Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Engineering metal-carbide hydrogen traps in steels
Engineering metal-carbide hydrogen traps in steels
Understanding how hydrogen embrittles steels and developing the solutions are crucial for enabling the hydrogen economy. Here, the authors report a materials design strategy that can increase the hydrogen trapping capacity by creating carbon vacancies in metal carbide precipitates via microalloying.
- Pang-Yu Liu
- , Boning Zhang
- & Yi-Sheng Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Sub-micro porous thin polymer membranes for discriminating H2 and CO2
Sub-micro porous thin polymer membranes for discriminating H2 and CO2
The fabrication of polymeric membranes with high permeance and remarkable selectivity for simultaneous H2 purification and CO2 capture is challenging. Here, the authors design a polymer membrane with sub-micro pores via controlled transformation of amine-linked polymer films into benzimidazole- and amine-linked polymer layers.
- Xueru Yan
- , Tianqi Song
- & Xinlei Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Accelerating process development for 3D printing of new metal alloys
Accelerating process development for 3D printing of new metal alloys
Process development for 3D printing of new metal alloys can be time-consuming and variability in the printing outcome makes it even more challenging. Here, authors demonstrate an in-situ method using high-speed imaging and deep learning to accelerate the process design for a more consistent quality.
- David Guirguis
- , Conrad Tucker
- & Jack Beuth
-
Article
| Open Access Atomic-scale observation of nucleation- and growth-controlled deformation twinning in body-centered cubic nanocrystals
Atomic-scale observation of nucleation- and growth-controlled deformation twinning in body-centered cubic nanocrystals
Deformation twinning in body-centered cubic (BCC) metals is generally believed to be controlled by twin nucleation, but facilitated by rapid twin growth once the nucleation energy barrier is overcome. Here, the authors demonstrate both nucleation- and growth-controlled twinning modes in BCC Ta nanocrystals depending on the crystal size.
- Li Zhong
- , Yin Zhang
- & Scott X. Mao
-
Article
| Open Access How solute atoms control aqueous corrosion of Al-alloys
How solute atoms control aqueous corrosion of Al-alloys
Understanding the underlying mechanisms during corrosion is one of the grand key missions to improve the sustainability of the material world. Here, the authors combine atomic scale imaging and calculations to show how solute atoms react during aqueous corrosion of a multicomponent Al alloy.
- Huan Zhao
- , Yue Yin
- & Dierk Raabe
-
Article
| Open Access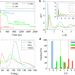 Microscopic mechanisms of pressure-induced amorphous-amorphous transitions and crystallisation in silicon
Microscopic mechanisms of pressure-induced amorphous-amorphous transitions and crystallisation in silicon
The mechanism of amorphous-amorphous transitions is highly debated. Here, the authors use molecular dynamics simulations to reveal transitions via nucleation-growth or spinodal decomposition, resembling a thermodynamic phase transition but influenced by mechanics.
- Zhao Fan
- & Hajime Tanaka
-
Article
| Open Access Stretchable and negative-Poisson-ratio porous metamaterials
Stretchable and negative-Poisson-ratio porous metamaterials
In this work, authors demonstrate highly stretchable conductive porous elastomers that can achieve up to 1200% strain with low or negative Poisson’s ratios by uniaxial, biaxial, and triaxial hot-pressing strategies.
- Xiaoyu Zhang
- , Qi Sun
- & Guoqing Zu
-
Article
| Open Access A micro-architectured material as a pressure vessel for green mobility
A micro-architectured material as a pressure vessel for green mobility
A shellular is a micro-architectured material, composed of a continuous smooth-curved thin shell in the form of a triply periodic minimal surface. Here, authors propose schellular designs applied to pressure vessels and demonstrate its competitive practical features against spherical and cylindrical vessels.
- Yoon Chang Jeong
- , Seung Chul Han
- & Kiju Kang
-
Article
| Open Access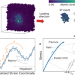 Anomalous temperature dependence of elastic limit in metallic glasses
Anomalous temperature dependence of elastic limit in metallic glasses
It is still challenging to study the atomistic mechanism of inelastic deformation in metallic glasses owing to their amorphous structure. Here, the authors report an anomalous temperature dependence of the onset of plasticity in metallic glasses at low temperature.
