Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Iterative SuFEx approach for sequence-regulated oligosulfates and its extension to periodic copolymers
Iterative SuFEx approach for sequence-regulated oligosulfates and its extension to periodic copolymers
The synthesis of sequence-regulated oligosulfates has not yet been established due to the difficulties in precise reactivity control. Here, the authors report a multi-directional divergent iterative method to furnish oligosulfates based on a chain homologation approach, in which the fluorosulfate unit is regenerated.
- Min Pyeong Kim
- , Swatilekha Kayal
- & Sung You Hong
-
Article
| Open Access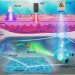 X-ray-activated polymerization expanding the frontiers of deep-tissue hydrogel formation
X-ray-activated polymerization expanding the frontiers of deep-tissue hydrogel formation
Photo-crosslinking polymerization facilitates precise control of hydrogel formation for various applications including tissue engineering, but most existing photo-crosslinking methods fail to achieve deep-tissue penetration, especially within bone structures. Here the authors report a strategy of low-dose X-ray-activated polymerization that enables deep-tissue hydrogel formation.
- Hailei Zhang
- , Boyan Tang
- & Gang Han
-
Article
| Open Access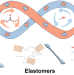 Closed-loop recycling of sulfur-rich polymers with tunable properties spanning thermoplastics, elastomers, and vitrimers
Closed-loop recycling of sulfur-rich polymers with tunable properties spanning thermoplastics, elastomers, and vitrimers
Sulfur-rich polymers are promising candidates for chemical recycling but lack efficient synthetic strategies for achieving diverse structures. Here, the authors report a synthesis strategy for polytrithiocarbonates which is compatible with a wide range of monomers enabling diverse structures via polycondensation of dithiols and dimethyl trithiocarbonate.
- Jin-Zhuo Zhao
- , Tian-Jun Yue
- & Wei-Min Ren
-
Article
| Open Access Long lifetimes white afterglow in slightly crosslinked polymer systems
Long lifetimes white afterglow in slightly crosslinked polymer systems
It is challenging to achieve multicolor long-lived room temperature phosphorescence in intrinsic polymers, especially for white afterglow. Here, the authors report a strategy to obtain pure white afterglow micro-crosslinked polymers by covalently coupling different conjugated chromophores with precursors through a simple and rapid one-pot reaction.
- Qingao Chen
- , Lunjun Qu
- & Chaolong Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Ultraviolet light blocking optically clear adhesives for foldable displays via highly efficient visible-light curing
Ultraviolet light blocking optically clear adhesives for foldable displays via highly efficient visible-light curing
The slow curing speed of UV-based methods to produce UV-blocking optically clear adhesive (OCA) for display panels poses a barrier to commercialization. Here, authors introduce a visible-light driven photo-initiating system for rapid production of OCAs, demonstrating efficient UV-blocking ability.
- Yonghwan Kwon
- , Seokju Lee
- & Min Sang Kwon
-
Article
| Open Access Encoding ordered structural complexity to covalent organic frameworks
Encoding ordered structural complexity to covalent organic frameworks
Starting from simple building blocks with specific molecular packing geometries, here, the authors synthesized structurally complex covalent organic framework COF-305 with nine different stereoisomers of its constituents showing specific sequences on topologically equivalent sites.
- Lei Wei
- , Xinyue Hai
- & Yingbo Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access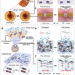 Ultrafast underwater self-healing piezo-ionic elastomer via dynamic hydrophobic-hydrolytic domains
Ultrafast underwater self-healing piezo-ionic elastomer via dynamic hydrophobic-hydrolytic domains
Elastomers capable of autonomous self-healing and mechanical stimulus sensing in aquatic environments are interesting for applications in underwater soft electronics. Here, the authors present a hydrophobic-hydrolytic molecularly engineered self-healing piezo-ionic elastomer with underwater self-healing properties and mechanosensitive ion channels.
