Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access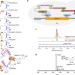 Engineering yeast for the production of breviscapine by genomic analysis and synthetic biology approaches
Engineering yeast for the production of breviscapine by genomic analysis and synthetic biology approaches
Breviscapine is the flavonoid extract from medical plant Erigeron breviscapus for the treatment of cardio- and cerebrovascular disease. Here, the authors identify the key enzymes of the biosynthetic pathway from the plant genome and engineer yeast to produce breviscapine from glucose.
- Xiaonan Liu
- , Jian Cheng
- & Huifeng Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access Control of primary metabolism by a virulence regulatory network promotes robustness in a plant pathogen
Control of primary metabolism by a virulence regulatory network promotes robustness in a plant pathogen
How pathogens maintain phenotypic robustness during infection is poorly understood. Here the authors couple the virulence regulatory network (VRN) of the pathogen R. solanacearum to a model of its metabolic network, and find that the VRN activates functionally redundant primary metabolism genes to promote phenotypic robustness during infection.
- Rémi Peyraud
- , Ludovic Cottret
- & Stéphane Genin
-
Article
| Open Access Mitochondrial levels determine variability in cell death by modulating apoptotic gene expression
Mitochondrial levels determine variability in cell death by modulating apoptotic gene expression
It is unclear what causes variation in cell death in response to chemotherapy. Here, the authors show that cellular mitochondrial content modulates apoptotic protein levels, which in turn regulates response to agents such as TRAIL.
- Silvia Márquez-Jurado
- , Juan Díaz-Colunga
- & Francisco J. Iborra
-
Article
| Open Access Comprehensive profiling of the ligand binding landscapes of duplexed aptamer families reveals widespread induced fit
Comprehensive profiling of the ligand binding landscapes of duplexed aptamer families reveals widespread induced fit
Duplexed aptamers are a common biosensor format; however, how complementary strand sequence, length, and position modulate ligand binding is not well understood. Here, the authors introduce ACE-Scan to comprehensively map binding landscapes, uncovering hotspots of enhanced binding by induced fit.
- Jeffrey D. Munzar
- , Andy Ng
- & David Juncker
-
Article
| Open Access Single-cell variability in multicellular organisms
Single-cell variability in multicellular organisms
While gene expression noise in single-celled organisms is well understood, it is less so in the context of tissues. Here the authors show that coupling between cells in tissues can increase or decrease cell-to-cell variability depending on the level of noise intrinsic to the regulatory networks.
- Stephen Smith
- & Ramon Grima
-
Article
| Open Access The Chemical Fluctuation Theorem governing gene expression
The Chemical Fluctuation Theorem governing gene expression
A unified framework to understand gene expression noise is still lacking. Here the authors derive a universal theorem relating the biological noise with dynamics of birth and death processes and present a model of transcription dynamics, allowing analytical prediction of the dependence of mRNA noise on mRNA lifetime variability.
- Seong Jun Park
- , Sanggeun Song
- & Jaeyoung Sung
-
Article
| Open Access A general and flexible method for signal extraction from single-cell RNA-seq data
A general and flexible method for signal extraction from single-cell RNA-seq data
Single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) data provides information on transcriptomic heterogeneity within cell populations. Here, Risso et al develop ZINB-WaVE for low-dimensional representations of scRNA-seq data that account for zero inflation, over-dispersion, and the count nature of the data.
- Davide Risso
- , Fanny Perraudeau
- & Jean-Philippe Vert
-
Article
| Open Access Monitoring single-cell gene regulation under dynamically controllable conditions with integrated microfluidics and software
Monitoring single-cell gene regulation under dynamically controllable conditions with integrated microfluidics and software
How gene regulatory pathways control cell fate decisions in single cells is not fully understood. Here the authors present an integrated dual-input microfluidic chip and a linked analysis software, enabling tracking of gene regulatory responses of single bacterial cells to changing conditions.
- Matthias Kaiser
- , Florian Jug
- & Erik van Nimwegen
-
Article
| Open Access Intelligent image-based in situ single-cell isolation
Intelligent image-based in situ single-cell isolation
The isolation of single cells while retaining context is important for quantifying cellular heterogeneity but technically challenging. Here, the authors develop a high-throughput, scalable workflow for microscopy-based single cell isolation using machine-learning, high-throughput microscopy and laser capture microdissection.