- Yifan Wang
- , Jing Liu
- & Wei Cai
-
Article
| Open Access Physics-aware differentiable design of magnetically actuated kirigami for shape morphing
Physics-aware differentiable design of magnetically actuated kirigami for shape morphing
A differentiable design framework that integrates both geometrical and magnetomechanical analyses to inversely program the shape morphing in magnetically actuated kirigami is proposed, achieving intricate shapes and multistate transitions.
- Liwei Wang
- , Yilong Chang
- & Wei Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Strain-driven Kovacs-like memory effect in glasses
Strain-driven Kovacs-like memory effect in glasses
An abnormal stress memory effect is discovered in different types of glassy materials when they are subjected to a low strain after a high strain. This strategy can be used to depress the stress relaxation and increase the stability under loading.
- Yu Tong
- , Lijian Song
- & Jun-Qiang Wang
-
Article
| Open Access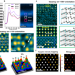 Large mechanical properties enhancement in ceramics through vacancy-mediated unit cell disturbance
Large mechanical properties enhancement in ceramics through vacancy-mediated unit cell disturbance
Ceramics are very brittle and hard to be plastically deformed. Here, the authors report a unit-cell scale disturbance mechanism to improve the deformation ability of ceramics and ultimately achieve large mechanical property enhancement.
- Zhuo Chen
- , Yong Huang
- & Zaoli Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Revealing the room temperature superplasticity in bulk recrystallized molybdenum
Revealing the room temperature superplasticity in bulk recrystallized molybdenum
Body-centered cubic refractory metals are known to exhibit excellent high-temperature strength, but often suffer from brittle fracture. Here, the authors produce a bulk pure Mo with stable fine-grain structure after powder metallurgy, Y-type hot rolling and ultra-high temperature annealing (1000~1700 °C) that exhibits room temperature superplasticity.
- Wenshuai Chen
- , Xiyao Li
- & Zenglin Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access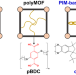 PolyMOF nanoparticles constructed from intrinsically microporous polymer ligand towards scalable composite membranes for CO2 separation
PolyMOF nanoparticles constructed from intrinsically microporous polymer ligand towards scalable composite membranes for CO2 separation
Microporous polymer ligand provides particle size reduction, enhanced ultramicroporosity (3–4 Å), and better colloidal stability in the polymer–metal–organic framework (polyMOF) system. This leads to defect-free and scalable composite membranes for efficient CO2 separation.
- Tae Hoon Lee
- , Byung Kwan Lee
- & Ho Bum Park
-
Article
| Open Access Bioinspired rational design of bi-material 3D printed soft-hard interfaces
Bioinspired rational design of bi-material 3D printed soft-hard interfaces
Stress concentrations make the design of durable interfaces between hard and soft materials a challenging task. Here, the authors, inspired by nature, combine mechanical tests and simulations on multiple geometries to generate design guidelines that yield strong and tough soft-hard interfaces.
- M. C. Saldívar
- , E. Tay
- & A. A. Zadpoor
-
Article
| Open Access Harmonizing sound and light: X-ray imaging unveils acoustic signatures of stochastic inter-regime instabilities during laser melting
Harmonizing sound and light: X-ray imaging unveils acoustic signatures of stochastic inter-regime instabilities during laser melting
In the pursuit of advancing laser powder bed fusion (LPBF) technology, researchers have successfully converged the realms of sound and light. Here, the authors unveil the synergistic potential of synchronized x-ray imaging and acoustics to illuminate hidden instabilities in LPBF process.
- Milad Hamidi Nasab
- , Giulio Masinelli
- & Roland E. Logé
-
Article
| Open Access Multi-step nucleation pathway of C-S-H during cement hydration from atomistic simulations
Multi-step nucleation pathway of C-S-H during cement hydration from atomistic simulations
The nucleation of calcium silicate hydrate is a crucial step in cement hydration, but is still a poorly understood process. Here the authors use atomistic simulations to study primary particles and their aggregation, revealing a potential C-S-H “basic building block”.
