Perspective
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Deep-potential enabled multiscale simulation of gallium nitride devices on boron arsenide cooling substrates
Deep-potential enabled multiscale simulation of gallium nitride devices on boron arsenide cooling substrates
Efficient heat dissipation is critical to optimize high-power devices. Here, the authors report high interfacial thermal conductance in GaN-BAs heterostructures and investigate the competition between grain size and boundary resistance by multiscale simulations.
- Jing Wu
- , E Zhou
- & Guangzhao Qin
-
Article
| Open Access Float-stacked graphene–PMMA laminate
Float-stacked graphene–PMMA laminate
To maximize composite reinforcing efficiency, a semi-infinite reinforcement should be aligned in the matrix. Here, the authors report a float-stacking strategy for graphene-PMMA laminate with precisely aligned monolayer graphene in a polymer matrix.
- Seung-Il Kim
- , Ji-Yun Moon
- & Jae-Hyun Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Effect of inorganic material surface chemistry on structures and fracture behaviours of epoxy resin
Effect of inorganic material surface chemistry on structures and fracture behaviours of epoxy resin
The mechanisms of adhesion between polymers and inorganic materials are not fully understood. Here, authors demonstrate the clear evidence that the surface chemistry impacts the crosslinked structures of resins near the interfaces, resulting in different fracture behaviours and adhesive strengths.
- Tomohiro Miyata
- , Yohei K. Sato
- & Hiroshi Jinnai
-
Article
| Open Access Simultaneous enhancement of strength and conductivity via self-assembled lamellar architecture
Simultaneous enhancement of strength and conductivity via self-assembled lamellar architecture
Simultaneous increase of mechanical and physical properties is highly desirable, but challenging for bimetallic materials. Here, the authors use W-Cu as an example to achieve both high strength and conductivity of the bimetal with a large plasticity by a self-assembled lamellar architecture.
- Tielong Han
- , Chao Hou
- & Xiaoyan Song
-
Article
| Open Access Elasticity-controlled jamming criticality in soft composite solids
Elasticity-controlled jamming criticality in soft composite solids
Soft composite solids are building blocks for many functional and biological materials, yet it remains challenging to predict their mechanical properties. Zhao et al. propose a criticality framework to connect the mechanics to the critical behaviour near the shear-jamming transition of the dispersed inclusions.
- Yiqiu Zhao
- , Haitao Hu
- & Qin Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrathin, ultralight dual-scale fibrous networks with high-infrared transmittance for high-performance, comfortable and sustainable PM0.3 filter
Ultrathin, ultralight dual-scale fibrous networks with high-infrared transmittance for high-performance, comfortable and sustainable PM0.3 filter
Development of high-performance, comfortable and sustainable air filters is challenging. Here, authors design an ultrathin, ultralight dual scale fiber mat composed of true nanofibers and submicron-fibers to integrate the high protection, thermal wet comfort and save raw materials.
- Yuchen Yang
- , Xiangshun Li
- & Yuekun Lai
-
Article
| Open Access Hydraulic-driven adaptable morphing active-cooling elastomer with bioinspired bicontinuous phases
Hydraulic-driven adaptable morphing active-cooling elastomer with bioinspired bicontinuous phases
Low thermal conduction and conformability of traditional rigid heat sinks limit their adoption in flexible electronics and soft robotics. Here, authors report a liquid metal skeleton-based active-cooling elastomer with high thermal conductivity, stretchability, and hydraulic-driven adaptable morphing.
- Dehai Yu
- , Zhonghao Wang
- & Zhizhu He
-
Article
| Open Access Accurate additive manufacturing of lightweight and elastic carbons using plastic precursors
Accurate additive manufacturing of lightweight and elastic carbons using plastic precursors
This work reports a simple method to produce 3D printed complex carbon materials with low dimensional shrinkage (<4%) from printed to carbonized state, using commercially available carbon fiber-reinforced polypropylene precursors and a fused filament fabrication-based process.
- Paul Smith
- , Jiayue Hu
- & Zhe Qiang
-
Article
| Open Access Stretchable and negative-Poisson-ratio porous metamaterials
Stretchable and negative-Poisson-ratio porous metamaterials
In this work, authors demonstrate highly stretchable conductive porous elastomers that can achieve up to 1200% strain with low or negative Poisson’s ratios by uniaxial, biaxial, and triaxial hot-pressing strategies.
