Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Insulated conjugated bimetallopolymer with sigmoidal response by dual self-controlling system as a biomimetic material
Insulated conjugated bimetallopolymer with sigmoidal response by dual self-controlling system as a biomimetic material
Molecules can serve as biomimetic sensors, but dual self-controlling systems that involve self-activation and self-regulation are difficult to mimic. Here the authors report an insulated conjugated bimetallopolymer with cooperative multiple transition metals that phosphoresces in response to carbon monoxide.
- Hiroshi Masai
- , Takuya Yokoyama
- & Jun Terao
-
Article
| Open Access Emergence of chirality and structural complexity in single crystals at the molecular and morphological levels
Emergence of chirality and structural complexity in single crystals at the molecular and morphological levels
Single crystallinity combined with multidomain morphology is counterintuitive. Here, the authors achieve such a phenomenon in a metal-organic framework that also displays chirality at both the molecular and morphological levels.
- Maria Chiara di Gregorio
- , Linda J. W. Shimon
- & Milko E. van der Boom
-
Article
| Open Access Self-assembled single-atom nanozyme for enhanced photodynamic therapy treatment of tumor
Self-assembled single-atom nanozyme for enhanced photodynamic therapy treatment of tumor
The hypoxic microenvironment in solid tumors limits the efficacy of photodynamic therapy (PDT) since oxygen is necessary to produce high cytotoxic singlet oxygen species. Here, the authors develop an improved self-assembled single-atom nanozyme which allows oxygen generation to enhance PDT efficacy.
- Dongdong Wang
- , Huihui Wu
- & Yanli Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Selection from a pool of self-assembling lipid replicators
Selection from a pool of self-assembling lipid replicators
Selection in compartmentalized self-replicating systems might provide a way for life to arise from abiotic environments. Here, the authors explore selection in a system of transient autocatalytic lipids and find that autocatalytic kinetics and phase separation are the key selection factors.
- Ignacio Colomer
- , Arseni Borissov
- & Stephen P. Fletcher
-
Article
| Open Access Color-tunable single-fluorophore supramolecular system with assembly-encoded emission
Color-tunable single-fluorophore supramolecular system with assembly-encoded emission
Regulating fluorescent properties of small molecules in a controlled manner has been a fundamental research goal but realizing multi-color emission from a single fluorophore remains challenging. Here the authros demonstrate that combined pyrene fluorophore and acylhydrazone units show multi-color switchable fluorescent at different assembled states.
- Qian Wang
- , Qi Zhang
- & He Tian
-
Article
| Open Access Time-dependent solid-state molecular motion and colour tuning of host-guest systems by organic solvents
Time-dependent solid-state molecular motion and colour tuning of host-guest systems by organic solvents
Host-guest solid state molecular motion is a critical but underexplored phenomenon which can be used to control molecular machines that function in the solid state. Here, the authors describe a solid state machine that shows solvent vapour- and mechanically-induced molecular motion that allows access to different crystalline and amorphous forms.
- Yu-Dong Yang
- , Xiaofan Ji
- & Han-Yuan Gong
-
Article
| Open Access Guanidinocalix[5]arene for sensitive fluorescence detection and magnetic removal of perfluorinated pollutants
Guanidinocalix[5]arene for sensitive fluorescence detection and magnetic removal of perfluorinated pollutants
Design of materials which allow for simultaneous detection and removal of water pollutants is challenging. Here the authors develop a guanidinocalix[5]arene that selectively binds perfluorinated alkyl substances and allows for fluorescence detection as well as removal of the pollutants in contaminated water.
- Zhe Zheng
- , Huijuan Yu
- & Dong-Sheng Guo
-
Article
| Open Access A metal–peptide capsule by multiple ring threading
A metal–peptide capsule by multiple ring threading
Constructing molecular cages from entangled molecules is a complex task requiring precise topological control. Here, the authors thread together six metal-peptide rings into a giant cubic molecular capsule with a defined cavity and 24 crossover points.