- Csilla Brasko
- , Kevin Smith
- & Peter Horvath
-
Article
| Open Access Integrated omics dissection of proteome dynamics during cardiac remodeling
Integrated omics dissection of proteome dynamics during cardiac remodeling
Transcriptome data provide only a partial picture of disease states. Here, via integration of transcript-, protein abundance and protein turnover data for a mouse model of cardiac hypertrophy, the authors uncover additional disease gene signatures, and show that turnover data sheds unique light on posttranslational regulation.
- Edward Lau
- , Quan Cao
- & Peipei Ping
-
Article
| Open Access Experimental noise cutoff boosts inferability of transcriptional networks in large-scale gene-deletion studies
Experimental noise cutoff boosts inferability of transcriptional networks in large-scale gene-deletion studies
Reliable inference of gene interactions from perturbation experiments remains a challenge. Here, the authors quantify the upper limits of transcriptional network inference from knockout screens, identify the key determinants of accuracy, and introduce an unbiased and scalable inference algorithm.
- C. F. Blum
- , N. Heramvand
- & M. Kollmann
-
Article
| Open Access Versatile and on-demand biologics co-production in yeast
Versatile and on-demand biologics co-production in yeast
The ability to combine the production of multiple biologics into a single ‘on demand’ system could help in situations where resources are limited. Here the authors demonstrate a proof-of-concept approach for the co-production of three biologics, allowing singular, mixed and combination drug products.
- Jicong Cao
- , Pablo Perez-Pinera
- & Timothy K. Lu
-
Article
| Open Access Tuning the dynamic range of bacterial promoters regulated by ligand-inducible transcription factors
Tuning the dynamic range of bacterial promoters regulated by ligand-inducible transcription factors
For synthetic gene circuits to behave as designed, ligand-inducible promoters should display predictable ON/OFF characteristics. Here the authors design multi-input hybrid promoters to build transcriptional logic gates.
- Ye Chen
- , Joanne M. L. Ho
- & Matthew R. Bennett
-
Article
| Open Access Genomic regression analysis of coordinated expression
Genomic regression analysis of coordinated expression
Somatic copy number alterations (SCNA) can confound gene co-expression analysis in cancers. Here the authors develop a method to remove the effects of SCNA in co-expression analysis, improving the analysis of network rewiring in cancer, and provide a database with adjusted data from TCGA.
- Ling Cai
- , Qiwei Li
- & Guanghua Xiao
-
Article
| Open Access Stochastic gene expression in Arabidopsis thaliana
Stochastic gene expression in Arabidopsis thaliana
Noisy gene expression can cause stochasticity in the expression of plant traits. Here, Araújo et al. use a dual reporter system of protein expression in Arabidopsis to show that expression noise is lowest in stomata relative to other tissues and that leaf cells are coupled with respect to noise.
- Ilka Schultheiß Araújo
- , Jessica Magdalena Pietsch
- & Martin Hülskamp
-
Article
| Open Access Network dynamics-based cancer panel stratification for systemic prediction of anticancer drug response
Network dynamics-based cancer panel stratification for systemic prediction of anticancer drug response
Genomic alterations underlie the variability of drug responses between cancers, but our mechanistic understanding is limited. Here the authors use the p53 network to study how rewiring of signalling networks by genomic alterations impact their dynamic response to pharmacological perturbation.
- Minsoo Choi
- , Jue Shi
- & Kwang-Hyun Cho
-
Article
| Open Access Integrative transcriptomic analysis reveals key drivers of acute peanut allergic reactions
Integrative transcriptomic analysis reveals key drivers of acute peanut allergic reactions
Rising rates of peanut allergy pose a public health problem. Here, the authors profile blood transcriptomes during double-blind, placebo-controlled oral challenge in peanut-allergic children to identify gene and cell composition changes, and construct causal networks to detect key allergic reaction drivers.
- C. T. Watson
- , A. T. Cohain
- & S. Bunyavanich
-
Article
| Open Access The genetic basis for the adaptation of E. coli to sugar synthesis from CO2
The genetic basis for the adaptation of E. coli to sugar synthesis from CO2
An E. coli strain able to use CO2 fixation for sugar synthesis was previously generated by experimental evolution of an engineered strain. Here, Herz et al. show that specific mutations in five genes, encoding carbon metabolism enzymes or key regulators, are sufficient to enable robust growth of the strain.
