Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Dehydrative π-extension to nanographenes with zig-zag edges
Dehydrative π-extension to nanographenes with zig-zag edges
Nanographenes with zig-zag peripheries are expected to have unique electronic properties, but their application in organic electronics has been curbed by their difficult synthesis. Here, the authors develop a facile route to zig-zag nanographenes based on a key dehydrative π-extension reaction.
- Dominik Lungerich
- , Olena Papaianina
- & Konstantin Amsharov
-
Article
| Open Access A Chiron approach towards the stereoselective synthesis of polyfluorinated carbohydrates
A Chiron approach towards the stereoselective synthesis of polyfluorinated carbohydrates
Polyfluorinated hexopyranoses display unique physical, chemical and biological properties, however their stereoselective synthesis is highly challenging. Here, the authors report a synthetic approach based on the chemical manipulation of inexpensive levoglucosan to obtain heavily fluorinated monosaccharides stereoselectively.
- Vincent Denavit
- , Danny Lainé
- & Denis Giguère
-
Article
| Open Access Chromium-catalyzed para-selective formation of quaternary carbon centers by alkylation of benzamide derivatives
Chromium-catalyzed para-selective formation of quaternary carbon centers by alkylation of benzamide derivatives
The selective installation of quaternary carbon substituents on arenes is a highly challenging synthetic goal. Here, the authors report a chromium-catalyzed para-selective functionalization of benzamides with tertiary organometallic reagents under mild conditions.
- Pei Liu
- , Changpeng Chen
- & Xiaoming Zeng
-
Article
| Open Access Self-assembly of polycyclic supramolecules using linear metal-organic ligands
Self-assembly of polycyclic supramolecules using linear metal-organic ligands
Coordination-driven supramolecular assembly provides the ability to build molecular architectures of impressive complexity. Here, the authors use a series of linear metal-organic ligands with specific sequences to construct multiple generations of precisely-controlled, 2D fractal polycyclic supramolecules.
- Bo Song
- , Sneha Kandapal
- & Xiaopeng Li
-
Article
| Open Access Deconvolution of octahedral Pt3Ni nanoparticle growth pathway from in situ characterizations
Deconvolution of octahedral Pt3Ni nanoparticle growth pathway from in situ characterizations
Understanding the growth pathway of faceted alloy nanoparticles at the atomic level is crucial to morphology control and property tuning, but remains a challenge. Here, the authors reveal the particle growth and facet formation mechanisms of octahedral Pt3Ni nanoparticles using multiple cutting-edge in situ techniques.
- Xiaochen Shen
- , Changlin Zhang
- & Zhenmeng Peng
-
Article
| Open Access Deciphering synergetic core-shell transformation from [Mo6O22@Ag44] to [Mo8O28@Ag50]
Deciphering synergetic core-shell transformation from [Mo6O22@Ag44] to [Mo8O28@Ag50]
Understanding how one metal nanocluster transforms into another is of synthetic and fundamental importance. Here, the authors use mass spectrometry to reveal an acid-induced structural transformation between two Ag clusters that proceeds via a breakage-growth-reassembly mechanism.
- Zhi Wang
- , Hai-Feng Su
- & Lan-Sun Zheng
-
Article
| Open Access Designed synthesis of stable light-emitting two-dimensional sp2 carbon-conjugated covalent organic frameworks
Designed synthesis of stable light-emitting two-dimensional sp2 carbon-conjugated covalent organic frameworks
Topological connection of organic chromophores is an attractive way to design light-emitting covalent organic frameworks but the synthesis of stable light-emitting frameworks remains challenging. Here the authors report the designed synthesis of sp2 carbon conjugated frameworks that combine stability with light-emitting activity
- Enquan Jin
- , Juan Li
- & Donglin Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access An ultra-low thiourea catalyzed strain-release glycosylation and a multicatalytic diversification strategy
An ultra-low thiourea catalyzed strain-release glycosylation and a multicatalytic diversification strategy
Non-covalent glycosyl donor activation often requires high organocatalyst loadings. Here, the authors demonstrate that strain-release glycosylations can take place at very low thiourea catalyst loadings. In addition, the authors developed a one-pot multicatalytic strategy that can diversify glycosides rapidly.
