News & Views |
Featured
-
-
Article |
 Airway hillocks are injury-resistant reservoirs of unique plastic stem cells
Airway hillocks are injury-resistant reservoirs of unique plastic stem cells
In the lungs, recently identified epithelial structures known as hillocks can act as injury-resistant reservoirs of stem cells.
- Brian Lin
- , Viral S. Shah
- & Jayaraj Rajagopal
-
News |
 Rat neurons repair mouse brains — and restore sense of smell
Rat neurons repair mouse brains — and restore sense of smell
Scientists develop hybrid mice by filling in missing cells and structures in their brains with rat stem cells.
- Sara Reardon
-
News & Views |
 Targeting RNA opens therapeutic avenues for Timothy syndrome
Targeting RNA opens therapeutic avenues for Timothy syndrome
A therapeutic strategy that alters gene expression in a rare and severe neurodevelopmental condition has been tested in stem-cell-based models of the disease, and has been shown to correct genetic and cellular defects.
- Silvia Velasco
-
News |
 ‘Mini liver’ will grow in person’s own lymph node in bold new trial
‘Mini liver’ will grow in person’s own lymph node in bold new trial
Biotechnology firm LyGenesis has injected donor cells into a person with liver failure for the first time.
- Max Kozlov
-
Article |
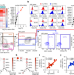 Depleting myeloid-biased haematopoietic stem cells rejuvenates aged immunity
Depleting myeloid-biased haematopoietic stem cells rejuvenates aged immunity
Antibody-mediated depletion of myeloid-biased haematopoietic stem cells in aged mice restores characteristic features of a more youthful immune system.
- Jason B. Ross
- , Lara M. Myers
- & Irving L. Weissman
-
News & Views |
 Powerful microscopy reveals blood-cell production in bone marrow
Powerful microscopy reveals blood-cell production in bone marrow
A method for imaging the production of blood cells in the bones of mice has revealed the organization of cell lineages, both in a steady state and in response to stressors, such as bleeding and infection.
- M. Carolina Florian
-
Article
| Open Access Resilient anatomy and local plasticity of naive and stress haematopoiesis
Resilient anatomy and local plasticity of naive and stress haematopoiesis
This study develops a method for spatially resolving multipotent haematopoiesis, erythropoiesis and lymphopoiesis in mice and uncovers heterogeneous haematopoietic stress responses in different bones.
- Qingqing Wu
- , Jizhou Zhang
- & Daniel Lucas
-
News |
 Will these reprogrammed elephant cells ever make a mammoth?
Will these reprogrammed elephant cells ever make a mammoth?
The de-extinction company Colossal is the first to convert elephant cells to an embryonic state, but using them to make mammoths won’t be easy, say researchers.
- Ewen Callaway
-
News |
 Organoids grown from amniotic fluid could shed light on rare diseases
Organoids grown from amniotic fluid could shed light on rare diseases
Organ-like groups of cells can be grown from amniotic fluid samples and offer hope for studying congenital conditions.
- Lilly Tozer
-
Research Briefing |
 Mechanisms guiding the slow pace of maturation in human neurons uncovered
Mechanisms guiding the slow pace of maturation in human neurons uncovered
Nerve cells in the human brain take a remarkably long time to mature. This study identifies an epigenetic ‘barrier’ in neural precursor cells that determines the rate of neuronal maturation and is slowly released during the process. Inhibition of the barrier is shown to accelerate maturation in multiple human stem-cell-based models.
-
Article |
 SOX17 enables immune evasion of early colorectal adenomas and cancers
SOX17 enables immune evasion of early colorectal adenomas and cancers
Transcriptomic and chromatin accessibility analyses of naive and transplanted colon cancer organoids in a mouse model reveal a key role for the transcription factor SOX17 in establishing a permissive immune environment for tumour cells.