- Tomohisa Sawada
- , Yuuki Inomata
- & Makoto Fujita
-
Article
| Open Access Diverse protein assembly driven by metal and chelating amino acids with selectivity and tunability
Diverse protein assembly driven by metal and chelating amino acids with selectivity and tunability
Precise manipulation of protein self-assembly in vitro is challenging. Here, the authors developed an approach for driving metal-mediated reversible protein assembly by genetically installing a bipyridine residue into an oligomeric (D3) protein.
- Minwoo Yang
- & Woon Ju Song
-
Article
| Open Access Orthogonal regulation of DNA nanostructure self-assembly and disassembly using antibodies
Orthogonal regulation of DNA nanostructure self-assembly and disassembly using antibodies
Antibodies are useful biomarkers and are emerging as powerful therapeutic tools. Here the authors report a rational strategy to orthogonally control assembly and disassembly of DNA-based nanostructures using specific IgG antibodies as molecular inputs.
- Simona Ranallo
- , Daniela Sorrentino
- & Francesco Ricci
-
Article
| Open Access DNA origami cryptography for secure communication
DNA origami cryptography for secure communication
Biomolecular cyptography that exploits specific interactions could be used for data encryption. Here the authors use the folding of M13 DNA to encrypt information for secure communication.
- Yinan Zhang
- , Fei Wang
- & Chunhai Fan
-
Article
| Open Access Spatial control over catalyst positioning on biodegradable polymeric nanomotors
Spatial control over catalyst positioning on biodegradable polymeric nanomotors
Multiple nanomotors for application in various fields have been fabricated, but so far only relatively simple designs for synthetic nanomotors are reported. Here, the authors report on a biodegradable polymeric nanomotor and demonstrate spatial control for catalyst positioning.
- B. Jelle Toebes
- , F. Cao
- & Daniela A. Wilson
-
Article
| Open Access Reorientation behavior in the helical motility of light-responsive spiral droplets
Reorientation behavior in the helical motility of light-responsive spiral droplets
Converting chemical energy into movement is essential to all forms of life, but the molecular processes are yet to be uncovered. Here the authors show a light-responsive reorientation behavior in liquid crystal droplets which stems from dynamic inversion of chirality from molecules to liquid crystals in confinement.
- Federico Lancia
- , Takaki Yamamoto
- & Nathalie Katsonis
-
Article
| Open Access Cation-induced chirality in a bifunctional metal-organic framework for quantitative enantioselective recognition
Cation-induced chirality in a bifunctional metal-organic framework for quantitative enantioselective recognition
Metal-organic frameworks with luminescence and chirality are promising for luminescent sensors for chiral molecules. Here, the authors use cation exchange to introduce chirality in multifunctional metal-organic framework systems for rapid enantioselective luminescent sensing.
- Zongsu Han
- , Kunyu Wang
- & Peng Cheng
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular basis for chirality-regulated Aβ self-assembly and receptor recognition revealed by ion mobility-mass spectrometry
Molecular basis for chirality-regulated Aβ self-assembly and receptor recognition revealed by ion mobility-mass spectrometry
Chiral inversion of amino acids is thought to modulate the structure and function of amyloid beta (Aβ) but these processes are poorly understood. Here, the authors develop an ion mobility-mass spectrometry based approach to study chirality-regulated structural features of Aβ fragments and their influence on receptor recognition.
- Gongyu Li
- , Kellen DeLaney
- & Lingjun Li
-
Article
| Open Access Synthetic asters as elastic and radial skeletons
Synthetic asters as elastic and radial skeletons
Nanosystems capable of organisation and the formation of structures are of interest in nanotechnology. Here, the authors report on synthetic asters made of gemini surfactant which are able to position microparticles based on size and chemical composition which can also be organised into higher order structures.
- Qingqiao Xie
- , Xixi Chen
- & Lingxiang Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access Active generation of nanoholes in DNA origami scaffolds for programmed catalysis in nanocavities
Active generation of nanoholes in DNA origami scaffolds for programmed catalysis in nanocavities
DNA origami provide scaffolds for spatial and temporal control of catalytic functions in confined nanocavities. Here the authors engineer nanoholes in DNA origami scaffolds.