- Chunfa Xu
- & Charles C. J. Loh
-
Article
| Open Access Dye-incorporated coordination polymers for direct photocatalytic trifluoromethylation of aromatics at metabolically susceptible positions
Dye-incorporated coordination polymers for direct photocatalytic trifluoromethylation of aromatics at metabolically susceptible positions
Direct trifluoromethylation of unactivated aromatic rings at metabolically susceptible positions is highly desirable in pharmaceutical fields. Here, the authors report a new approach for direct trifluoromethylation of unactivated aromatics by incorporating thiophenes into the backbone of triphenylamine-based ligand.
- Tiexin Zhang
- , Xiangyang Guo
- & Chunying Duan
-
Article
| Open Access Asymmetric remote C-H borylation of internal alkenes via alkene isomerization
Asymmetric remote C-H borylation of internal alkenes via alkene isomerization
Sequential alkene isomerization/functionalization enables enantioselective transformations of remote C–H bonds. Here, the authors report a chiral cobalt catalytic system for the highly enantioselective, remote C–H borylation of internal alkenes via an isomerization/hydroboration sequence.
- Xu Chen
- , Zhaoyang Cheng
- & Zhan Lu
-
Article
| Open Access The evolution of multiple active site configurations in a designed enzyme
The evolution of multiple active site configurations in a designed enzyme
Generation and iterative optimization of designed enzymes can provide valuable insights for a more efficient catalysis. Here the authors have followed the iterative improvement of a designed Kemp eliminase and show that remote point mutations could remodel the designed active site via substantial conformational reorganization.
- Nan-Sook Hong
- , Dušan Petrović
- & Colin J. Jackson
-
Article
| Open Access Rechargeable potassium-ion batteries with honeycomb-layered tellurates as high voltage cathodes and fast potassium-ion conductors
Rechargeable potassium-ion batteries with honeycomb-layered tellurates as high voltage cathodes and fast potassium-ion conductors
The development of potassium-ion batteries requires cathode materials that can maintain the structural stability during cycling. Here the authors have developed honeycomb-layered tellurates K2M2TeO6 that afford high ionic conductivity and reversible intercalation of large K ions at high voltages.
- Titus Masese
- , Kazuki Yoshii
- & Masahiro Shikano
-
Article
| Open Access Copper-catalyzed methylative difunctionalization of alkenes
Copper-catalyzed methylative difunctionalization of alkenes
While the trifluoromethylative difunctionalization of unactivated alkenes has been largely explored, methylative difunctionalization remains underinvestigated. Here, the authors report copper-catalyzed alkoxy- and azido-methylation reactions of alkenes leading to important synthetic building blocks and valuable O- and N-heterocycles.
- Xu Bao
- , Takayuki Yokoe
- & Jieping Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access Stereoselective oxidative glycosylation of anomeric nucleophiles with alcohols and carboxylic acids
Stereoselective oxidative glycosylation of anomeric nucleophiles with alcohols and carboxylic acids
Glycosylation of partially protected sugars is usually limited by suboptimal regio- and stereo-selectivities. Here, the authors show a general oxidative glycosylation between anomeric stannanes with a nonprotected hydroxyl group and oxygen nucleophiles, additionally providing mechanistic insights into the origin of selectivity.
- Tianyi Yang
- , Feng Zhu
- & Maciej A. Walczak
-
Article
| Open Access Realization of vertical metal semiconductor heterostructures via solution phase epitaxy
Realization of vertical metal semiconductor heterostructures via solution phase epitaxy
Controlling the composition and crystal phase of layered heterostructures is important. Here, the authors report the liquid-phase epitaxial growth of Sn0.5W0.5S2 nanosheets with 83% metallic phase on SnS2 nanoplates, which are used as 100 ppb level chemiresistive gas sensors at room temperature.
- Xiaoshan Wang
- , Zhiwei Wang
- & Wei Huang
-
Article
| Open Access H-bonded reusable template assisted para-selective ketonisation using soft electrophilic vinyl ethers
H-bonded reusable template assisted para-selective ketonisation using soft electrophilic vinyl ethers
Electrophilic acylation of arenes is largely limited to electron rich systems, non-polar medium and often displays moderate selectivity. Here, the authors show a directed para-selective ketonisation of arenes, overriding electronic bias and structural congestion, and apply it to the synthesis of bioactive compounds.
- Arun Maji
- , Amit Dahiya
- & Debabrata Maiti
-
Article
| Open Access A general deoxygenation approach for synthesis of ketones from aromatic carboxylic acids and alkenes
A general deoxygenation approach for synthesis of ketones from aromatic carboxylic acids and alkenes
Synthesis of aryl ketones can be generally achieved via C–C coupling strategies. Here, the authors show a deoxygenative coupling of carboxylic acids and alkenes enabled by photoredox catalysis and report a wide scope of products, including bioactive and macrocyclic ketones.
