Perspective
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Direct 4D printing of ceramics driven by hydrogel dehydration
Direct 4D printing of ceramics driven by hydrogel dehydration
Four-dimensional (4D) printing ceramics is a challenge due to their weak deformability. Here, the authors report a hydrogel-dehydration-driven direct 4D printing approach, enabling simple and efficient manufacturing of various complex ceramic objects
- Rong Wang
- , Chao Yuan
- & Qi Ge
-
Article
| Open Access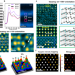 Large mechanical properties enhancement in ceramics through vacancy-mediated unit cell disturbance
Large mechanical properties enhancement in ceramics through vacancy-mediated unit cell disturbance
Ceramics are very brittle and hard to be plastically deformed. Here, the authors report a unit-cell scale disturbance mechanism to improve the deformation ability of ceramics and ultimately achieve large mechanical property enhancement.
- Zhuo Chen
- , Yong Huang
- & Zaoli Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access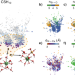 Multi-step nucleation pathway of C-S-H during cement hydration from atomistic simulations
Multi-step nucleation pathway of C-S-H during cement hydration from atomistic simulations
The nucleation of calcium silicate hydrate is a crucial step in cement hydration, but is still a poorly understood process. Here the authors use atomistic simulations to study primary particles and their aggregation, revealing a potential C-S-H “basic building block”.
- Xabier M. Aretxabaleta
- , Jon López-Zorrilla
- & Hegoi Manzano
-
Article
| Open Access Strong yet flexible ceramic aerogel
Strong yet flexible ceramic aerogel
Mechanically robust, flexible and thermally insulating ceramic aerogels are challenging to obtain due to the conflicting nature of these properties. Here the authors resolved these contradictions and developed a strong yet flexible aerogel, for application in extreme conditions, by laminated structure design.
- Lei Su
- , Shuhai Jia
- & Hongjie Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Boosting lithium ion conductivity of antiperovskite solid electrolyte by potassium ions substitution for cation clusters
Boosting lithium ion conductivity of antiperovskite solid electrolyte by potassium ions substitution for cation clusters
All-solid-state electrolytes for lithium batteries generally suffer from low ionic conductivity. Here, authors manipulate the lattice of antiperovskite-type Li2OHCl by potassium ion substitution, which alters the lattice structure and improves the lithium ion transport properties.
- Lei Gao
- , Xinyu Zhang
- & Ruqiang Zou
-
Article
| Open Access Superhard bulk high-entropy carbides with enhanced toughness via metastable in-situ particles
Superhard bulk high-entropy carbides with enhanced toughness via metastable in-situ particles
High-entropy carbides (HECs) with high hardness usually suffer from low fracture toughness. Here, the authors demonstrate a metastability engineering strategy for toughening superhard HECs by introducing in situ metastable ceramic particles, which are transformable under mechanical loading.
- Jiaojiao Hu
- , Qiankun Yang
- & Zhiming Li
-
Article
| Open Access Large-scale assembly of isotropic nanofiber aerogels based on columnar-equiaxed crystal transition
Large-scale assembly of isotropic nanofiber aerogels based on columnar-equiaxed crystal transition
In this work, the authors present an ice-templating strategy to produce large-scale isotropic nanofiber aerogels using a unique process of freezing the material on a rotating cryogenic drum surface, crushing it, and then re-casting the nanofiber slurry enabling high-throughput and design flexibility.
- Lei Li
- , Yiqian Zhou
- & Hui Wu
-
Article
| Open Access Contribution of boundary non-stoichiometry to the lower-temperature plasticity in high-pressure sintered boron carbide
Contribution of boundary non-stoichiometry to the lower-temperature plasticity in high-pressure sintered boron carbide
Improving plasticity in non-oxide ceramics while maintaining their high-temperature strength is challenging. Here, the authors report an enhancement of plasticity in B4C owing to the boundary non-stoichiometry. The results show excellent strength maintenance before the onset of plasticity.
- Haiyue Xu
- , Wei Ji
- & Zhengyi Fu
-
Article
| Open Access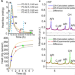 4D nanoimaging of early age cement hydration
4D nanoimaging of early age cement hydration
In this work, the authors use near-field ptychographic nanotomography to visualize cement hydration in situ. They report hydration features with submicrometer detail including calcium silicate dissolution rates, etch-pit growth rates and water-to-air porosity evolution.
- Shiva Shirani
- , Ana Cuesta
- & Miguel A. G. Aranda
-
Article
| Open Access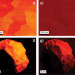 Deconvoluting Cr states in Cr-doped UO2 nuclear fuels via bulk and single crystal spectroscopic studies
Deconvoluting Cr states in Cr-doped UO2 nuclear fuels via bulk and single crystal spectroscopic studies
Additive based UO2 nuclear fuels, which incorporate small amounts of metal oxides such as chromia (Cr2O3), are an important class of accident tolerant fuels. Here authors determine the structural-redox mechanism for Cr lattice incorporation into UO2 nuclear fuels.