- Jianbang Wang
- , Liang Yue
- & Itamar Willner
-
Article
| Open Access A domino reaction for generating β-aryl aldehydes from alkynes by substrate recognition catalysis
A domino reaction for generating β-aryl aldehydes from alkynes by substrate recognition catalysis
Supramolecular interactions may be responsible for higher degree of efficiency and selectivity in homogeneous catalysis. Here, the authors exploit the concept of supramolecular catalysis to develop a domino rhodium-catalyzed hydroformylation of α-alkynoic acids followed by Michael addition of nucleophiles.
- Weiwei Fang
- , Felix Bauer
- & Bernhard Breit
-
Article
| Open Access A merged copper(I/II) cluster isolated from Glaser coupling
A merged copper(I/II) cluster isolated from Glaser coupling
Copper-oxygen species in organometallic complexes and enzymes are involved in many oxidation reactions. Here, the authors synthesize a macrocycle-protected mixed valence Cu(I/II) cluster with an unusually strong oxidation capacity and apply it to hydrogen atom transfer reactions with inert hydrocarbons.
- Siqi Zhang
- & Liang Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Stiffness-switchable DNA-based constitutional dynamic network hydrogels for self-healing and matrix-guided controlled chemical processes
Stiffness-switchable DNA-based constitutional dynamic network hydrogels for self-healing and matrix-guided controlled chemical processes
Dynamic hydrogels with controllable properties are of interest for a range of applications. Here, the authors report on a DNA hydrogel system which can be tailored to have reversible mechanical changes, reversible shape changes, is self-healing and can be used for controlled release applications.
- Liang Yue
- , Shan Wang
- & Itamar Willner
-
Article
| Open Access Dual self-assembly of supramolecular peptide nanotubes to provide stabilisation in water
Dual self-assembly of supramolecular peptide nanotubes to provide stabilisation in water
Reversibility of peptide hydrogen bonded supramolecular assemblies makes them tunable but highly dynamic and prone to disassembly at the low concentration. Here the authors show a secondary hydrophobic interaction, near the peptide core that stabilises the peptide bonds, without losing the solubility of the systems in aqueous conditions.
- Julia Y. Rho
- , Henry Cox
- & Sébastien Perrier
-
Article
| Open Access A chemically fueled non-enzymatic bistable network
A chemically fueled non-enzymatic bistable network
Although bistability is common in biology, it is very difficult to design de novo into synthetic systems. Here, the authors present an experimental and theoretical analysis of a chemical network that displays bistable behavior under certain far-from-equilibrium conditions, and map the parameter space in which bistability operates.
- Indrajit Maity
- , Nathaniel Wagner
- & Gonen Ashkenasy
-
Article
| Open Access Single-molecule level control of host-guest interactions in metallocycle-C60 complexes
Single-molecule level control of host-guest interactions in metallocycle-C60 complexes
Studying the single-molecule behavior of host-guest complexes can provide fundamental insights into their supramolecular interactions. Here, the authors use the scanning tunneling microscopy break junction technique to show that encapsulation of a C60 molecule significantly enhances the conductance of an organoplatinum metallocycle; mechanical stretching of the junction releases the guest, returning the conductance to free-host level.
- Jian-Hong Tang
- , Yueqi Li
- & Peter J. Stang
-
Article
| Open Access Hydrogen-bonded frameworks for molecular structure determination
Hydrogen-bonded frameworks for molecular structure determination
Single crystal X-ray diffraction is an invaluable tool for molecular structure determination, but growing single crystals is often an arduous process. Here the authors find that the structures of a wide array of molecules can be determined by SCXRD when included in hydrogen-bonded guanidinium organosulfonate host frameworks in a single-step crystallization.
- Yuantao Li
- , Sishuang Tang
- & Michael D. Ward
-
Article
| Open Access Soft chromophore featured liquid porphyrins and their utilization toward liquid electret applications
Soft chromophore featured liquid porphyrins and their utilization toward liquid electret applications
Though electret materials are attractive for realizing flexible mechanoelectrical devices, these materials are typically solid films. Here, the authors report stretchable ‘liquid-electret’ devices consisting solvent-free liquid porphyrins that show piezoelectric and electroacoustic functionality.