- Norihiro Goto
- , Peter M. K. Westcott
- & Ömer H. Yilmaz
-
Article |
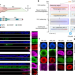 A patterned human neural tube model using microfluidic gradients
A patterned human neural tube model using microfluidic gradients
Newly developed microfluidic neural tube-like and forebrain-like structures based on human pluripotent stem cells can model pivotal aspects of neural patterning along both the rostral–caudal and dorsal–ventral axes.
- Xufeng Xue
- , Yung Su Kim
- & Jianping Fu
-
Research Briefing |
 A human embryo model mimics early development and blood-cell formation
A human embryo model mimics early development and blood-cell formation
Human embryos are extremely difficult to study. This lack of samples limits our understanding of crucial developmental stages, such as the early formation of blood cells. A stem-cell-based model closely captures the development of human embryonic and key extra-embryonic tissues after implantation, as well as the formation of early blood cells.
-
Research Briefing |
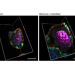 Embryo model made using pluripotent stem cells reveals details of early development in humans
Embryo model made using pluripotent stem cells reveals details of early development in humans
Early embryonic development in humans remains poorly understood. A 3D cellular model called bilaminoids, generated using ‘naive’ pluripotent stem cells and derived cell types, successfully recapitulates early development and enables mechanistic studies to examine how various cellular components interact to regulate early embryogenesis.
-
Article
| Open Access An epigenetic barrier sets the timing of human neuronal maturation
An epigenetic barrier sets the timing of human neuronal maturation
The slow maturation of human neurons is regulated by epigenetic modification in nascent neurons, mediated by EZH2, EHMT1, EHMT2 and DOT1L.
- Gabriele Ciceri
- , Arianna Baggiolini
- & Lorenz Studer
-
News Feature |
 Making mice with two dads: this biologist rewrote the rules on sexual reproduction
Making mice with two dads: this biologist rewrote the rules on sexual reproduction
Katsuhiko Hayashi created viable mouse eggs from male cells, a feat that could help to save species on the brink of extinction.
- Heidi Ledford
-
Article
| Open Access Modelling post-implantation human development to yolk sac blood emergence
Modelling post-implantation human development to yolk sac blood emergence
A genetically inducible stem cell-derived embryoid model of early post-implantation human embryogenesis captures the codevelopment of embryonic tissue and extra-embryonic endoderm and mesoderm niche with early haematopoiesis, with potential for drug testing and disease modelling.
- Joshua Hislop
- , Qi Song
- & Mo R. Ebrahimkhani
-
Article
| Open Access Hypoblast from human pluripotent stem cells regulates epiblast development
Hypoblast from human pluripotent stem cells regulates epiblast development
Authentic hypoblast cells created from naive human pluripotent stem cells (hPSCs) spontaneously assemble with naive hPSCs to form a three-dimensional bilaminar structure (bilaminoids) with a pro-amniotic-like cavity.
- Takumi Okubo
- , Nicolas Rivron
- & Yasuhiro Takashima
-
World View |
 Yes to global standards for research — as long as they are truly global
Yes to global standards for research — as long as they are truly global
Guidelines for research can level the playing field for scientists in low-resource settings — but diverse voices are needed to ensure that people worldwide can actually follow them.
- Maneesha S. Inamdar
-
News |
 This hybrid baby monkey is made of cells from two embryos
This hybrid baby monkey is made of cells from two embryos
The work paves the way for scientists to use chimeric primates to study human diseases.
- Carissa Wong
-
Obituary |
 Ian Wilmut, embryologist who helped to produce Dolly the sheep (1944–2023)
Ian Wilmut, embryologist who helped to produce Dolly the sheep (1944–2023)
Developmental biologist who led team that cloned the first mammal using adult cells.
- Sarah Franklin
-
News & Views |
 Stem cells used to model a two-week-old human embryo
Stem cells used to model a two-week-old human embryo
Researchers have used stem cells to create models that resemble human embryos at two weeks old, but bypass the earliest developmental stages — paving the way for studies that are not possible in human embryos.