- Gabriel L. Murphy
- , Robert Gericke
- & Nina Huittinen
-
Article
| Open Access 3D Printing and processing of miniaturized transducers with near-pristine piezoelectric ceramics for localized cavitation
3D Printing and processing of miniaturized transducers with near-pristine piezoelectric ceramics for localized cavitation
Despite advances in additive manufacturing of piezoceramics, resultant transducers generally suffer from high porosity, weak piezoelectric responses, and limited geometry. Here, authors report the design and printing of fully packaged freeform ultrasonic transducers capable of traveling inside mm-sized channels and deliver localized high ultrasound energy.
- Haotian Lu
- , Huachen Cui
- & Xiaoyu (Rayne) Zheng
-
Article
| Open Access 3D printing of unsupported multi-scale and large-span ceramic via near-infrared assisted direct ink writing
3D printing of unsupported multi-scale and large-span ceramic via near-infrared assisted direct ink writing
In 3D ceramic printing, the need for additional supports can increase processing time and introduce defects during post-processing removal. Here, authors merge direct ink writing and up-conversion particles-assisted photopolymerization under near-infrared irradiation for support-free printing with controlled curing rates reducing material waste, printing time, and post-processing steps.
- Yongqin Zhao
- , Junzhe Zhu
- & Ren Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Phase formation capability and compositional design of β-phase multiple rare-earth principal component disilicates
Phase formation capability and compositional design of β-phase multiple rare-earth principal component disilicates
Developing high-entropy environmental barrier coatings is challenged by the intricacy to form stable multicomponent materials. Here the authors report the phases of high-entropy β-RE2Si2O7 could be precisely designed by monitoring the entropy descriptor and the cationic radii on rare earth sites.
- Yixiu Luo
- , Luchao Sun
- & Jingyang Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Theoretical insights into the Peierls plasticity in SrTiO3 ceramics via dislocation remodelling
Theoretical insights into the Peierls plasticity in SrTiO3 ceramics via dislocation remodelling
Many ceramics and semiconductors are brittle at moderate temperatures, which can be a concern for applications. Here authors present a theoretical approach based on local misfit energy to accurately derive the Peierls stress and model the dislocation process in SrTiO3, which provides insights into the plasticity around room temperature.
- Yi Li
- , Xiangyang Liu
- & Chunlei Wan
-
Article
| Open Access Cement substitution with secondary materials can reduce annual global CO2 emissions by up to 1.3 gigatons
Cement substitution with secondary materials can reduce annual global CO2 emissions by up to 1.3 gigatons
In this paper we report the maximum potential for cement substitution with secondary materials to reduce CO2 emissions globally (1.3 Gt CO2-eq. in 2018) and on a country-by-country basis.
- Izhar Hussain Shah
- , Sabbie A. Miller
- & Rupert J. Myers
-
Article
| Open Access Grain boundary structural transformation induced by co-segregation of aliovalent dopants
Grain boundary structural transformation induced by co-segregation of aliovalent dopants
The effect of aliovalent doping on grain boundary is not yet fully understood at the atomic level. Here, the authors report grain boundary structural transformation in α-Al2O3 is induced by co-segregation of multiple dopants using atomic-resolution electron microscopy and theoretical calculations.
- Toshihiro Futazuka
- , Ryo Ishikawa
- & Yuichi Ikuhara
-
Article
| Open Access Giant energy-storage density with ultrahigh efficiency in lead-free relaxors via high-entropy design
Giant energy-storage density with ultrahigh efficiency in lead-free relaxors via high-entropy design
Dielectric ceramics are widely used in advanced high/pulsed power capacitors. Here, the authors propose a high-entropy strategy to design “local polymorphic distortion” in lead-free ceramics, achieving high energy storage performance.
- Liang Chen
- , Shiqing Deng
- & Jun Chen
-
Matters Arising
| Open Access Is configurational entropy the main stabilizing term in rock-salt Mg0.2Co0.2Ni0.2Cu0.2Zn0.2O high entropy oxide?
Is configurational entropy the main stabilizing term in rock-salt Mg0.2Co0.2Ni0.2Cu0.2Zn0.2O high entropy oxide?
- Martina Fracchia
- , Mauro Coduri
- & Umberto Anselmi Tamburini
-
Article
| Open Access Ultra-dense dislocations stabilized in high entropy oxide ceramics
Ultra-dense dislocations stabilized in high entropy oxide ceramics
Dislocation engineering is important for designing structural materials. Here the authors demonstrate that a high-entropy oxide ceramic with a high density of edge dislocations can be stabilized by increasing the compositional complexity, resulting in enhanced fracture toughness.