- Elad Herz
- , Niv Antonovsky
- & Ron Milo
-
Article
| Open Access Programmable DNA looping using engineered bivalent dCas9 complexes
Programmable DNA looping using engineered bivalent dCas9 complexes
DNA loops are a ubiquitious feature of gene regulation across the kingdoms of life. Here the authors design a Cas9-based dimerization system for inducing DNA loops in E. coli, allowing activation and rewiring of gene expression.
- Nan Hao
- , Keith E. Shearwin
- & Ian B. Dodd
-
Article
| Open Access Balancing a genetic toggle switch by real-time feedback control and periodic forcing
Balancing a genetic toggle switch by real-time feedback control and periodic forcing
Cybergenetics aims to monitor and regulate cellular processes in real-time using computer monitoring and feedback of biological readouts. Here the authors use a feedback loop and periodic forcing to maintain cells with a bistable synthetic circuit near its unstable state.
- Jean-Baptiste Lugagne
- , Sebastián Sosa Carrillo
- & Pascal Hersen
-
Article
| Open Access Shaping bacterial population behavior through computer-interfaced control of individual cells
Shaping bacterial population behavior through computer-interfaced control of individual cells
Individual bacteria interact with each other and their environment to produce population-level patterns of gene expression. Here the authors use an automated platform combined with optogenetic feedback to manipulate population behaviors through dynamic control of individual cells.
- Remy Chait
- , Jakob Ruess
- & Călin C. Guet
-
Article
| Open Access Network inference from glycoproteomics data reveals new reactions in the IgG glycosylation pathway
Network inference from glycoproteomics data reveals new reactions in the IgG glycosylation pathway
IgG glycosylation is an important factor in immune function, yet the molecular details of protein glycosylation remain poorly understood. The data-driven approach presented here uses large-scale plasma IgG mass spectrometry measurements to infer new biochemical reactions in the glycosylation pathway.
- Elisa Benedetti
- , Maja Pučić-Baković
- & Jan Krumsiek
-
Article
| Open Access A mathematical model of the impact of insulin secretion dynamics on selective hepatic insulin resistance
A mathematical model of the impact of insulin secretion dynamics on selective hepatic insulin resistance
Dysregulation of insulin secretion dynamics plays a role in diabetes development. Here, the authors build a mathematical model of hepatic insulin signaling and propose a sequential model of post-meal control of glucose and lipids, according to which delayed aPKC suppression would contribute to selective hepatic insulin resistance.
- Gang Zhao
- , Dagmar Wirth
- & Michael Meyer-Hermann
-
Article
| Open Access Percolation transition of cooperative mutational effects in colorectal tumorigenesis
Percolation transition of cooperative mutational effects in colorectal tumorigenesis
Cancer is caused by accumulating genetic mutations. Here, the authors investigate the cooperative effect of these mutations in colorectal cancer patients and identify a giant cluster of mutation-propagating modules that undergoes percolation transition during tumorigenesis.
- Dongkwan Shin
- , Jonghoon Lee
- & Kwang-Hyun Cho
-
Article
| Open Access Quantifying the benefit of a proteome reserve in fluctuating environments
Quantifying the benefit of a proteome reserve in fluctuating environments
Fast-growing bacteria produce many proteins in excess of what seems optimal for exponential growth. Here, the authors present a mathematical model and experimental evidence supporting that this overexpression serves as a strategic reserve to quickly meet demand upon sudden improvement in growth conditions.
- Matteo Mori
- , Severin Schink
- & Terence Hwa
-
Article
| Open Access Systematic proteome and proteostasis profiling in human Trisomy 21 fibroblast cells
Systematic proteome and proteostasis profiling in human Trisomy 21 fibroblast cells
Trisomy 21 (T21) is a major cause of Down syndrome but little is known about its impact on the cellular proteome. Here, the authors define the proteome of T21 fibroblasts and its turnover and also map proteomic differences in monozygotic T21-discordant twins, revealing extensive, organelle-specific changes caused by T21.