- Xiaoyu Zhang
- , Qi Sun
- & Guoqing Zu
-
Article
| Open Access PolyMOF nanoparticles constructed from intrinsically microporous polymer ligand towards scalable composite membranes for CO2 separation
PolyMOF nanoparticles constructed from intrinsically microporous polymer ligand towards scalable composite membranes for CO2 separation
Microporous polymer ligand provides particle size reduction, enhanced ultramicroporosity (3–4 Å), and better colloidal stability in the polymer–metal–organic framework (polyMOF) system. This leads to defect-free and scalable composite membranes for efficient CO2 separation.
- Tae Hoon Lee
- , Byung Kwan Lee
- & Ho Bum Park
-
Article
| Open Access Bioinspired rational design of bi-material 3D printed soft-hard interfaces
Bioinspired rational design of bi-material 3D printed soft-hard interfaces
Stress concentrations make the design of durable interfaces between hard and soft materials a challenging task. Here, the authors, inspired by nature, combine mechanical tests and simulations on multiple geometries to generate design guidelines that yield strong and tough soft-hard interfaces.
- M. C. Saldívar
- , E. Tay
- & A. A. Zadpoor
-
Article
| Open Access Anhydrous interfacial polymerization of sub-1 Å sieving polyamide membrane
Anhydrous interfacial polymerization of sub-1 Å sieving polyamide membrane
The design of highly permeable polyamide (PA) membrane capable of precise ionic sieving remains challenging. Here, the authors report an anhydrous interfacial polymerization on the solid-liquid interface to eliminate water-caused side reactions, leading to a PA layer with an ionic sieving accuracy of 0.5 Å.
- Guangjin Zhao
- , Haiqi Gao
- & Hong Meng
-
Article
| Open Access Realizing reversible phase transformation of shape memory ceramics constrained in aluminum
Realizing reversible phase transformation of shape memory ceramics constrained in aluminum
Achieving reversible phase transformation of shape memory ceramics (SMCs) in a densified composite can have scientific and technological impacts, but is challenging. Here, the authors demonstrate the reversible martensitic transformation of SMCs confined in aluminum without destructive impact.
- Wangshu Zheng
- , Yan Shi
- & Qiang Guo
-
Article
| Open Access Growing recyclable and healable piezoelectric composites in 3D printed bioinspired structure for protective wearable sensor
Growing recyclable and healable piezoelectric composites in 3D printed bioinspired structure for protective wearable sensor
Smart monitoring devices with integrated mechanical protection and piezoelectric induction are limited. Here, the authors report a strategy to grow piezoelectric Rochelle salt crystals in 3D-printed cuttlebone-inspired structures to produce smart monitoring devices with integrated mechanical protection and electrical sensing capability.
- Qingqing He
- , Yushun Zeng
- & Yang Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Realization of an inherent time crystal in a dissipative many-body system
Realization of an inherent time crystal in a dissipative many-body system
Physical realizations of time crystals, non-equilibrium many-body systems with broken time-translation symmetry, typically require periodic driving. Here the authors demonstrate a time crystal without external periodic drive in a collection of erbium atoms under a continuous laser excitation.
- Yu-Hui Chen
- & Xiangdong Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access High-performance cost efficient simultaneous wireless information and power transfers deploying jointly modulated amplifying programmable metasurface
High-performance cost efficient simultaneous wireless information and power transfers deploying jointly modulated amplifying programmable metasurface
In this work, the authors demonstrate a ‘jointly modulated’ amplifying programmable metasurface (APM) for simultaneous wireless information and power transmission (SWIPT). Their technique outperforms existing methods, significantly improving power transmission and adaptability for conveying energy and data across various domains, including wireless implants, 6 G networks, and IoT systems.
- Xin Wang
- , Jia Qi Han
- & Tie Jun Cui
-
Article
| Open Access Synthesis of CuCo2S4@Expanded Graphite with crystal/amorphous heterointerface and defects for electromagnetic wave absorption
Synthesis of CuCo2S4@Expanded Graphite with crystal/amorphous heterointerface and defects for electromagnetic wave absorption
Heterointerface and defect promote the development of electromagnetic wave absorbers. Here, the authors show the 3D flower-honeycomb CuCo2S4@Expanded Graphite heterostructure, report the mechanism of crystal-crystal/amorphous heterointerfaces and cation defects on electromagnetic wave absorption.