- Yi Han
- , Xiangyang Liu
- & Chunlei Wan
-
Article
| Open Access Production of a monolithic fuel cell stack with high power density
Production of a monolithic fuel cell stack with high power density
The transportation sector is gradually evolving to become independent of fossil fuels. Here, the authors report a metal-based monolithic solid oxide fuel cell with a power density of 5.6 kW/L suitable for transport applications.
- Stéven Pirou
- , Belma Talic
- & Anke Hagen
-
Article
| Open Access Flexible ceramic nanofibrous sponges with hierarchically entangled graphene networks enable noise absorption
Flexible ceramic nanofibrous sponges with hierarchically entangled graphene networks enable noise absorption
Noise pollution has been a burden to the global economy, environment, and human health. Here the authors demonstrate a facile route to produce flexible ceramic nanofibrous sponges with hierarchically entangled graphene networks and its excellent noise absorption properties at elevated temperatures.
- Dingding Zong
- , Leitao Cao
- & Bin Ding
-
Article
| Open Access Settling the matter of the role of vibrations in the stability of high-entropy carbides
Settling the matter of the role of vibrations in the stability of high-entropy carbides
The contribution of vibrations to the stability of high-entropy ceramics is still controversial. Here the authors computationally integrate disorder parameterization, phonon modelling, and thermodynamic characterization to investigate the role of vibrations to the stability of high-entropy carbides.
- Marco Esters
- , Corey Oses
- & Stefano Curtarolo
-
Article
| Open Access Fast and quantitative 2D and 3D orientation mapping using Raman microscopy
Fast and quantitative 2D and 3D orientation mapping using Raman microscopy
Although polarized Raman microscopy is sensitive to orientation changes, quantitative information has been missing. Here, the authors use simultaneous registration of multiple Raman scattering spectra obtained at different polarizations and show quantitative orientation mapping
- Oleksii Ilchenko
- , Yuriy Pilgun
- & Anja Boisen
-
Article
| Open Access Direct observation of atomic-scale fracture path within ceramic grain boundary core
Direct observation of atomic-scale fracture path within ceramic grain boundary core
Cracks propagate preferentially along grain boundaries, but what happens exactly at the atomic scale remains unclear. Here, the authors combine atomic-scale observations and first-principles calculations to show local coordination chemistry at a dopant-segregated alumina grain boundary core dictates the atomic bond-breaking path.
- Shun Kondo
- , Akihito Ishihara
- & Yuichi Ikuhara
-
Article
| Open Access Low temperature self-densification of high strength bulk hexagonal boron nitride
Low temperature self-densification of high strength bulk hexagonal boron nitride
Sintering hexagonal boron nitride until it is more than 96% dense remains a challenge. Here, the authors mix cubic boron nitride particles into hexagonal boron nitride flakes and sinter the combined powders to obtain dense hexagonal boron nitride ceramics with significantly increased strength.
- Haotian Yang
- , Hailiang Fang
- & Jianlin Li
-
Article
| Open Access Disorder in Mn+1AXn phases at the atomic scale
Disorder in Mn+1AXn phases at the atomic scale
Highly ordered and compositionally complex ceramics are prone to disordering under irradiation, but exactly how is unclear. Here, the authors use high resolution microscopy to directly image the order-to-disorder phase transformations in Ti3AlC2 into otherwise unattainable solid solutions.
- Chenxu Wang
- , Tengfei Yang
- & Yugang Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Anomalous diffusion along metal/ceramic interfaces
Anomalous diffusion along metal/ceramic interfaces
Little is known about diffusion along metal/ceramic interfaces even though it controls the physical behavior and lifetimes of many devices (including batteries, microelectronics, and jet engines). Here, the authors show that diffusion along a nickel/sapphire interface is abnormally fast due to nickel vacancies and generalise their findings to a wide-range of metal/ceramic systems.
- Aakash Kumar
- , Hagit Barda
- & David J. Srolovitz
-
Article
| Open Access Nanocardboard as a nanoscale analog of hollow sandwich plates
Nanocardboard as a nanoscale analog of hollow sandwich plates
Sandwich structures such as corrugated cardboard offer low weight and high bending stiffness, but they are difficult to produce at the nanoscale. Here, the authors combine webbing and perforation to produce alumina ‘nanocardboard’ with ultralow areal density that recovers without damage from extreme deformation.
- Chen Lin
- , Samuel M. Nicaise
- & Igor Bargatin
-
Article
| Open Access Rechargeable potassium-ion batteries with honeycomb-layered tellurates as high voltage cathodes and fast potassium-ion conductors
Rechargeable potassium-ion batteries with honeycomb-layered tellurates as high voltage cathodes and fast potassium-ion conductors
The development of potassium-ion batteries requires cathode materials that can maintain the structural stability during cycling. Here the authors have developed honeycomb-layered tellurates K2M2TeO6 that afford high ionic conductivity and reversible intercalation of large K ions at high voltages.