- Naomi Moris
-
Comment |
 Why researchers should use human embryo models with caution
Why researchers should use human embryo models with caution
Scientists should carefully consider whether embryo models based on human stem cells are essential to their work because of the associated practical and ethical challenges.
- Janet Rossant
- & Jianping Fu
-
News & Views |
 Dual stem-cell populations interact in the skull
Dual stem-cell populations interact in the skull
The discovery that the skull has two groups of stem cell that produce similar types of descendant cell has big implications for the field of stem-cell research — and casts light on a developmental disorder that affects many children.
- Andrei S. Chagin
- & Dana Trompet
-
Nature Podcast |
 Why does cancer spread to the spine? Newly discovered stem cells might be the key
Why does cancer spread to the spine? Newly discovered stem cells might be the key
A stem cell vital for vertebral growth also drives spine metastases, and the use of MDMA in the treatment of PTSD.
- Benjamin Thompson
- & Shamini Bundell
-
Article
| Open Access Transgenic ferret models define pulmonary ionocyte diversity and function
Transgenic ferret models define pulmonary ionocyte diversity and function
Conditional genetic ferret models enable ionocyte lineage tracing, ionocyte ablation and ionocyte-specific deletion of CFTR to elucidate the roles of pulmonary ionocyte biology and function during human health and disease.
- Feng Yuan
- , Grace N. Gasser
- & John F. Engelhardt
-
Article |
 A multi-stem cell basis for craniosynostosis and calvarial mineralization
A multi-stem cell basis for craniosynostosis and calvarial mineralization
The calvarial stem cell niche is populated by a cathepsin K-expressing cell lineage and a newly identified discoidin domain-containing receptor 2-expressing lineage, both of which are required for proper calvarial mineralization.
- Seoyeon Bok
- , Alisha R. Yallowitz
- & Matthew B. Greenblatt
-
Article |
 Cholinergic neurons trigger epithelial Ca2+ currents to heal the gut
Cholinergic neurons trigger epithelial Ca2+ currents to heal the gut
A subpopulation of cholinergic neurons triggers Ca2+ currents among enterocytes to promote return to homeostasis after injury, and disruption of this process leads to gut inflammation and hyperplasia in Drosophila.
- Afroditi Petsakou
- , Yifang Liu
- & Norbert Perrimon
-
News & Views |
 Stem cells provide clues to why vertebrae attract tumour cells
Stem cells provide clues to why vertebrae attract tumour cells
Tumour cells tend to migrate to the vertebrae rather than to long bones, but the mechanism underlying this has been unclear. It emerges that the stem cells from which vertebrae are derived make a factor that attracts tumour cells.
- Geert Carmeliet
-
News |
 Breast cancer often spreads to the spine — newfound stem cell can explain why
Breast cancer often spreads to the spine — newfound stem cell can explain why
A stem cell that contributes to vertebra formation also encourages the growth of tumours that move to the backbone from elsewhere.
- Saima Sidik
-
Article
| Open Access Single-cell brain organoid screening identifies developmental defects in autism
Single-cell brain organoid screening identifies developmental defects in autism
We develop a high-throughput CRISPR screening system in cerebral organoids and identify vulnerable cell types and gene regulatory networks associated with autism spectrum disorder from single-cell transcriptomes and chromatin modalities.
- Chong Li
- , Jonas Simon Fleck
- & Juergen A. Knoblich
-
Article |
 A vertebral skeletal stem cell lineage driving metastasis
A vertebral skeletal stem cell lineage driving metastasis
Vertebral osteoblasts in mouse and human are formed from a precursor skeletal stem cell population that is distinct from long bone skeletal stem cells in function, location and transcriptional programme.
- Jun Sun
- , Lingling Hu
- & Matthew B. Greenblatt
-
Article
| Open Access Complete human day 14 post-implantation embryo models from naive ES cells
Complete human day 14 post-implantation embryo models from naive ES cells
The culture of genetically unmodified human naive embryonic stem cells in specific growth conditions gives rise to structures that recapitulate those of post-implantation human embryos up to 13–14 days after fertilization.