- Zhengyang Kong
- , Elvis K. Boahen
- & Do Hwan Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Photocured room temperature phosphorescent materials from lignosulfonate
Photocured room temperature phosphorescent materials from lignosulfonate
It is elusive to manufacture room temperature phosphorescent (RTP) materials through effective and ambient processing approaches. Here the authors report the production of photocured RTP materials using lignosulfonate to act as RTP chromophore and photoinitiator, achieving easy preparation, low cost and good performance.
- Hongda Guo
- , Mengnan Cao
- & Zhijun Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Circular olefin copolymers made de novo from ethylene and α-olefins
Circular olefin copolymers made de novo from ethylene and α-olefins
Although several advances have been made in chemical Polyethylene (PE) re- and upcycling, energy-efficient and selective catalytic processes are still lacking. Here, the authors show coupling of an industrially relevant coordination copolymerization olefins with a functionalized chain-transfer agent, followed by modular assembly of the resulting telechelic polyolefin building blocks by polycondensation to afford ester-linked PE-based random and block copolymers which exhibit full chemical circularity.
- Xing-Wang Han
- , Xun Zhang
- & Yong Tang
-
Article
| Open Access Oxygen-tolerant CO2 electroreduction over covalent organic frameworks via photoswitching control oxygen passivation strategy
Oxygen-tolerant CO2 electroreduction over covalent organic frameworks via photoswitching control oxygen passivation strategy
Direct use of flue gas for the electrocatalytic CO2 reduction reaction is desirable but severely limited by the thermodynamically favorable oxygen reduction reaction. Here the authors report an oxygen passivation strategy to improve electrocatalytic CO2 reduction reaction under aerobic conditions using a covalent organic frameworks with a photoswitching unit.
- Hong-Jing Zhu
- , Duan-Hui Si
- & Yuan-Biao Huang
-
Article
| Open Access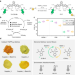 Real-time monitoring polymerization degree of organic photovoltaic materials toward no batch-to-batch variations in device performance
Real-time monitoring polymerization degree of organic photovoltaic materials toward no batch-to-batch variations in device performance
Polymerization degree plays a vital role in controlling material properties and batch-to-batch variations in device performance of polymer solar cells. Here, authors develop in-situ photoluminescence system in tandem to track and estimate the polymerization degree of organic photovoltaic materials.
- Lin-Yong Xu
- , Wei Wang
- & Jie Min
-
Article
| Open Access Helical-caging enables single-emitted large asymmetric full-color circularly polarized luminescence
Helical-caging enables single-emitted large asymmetric full-color circularly polarized luminescence
Circularly polarised luminescence (CPL) is essential for asymmetric synthetic photochemistry. Here, the authors integrate white quantum dots with chiral nematic liquid crystal or liquid crystal polymer to achieve single-emitted tuneable full-colour or white CPL for enantioselective polymerization.
- Yajie Zhou
- , Yaxin Wang
- & Taotao Zhuang
-
Article
| Open Access A highly proton conductive perfluorinated covalent triazine framework via low-temperature synthesis
A highly proton conductive perfluorinated covalent triazine framework via low-temperature synthesis
Perfluorinated covalent triazine frameworks are promising proton-conducting materials with high content of phosphoric acid anchor sites to enhance proton conductivity but their synthesis is challenging. Here, the authors report a mild method to produce perfluorinated covalent triazine frameworks displaying high proton conductivity.
- Lijiang Guan
- , Zhaoqi Guo
- & Shangbin Jin
-
Article
| Open Access Anhydrous interfacial polymerization of sub-1 Å sieving polyamide membrane
Anhydrous interfacial polymerization of sub-1 Å sieving polyamide membrane
The design of highly permeable polyamide (PA) membrane capable of precise ionic sieving remains challenging. Here, the authors report an anhydrous interfacial polymerization on the solid-liquid interface to eliminate water-caused side reactions, leading to a PA layer with an ionic sieving accuracy of 0.5 Å.