- Titus Masese
- , Kazuki Yoshii
- & Masahiro Shikano
-
Article
| Open Access High temperature deformability of ductile flash-sintered ceramics via in-situ compression
High temperature deformability of ductile flash-sintered ceramics via in-situ compression
Flash sintering allows for rapid ceramic processing, but the mechanical behavior of such ceramics remains poorly understood. Here, the authors compress micropillars of yttria stabilized zirconia to show flash sintering promotes outstanding plasticity.
- Jaehun Cho
- , Qiang Li
- & Xinghang Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Ceramic nanowelding
Ceramic nanowelding
Fabricating complex nanodevices requires joining techniques such as welding, common for metals but still out of reach for ceramics. Here the authors use MgO as a solder in a transmission electron microscope with a CO2 atmosphere to weld ceramic nanowires, and show their novel technique can also weld bulk ceramics.
- Liqiang Zhang
- , Yushu Tang
- & Jianyu Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Probing dopant segregation in distinct cation sites at perovskite oxide polycrystal interfaces
Probing dopant segregation in distinct cation sites at perovskite oxide polycrystal interfaces
Space-charges in polycrystalline materials can drive segregation of dopants, however an in-depth understanding of this process is still missing. Here, the authors show that in polycrystalline perovskites the space-charge segregation and interfacial structure are nearly identical irrespective of the interface type.
- Hye-In Yoon
- , Dong-Kyu Lee
- & Sung-Yoon Chung
-
Article
| Open Access Evidence for percolation diffusion of cations and reordering in disordered pyrochlore from accelerated molecular dynamics
Evidence for percolation diffusion of cations and reordering in disordered pyrochlore from accelerated molecular dynamics
Diffusion plays an important role in sintering, damage tolerance and transport. Here authors perform classical and accelerated molecular dynamics simulations of vacancy-mediated cation diffusion in Gd2Ti2O7 pyrochlore and report non-monotonic evolution of cation diffusivity.
- Romain Perriot
- , Blas P. Uberuaga
- & Arthur F. Voter
-
Article
| Open Access In situ stable crack growth at the micron scale
In situ stable crack growth at the micron scale
To improve mechanical properties in ceramics through grain boundary engineering, precise mechanical characterization of individual boundaries is vital yet difficult to achieve. Here authors perform experiments using an in situ scanning electron microscopy based double cantilever beam test, allowing to directly view and measure stable crack growth in silicon carbide.
- Giorgio Sernicola
- , Tommaso Giovannini
- & Finn Giuliani
-
Article
| Open Access Ablation-resistant carbide Zr0.8Ti0.2C0.74B0.26 for oxidizing environments up to 3,000 °C
Ablation-resistant carbide Zr0.8Ti0.2C0.74B0.26 for oxidizing environments up to 3,000 °C
Hypersonic and aerospace applications motivate development of materials with improved resistance against ablation and oxidation at high temperatures. Here authors demonstrate a quaternary carbide, where sealing by surface oxides, slow oxygen diffusion and a graded structure yield improved ablation resistance over established ceramics.
- Yi Zeng
- , Dini Wang
- & Ping Xiao
-
Article
| Open Access Bio-inspired self-shaping ceramics
Bio-inspired self-shaping ceramics
Shaping ceramics into complex forms is a formidable goal. Here, the authors present an approach to self-shaping ceramics, inspired by self-folding processes in plants, in which the ceramic microstructure is embedded with aligned platelets that control the orientation of heat-induced shrinkage.
- Fabio L. Bargardi
- , Hortense Le Ferrand
- & André R. Studart
-
Article
| Open Access Pressure-induced nano-crystallization of silicate garnets from glass
Pressure-induced nano-crystallization of silicate garnets from glass
It is suggested that the optical and mechanical properties of transparent ceramics become very favourable if they can be synthesized as nanocrystals. Here, the authors report direct conversion of bulk glass starting material to pore-free nano-polycrystalline silicate garnet at high pressure and temperature.
- T. Irifune
- , K. Kawakami
- & T. Shinmei
-
Article
| Open Access External stimulation-controllable heat-storage ceramics
External stimulation-controllable heat-storage ceramics
Materials that can store and release heat on demand are of use for energy storage applications. Here, the authors discover a ceramic material that can reversibly store energy from heat, light or electricity and release this energy as heat through the application of pressure.
- Hiroko Tokoro
- , Marie Yoshikiyo
- & Shin-ichi Ohkoshi

 Materials design for hypersonics
Materials design for hypersonics