- Xabier M. Aretxabaleta
- , Jon López-Zorrilla
- & Hegoi Manzano
-
Article
| Open Access Solute trapping and non-equilibrium microstructure during rapid solidification of additive manufacturing
Solute trapping and non-equilibrium microstructure during rapid solidification of additive manufacturing
Solute transport during rapid and repeated thermal cycles is important in additive manufacturing process. Here, the authors develop a fully-coupled model to rationalise solute transport process, elemental segregation, and non-equilibrium solid/liquid interfacial evolution at sub-grain scale.
- Neng Ren
- , Jun Li
- & Jianguo Li
-
Article
| Open Access Origamic metal-organic framework toward mechanical metamaterial
Origamic metal-organic framework toward mechanical metamaterial
This work introduces a 2D porphyrinic metal-organic framework based on DCS origami tessellation, displaying unique folding behavior inspired by origami mechanics. This breakthrough paves the way for MOFs toward mechanical metamaterials.
- Eunji Jin
- , In Seong Lee
- & Wonyoung Choe
-
Article
| Open Access Design for improving corrosion resistance of duplex stainless steels by wrapping inclusions with niobium armour
Design for improving corrosion resistance of duplex stainless steels by wrapping inclusions with niobium armour
Nonmetallic inclusions often induce serious corrosion failure of steel, causing catastrophic accidents and economic losses. Here, the authors propose a strategy of wrapping deleterious inclusions with niobium armour (Z phase), improving the corrosion resistance of duplex stainless steel.
- Shucai Zhang
- , Hao Feng
- & Guoping Li
-
Article
| Open Access Preferential ice growth on grooved surface for crisscross-aligned graphene aerogel with large negative Poisson’s ratio
Preferential ice growth on grooved surface for crisscross-aligned graphene aerogel with large negative Poisson’s ratio
Ice formation on grooved surfaces is ubiquitous, but controlling orientation is difficult due to lack of mechanistic insight. Here, the authors observed oriented growth using graphene oxide nanosheets as probes, revealing the effect of groove size, and programmed ice growth to fabricate freeze-cast metamaterials.
- Meng Li
- , Nifang Zhao
- & Hao Bai
-
Article
| Open Access Anhydrous interfacial polymerization of sub-1 Å sieving polyamide membrane
Anhydrous interfacial polymerization of sub-1 Å sieving polyamide membrane
The design of highly permeable polyamide (PA) membrane capable of precise ionic sieving remains challenging. Here, the authors report an anhydrous interfacial polymerization on the solid-liquid interface to eliminate water-caused side reactions, leading to a PA layer with an ionic sieving accuracy of 0.5 Å.
- Guangjin Zhao
- , Haiqi Gao
- & Hong Meng
-
Comment
| Open Access Exploration of truss metamaterials with graph based generative modeling
Exploration of truss metamaterials with graph based generative modeling
Optimisation tasks in the inverse design of metamaterials with machine learning were limited due to the representations of generative models. Here the author comments a recent publication in Nature Communications which generates a latent space representation that unlocks non-linear optimisations.
- Angkur Jyoti Dipanka Shaikeea
-
Article
| Open Access Unifying the design space and optimizing linear and nonlinear truss metamaterials by generative modeling
Unifying the design space and optimizing linear and nonlinear truss metamaterials by generative modeling
Truss metamaterials are ubiquitous but their vast design space is far from fully explored. Here, authors use machine learning to present a unified, continuous latent space description, enabling the rapid generation of trusses with tunable or exceptional linear and nonlinear mechanical properties.
- Li Zheng
- , Konstantinos Karapiperis
- & Dennis M. Kochmann
-
Article
| Open Access Woven organic crystals
Woven organic crystals
The entanglement of fibrous elements produces flexible structures with enhanced strength and resilience to abrasion. Here, the authors report the weaving of organic crystals into flexible and robust patches with plain, twill, and satin topologies of arbitrary porosity, expanding one-dimensional crystals into flexible, two-dimensional planar structures with potential for future applications in flexible electronics.
- Linfeng Lan
- , Liang Li
- & Hongyu Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Room-temperature super-elongation in high-entropy alloy nanopillars
Room-temperature super-elongation in high-entropy alloy nanopillars
Small-scale metallic materials often suffer from a lack of tensile ductility. Here, the authors report an unusual room-temperature super-elongation in CoCrFeNi nanopillars from spatial and synergistic coordination of deformation twinning and dislocation slips due to chemical heterogeneities.