- Avijit Ghosh
- , Manabu Yoshida
- & Takashi Nakanishi
-
Article
| Open Access Switchable organoplatinum metallacycles with high quantum yields and tunable fluorescence wavelengths
Switchable organoplatinum metallacycles with high quantum yields and tunable fluorescence wavelengths
Fluorescent supramolecular coordination complexes are of interest for chemical sensing and optical devices. Here the authors synthesize nine organoplatinum metallacycles with high quantum yields, whose fluorescence wavelengths are tuned through manipulation of their photoinduced electron transfer and intramolecular charge transfer properties.
- Jun-Long Zhu
- , Lin Xu
- & Hai-Bo Yang
-
Article
| Open Access A building-block design for enhanced visible-light switching of diarylethenes
A building-block design for enhanced visible-light switching of diarylethenes
Development of light-responsive materials imposes a demand on visible-light photoswitching but this is often achieved at expense of photochromic performance. Here the authors use a building-block design to achieve a diarylethene all-visible-light photoswitch with improved photochromic efficiency and enhanced photo-fatigue resistance.
- Zhiwei Zhang
- , Wenhui Wang
- & He Tian
-
Article
| Open Access Moebius strips of chiral block copolymers
Moebius strips of chiral block copolymers
The Moebius topology is intriguing because of its structural elegance and distinct properties. Here the authors report block copolymer Moebius strips via a fast self-assembly of chiral block copolymer polystyrene-block-poly(D-lactide acid) in tetrahydrofuran/water mixed solvents.
- Zhen Geng
- , Bijin Xiong
- & Zhenzhong Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Asymmetric catalysis mediated by a mirror symmetry-broken helical nanoribbon
Asymmetric catalysis mediated by a mirror symmetry-broken helical nanoribbon
If asymmetric catalysts were available by mirror symmetry breaking, an important insight may be given to how the biomolecular homochirality emerged in nature. Here, the authors report the first example of asymmetric catalysis by employing mirror symmetry-broken helical nanoribbons as the ligand.
- Zhaocun Shen
- , Yutao Sang
- & Minghua Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Thermodynamic efficiency in dissipative chemistry
Thermodynamic efficiency in dissipative chemistry
Open chemical systems operate out of equilibrium, providing more opportunities than closed systems, but a theoretical framework to describe their performance is lacking. Here, the authors assess the efficiency of two classes of dissipative processes with a method applicable to any open chemical reaction network.
- Emanuele Penocchio
- , Riccardo Rao
- & Massimiliano Esposito
-
Article
| Open Access Hierarchical self-assembly of organic heterostructure nanowires
Hierarchical self-assembly of organic heterostructure nanowires
Organic heterostructures attract attention in material chemistry but the precise bottom-up synthesis is still challenging. Herein the authors present a hierarchical self-assembly approach to synthesize one-dimensional organic heterostructures by regulating the noncovalent interactions.
- Ming-Peng Zhuo
- , Jun-Jie Wu
- & Liang-Sheng Liao
-
Perspective
| Open Access Kinetic asymmetry allows macromolecular catalysts to drive an information ratchet
Kinetic asymmetry allows macromolecular catalysts to drive an information ratchet
The mechanism by which macromolecular catalysts use energy from exergonic reactions to move, adapt, and assemble has been unclear. In this Perspective article, R. Dean Astumian shows that in addition to disequilibrium of the catalyzed reaction, kinetic asymmetry is the essential feature required to drive non-equilibrium response by an information ratchet mechanism.
- R. Dean Astumian
-
Article
| Open Access TriQuinoline
TriQuinoline
In this paper, the authors introduce a structurally elegant 2D triquinoline molecule as a discrete model for graphitic materials with atom-sized voids. The compound has unusual chemical properties, including high proton affinity and rich supramolecular behavior, forming complexes via both π-π and CH-π contact modes.
- Shinya Adachi
- , Masakatsu Shibasaki
- & Naoya Kumagai
-
Article
| Open Access Compartmentalization-induced phosphorescent emission enhancement and triplet energy transfer in aqueous medium
Compartmentalization-induced phosphorescent emission enhancement and triplet energy transfer in aqueous medium
Artificial light harvesting systems in aqueous medium are challenging to realize due to quenching effects from water and oxygen. Here the authors demonstrate rod-coil amphiphiles which act as compartmentalization agent to shield platinum(II) phosphors and enable their ordered spatial organization.