- Zhimeng Tang
- , Lei Xu
- & Jinhui Peng
-
Article
| Open Access Smart dynamic hybrid membranes with self-cleaning capability
Smart dynamic hybrid membranes with self-cleaning capability
The performance of membrane desalination of seawater is hampered by fouling. Here the authors develop smart gating hybrid membranes by surface coating with polymer-embedded thermosalient crystals. These membranes enhance pure water flux by over 40% in saltwater desalination by osmotic distillation.
- Elvira Pantuso
- , Ejaz Ahmed
- & Gianluca Di Profio
-
Article
| Open Access Electrically insulating PBO/MXene film with superior thermal conductivity, mechanical properties, thermal stability, and flame retardancy
Electrically insulating PBO/MXene film with superior thermal conductivity, mechanical properties, thermal stability, and flame retardancy
Constructing thermally conductive but electrically insulating composites remains a challenge. Here, Ti3C2 MXene is combined in a nacre-like structure with the polymer PBO to form such materials, also exhibiting high thermal stability and flame retardancy.
- Yong Liu
- , Weizhi Zou
- & Jian Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Impact damage reduction of woven composites subject to pulse current
Impact damage reduction of woven composites subject to pulse current
In this work, the authors demonstrate that pulse current can effectively be used to reduce delamination damage and residual deformation in 3D orthogonal woven composites, enhancing mechanical properties and damage tolerance.
- Yan Li
- , Fusheng Wang
- & Laohu Long
-
Article
| Open Access Programmable spatial deformation by controllable off-center freestanding 4D printing of continuous fiber reinforced liquid crystal elastomer composites
Programmable spatial deformation by controllable off-center freestanding 4D printing of continuous fiber reinforced liquid crystal elastomer composites
Liquid crystal elastomer printing methods are often limited to planar structures. In this work, authors integrate 4D printed structures with fully impregnated composite interfaces to enable programmable deformation ability and high bearing capacity by adjusting the off-centre distribution of the fibres.
- Qingrui Wang
- , Xiaoyong Tian
- & Dichen Li
-
Article
| Open Access Multi-layered cement-hydrogel composite with high toughness, low thermal conductivity, and self-healing capability
Multi-layered cement-hydrogel composite with high toughness, low thermal conductivity, and self-healing capability
Despite widely used in the construction sector, Portland cement’s high brittleness and low toughness still pose challenges in some applications. Here, authors apply an ice-templating method to fabricate a cement-hydrogel composite with alternating layered microstructure resulting in significantly increased toughness.
- Yuan Chen
- , Yangzezhi Zheng
- & Changwen Miao
-
Article
| Open Access Cryogenic characteristics of graphene composites—evolution from thermal conductors to thermal insulators
Cryogenic characteristics of graphene composites—evolution from thermal conductors to thermal insulators
Graphene composites can serve both as efficient thermal insulators at low temperatures and thermal conductors at high temperatures. Here, the authors report the evolution of thermal conductivity of composites with graphene fillers from cryogenic to room temperature.
- Zahra Ebrahim Nataj
- , Youming Xu
- & Alexander A. Balandin
-
Article
| Open Access Bidirectional thermo-regulating hydrogel composite for autonomic thermal homeostasis
Bidirectional thermo-regulating hydrogel composite for autonomic thermal homeostasis
Developing materials which mimic thermal homeostasis is limited by complicated fabrication steps or unidirectional temperature transport. Here, the authors develop a homeostatic hydrogel that shows improved heat trapping at low temperatures, and enhanced evaporative cooling at high temperatures.
- Gyeongsuk Park
- , Hyunmin Park
- & Steve Park
-
Article
| Open Access Fabricating strong and tough aramid fibers by small addition of carbon nanotubes
Fabricating strong and tough aramid fibers by small addition of carbon nanotubes
High-performance fibers are promising materials in the impact protection field but fabricating fibers with high strength and high toughness is challenging. Here, the authors polymerize carbon nanotubes into aramid fibers to simultaneously improve strength and toughness.