- Guangjin Zhao
- , Haiqi Gao
- & Hong Meng
-
Article
| Open Access Resorbable barrier polymers for flexible bioelectronics
Resorbable barrier polymers for flexible bioelectronics
Resorbable bioelectronic devices have potential as tools for monitoring physiological parameters, but short functional lifetimes have slowed translation. Here, the authors report succinate-based copolyesters with barrier properties able to extend the functional lifetime of devices.
- Samantha M. McDonald
- , Quansan Yang
- & Matthew L. Becker
-
Article
| Open Access Stepwise taming of triplet excitons via multiple confinements in intrinsic polymers for long-lived room-temperature phosphorescence
Stepwise taming of triplet excitons via multiple confinements in intrinsic polymers for long-lived room-temperature phosphorescence
Materials with room temperature phosphorescence have potential in a range of applications, but preparing the systems can still be challenging. Here, the authors report an intrinsically polymeric room temperature phosphorescent material, applied in crack detection.
- Liang Gao
- , Jiayue Huang
- & Chaolong Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Photocatalytic CO2 reduction to syngas using metallosalen covalent organic frameworks
Photocatalytic CO2 reduction to syngas using metallosalen covalent organic frameworks
Here, the authors report a gram-scale, one-step synthesis of metallosalen-covalent organic frameworks (M(salen)-COFs) without vacuum evacuation. M(salen)-COFs exhibit good crystallinity and adjustable activities in CO2 photoreduction to syngas.
- Wei Zhou
- , Xiao Wang
- & Wei-Qiao Deng
-
Article
| Open Access Charge-altering releasable transporters enhance mRNA delivery in vitro and exhibit in vivo tropism
Charge-altering releasable transporters enhance mRNA delivery in vitro and exhibit in vivo tropism
Polymers are promising for mRNA delivery, but can have limited efficacy in hard to transfect cells. Here, the authors report charge-altering releasable transporters for improved mRNA transfection in primary T-lymphocytes and enhanced and selective protein expression in vivo.
- Zhijian Li
- , Laura Amaya
- & Paul A. Wender
-
Article
| Open Access Porphene and porphite as porphyrin analogs of graphene and graphite
Porphene and porphite as porphyrin analogs of graphene and graphite
Here the authors report Zn porphene, a member of a new organic metalloporphene family. Similar to graphene, these also are fully conjugated 2D polymers, but are composed of fused metalloporphyrin rings.
- Thomas F. Magnera
- , Paul I. Dron
- & Josef Michl
-
Article
| Open Access Tunable backbone-degradable robust tissue adhesives via in situ radical ring-opening polymerization
Tunable backbone-degradable robust tissue adhesives via in situ radical ring-opening polymerization
Adhesives with both robust adhesion and tunable degradability are clinically and ecologically vital, but their fabrication remains a formidable challenge. Here, the authors report in situ radical ring-opening polymerization-based design and potential biomedical applications of a backbone degradable robust adhesive.
- Ran Yang
- , Xu Zhang
- & Shifang Luan
-
Article
| Open Access Anionic ring-opening polymerization of functional epoxide monomers in the solid state
Anionic ring-opening polymerization of functional epoxide monomers in the solid state
Despite recent advancements in mechanochemical polymerization, understanding the unique mechanochemical reactivity during the ball milling polymerization process still requires extensive investigations. Here the authors use solid-state anionic ring-opening polymerization to synthesize polyethers from various functional epoxide monomers.
- Jihye Park
- , Ahyun Kim
- & Byeong-Su Kim
-
Article
| Open Access A nanoscale MOF-based heterogeneous catalytic system for the polymerization of N-carboxyanhydrides enables direct routes toward both polypeptides and related hybrid materials
A nanoscale MOF-based heterogeneous catalytic system for the polymerization of N-carboxyanhydrides enables direct routes toward both polypeptides and related hybrid materials
Metal-based heterogeneous catalysts are widely employed in ring-opening polymerization (ROP) but up to now the exploration of metal-organic frameworks (MOF) as catalysts in ROP remains underdeveloped. Here, the authors report a MOF heterogeneous catalytic system for fast, controllable, air- and moisture-insensitive ring-opening polymerization of α-amino acid N-carboxyanhydrides, and its seamless integration with hybrid material preparation.