- Muliang Zhang
- , Jin Xie
- & Chengjian Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access Formal group insertion into aryl C‒N bonds through an aromaticity destruction-reconstruction process
Formal group insertion into aryl C‒N bonds through an aromaticity destruction-reconstruction process
Activation of C–N bonds of anilines requires transformation of the amino group into a more reactive functionality. Here, the authors report an aromaticity destruction-reconstruction process that converts abundant anilines into valuable amines through group insertion into the C–N bond and benzylic C–H functionalization.
- Dandan Han
- , Qiuqin He
- & Renhua Fan
-
Article
| Open Access Design principles of chiral carbon nanodots help convey chirality from molecular to nanoscale level
Design principles of chiral carbon nanodots help convey chirality from molecular to nanoscale level
A promising and efficient route to chiral materials involves the transfer of chirality across length scales. Here, the authors use chiral molecular precursors to synthesize chiral carbon nanodots, which in turn can template the formation of chiral supramolecular assemblies.
- Luka Ðorđević
- , Francesca Arcudi
- & Maurizio Prato
-
Article
| Open Access Networking chemical robots for reaction multitasking
Networking chemical robots for reaction multitasking
Distributing a reaction workload across laboratories can solve chemical problems more efficiently, but it is challenging to develop viable hardware and software. Here, the authors present an internet-connected network of cheap robots that can perform chemical reactions and share outcomes in real time, demonstrating a digitized approach to chemical collaboration.
- Dario Caramelli
- , Daniel Salley
- & Leroy Cronin
-
Article
| Open Access Peptide-guided functionalization and macrocyclization of bioactive peptidosulfonamides by Pd(II)-catalyzed late-stage C–H activation
Peptide-guided functionalization and macrocyclization of bioactive peptidosulfonamides by Pd(II)-catalyzed late-stage C–H activation
Aryl sulfonamides and sultams are important pharmacophores in medicinal chemistry. Here, the authors report a practical palladium-catalyzed C–H activation assisted by amino-acid residues in the substrate leading to arylsulfonamides and bioactive peptidosulfonamide macrocycles.
- Jian Tang
- , Hongfei Chen
- & Huan Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Metal-free alcohol-directed regioselective heteroarylation of remote unactivated C(sp3)–H bonds
Metal-free alcohol-directed regioselective heteroarylation of remote unactivated C(sp3)–H bonds
Direct remote C–H functionalization of aliphatic alcohols via alkoxy radicals is largely unexplored. Here, the authors report the C(sp3)-heteroaryl bond formation in aliphatic alcohols mediated by alkoxy radicals formed with a hypervalent iodine reagent.
- Xinxin Wu
- , Hong Zhang
- & Chen Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access Symmetry breakdown of 4,4″-diamino-p-terphenyl on a Cu(111) surface by lattice mismatch
Symmetry breakdown of 4,4″-diamino-p-terphenyl on a Cu(111) surface by lattice mismatch
In a symmetric molecule with identical functional groups, selective activation of only one site is challenging. Here, the authors show that 4,4″-diamino-p-terphenyl adsorbs asymmetrically to a metal surface, leading to a change in binding affinity of one of its amine groups.
- Qigang Zhong
- , Daniel Ebeling
- & André Schirmeisen
-
Article
| Open Access N2 activation on a molybdenum–titanium–sulfur cluster
N2 activation on a molybdenum–titanium–sulfur cluster
Nitrogenase—whose cofactor consists of a metal–sulfur cluster—catalyzes the production of NH3 from N2, but designing metal–sulfur complexes capable of promoting this conversion remains challenging. Here, the authors report on the activation of N2 by a metal–sulfur cluster containing [Mo3S4Ti] cubes, demonstrating NH3 and N2H4 production.
- Yasuhiro Ohki
- , Keisuke Uchida
- & Takehiro Ohta
-
Article
| Open Access Crystalline functionalized endohedral C60 metallofullerides
Crystalline functionalized endohedral C60 metallofullerides
While endohedral metallofullerenes have demonstrated advantageous electronic and magnetic properties, the isolation of monomeric M@C60 remains highly challenging. Here, the authors prepare trifluoromethylated Gd@C60 and La@C60, where the functionalization of C60 allows for the stabilization of these otherwise reactive species.