- Jiajun Luo
- , Yeye Wen
- & Jin Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Wood xerogel for fabrication of high-performance transparent wood
Wood xerogel for fabrication of high-performance transparent wood
Optically transparent wood composites are commonly prepared by delignification of wood and subsequent infiltration of thermo- or photocurable polymer resins but the fabrication is still limited by the intrinsic low mesopore volume of the delignified wood. Here, the authors report a facile approach to fabricate transparent wood using wood xerogel which allows solvent-free infiltration of resin monomers into the wood cell wall under ambient conditions.’
- Shennan Wang
- , Lengwan Li
- & Qi Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access Evanescent field trapping and propulsion of Janus particles along optical nanofibers
Evanescent field trapping and propulsion of Janus particles along optical nanofibers
Manipulation of Janus particles is challenging and has limited precision. Here, the authors propose manipulation of Janus particles by optical forces in the evanescent field of an optical nanofiber, and demonstrate that they exhibit strong transverse localization on the nanofiber and much faster propulsion compared to all-dielectric particles of the same size.
- Georgiy Tkachenko
- , Viet Giang Truong
- & Síle Nic Chormaic
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrarobust subzero healable materials enabled by polyphenol nano-assemblies
Ultrarobust subzero healable materials enabled by polyphenol nano-assemblies
Self-healing materials hold great promise for applications in wearable electronics, artificial muscles and soft robots but selfhealing at subzero temperatures remains a great challenge. Here, the authors present a robust subzero healable glassy polymer by incorporating polyphenol nano-assemblies with a large number of end groups into polymerizable deep eutectic solvent elastomers.
- Nan Wang
- , Xin Yang
- & Xinxing Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Polymer-dispersed liquid crystal elastomers as moldable shape-programmable material
Polymer-dispersed liquid crystal elastomers as moldable shape-programmable material
Development of Soft shape-memory materials is often limited to the synthesis of two-dimensional specimens and rely on bending mechanisms and scaffolding topology to perform three-dimensional morphing. Here, the authors demonstrate a shape-memory composite material made from main-chain liquid crystal elastomer microparticles dispersed in a silicone polymer matrix which enables molding into full-volume objects of any shape or size.
- Matej Bobnar
- , Nikita Derets
- & Andraž Rešetič
-
Article
| Open Access Bio-inspired magnetic-driven folded diaphragm for biomimetic robot
Bio-inspired magnetic-driven folded diaphragm for biomimetic robot
Soft robotics holds promise for realizing easy control over complex locomotion and deformation. Lin et al. report an earthworm-inspired untethered magnetic robot that consists one-piece-mold folded diaphragm to achieve large three-dimensional deformation with inside-volume change capability.
- Dezhao Lin
- , Fan Yang
- & Ruihong Li
-
Article
| Open Access Vascular smooth muscle-inspired architecture enables soft yet tough self-healing materials for durable capacitive strain-sensor
Vascular smooth muscle-inspired architecture enables soft yet tough self-healing materials for durable capacitive strain-sensor
Catastrophically mechanical failure, of soft self-healing materials often stems from its poor resistance to crack, propagation. Here, the authors present a strategy of surpassing trade-off, between soft self-healing and high fracture toughness, enabling the, conversion of soft and weak into soft yet tough self-healing materials.
- FuYao Sun
- , LongFei Liu
- & JiaJun Fu
-
Article
| Open Access Antifouling graphene oxide membranes for oil-water separation via hydrophobic chain engineering
Antifouling graphene oxide membranes for oil-water separation via hydrophobic chain engineering
Fouling is a continuous challenge for the effective application of membranes in oily wastewater treatment. Here, the authors present a hydrophobic chain engineering strategy to regulate the surface of graphene oxide-based membranes at a molecular scale for increased antifouling even at high permeance.
- Chao Yang
- , Mengying Long
- & Zhongyi Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access Prolonged in situ self-healing in structural composites via thermo-reversible entanglement
Prolonged in situ self-healing in structural composites via thermo-reversible entanglement
Synthetic materials that can repeatedly self-repair, akin to biological systems, are vital to meeting the 21st century’s infrastructural demands. Here, authors develop fiber-reinforced composites with rapid and prolonged in situ self-healing while also preserving structural integrity.