- Ying Liu
- , Zhongwu Ren
- & Yugang Bai
-
Article
| Open Access Recyclable photoresins for light-mediated additive manufacturing towards Loop 3D printing
Recyclable photoresins for light-mediated additive manufacturing towards Loop 3D printing
Among additive manufacturing methods vat photopolymerization (VP) is desired owing to improved efficiency, excellent surface finish, and printing resolution at the micron-scale but the major portion of resins available for VP are based on systems with limited or negligible recyclability. Here, the authors describe an approach that enables the printing of a resin that is amenable to re-printing with retained properties and appearance.
- Xabier Lopez de Pariza
- , Oihane Varela
- & Haritz Sardon
-
Article
| Open Access A recyclable polyester library from reversible alternating copolymerization of aldehyde and cyclic anhydride
A recyclable polyester library from reversible alternating copolymerization of aldehyde and cyclic anhydride
Alternating copolymerization of cyclic anhydrides and epoxides is an interesting platform for the synthesis of polyesters from renewable resources, but the near irreversibility of the copolymerization makes it challenging to develop chemically recyclable polyesters with easy-to-tune structure. Here, the authors develop a recyclable polyester library from alternating copolymerization of aldehyde and cyclic anhydride.
- Xun Zhang
- , Wenqi Guo
- & Xinghong Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Nanocompartment-confined polymerization in living systems
Nanocompartment-confined polymerization in living systems
Polymerizations in living systems can effectively regulate cell functions and behaviors, but their uses have been hindered by the existence of complicated intracorporal interferences, the needs of high concentration of monomers and extra stimulates. Here, the authors address these issues by developing a nanocompartment-confined strategy to achieve broad-spectrum polymerizations in living systems.
- Yun Chen
- , Mengxuan Zuo
- & Yanli Zhao
-
Perspective
| Open Access Applied machine learning as a driver for polymeric biomaterials design
Applied machine learning as a driver for polymeric biomaterials design
The design of polymers for regenerative medicine could be accelerated with the help of machine learning. Here the authors note that machine learning has been applied successfully in other areas of polymer chemistry, while highlighting that data limitations must be overcome to enable widespread adoption within polymeric biomaterials.
- Samantha M. McDonald
- , Emily K. Augustine
- & Matthew L. Becker
-
Article
| Open Access Precise cooperative sulfur placement leads to semi-crystallinity and selective depolymerisability in CS2/oxetane copolymers
Precise cooperative sulfur placement leads to semi-crystallinity and selective depolymerisability in CS2/oxetane copolymers
CS2 promises easy access to degradable sulfur-rich polymers, but ring-opening copolymerisation using CS2 is challenging due to low linkage selectivity and small-molecule by-products. Here, the authors report a cooperative Cr(III)/K catalyst which selectively delivers poly(dithiocarbonates) from CS2 and oxetanes.
- Christoph Fornacon-Wood
- , Bhargav R. Manjunatha
- & Alex J. Plajer
-
Article
| Open Access Artificial intelligence driven design of catalysts and materials for ring opening polymerization using a domain-specific language
Artificial intelligence driven design of catalysts and materials for ring opening polymerization using a domain-specific language
Developing accessible polymeric materials is a challenging task for generative AI models. Here, the authors show that a domain-specific language enables the use of historical data to tune generative models to produce experimentally achievable material designs.
