sciences (2021)
-
Effects of X-chromosome Tenomodulin Genetic Variants on Obesity in a Children’s Cohort and Implications of the Gene in Adipocyte Metabolism
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
New association of bone morphogenetic protein 4 concentrations with fat distribution in obesity and Exenatide intervention on it
Lipids in Health and Disease (2017)
-
BMPs as new insulin sensitizers: enhanced glucose uptake in mature 3T3-L1 adipocytes via PPARγ and GLUT4 upregulation
Scientific Reports (2017)