- Alexander D. Snyder
- , Zachary J. Phillips
- & Jason F. Patrick
-
Article
| Open Access A biomimetic laminated strategy enabled strain-interference free and durable flexible thermistor electronics
A biomimetic laminated strategy enabled strain-interference free and durable flexible thermistor electronics
Flexible thermistor epidermal electronics is desired to continuously monitor skin temperature in medical applications. Hao et al. report a nacre mimetic laminated strategy to fabricate thermistors with large mechanical durability for high-fidelity temperature discrimination without signal distortion.
- Sanwei Hao
- , Qingjin Fu
- & Jun Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Highly reinforced and degradable lignocellulose biocomposites by polymerization of new polyester oligomers
Highly reinforced and degradable lignocellulose biocomposites by polymerization of new polyester oligomers
Cellulose biocomposites from nanocellulose or plant fibers with polymer matrix are often not degradable and suffer from insufficient mechanical properties to replace established materials. Here, the authors demonstrate the fabrication of hydrolytically degradable polymers through in-situ polymerization of new functionally balanced oligomers within high-content lignocellulose reinforcement networks.
- Erfan Oliaei
- , Peter Olsén
- & Lars A. Berglund
-
Article
| Open Access A nanodispersion-in-nanograins strategy for ultra-strong, ductile and stable metal nanocomposites
A nanodispersion-in-nanograins strategy for ultra-strong, ductile and stable metal nanocomposites
High-strength nanocrystalline materials come at the expense of tensile ductility, thermal stability, and electrical conductivity. Here the authors report a nanodispersion-in-nanograins strategy where ultra-nano-carbon was used to concurrently achieve above four mutually exclusive properties.
- Zan Li
- , Yin Zhang
- & Y. Morris Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Lattice-mismatch-free growth of organic heterostructure nanowires from cocrystals to alloys
Lattice-mismatch-free growth of organic heterostructure nanowires from cocrystals to alloys
The large-scale synthesis of organic heterostructure nanowires is challenging. Here, the authors report the synthesis of organic triblock nanowires via a lattice mismatch-free strategy.
- Qiang Lv
- , Xue-Dong Wang
- & Liang-Sheng Liao
-
Article
| Open Access Local large temperature difference and ultra-wideband photothermoelectric response of the silver nanostructure film/carbon nanotube film heterostructure
Local large temperature difference and ultra-wideband photothermoelectric response of the silver nanostructure film/carbon nanotube film heterostructure
Finding efficient photothermoelectric materials remains critical to the development of clean and renewable energy conversion technologies. Here, authors prepare a silver nanostructure film/carbon nanotube film heterojunction with excellent photothermal and photoelectric conversion performance.
- Bocheng Lv
- , Yu Liu
- & Jia-Lin Sun
-
Article
| Open Access Topoarchitected polymer networks expand the space of material properties
Topoarchitected polymer networks expand the space of material properties
Synthesizing architected materials with strong adhesion has been challenging. Here the authors fabricate architected polymer networks by sequential polymerization and photolithography, and attain adherent interface by topological entanglement.
- Xiao Liu
- , Jingping Wu
- & Jian Hu
-
Article
| Open Access Damage-tolerant material design motif derived from asymmetrical rotation
Damage-tolerant material design motif derived from asymmetrical rotation
Nature-inspired design motifs have contributed to the development of advanced materials. Here the authors present a segmental design motif to realize a compression-resisting lightweight mechanical metamaterial with a progressive failure behavior and rotational degree of freedom.
- Wei Wang
- , Shu Jian Chen
- & Kwesi Sagoe-Crentsil
-
Article
| Open Access Polyamide-based membranes with structural homogeneity for ultrafast molecular sieving
Polyamide-based membranes with structural homogeneity for ultrafast molecular sieving
Thin-film composite membranes formed by conventional interfacial polymerization generally suffer from depth heterogeneity of the polyamide layer. Here, authors investigate salt-mediated polymerization approaches to achieve membranes with tuneable structural homogeneity.
- Liang Shen
- , Ruihuan Cheng
- & Yan Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Additive manufacturing of strong silica sand structures enabled by polyethyleneimine binder
Additive manufacturing of strong silica sand structures enabled by polyethyleneimine binder
The limited strength of green parts have been a major hurdle in the Binder Jet Additive Manufacturing. Here the authors apply polyethyleneimine binder to print silica sand structures with double the flexural strength of green parts and 8-fold increase in the strength upon reactive infiltration.