- Nathaniel H. Park
- , Matteo Manica
- & Pedro L. Arrechea
-
Article
| Open Access Bayesian-optimization-assisted discovery of stereoselective aluminum complexes for ring-opening polymerization of racemic lactide
Bayesian-optimization-assisted discovery of stereoselective aluminum complexes for ring-opening polymerization of racemic lactide
Stereoselective catalysts impact polymer’s properties, but discovering such catalysts is expensive and based on trial-and-error. Here, the authors develop a machine-learning tool to guide catalyst discovery and reveal mechanistic features affecting stereoselectivity.
- Xiaoqian Wang
- , Yang Huang
- & Rong Tong
-
Article
| Open Access Tyrosine residues initiated photopolymerization in living organisms
Tyrosine residues initiated photopolymerization in living organisms
Developing a biocompatible polymerization system applicable for the synthesis of intrinsically non-natural polymers is a key step towards intracellular engineering of living organism. Here the authors report tyrosine residues-mediated radical photopolymerizations for intracellular synthesis of non-natural macromolecules
- Mei Zhu
- , Shengliang Wang
- & Xin Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Insights into substitution strategy towards thermodynamic and property regulation of chemically recyclable polymers
Insights into substitution strategy towards thermodynamic and property regulation of chemically recyclable polymers
The global plastic pollution crisis can be mitigated by developing chemically recyclable polymers following the monomer design principle. Here, the authors evaluate substitution effects and structure−property relationships in the ɛ-caprolactone system to guide the design of monomers for the preparation of chemically recyclable polymers.
- Yi-Min Tu
- , Fu-Long Gong
- & Jian-Bo Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access Conjugated cross-linked phosphine as broadband light or sunlight-driven photocatalyst for large-scale atom transfer radical polymerization
Conjugated cross-linked phosphine as broadband light or sunlight-driven photocatalyst for large-scale atom transfer radical polymerization
The application for large-scale production of polymers using photocatalyzed reversible deactivation radical polymerization remains challenging. Here, the authors report the development of a phosphine-based conjugated hypercrosslinked polymer as photocatalyst for an efficient photoinduced and oxygen tolerant copper-catalyzed atom transfer radical polymerization.
- Wei-Wei Fang
- , Gui-Yu Yang
- & Bi-En Tan
-
Article
| Open Access Smart thrombosis inhibitors without bleeding side effects via charge tunable ligand design
Smart thrombosis inhibitors without bleeding side effects via charge tunable ligand design
Treatments to prevent thrombosis are suboptimal. Here, the authors identify a lead an antithrombotic drug targeting polyphosphate based on switchable protonation states for the anion-binding groups, demonstrating antithrombotic activity in multiple mouse models, not causing bleeding, and well tolerated.
- Chanel C. La
- , Stephanie A. Smith
- & Jayachandran N. Kizhakkedathu
-
Article
| Open Access One-pot synthesis of hyperbranched polymers via visible light regulated switchable catalysis
One-pot synthesis of hyperbranched polymers via visible light regulated switchable catalysis
Switchable catalysis promises exceptional efficiency in synthesizing polymers with increasing structural complexity but current achievements in such attempts are limited to constructing linear block copolymers. Here the authors report a visible light regulated switchable catalytic system capable of synthesizing hyperbranched polymers in a one-pot/two-stage procedure with commercial glycidyl acrylate as a heterofunctional monomer.
- Shuaishuai Zhu
- , Maoji Zhao
- & Xiaolin Xie
-
Article
| Open Access A co-anchoring strategy for the synthesis of polar bimodal polyethylene
A co-anchoring strategy for the synthesis of polar bimodal polyethylene
Polar functional groups can improve the polymer properties of polyolefins but also poison the metal catalyst used during the polymerization reaction. Here, the authors show that functionalized bimodal polyolefins in which the high-molecular-weight fraction bears few functional groups and possesses high mechanical and melt properties can be used to implement both polarity and processability
- Chen Zou
- , Quan Wang
- & Changle Chen
-
Article
| Open Access In-situ forming dynamic covalently crosslinked nanofibers with one-pot closed-loop recyclability
In-situ forming dynamic covalently crosslinked nanofibers with one-pot closed-loop recyclability
Polymeric nanofibers are attractive nanomaterials owing to their high surfacearea- to-volume ratio and superior flexibility but designing durable and recyclable polymer nanofibers is challenging. Here, the authors integrate the concept of covalent adaptable networks to produce dynamic covalently crosslinked nanofibers via electrospinning.