- Ayano Nakagawa
- , Makiko Nishino
- & Hisanori Shinohara
-
Article
| Open Access An isolable catenane consisting of two Möbius conjugated nanohoops
An isolable catenane consisting of two Möbius conjugated nanohoops
Molecules exhibiting Möbius topology are fascinating but challenging synthetic targets. Here, the authors report the elegant synthesis and crystal structure of a catenane formed from two fully conjugated, interlocked Möbius nanohoops, and use theoretical calculations to understand its conformational stability and aromaticity.
- Yang-Yang Fan
- , Dandan Chen
- & Huan Cong
-
Article
| Open Access Facile transformation of imine covalent organic frameworks into ultrastable crystalline porous aromatic frameworks
Facile transformation of imine covalent organic frameworks into ultrastable crystalline porous aromatic frameworks
Despite recent success in developing new covalent organic frameworks (COFs) materials, synthesis of chemically stable COFs still remains challenging. Here the authors demonstrate a facile strategy that transforms imine-linked COFs into robust porous aromatic frameworks by kinetically fixing the reversible imine linkage via an aza-Diels-Alder cycloaddition reaction.
- Xinle Li
- , Changlin Zhang
- & Yi Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Accelerated microfluidic native chemical ligation at difficult amino acids toward cyclic peptides
Accelerated microfluidic native chemical ligation at difficult amino acids toward cyclic peptides
Flow-based peptide synthesis is a well-established method, yet difficult to combine with native chemical ligation (NCL), the go-to method for peptide cyclization. Here, the authors developed a microfluidic procedure for peptide cyclization within minutes, using NCL and an SEA alkylthioester peptide.
- Nathalie Ollivier
- , Thomas Toupy
- & Oleg Melnyk
-
Article
| Open Access Remote C−H functionalization using radical translocating arylating groups
Remote C−H functionalization using radical translocating arylating groups
Selective remote functionalization of aliphatic C(sp3)−H bonds is highly challenging and often requires transition metals and/or directing groups. Here, the authors show the γ-arylation of aliphatic alcohols via a two-step radical translocation and subsequent radical aryl migration.
- Florian W. Friese
- , Christian Mück-Lichtenfeld
- & Armido Studer
-
Article
| Open Access Adding chemically selective subtraction to multi-material 3D additive manufacturing
Adding chemically selective subtraction to multi-material 3D additive manufacturing
Subtractive manufacturing of microstructures is important for many applications, yet photoresists for 3D laser lithography allow only removal after development under harsh cleavage conditions. Here, the authors introduce a set of chemoselective cleavable photoresists allowing the orthogonal cleavage of microstructures under mild conditions.
- David Gräfe
- , Andreas Wickberg
- & Christopher Barner-Kowollik
-
Article
| Open Access Fe-N system at high pressure reveals a compound featuring polymeric nitrogen chains
Fe-N system at high pressure reveals a compound featuring polymeric nitrogen chains
Owing to the energetic nature of N–N bonds, poly-nitrogen compounds are considered promising high energy density materials. Here, the authors synthesize three iron–nitrogen compounds at high pressure, including FeN4, which features polymeric nitrogen chains of [N42−]n units.
- M. Bykov
- , E. Bykova
- & L. Dubrovinsky
-
Article
| Open Access Silver-catalyzed remote Csp3-H functionalization of aliphatic alcohols
Silver-catalyzed remote Csp3-H functionalization of aliphatic alcohols
Aliphatic alcohols usually require pre-activation for successful functionalization of their carbon chain. Here, the authors report a silver-catalyzed δ-selective functionalization of aliphatic alcohols via Csp3-H bond cleavage under mild conditions without the need of substrate pre-activation.
- Yuchao Zhu
- , Kaimeng Huang
- & Ning Jiao
-
Article
| Open Access Corrosion engineering towards efficient oxygen evolution electrodes with stable catalytic activity for over 6000 hours
Corrosion engineering towards efficient oxygen evolution electrodes with stable catalytic activity for over 6000 hours
Earth-abundant water splitting materials are highly desirable for renewable fuel production, but such catalysts are rarely tested for long-term use. Here, the authors prepare active water-splitting electrocatalysts via corrosion engineering that are stable for thousands of hours.
- Yipu Liu
- , Xiao Liang
- & Jie-Sheng Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Stable complete methane oxidation over palladium based zeolite catalysts
Stable complete methane oxidation over palladium based zeolite catalysts
Palladium supported on zeolite is a highly active catalyst for complete methane oxidation, but its stability needs to be improved. Here, the authors design a highly active catalyst resistant to steam-induced sintering under reaction conditions by alleviating the high mobility of palladium nanoparticles and zeolite degradation.