- Bernardo Oldak
- , Emilie Wildschutz
- & Jacob H. Hanna
-
Article
| Open Access Epitope editing enables targeted immunotherapy of acute myeloid leukaemia
Epitope editing enables targeted immunotherapy of acute myeloid leukaemia
Epitope engineering of donor haematopoietic stem/progenitor cells endows haematopoietic lineages with selective resistance to CAR T cells or monoclonal antibodies, without affecting protein function or regulation, enabling the targeting of genes that are essential for leukaemia survival and reducing the risk of tumour immune escape.
- Gabriele Casirati
- , Andrea Cosentino
- & Pietro Genovese
-
Research Briefing |
 A way to wipe a cell’s memory
A way to wipe a cell’s memory
Cells that have been artificially reprogrammed into states similar to embryonic stem cells — known as induced pluripotent stem cells — can bear a memory of their previous history. An innovative method that incorporates a step mimicking early development yields pluripotent cells that more closely resemble those in embryos, both on a molecular and functional level.
-
Article
| Open Access Transient naive reprogramming corrects hiPS cells functionally and epigenetically
Transient naive reprogramming corrects hiPS cells functionally and epigenetically
A new reprogramming strategy used to produce human induced pluripotent stem cells from somatic cells results in epigenetic and functional profiles that are highly similar to those of human embryonic stem cells.
- Sam Buckberry
- , Xiaodong Liu
- & Ryan Lister
-
Research Briefing |
 Salamanders’ regenerative potential might be driven by a specific protein variant
Salamanders’ regenerative potential might be driven by a specific protein variant
Axolotls — aquatic salamanders with an exceptional regenerative ability — rapidly increase their production of proteins in response to wounds. An axolotl-specific evolutionary divergence in a key protein called mTOR might drive this protein response and thus the regenerative potential of these amphibians, with possible implications for improving healing in mammals.
-
Article |
 Evolutionarily divergent mTOR remodels translatome for tissue regeneration
Evolutionarily divergent mTOR remodels translatome for tissue regeneration
Rapid activation of protein synthesis in the axolotl highlights the unanticipated impact of a translatome on orchestrating the early steps of wound healing and provides a missing link in our understanding of vertebrate regenerative potential.
- Olena Zhulyn
- , Hannah D. Rosenblatt
- & Maria Barna
-
Research Briefing |
 Tissue-regeneration program underlies lung-cancer suppression
Tissue-regeneration program underlies lung-cancer suppression
How the protein p53 suppresses lung cancer, the most common cause of cancer deaths worldwide, has remained unclear. It has been found that p53 impedes the development of lung cancer by promoting a highly specific cell-differentiation program that is characteristic of normal tissue regeneration after an injury.
-
Article |
 KRAS(G12D) drives lepidic adenocarcinoma through stem-cell reprogramming
KRAS(G12D) drives lepidic adenocarcinoma through stem-cell reprogramming
A study identifies the AT1 cell as a cell of origin for lung adenocarcinoma, and demonstrates that expression of oncogenic KRAS in differentiated AT1 cells reprograms them back into AT2 stem cells that generate indolent lepidic tumours.
- Nicholas H. Juul
- , Jung-Ki Yoon
- & Tushar J. Desai
-
Article |
 Co-transplantation of autologous Treg cells in a cell therapy for Parkinson’s disease
Co-transplantation of autologous Treg cells in a cell therapy for Parkinson’s disease
In mouse and rat models of Parkinson’s disease, co-transplanting regulatory T cells (Treg cells) improves the survival of grafted midbrain dopamine neurons in cell therapies by reducing the inflammatory response caused by surgical injury.