- Yansheng Liu
- , Christelle Borel
- & Ruedi Aebersold
-
Article
| Open Access Drug-tunable multidimensional synthetic gene control using inducible degron-tagged dCas9 effectors
Drug-tunable multidimensional synthetic gene control using inducible degron-tagged dCas9 effectors
Deactivated Cas9 fused to transactivation domains can be used to control gene expression, however its presence can prevent rapid switching between different regulatory states. Here the authors generate conditionally degradable dCas9 and Cpf1 proteins for multidimensional control of functional activity.
- Dirk A. Kleinjan
- , Caroline Wardrope
- & Susan J. Rosser
-
Article
| Open Access Efficient protein production by yeast requires global tuning of metabolism
Efficient protein production by yeast requires global tuning of metabolism
The contribution of metabolic pathways to protein secretion is largely unknown. Here, the authors find conserved metabolic patterns in yeast by examining genome-wide transcriptional responses in high protein secretion mutants and reveal critical factors that can be tuned for efficient protein secretion.
- Mingtao Huang
- , Jichen Bao
- & Jens Nielsen
-
Article
| Open Access Hierarchical control of enzymatic actuators using DNA-based switchable memories
Hierarchical control of enzymatic actuators using DNA-based switchable memories
Naturally evolved regulatory circuits have hierarchical layers of signal generation and processing. Here, the authors emulate these networks using feedback-controlled DNA circuits that convert upstream signaling to downstream enzyme activity in a switchable memories circuit.
- Lenny H. H. Meijer
- , Alex Joesaar
- & Tom F. A. de Greef
-
Article
| Open Access Sensing and responding to allergic response cytokines through a genetically encoded circuit
Sensing and responding to allergic response cytokines through a genetically encoded circuit
The standard treatment for an allergic response is anti-histamines, steroids and anti-IgE antibodies. Here the authors present a genetic circuit that senses IL-4 and IL-13 and responses with DARPin production to bind IgE.
- Hélène Chassin
- , Barbara Geering
- & Martin Fussenegger
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamics of lineage commitment revealed by single-cell transcriptomics of differentiating embryonic stem cells
Dynamics of lineage commitment revealed by single-cell transcriptomics of differentiating embryonic stem cells
Commitment to different fates by differentiating pluripotent cells depends upon integration of external and internal signals. Here the authors analyse the entry of mouse embryonic stem cells into retinoic acid-mediated differentiation using single cell transcriptomics with high temporal resolution.
- Stefan Semrau
- , Johanna E. Goldmann
- & Alexander van Oudenaarden
-
Article
| Open Access An integrative method to decode regulatory logics in gene transcription
An integrative method to decode regulatory logics in gene transcription
Existing transcriptional regulatory networks models fall short of deciphering the cooperation between multiple transcription factors on dynamic gene expression. Here the authors develop an integrative method that combines gene expression and transcription factor-DNA binding data to decode transcription regulatory logics.
- Bin Yan
- , Daogang Guan
- & Hailong Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access Evolution of drift robustness in small populations
Evolution of drift robustness in small populations
Genetic drift can reduce fitness in small populations by counteracting selection against deleterious mutations. Here, LaBar and Adami demonstrate through a mathematical model and simulations that small populations tend to evolve to drift-robust fitness peaks, which have a low likelihood of slightly-deleterious mutations.
- Thomas LaBar
- & Christoph Adami
-
Article
| Open Access Engineering species-like barriers to sexual reproduction
Engineering species-like barriers to sexual reproduction
Genetic isolation of a genetically modified organism represents a useful strategy for biocontainment. Here the authors use dCas9-VP64-driven gene expression to construct a ‘species-like’ barrier to reproduction between two otherwise compatible populations.
- Maciej Maselko
- , Stephen C. Heinsch
- & Michael J. Smanski
-
Article
| Open Access Quorum sensing integrates environmental cues, cell density and cell history to control bacterial competence
Quorum sensing integrates environmental cues, cell density and cell history to control bacterial competence
Peptide CSP regulates natural competence in pneumococci and has been proposed as a quorum-sensing signal or a probe for sensing environmental cues. Here, the authors show that CSP levels can indeed act as an indicator of cell density and also incorporate information on environmental factors or cell history.