- Sheng Wang
- , Nannan Wang
- & Zibiao Li
-
Article
| Open Access Achiral organoiodine-functionalized helical polyisocyanides for multiple asymmetric dearomative oxidations
Achiral organoiodine-functionalized helical polyisocyanides for multiple asymmetric dearomative oxidations
Immobilizing organocatalysts onto helical polymers can facilitate catalyst recycling and boost enantioselectivity. Here, the authors prepare achiral organoiodine-functionalized single left- and right-handed helical polyisocyanides from the same monomers and demonstrate their use in three asymmetric oxidations.
- Zong-Quan Wu
- , Xue Song
- & Na Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Phosphorescent extensophores expose elastic nonuniformity in polymer networks
Phosphorescent extensophores expose elastic nonuniformity in polymer networks
The macroscopic mechanical response in cross-linked polymer networks has been well investigated but an understanding of pre-failure local mechanical responses at the level of individual crosslinks is still lacking. Here, using an extensophore concept, the authors show that the crosslinks in an elastic polymer network extend, fluctuate, and deform with a wide range of molecular individuality
- Kaikai Zheng
- , Yifan Zhang
- & Steve Granick
-
Article
| Open Access Stabilizing copper sites in coordination polymers toward efficient electrochemical C-C coupling
Stabilizing copper sites in coordination polymers toward efficient electrochemical C-C coupling
Typically, Cu catalysts agglomerate under electrochemical conditions. Here, the authors report a coordination polymer catalyst with neighboring Cu sites which remain isolated and reduce CO2 to C2H4 with high selectivity and stability
- Yongxiang Liang
- , Jiankang Zhao
- & Jie Zeng
-
Article
| Open Access Multicolor hyperafterglow from isolated fluorescence chromophores
Multicolor hyperafterglow from isolated fluorescence chromophores
The development of organic afterglow materials with sufficient color purity and high quantum efficiency for hyperafterglow is a great challenging. Here, the authors demonstrate an efficient strategy to achieve hyperafterglow emission through sensitizing and stabilizing isolated fluorescence chromophores by integrating multiresonance fluorescence chromophores into afterglow host in a singlecomponent copolymer.
- Xiao Zhang
- , Mingjian Zeng
- & Wei Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanochemically accessing a challenging-to-synthesize depolymerizable polymer
Mechanochemically accessing a challenging-to-synthesize depolymerizable polymer
Polymers with low ceiling temperatures (Tc) are highly desirable as they can depolymerize under mild conditions, but they typically suffer from demanding synthetic conditions and poor stability. Here, the authors envision that this challenge can be addressed by developing high-Tc polymers that can be converted into low-Tc polymers on demand.
- Tze-Gang Hsu
- , Shiqi Liu
- & Junpeng Wang
-
Article
| Open Access 2D conjugated microporous polyacetylenes synthesized via halogen-bond-assisted radical solid-phase polymerization for high-performance metal-ion absorbents
2D conjugated microporous polyacetylenes synthesized via halogen-bond-assisted radical solid-phase polymerization for high-performance metal-ion absorbents
Polyacetylenes are an important class of conjugated polymers but are generally synthesized via metal-catalyzed coordination polymerization leaving trace metals as impurities. Here the authors demonstrate a free radical polymerization of co-crystalized acetylene monomers without the need of a metal catalyst.