- Tae-Yoon Park
- , Jeha Jeon
- & Kwang-Soo Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Pluripotent stem cell-derived model of the post-implantation human embryo
Pluripotent stem cell-derived model of the post-implantation human embryo
Co-culture of wild-type human embryonic stem cells with two types of extraembryonic-like cell engineered to overexpress specific transcription factors results in an embryoid model that recapitulates multiple features of the post-implantation human embryo.
- Bailey A. T. Weatherbee
- , Carlos W. Gantner
- & Magdalena Zernicka-Goetz
-
Article
| Open Access Self-patterning of human stem cells into post-implantation lineages
Self-patterning of human stem cells into post-implantation lineages
Human pluripotent stem cells can be triggered to self-organize into structures recapitulating early human post-implantation embryonic development.
- Monique Pedroza
- , Seher Ipek Gassaloglu
- & Berna Sozen
-
Article
| Open Access Signalling by senescent melanocytes hyperactivates hair growth
Signalling by senescent melanocytes hyperactivates hair growth
Senescent melanocytes of skin nevi drive hyperactivation of hair growth through the signalling factor SPP1.
- Xiaojie Wang
- , Raul Ramos
- & Maksim V. Plikus
-
Article
| Open Access Ultraviolet radiation shapes dendritic cell leukaemia transformation in the skin
Ultraviolet radiation shapes dendritic cell leukaemia transformation in the skin
Blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm (BPDCN) arises from clonal (premalignant) haematopoietic precursors in the bone marrow, and BPDCN skin tumours first develop at sun-exposed anatomical sites and are distinguished by clonally expanded mutations induced by ultraviolet radiation.
- Gabriel K. Griffin
- , Christopher A. G. Booth
- & Andrew A. Lane
-
News & Views |
 A step closer to making the mother of stem cells
A step closer to making the mother of stem cells
In the earliest stages of mammalian development, individual cells possess the unrestricted potential to form a new organism. Researchers are closing in on the goal of growing these cells in the laboratory.
- Martin F. Pera
-
Article |
 Lysine catabolism reprograms tumour immunity through histone crotonylation
Lysine catabolism reprograms tumour immunity through histone crotonylation
Glioblastoma stem cells co-opt lysine uptake and degradation to shunt the production of crotonyl-CoA, remodelling the chromatin landscape to evade interferon-induced intrinsic effects on glioblastoma stem cell maintenance and extrinsic effects on immune response.
- Huairui Yuan
- , Xujia Wu
- & Jeremy N. Rich
-
Article |
 A phosphate-sensing organelle regulates phosphate and tissue homeostasis
A phosphate-sensing organelle regulates phosphate and tissue homeostasis
PXo bodies, non-canonical multilamellar organelles, serve as a reservoir for intracellular inorganic phosphate and are a critical regulator of both cytosolic phosphate levels and tissue homeostasis.
- Chiwei Xu
- , Jun Xu
- & Norbert Perrimon
-
News & Views |
 Yo-yoing stem cells defy dogma to maintain hair colour
Yo-yoing stem cells defy dogma to maintain hair colour
The observation that melanocyte stem cells migrate up and down the hair follicle, differentiating into melanocytes and then returning to a stem-cell identity, calls into question long-held assumptions about adult stem cells.
- Carlos Galvan
- & William E. Lowry
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Adult stem cells
- Ageing
- Cancer stem cells
- Embryonic germ cells
- Embryonic stem cells
- Epigenetic memory
- Haematopoietic stem cells
- Heart stem cells
- Intestinal stem cells
- Mammary stem cells
- Mesenchymal stem cells
- Multipotent stem cells
- Muscle stem cells
- Neural stem cells
- Pluripotent stem cells
- Quiescence
- Regeneration
- Reprogramming
- Self-renewal
- Skin stem cells
- Stem-cell differentiation
- Stem-cell niche
- Totipotent stem cells
- Transdifferentiation

 Cells destroy donated mitochondria to build blood vessels
Cells destroy donated mitochondria to build blood vessels