- Qian Zhang
- , Ranming Niu
- & Xiaoyan Li
-
Article
| Open Access Quantitative three-dimensional imaging of chemical short-range order via machine learning enhanced atom probe tomography
Quantitative three-dimensional imaging of chemical short-range order via machine learning enhanced atom probe tomography
Quantifying chemical short-range order (CSRO) remains a formidable for volume-averaged or 2D microscopy methods. Here the authors introduce a machine-learning approach that breaks the resolution limitations of atom probe tomography to reveal the 3D atomistic architecture of CSRO in Fe-based alloys.
- Yue Li
- , Ye Wei
- & Baptiste Gault
-
Article
| Open Access Realizing reversible phase transformation of shape memory ceramics constrained in aluminum
Realizing reversible phase transformation of shape memory ceramics constrained in aluminum
Achieving reversible phase transformation of shape memory ceramics (SMCs) in a densified composite can have scientific and technological impacts, but is challenging. Here, the authors demonstrate the reversible martensitic transformation of SMCs confined in aluminum without destructive impact.
- Wangshu Zheng
- , Yan Shi
- & Qiang Guo
-
Article
| Open Access Strong yet flexible ceramic aerogel
Strong yet flexible ceramic aerogel
Mechanically robust, flexible and thermally insulating ceramic aerogels are challenging to obtain due to the conflicting nature of these properties. Here the authors resolved these contradictions and developed a strong yet flexible aerogel, for application in extreme conditions, by laminated structure design.
- Lei Su
- , Shuhai Jia
- & Hongjie Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Additive manufacturing of alloys with programmable microstructure and properties
Additive manufacturing of alloys with programmable microstructure and properties
The traditional way of beating metals to improve their properties is not practical to 3D printed parts with intricate geometry. Here, the authors demonstrate how to program microstructural modifications of metals site-specifically during 3D printing to tune their properties.
- Shubo Gao
- , Zhi Li
- & Matteo Seita
-
Article
| Open Access Boosting lithium ion conductivity of antiperovskite solid electrolyte by potassium ions substitution for cation clusters
Boosting lithium ion conductivity of antiperovskite solid electrolyte by potassium ions substitution for cation clusters
All-solid-state electrolytes for lithium batteries generally suffer from low ionic conductivity. Here, authors manipulate the lattice of antiperovskite-type Li2OHCl by potassium ion substitution, which alters the lattice structure and improves the lithium ion transport properties.
- Lei Gao
- , Xinyu Zhang
- & Ruqiang Zou
-
Article
| Open Access A reprogrammable mechanical metamaterial with origami functional-group transformation and ring reconfiguration
A reprogrammable mechanical metamaterial with origami functional-group transformation and ring reconfiguration
Programmability is a key property for multifunctional metamaterials, but it is limited by homo-element. Here, the authors show a mechanical metamaterials with heterogeneous elements, achieving various mechanical behaviours by functional group transformation and ring configuration.
- Xinyu Hu
- , Ting Tan
- & Zhimiao Yan
-
Article
| Open Access Light-oriented 3D printing of liquid crystal/photocurable resins and in-situ enhancement of mechanical performance
Light-oriented 3D printing of liquid crystal/photocurable resins and in-situ enhancement of mechanical performance
Complex computerized geometries can be obtained by additive manufacturing. However, the printing of purely three-dimensional polymer shapes possesses inherent poor mechanical stability. Here, the authors overcome this drawback by the light-driven orientation of liquid crystals to guide the alignment of acrylate prepolymers along the direction parallel to UV light vibrations.
- Xiaolu Sun
- , Shaoyun Chen
- & Dongxian Zhuo
-
Article
| Open Access Material-agnostic machine learning approach enables high relative density in powder bed fusion products
Material-agnostic machine learning approach enables high relative density in powder bed fusion products
Exploring laser powder bed fusion in manufacturing, the authors demonstrate a machine learning-based method to optimize processing conditions achieving materials with relative density greater than 98% and experimentally verify its generality for multiple distinct powder materials.