- Zijian Li
- , Yifei Han
- & Feng Wang
-
Article
| Open Access A [13]rotaxane assembled via a palladium molecular capsule
A [13]rotaxane assembled via a palladium molecular capsule
Mechanically interlocked molecules and molecular cages are two important themes in supramolecular chemistry. Here, the authors combine these concepts to construct a giant [13]rotaxane built around a palladium capsule, one of the most complex metallosupramolecular assemblies yet.
- Jesus Ferrando-Soria
- , Antonio Fernandez
- & Richard E. P. Winpenny
-
Article
| Open Access Single-handed supramolecular double helix of homochiral bis(N-amidothiourea) supported by double crossed C−I···S halogen bonds
Single-handed supramolecular double helix of homochiral bis(N-amidothiourea) supported by double crossed C−I···S halogen bonds
Building an artificial double helix is a compelling challenge, and most strategies rely on the intertwining of two helical strands. Here, in a very different approach, the authors construct a supramolecular double helix from multiple synthetic small molecules chained together by double crossed halogen bonds.
- Xiaosheng Yan
- , Kunshan Zou
- & Yunbao Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access Supramolecular trap for catching polyamines in cells as an anti-tumor strategy
Supramolecular trap for catching polyamines in cells as an anti-tumor strategy
Polyamines are essential for cell growth and are frequently increased in concentration in cancer cells. Here, the authors use a macrocycle to generate a supramolecular trap, which depletes the polyamines in cells, induces apoptosis and reduces cancer cell growth in mice.
- Junyi Chen
- , Hanzhi Ni
- & Chunju Li
-
Article
| Open Access Chemical mimicry of viral capsid self-assembly via corannulene-based pentatopic tectons
Chemical mimicry of viral capsid self-assembly via corannulene-based pentatopic tectons
The icosahedron, as the polyhedron closest in symmetry to the sphere, is one of the most compelling Platonic solids for chemists to construct. Here, the authors assemble a supramolecular icosahedron from twelve pentatopic corannulene-based tectons, a strategy that was proposed over a decade ago but only now synthetically realized.
- Yu-Sheng Chen
- , Ephrath Solel
- & Yi-Tsu Chan
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular bilayer graphene
Molecular bilayer graphene
Molecular bilayer graphene — a discrete assembly of two stacked graphene fragments — is challenging to produce in pure form. Here, the authors are able to synthesize and characterize stable molecular bilayer graphenes by the π−π stacking of two identical, well-defined nanographene sheets.
- Xin-Jing Zhao
- , Hao Hou
- & Yuan-Zhi Tan
-
Article
| Open Access Bio-inspired creation of heterogeneous reaction vessels via polymerization of supramolecular ion pair
Bio-inspired creation of heterogeneous reaction vessels via polymerization of supramolecular ion pair
Tuning the environment of catalytic active sites may improve the selectivity of heterogeneous catalysts. Here, the authors modify the outer-sphere environment of active sites in hydroformylation catalysts by encapsulating the active sites in nanovessels formed by ion pair-directed supramolecular assembly.
- Ke Dong
- , Qi Sun
- & Feng-Shou Xiao
-
Article
| Open Access Ordering, flexibility and frustration in arrays of porphyrin nanorings
Ordering, flexibility and frustration in arrays of porphyrin nanorings
The packing of spheres, disks and other simple shapes into arrays on surfaces is relevant to many problems across the physical sciences. Here the authors study the influence of flexibility and reduced symmetry on the packing of porphyrin nanorings which are deposited from solution onto a graphite surface.
- Alex Summerfield
- , Matteo Baldoni
- & Peter H. Beton
-
Article
| Open Access Supramolecular peptide constructed by molecular Lego allowing programmable self-assembly for photodynamic therapy
Supramolecular peptide constructed by molecular Lego allowing programmable self-assembly for photodynamic therapy
Despite its application in functional materials, covalent peptide modification and controlling peptide self-assembly remains challenging. Here the authors report a programmable supramolecular peptide by pillararene-based noncovalent interactions with multiple self-assembly morphologies and application in PDT.