- Andrey W. Petrov
- , Davide Ferri
- & Oliver Kröcher
-
Article
| Open Access Evolution of thiolate-stabilized Ag nanoclusters from Ag-thiolate cluster intermediates
Evolution of thiolate-stabilized Ag nanoclusters from Ag-thiolate cluster intermediates
Gold nanoclusters are known to grow stepwise from gold-thiolate monomers and oligomers. Here, the authors find that the evolution of silver nanoclusters differs completely from that of gold: rather than following a bottom-up pathway, the clusters evolve from similarly-sized Ag-thiolate cluster intermediates.
- Yitao Cao
- , Jiahao Guo
- & Tierui Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Carbon nitride supported Fe2 cluster catalysts with superior performance for alkene epoxidation
Carbon nitride supported Fe2 cluster catalysts with superior performance for alkene epoxidation
Sub-nano clusters with atomic precision provide a compelling platform for bridging heterogeneous and homogeneous catalysis, but their synthesis remains a great challenge. Here, the authors report a precursor-preselected wet-chemistry strategy to synthesize highly dispersed Fe2 clusters supported on mesoporous carbon nitride.
- Shubo Tian
- , Qiang Fu
- & Yadong Li
-
Article
| Open Access On-surface synthesis of poly(p-phenylene ethynylene) molecular wires via in situ formation of carbon-carbon triple bond
On-surface synthesis of poly(p-phenylene ethynylene) molecular wires via in situ formation of carbon-carbon triple bond
Incorporating carbon-carbon triple bonds into conjugated chains typically requires acetylenic precursors. Here, the authors synthesize poly(p-phenylene ethynylene) molecular wires on Cu(111) by directly coupling trichloromethyl-containing precursors, forming C-C triple bonds in situ
- Chen-Hui Shu
- , Meng-Xi Liu
- & Pei-Nian Liu
-
Article
| Open Access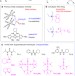 Precise synthesis of sulfur-containing polymers via cooperative dual organocatalysts with high activity
Precise synthesis of sulfur-containing polymers via cooperative dual organocatalysts with high activity
Sulfur-containing polymers are useful commodities, but there is still a big challenge to produce such polymers in a controlled fashion. Here the authors show a metal-free living copolymerization between carbonyl sulfide and epoxides via cooperative catalysis.
- Cheng-Jian Zhang
- , Hai-Lin Wu
- & Xing-Hong Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Trapping an octahedral Ag6 kernel in a seven-fold symmetric Ag56 nanowheel
Trapping an octahedral Ag6 kernel in a seven-fold symmetric Ag56 nanowheel
High-nuclearity silver clusters are appealing synthetic targets for their remarkable structures, but most are isolated serendipitously. Here, the authors describe the rational use of solvents to form cluster-in-cluster silver nanowheels, which comprise an octahedral Ag64+ core surrounded by a Ag56 cage of unusual seven-fold symmetry.
- Zhi Wang
- , Hai-Feng Su
- & Lan-Sun Zheng
-
Article
| Open Access Silicon-oriented regio- and enantioselective rhodium-catalyzed hydroformylation
Silicon-oriented regio- and enantioselective rhodium-catalyzed hydroformylation
Hydroformylation of 1,2-disubstituted alkenes usually occurs at the α position of the directing heteroatom. Here, the authors report the asymmetric rhodium-catalyzed hydroformylation of 1,2-disubstituted alkenylsilanes with excellent regioselectivity at the β position (relative to the silicon heteroatom) and enantioselectivity.
- Cai You
- , Xiuxiu Li
- & Xumu Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Enantioselective reduction of sulfur-containing cyclic imines through biocatalysis
Enantioselective reduction of sulfur-containing cyclic imines through biocatalysis
The 3-thiazolidine ring, a pharmaceutically interesting cyclic structural element found e.g. in some antibiotics, is hard to obtain via currently used approaches. Here, the authors developed a straightforward method to efficiently synthesize a variety of defined, pure 3-thiazolidines.
- Nadine Zumbrägel
- , Christian Merten
- & Harald Gröger
-
Article
| Open Access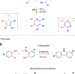 Catalytic condensation for the formation of polycyclic heteroaromatic compounds
Catalytic condensation for the formation of polycyclic heteroaromatic compounds
The development of novel chemical reactions converting biomass-derived alcohols into important classes of compounds is a particularly attractive strategy. Here, the authors report the catalytic condensation of phenols and aminophenols or aminoalcohols for the synthesis of carbazoles, quinolones and acridines.