- Jaemin Wang
- , Sang Guk Jeong
- & Byeong-Joo Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Growing recyclable and healable piezoelectric composites in 3D printed bioinspired structure for protective wearable sensor
Growing recyclable and healable piezoelectric composites in 3D printed bioinspired structure for protective wearable sensor
Smart monitoring devices with integrated mechanical protection and piezoelectric induction are limited. Here, the authors report a strategy to grow piezoelectric Rochelle salt crystals in 3D-printed cuttlebone-inspired structures to produce smart monitoring devices with integrated mechanical protection and electrical sensing capability.
- Qingqing He
- , Yushun Zeng
- & Yang Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Joining of metallic glasses in liquid via ultrasonic vibrations
Joining of metallic glasses in liquid via ultrasonic vibrations
Under-liquid joining of metals has far-reaching implications for energy storage, space exploration, offshore mining and defense. Here, the authors report an alternative method to join metallic glasses firmly under water, seawater, flammable alcohol and even cryogenic liquid nitrogen.
- Luyao Li
- , Xin Li
- & Jiang Ma
-
Article
| Open Access Realization of an inherent time crystal in a dissipative many-body system
Realization of an inherent time crystal in a dissipative many-body system
Physical realizations of time crystals, non-equilibrium many-body systems with broken time-translation symmetry, typically require periodic driving. Here the authors demonstrate a time crystal without external periodic drive in a collection of erbium atoms under a continuous laser excitation.
- Yu-Hui Chen
- & Xiangdong Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Thin lamellar films with enhanced mechanical properties for durable radiative cooling
Thin lamellar films with enhanced mechanical properties for durable radiative cooling
Practical application of radiative cooling technology in harsh outdoor conditions remains challenging. Here, the authors develop a lamellar ANFs/Mica@TiO2 composite via a “solvent exchange-reprotonation” process enabling durable outdoor cooling.
- Lianhu Xiong
- , Yun Wei
- & Hua Deng
-
Article
| Open Access Size-dependent deformation behavior in nanosized amorphous metals suggesting transition from collective to individual atomic transport
Size-dependent deformation behavior in nanosized amorphous metals suggesting transition from collective to individual atomic transport
How matter deform is a central question in mechanics of materials science. Here, the authors reveal a size-dependent deformation in amorphous metals changing at ~100 nanometer sample size from collective homogeneous flow to interface diffusion realized through individual atomic transport.
- Naijia Liu
- , Sungwoo Sohn
- & Jan Schroers
-
Article
| Open Access High-performance cost efficient simultaneous wireless information and power transfers deploying jointly modulated amplifying programmable metasurface
High-performance cost efficient simultaneous wireless information and power transfers deploying jointly modulated amplifying programmable metasurface
In this work, the authors demonstrate a ‘jointly modulated’ amplifying programmable metasurface (APM) for simultaneous wireless information and power transmission (SWIPT). Their technique outperforms existing methods, significantly improving power transmission and adaptability for conveying energy and data across various domains, including wireless implants, 6 G networks, and IoT systems.
- Xin Wang
- , Jia Qi Han
- & Tie Jun Cui
-
Article
| Open Access Synthesis of CuCo2S4@Expanded Graphite with crystal/amorphous heterointerface and defects for electromagnetic wave absorption
Synthesis of CuCo2S4@Expanded Graphite with crystal/amorphous heterointerface and defects for electromagnetic wave absorption
Heterointerface and defect promote the development of electromagnetic wave absorbers. Here, the authors show the 3D flower-honeycomb CuCo2S4@Expanded Graphite heterostructure, report the mechanism of crystal-crystal/amorphous heterointerfaces and cation defects on electromagnetic wave absorption.
- Zhimeng Tang
- , Lei Xu
- & Jinhui Peng
-
Article
| Open Access Tensorial stress-plastic strain fields in α - ω Zr mixture, transformation kinetics, and friction in diamond-anvil cell
Tensorial stress-plastic strain fields in α - ω Zr mixture, transformation kinetics, and friction in diamond-anvil cell
Fields of stress and plastic strain tensors in a sample under high pressures in diamond-anvil cells are important, but measuring them is difficult. Here, the authors suggest a coupled experimental-analytical-computational approach to measure them before, during, and after α−ω transformation in Zr.