- Stefany Moreno-Gámez
- , Robin A. Sorg
- & Jan-Willem Veening
-
Article
| Open Access Noise reduction as an emergent property of single-cell aging
Noise reduction as an emergent property of single-cell aging
Gene expression is a noisy process, but it is not known how noise in gene expression changes during the aging of single cells. Here the authors show that noise decreases during normal aging, and provide support for aging-associated increases in chromatin state transitions governing noise reduction.
- Ping Liu
- , Ruijie Song
- & Murat Acar
-
Article
| Open Access Identifying therapeutic targets by combining transcriptional data with ordinal clinical measurements
Identifying therapeutic targets by combining transcriptional data with ordinal clinical measurements
Identifying gene subsets affecting disease phenotypes from transcriptome data is challenge. Here, the authors develop a method that combines transcriptional data with disease ordinal clinical measurements to discover a sphingolipid metabolism regulator involving in Huntington’s disease progression.
- Leila Pirhaji
- , Pamela Milani
- & Ernest Fraenkel
-
Article
| Open Access The interdependent network of gene regulation and metabolism is robust where it needs to be
The interdependent network of gene regulation and metabolism is robust where it needs to be
Although networks of interacting genes and metabolic reactions are interdependent, they have largely been treated as separate systems. Here the authors apply a statistical framework for interdependent networks to E. coli, and show that it is sensitive to gene and protein perturbations but robust against metabolic changes.
- David F. Klosik
- , Anne Grimbs
- & Marc-Thorsten Hütt
-
Article
| Open Access Protein-driven RNA nanostructured devices that function in vitro and control mammalian cell fate
Protein-driven RNA nanostructured devices that function in vitro and control mammalian cell fate
Nucleic acid nanotechnology has great potential for future therapeutic applications. Here the authors build protein-driven RNA nanostructures that can function within mammalian cells and regulate the cell fate.
- Tomonori Shibata
- , Yoshihiko Fujita
- & Hirohide Saito
-
Article
| Open Access Engineering a riboswitch-based genetic platform for the self-directed evolution of acid-tolerant phenotypes
Engineering a riboswitch-based genetic platform for the self-directed evolution of acid-tolerant phenotypes
Cells are exposed to shifts in environmental pH, which direct their metabolism and behavior. Here the authors design pH-sensing riboswitches to create a gene expression program, digitalize the system to respond to a narrow pH range and apply it to evolve host cells with improved tolerance to a variety of organic acids.
- Hoang Long Pham
- , Adison Wong
- & Matthew Wook Chang
-
Article
| Open Access Variable repeats in the eukaryotic polyubiquitin gene ubi4 modulate proteostasis and stress survival
Variable repeats in the eukaryotic polyubiquitin gene ubi4 modulate proteostasis and stress survival
Eukaryotic cells rely on the ubiquitin-proteasome system for selective degradation of proteins, a process vital to organismal fitness. Here the authors show that the number of repeats in the polyubiquitin gene is evolutionarily unstable within and between yeast species, and that this variability may tune the cell’s capacity to respond to sudden environmental perturbations.
- Rita Gemayel
- , Yudi Yang
- & Kevin J. Verstrepen
-
Article
| Open Access A reporter system coupled with high-throughput sequencing unveils key bacterial transcription and translation determinants
A reporter system coupled with high-throughput sequencing unveils key bacterial transcription and translation determinants
Quantitative analysis of how DNA sequence determines transcription and translation regulation is of interest to systems and synthetic biologists. Here the authors present ELM-seq, which uses Dam activity as reporter for high-throughput analysis of promoter and 5’-UTR regions.
- Eva Yus
- , Jae-Seong Yang
- & Luis Serrano
-
Article
| Open Access Systems analysis of apoptotic priming in ovarian cancer identifies vulnerabilities and predictors of drug response
Systems analysis of apoptotic priming in ovarian cancer identifies vulnerabilities and predictors of drug response
High-grade serous ovarian cancers (HGS-OvCa) frequently develop chemotherapy resistance. Here, the authors through a systematic analysis of proteomic and drug response data of 14 HGS-OvCa PDXs demonstrate that targeting apoptosis regulators can improve response of these tumors to inhibitors of the PI3K/mTOR pathway.