- Daniel Forberg
- , Tobias Schwob
- & Rhett Kempe
-
Article
| Open Access Gold-catalyzed stereoselective cycloisomerization of allenoic acids for two types of common natural γ-butyrolactones
Gold-catalyzed stereoselective cycloisomerization of allenoic acids for two types of common natural γ-butyrolactones
Gamma-butyrolactones are widespread in Nature, however direct catalytic methods to access them are limited. Here, the authors report a gold-catalyzed cycloisomerization of allenoic acids to acces γ-butyrolactones and apply it to the asymmetric synthesis of xestospongienes E, F, G, and H and other naturally occurring lactones.
- Jing Zhou
- , Chunling Fu
- & Shengming Ma
-
Article
| Open Access The effect of crystallite size on pressure amplification in switchable porous solids
The effect of crystallite size on pressure amplification in switchable porous solids
Pressure amplification phenomena have recently been observed in ordered mesoporous solids, but little is understood about this counter-intuitive behaviour. Here, Kaskel and colleagues demonstrate that crystal size can play an important role in modulating pressure amplification in metal-organic frameworks.
- Simon Krause
- , Volodymyr Bon
- & Stefan Kaskel
-
Article
| Open Access Spontaneous formation of gold nanostructures in aqueous microdroplets
Spontaneous formation of gold nanostructures in aqueous microdroplets
Reactions in aqueous microdroplets can significantly differ from those in bulk. Here, the authors report microdroplets that not only accelerate gold nanoparticle formation by several orders of magnitude but also promote spontaneous nanostructure formation with no reducing agents or template.
- Jae Kyoo Lee
- , Devleena Samanta
- & Richard N. Zare
-
Article
| Open Access Synthesis of a molecularly defined single-active site heterogeneous catalyst for selective oxidation of N-heterocycles
Synthesis of a molecularly defined single-active site heterogeneous catalyst for selective oxidation of N-heterocycles
Synthesis of molecularly defined single-active site catalytic materials is the key to bridging the gap between homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysis. Here, the authors develop such catalysts for selective oxidation of heterocyclic compounds to quinoline and indole via the oxidative polymerization of pyrrole derivatives.
- Yujing Zhang
- , Shaofeng Pang
- & Feng Shi
-
Article
| Open Access Multicomponent reactions provide key molecules for secret communication
Multicomponent reactions provide key molecules for secret communication
Designing molecular keys and combining advanced encryption standard cryptography with molecular steganography is a secure way for encoding messages. Here, the authors use the Ugi four-component reaction of perfluorinated acids to create a library of 500,000 molecular keys for encryption and decryption.
- Andreas C. Boukis
- , Kevin Reiter
- & Michael A. R. Meier
-
Article
| Open Access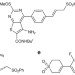 Water-promoted C-S bond formation reactions
Water-promoted C-S bond formation reactions
Despite the biological importance of sulfones, available synthetic methods usually involve toxic metals and reagents or harsh conditions. Here, the authors report an environmentally benign procedure for the metal-free carbon-sulfur bond formation of allylic sulfones in neutral aqueous medium at room temperature.
- Peizhong Xie
- , Jinyu Wang
- & Teck-Peng Loh
-
Article
| Open Access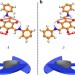 Chiral induction in covalent organic frameworks
Chiral induction in covalent organic frameworks
Controlling chirality and function in metal organic frameworks has been an achievement, but very difficult to carry out in covalent organic frameworks. Here the authors show chiral covalent organic frameworks that are crystallized from achiral precursors by chiral catalytic induction.
- Xing Han
- , Jie Zhang
- & Yong Cui
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Asymmetric synthesis
- Automation
- Biomimetic synthesis
- Catalyst synthesis
- Chemical libraries
- Diversity-oriented synthesis
- Flow chemistry
- Fluorescent labelling
- Synthetic chemistry methodology
- Microwave chemistry
- Nanoparticle synthesis
- Natural product synthesis
- Polymer synthesis
- Reactive precursors
- Solid-phase synthesis

 Samarium(II) folding cascades involving hydrogen atom transfer for the synthesis of complex polycycles
Samarium(II) folding cascades involving hydrogen atom transfer for the synthesis of complex polycycles