- Valery I. Levitas
- , Achyut Dhar
- & K. K. Pandey
-
Article
| Open Access Smart dynamic hybrid membranes with self-cleaning capability
Smart dynamic hybrid membranes with self-cleaning capability
The performance of membrane desalination of seawater is hampered by fouling. Here the authors develop smart gating hybrid membranes by surface coating with polymer-embedded thermosalient crystals. These membranes enhance pure water flux by over 40% in saltwater desalination by osmotic distillation.
- Elvira Pantuso
- , Ejaz Ahmed
- & Gianluca Di Profio
-
Article
| Open Access Superhard bulk high-entropy carbides with enhanced toughness via metastable in-situ particles
Superhard bulk high-entropy carbides with enhanced toughness via metastable in-situ particles
High-entropy carbides (HECs) with high hardness usually suffer from low fracture toughness. Here, the authors demonstrate a metastability engineering strategy for toughening superhard HECs by introducing in situ metastable ceramic particles, which are transformable under mechanical loading.
- Jiaojiao Hu
- , Qiankun Yang
- & Zhiming Li
-
Article
| Open Access Chemical inhomogeneity–induced profuse nanotwinning and phase transformation in AuCu nanowires
Chemical inhomogeneity–induced profuse nanotwinning and phase transformation in AuCu nanowires
How the random solid solution (RSS) alloys accommodate plasticity and overcome strength-ductility trade-off remain unresolved. Here, the authors reveal atomic-scale plastic deformation of AuCu alloy, which shed light on the effect of chemical inhomogeneity on plastic deformation of RSS alloys.
- Chengpeng Yang
- , Bozhao Zhang
- & Xiaodong Han
-
Article
| Open Access Atomically dispersed Cu coordinated Rh metallene arrays for simultaneously electrochemical aniline synthesis and biomass upgrading
Atomically dispersed Cu coordinated Rh metallene arrays for simultaneously electrochemical aniline synthesis and biomass upgrading
Electrocatalytic conversion of low-cost organic compounds to high-value chemicals urgently demands the development of efficient electrocatalysts. Mao et al. report the synthesis of Cu single-atom dispersed Rh metallene arrays for electrochemical aniline synthesis and biomass upgrading with enhanced electrocatalytic activity.
- Qiqi Mao
- , Xu Mu
- & Hongjing Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Unexpected doping effects on phonon transport in quasi-one-dimensional van der Waals crystal TiS3 nanoribbons
Unexpected doping effects on phonon transport in quasi-one-dimensional van der Waals crystal TiS3 nanoribbons
Doping generally hinders phonon transport. Here, authors significantly increase the thermal conductivity of TiS3 nanoribbons through doping, originating from the intensified bonding strength along the molecular chain direction without distorting the one-dimensional structure induced by doped atoms.
- Chenhan Liu
- , Chao Wu
- & Yunfei Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Janus particle-engineered structural lipiodol droplets for arterial embolization
Janus particle-engineered structural lipiodol droplets for arterial embolization
Embolization is one of the most promising strategies for clinical disease treatments, however, the existing embolic materials normally have poor embolization effectiveness. Here, the authors report Janus particle-engineered structural lipiodol droplets by programming the self-assembly of Janus particles at the lipiodol-water interface to achieve highly efficient renal embolization.
- Sijian Tao
- , Bingquan Lin
- & Jun-Bing Fan
-
Article
| Open Access Nanoscale ductile fracture and associated atomistic mechanisms in a body-centered cubic refractory metal
Nanoscale ductile fracture and associated atomistic mechanisms in a body-centered cubic refractory metal
Understanding the competing modes of brittle versus ductile fracture is critical for preventing material failure. Here, the authors reveal the atomic-scale processes of crack growth in Mo crystals, providing mechanistic insights into the ductile to brittle transition in BCC refractory metals.
- Yan Lu
- , Yongchao Chen
- & Xiaodong Han

 Direct 4D printing of ceramics driven by hydrogel dehydration
Direct 4D printing of ceramics driven by hydrogel dehydration