- Ioannis K. Zervantonakis
- , Claudia Iavarone
- & Joan S. Brugge
-
Article
| Open Access RNA-aptamers-in-droplets (RAPID) high-throughput screening for secretory phenotypes
RNA-aptamers-in-droplets (RAPID) high-throughput screening for secretory phenotypes
Screening libraries of genetically engineered microbes for secreted products is limited by the available assay throughput. Here the authors combine aptamer-based fluorescent detection with droplet microfluidics to achieve high throughput screening of yeast strains engineered for enhanced tyrosine or streptavidin production.
- Joseph Abatemarco
- , Maen F. Sarhan
- & Adam R. Abate
-
Article
| Open Access Exit from quiescence displays a memory of cell growth and division
Exit from quiescence displays a memory of cell growth and division
The quiescence-exit process is noisy even in genetically identical cells under the same environmental conditions. Here the authors show that the heterogeneity of quiescence exit reflects a memory of preceding cell growth at quiescence induction and immediate division history prior to quiescence entry.
- Xia Wang
- , Kotaro Fujimaki
- & Guang Yao
-
Article
| Open Access Evolution of new regulatory functions on biophysically realistic fitness landscapes
Evolution of new regulatory functions on biophysically realistic fitness landscapes
Gene networks evolve by transcription factor (TF) duplication and divergence of their binding site specificities, but little is known about the global constraints at play. Here, the authors study the coevolution of TFs and binding sites using a biophysical-evolutionary approach, and show that the emerging complex fitness landscapes strongly influence regulatory evolution with a role for crosstalk.
- Tamar Friedlander
- , Roshan Prizak
- & Gašper Tkačik
-
Article
| Open Access PLATE-Seq for genome-wide regulatory network analysis of high-throughput screens
PLATE-Seq for genome-wide regulatory network analysis of high-throughput screens
Despite the importance of pharmacological and functional genomic screens the readouts are of low complexity. Here the authors introduce PLATE-Seq, a low-cost genome-wide mRNA profiling method to complement high-throughput screening.
- Erin C. Bush
- , Forest Ray
- & Peter A. Sims
-
Article
| Open Access The self-inhibitory nature of metabolic networks and its alleviation through compartmentalization
The self-inhibitory nature of metabolic networks and its alleviation through compartmentalization
Metabolites act as enzyme inhibitors, but their global impact on metabolism has scarcely been considered. Here, the authors generate a human genome-wide metabolite-enzyme inhibition network, and find that inhibition occurs largely due to limited structural diversity of metabolites, leading to a global constraint on metabolism which subcellular compartmentalization minimizes.
- Mohammad Tauqeer Alam
- , Viridiana Olin-Sandoval
- & Markus Ralser
-
Article
| Open Access Crosstalk and the evolvability of intracellular communication
Crosstalk and the evolvability of intracellular communication
The evolutionary rationale behind the extensive crosstalk between Metazoan signalling pathways remains elusive. Here the authors provide evidence that crosstalk in the human signalling network evolves as a means to allow efficient diversification of cellular responses to the same signals between different cell types.
- Michael A. Rowland
- , Joseph M. Greenbaum
- & Eric J. Deeds
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Bayesian inference
- Biobricks
- Biochemical networks
- Bioenergetics
- Cellular noise
- Complexity
- Computer modelling
- Computer science
- Control theory
- Criticality
- Differential equations
- DNA computing and cryptography
- Dynamic networks
- Dynamical systems
- Emergence
- Evolvability
- Genetic circuit engineering
- Genetic interaction
- Genomic engineering
- Information theory
- Logic gates
- Metabolic engineering
- Modularity
- Molecular engineering
- Molecular fluctuations
- Multicellular systems
- Multistability
- Nonlinear dynamics
- Numerical simulations
- Oscillators
- Population dynamics
- Programming language
- Protein engineering
- Regulatory networks
- Reverse engineering
- Robustness
- Signal processing
- Single-cell imaging
- Software
- Standardization
- Stochastic modelling
- Stochastic networks
- Synthetic biology
- Systems analysis
- Time series

 Cell fate in antiviral response arises in the crosstalk of IRF, NF-κB and JAK/STAT pathways
Cell fate in antiviral response arises in the crosstalk of IRF, NF-κB and JAK/STAT pathways