- Huangtianzhi Zhu
- , Huanhuan Wang
- & Feihe Huang
-
Article
| Open Access One-pot universal initiation-growth methods from a liquid crystalline block copolymer
One-pot universal initiation-growth methods from a liquid crystalline block copolymer
Construction of hierarchical nanostructures is important in material science, but precise morphological control remains a challenge. Here, the authors report a one-pot in-situ initiation-growth process from a liquid crystalline block copolymer to precisely control the morphology and dimensions of hierarchical nanostructures.
- Bixin Jin
- , Koki Sano
- & Xiaoyu Li
-
Article
| Open Access Superlattice by charged block copolymer self-assembly
Superlattice by charged block copolymer self-assembly
Understanding the phase behavior of charged block copolymers may potentially lead to unexplored self-assembled morphologies. Here, the authors report the preparation of ion-containing diblock copolymers featuring a superlattice state varying between disordered and lamellar morphologies depending on the charge density.
- Jimin Shim
- , Frank S. Bates
- & Timothy P. Lodge
-
Article
| Open Access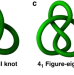 Coordination-driven self-assembly of a molecular figure-eight knot and other topologically complex architectures
Coordination-driven self-assembly of a molecular figure-eight knot and other topologically complex architectures
Molecular knots and links continue to fascinate synthetic chemists. Here, the authors use stacking and hydrogen-bonding interactions between a set of similar building blocks to construct several complex molecular topologies, including a figure-eight knot and a trefoil knot.
- Li-Long Dang
- , Zhen-Bo Sun
- & Guo-Xin Jin
-
Article
| Open Access Polyaromatic nanocapsules as photoresponsive hosts in water
Polyaromatic nanocapsules as photoresponsive hosts in water
Photoresponsive molecular capsules that can be used in water are rare. Here, the authors construct polyaromatic nanocapsules via self-assembly from photoswitch-bearing amphiphilic molecules in water. Light induces a structural change in the amphiphiles, triggering the capsule to disassemble into monomers and release encapsulated guests.
- Lorenzo Catti
- , Natsuki Kishida
- & Michito Yoshizawa
-
Article
| Open Access Enzyme-responsive progelator cyclic peptides for minimally invasive delivery to the heart post-myocardial infarction
Enzyme-responsive progelator cyclic peptides for minimally invasive delivery to the heart post-myocardial infarction
Injectable hydrogels have gained significant interest; yet, due to high viscosity, many are unsuitable for catheter delivery. Here, the authors report on cyclic peptides with low viscosity for catheter delivery, which form self-assembled peptide hydrogels following enzymatic cleavage and demonstrated delivery in vivo.
- Andrea S. Carlini
- , Roberto Gaetani
- & Nathan C. Gianneschi
-
Article
| Open Access Plant leaves inspired sunlight-driven purifier for high-efficiency clean water production
Plant leaves inspired sunlight-driven purifier for high-efficiency clean water production
Natural leaves can purify water under sunlight through a combination of osmotic pressure, transpiration, and guttation effects. Here the authors design a composite material mimicking these combined effects, achieving sunlight-driven pure water production from brine with high collection rate.
- Hongya Geng
- , Qiang Xu
- & Chun Li
-
Article
| Open Access Temperature-controlled repeatable scrambling and induced-sorting of building blocks between cubic assemblies
Temperature-controlled repeatable scrambling and induced-sorting of building blocks between cubic assemblies
In this paper, the authors study the temperature-controlled dynamic behavior of a system of nanocubes self-assembled from two different building blocks. Non-intuitively, the disordered, equilibrium state (a mixture of heteroleptic cubes) and the ordered, out-of-equilibrium state (a mixture of homoleptic cubes) are cycled by heating and subsequent rapid cooling.
- Yi-Yang Zhan
- , Tatsuo Kojima
- & Shuichi Hiraoka

 Interplay of water and a supramolecular capsule for catalysis of reductive elimination reaction from gold
Interplay of water and a supramolecular capsule for catalysis of reductive elimination reaction from gold