- Dustin B. Gilmer
- , Lu Han
- & Tomonori Saito
-
Article
| Open Access Bowls, vases and goblets—the microcrockery of polymer and nanocomposite morphology revealed by two-photon optical tomography
Bowls, vases and goblets—the microcrockery of polymer and nanocomposite morphology revealed by two-photon optical tomography
The morphology of semicrystalline plastics on the 1-100 μm scale, such as spherulites, strongly affect mechanical and other properties of the material but currently only 2D imaging techniques are available. Here, the authors use fluorescence labels and confocal microscopy to visualize the internal structure of neat polymers and composites in 3D and reveal unsuspected morphologies.
- Shu-Gui Yang
- , Zhen-Zhen Wei
- & Goran Ungar
-
Article
| Open Access Nanoengineering of cathode layers for solid oxide fuel cells to achieve superior power densities
Nanoengineering of cathode layers for solid oxide fuel cells to achieve superior power densities
High-performance cathode materials are crucial for the development of solid oxide fuel cells. Here, the authors present a nanoengineering approach to boost cathode performance in conventional anode-supported cells, demonstrating a viable route to attaining higher power output.
- Katherine Develos-Bagarinao
- , Tomohiro Ishiyama
- & Katsuhiko Yamaji
-
Article
| Open Access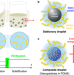 Static-state particle fabrication via rapid vitrification of a thixotropic medium
Static-state particle fabrication via rapid vitrification of a thixotropic medium
Upscale fabrication of functionalized microparticles is a pending challenge. Here, Kim et al. exploit the rheology of a thixotropic medium to grind sizeable amounts of raw material into well-defined colloidal dispersions, physically stabilized for further production steps.
- Sang Yup Kim
- , Shanliangzi Liu
- & Rebecca Kramer-Bottiglio
-
Article
| Open Access Ultra-strong polymeric hollow fiber membranes for saline dewatering and desalination
Ultra-strong polymeric hollow fiber membranes for saline dewatering and desalination
Osmotically assisted reverse osmosis can overcome limitations of the reverse osmosis process but a strong membrane which can withstand a high hydraulic pressure is crucial. Here, the authors develop strong polymer thin film composite hollow fiber membranes with exceptionally high hydraulic burst pressures of up to 110 bar, while maintaining high water permeance and salt rejection.
- Can Zeng Liang
- , Mohammad Askari
- & Tai-Shung Chung
-
Article
| Open Access Orthogonal photochemistry-assisted printing of 3D tough and stretchable conductive hydrogels
Orthogonal photochemistry-assisted printing of 3D tough and stretchable conductive hydrogels
3D-printing tough conductive hydrogels (TCHs) with complex structures is still a challenging task due to their inherent contrasting multinetworks, uncontrollable and slow polymerization. Here the authors show an orthogonal photochemistry-assisted printing strategy to make 3D TCHs in one pot.
- Hongqiu Wei
- , Ming Lei
- & You Yu
-
Article
| Open Access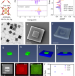 Phase-enabled metal-organic framework homojunction for highly selective CO2 photoreduction
Phase-enabled metal-organic framework homojunction for highly selective CO2 photoreduction
Homojunctions are very promising in photocatalysis, but challenging to achieve. Herein, authors report a well-defined hierarchical metal–organic framework-based homojunction, formed via a one-pot synthesis route directed by hollow transition metal nanoparticles, as photocatalysts for CO2 reduction.
- Yannan Liu
- , Chuanshuang Chen
- & Dongling Ma
-
Article
| Open Access Machine-learning-revealed statistics of the particle-carbon/binder detachment in lithium-ion battery cathodes
Machine-learning-revealed statistics of the particle-carbon/binder detachment in lithium-ion battery cathodes
Developing understanding of degradation phenomena in nickel rich cathodes is under intense investigation. Here the authors use learning-assisted statistical analysis and experiment-informed mathematical modelling to resolve the microstructure of a Ni-rich NMC composite cathode.
- Zhisen Jiang
- , Jizhou Li
- & Yijin Liu

 Materials design for hypersonics
Materials design for hypersonics