- Hong Tho Le
- , Chen-Gang Wang
- & Atsushi Goto
-
Article
| Open Access Closed-loop chemical recycling of cross-linked polymeric materials based on reversible amidation chemistry
Closed-loop chemical recycling of cross-linked polymeric materials based on reversible amidation chemistry
Closed-loop chemical recycling provides a solution to the end-of-use problem of synthetic polymers but the design of dynamic bonds for preparing chemically recyclable cross-linked polymers remains challenging. Here, the authors report a dynamic reversible amidation reaction between maleic anhydrides and secondary amines.
- Bo Qin
- , Siyuan Liu
- & Xi Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Overcoming the low reactivity of biobased, secondary diols in polyester synthesis
Overcoming the low reactivity of biobased, secondary diols in polyester synthesis
Glucose-derived isosorbide is a rigid polyester monomer with a low reactivity. Here, the authors report the synthesis of high molecular weight biobased polyesters with promising barrier and mechanical properties via in situ generation of reactive aryl ester groups.
- Daniel H. Weinland
- , Kevin van der Maas
- & Gert-Jan M. Gruter
-
Article
| Open Access Polymer nanoparticles pass the plant interface
Polymer nanoparticles pass the plant interface
Nanoplastic contamination is a serious environmental concern and could have implications on plant life depending upon interactions. Here, the authors study the effect of size and charge on the accumulation and uptake of model polymer nanoparticles by plant roots which has implications for environmental exposure and nanoparticle delivery to plants.
- Sam J. Parkinson
- , Sireethorn Tungsirisurp
- & Richard M. Napier
-
Article
| Open Access Highly reinforced and degradable lignocellulose biocomposites by polymerization of new polyester oligomers
Highly reinforced and degradable lignocellulose biocomposites by polymerization of new polyester oligomers
Cellulose biocomposites from nanocellulose or plant fibers with polymer matrix are often not degradable and suffer from insufficient mechanical properties to replace established materials. Here, the authors demonstrate the fabrication of hydrolytically degradable polymers through in-situ polymerization of new functionally balanced oligomers within high-content lignocellulose reinforcement networks.
- Erfan Oliaei
- , Peter Olsén
- & Lars A. Berglund
-
Article
| Open Access Microspheres from light—a sustainable materials platform
Microspheres from light—a sustainable materials platform
Photopolymerization provides a safe and mild fabrication pathway towards polymeric particles but the implementation of photochemistry from solution to dispersed media to produce particles is far from trivial. Here, the authors demonstrate an additive-free step-growth photopolymerization with sunlight, exploiting the photoinduced Diels-Alder to fabricate micrometer sized polymeric particles.
- Laura Delafresnaye
- , Florian Feist
- & Christopher Barner-Kowollik
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanochemical synthesis of inverse vulcanized polymers
Mechanochemical synthesis of inverse vulcanized polymers
Inverse vulcanization is a process that enables to convert sulfur, a by-product of the petroleum industry, into polymers. Here the authors report a synthetic method of inverse vulcanization via mechanochemical synthesis; compared to thermal routes, a broader range of monomers can be used, and the protocol yields materials with enhanced mercury capture capacity.
- Peiyao Yan
- , Wei Zhao
- & Tom Hasell
-
Article
| Open Access Copper-catalyzed Z-selective synthesis of acrylamides and polyacrylamides via alkylidene ketenimines
Copper-catalyzed Z-selective synthesis of acrylamides and polyacrylamides via alkylidene ketenimines
Alkylidene ketenimines are rarely reported, but synthetically useful, reactive intermediates. Here, the authors disclose a three-component reaction of alkyne, azide and water by cycloaddition, nitrogen extrusion, and carbene-assisted rearrangement, via in situ formation of alkylidene ketenimine.
- Xuelun Duan
- , Nan Zheng
- & Wangze Song

 Double cross-linked 3D layered PBI proton exchange membranes for stable fuel cell performance above 200 °C
Double cross-linked 3D layered PBI proton exchange membranes for stable fuel cell performance above 200 °C