Research Highlight |
Featured
-
-
Review Article |
 Cargo recognition and degradation by selective autophagy
Cargo recognition and degradation by selective autophagy
In this Review Article, Klionsky and co-authors discuss selective autophagy pathways that degrade unwanted cytosolic components and organelles, and how these pathways require ligand receptors and scaffold proteins for cargo specificity.
- Damián Gatica
- , Vikramjit Lahiri
- & Daniel J. Klionsky
-
Review Article |
 Emerging views of the nucleus as a cellular mechanosensor
Emerging views of the nucleus as a cellular mechanosensor
Mechanical forces influence both cytoplasmic and nuclear events. Kirby and Lammerding discuss recent evidence suggesting that the nucleus itself is a mechanosensor and methods to study nuclear mechanotransduction.
- Tyler J. Kirby
- & Jan Lammerding
-
News & Views |
 Mitochondrial DNA selection in human germ cells
Mitochondrial DNA selection in human germ cells
Mitochondria contain their own circular mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA), which, over time, is subjected to mutations that may eventually result in functional defects. A study now describes genetic and metabolic selection processes during germ cell development that prevent accumulation of harmful mtDNA variants.
- Di Chen
- & Amander T. Clark
-
Technical Report |
 Affinity purification of cell-specific mitochondria from whole animals resolves patterns of genetic mosaicism
Affinity purification of cell-specific mitochondria from whole animals resolves patterns of genetic mosaicism
Ahier et al. describe a method to isolate intact mitochondria from specific cells in Caenorhabditis elegans and show that the germline is more prone to propagating deleterious mitochondrial genomes than somatic lineages.
- Arnaud Ahier
- , Chuan-Yang Dai
- & Steven Zuryn
-
Letter |
 Segregation of mitochondrial DNA heteroplasmy through a developmental genetic bottleneck in human embryos
Segregation of mitochondrial DNA heteroplasmy through a developmental genetic bottleneck in human embryos
Floros et al. show that mtDNA copy number is reduced and non-synonymous mtDNA mutations are eliminated to prevent mtDNA mutation accumulation in germ cells during human primordial germ cell development.
- Vasileios I. Floros
- , Angela Pyle
- & Patrick F. Chinnery
-
Article |
 The autophagy receptor ALLO-1 and the IKKE-1 kinase control clearance of paternal mitochondria in Caenorhabditis elegans
The autophagy receptor ALLO-1 and the IKKE-1 kinase control clearance of paternal mitochondria in Caenorhabditis elegans
Sato et al. identify ALLO-1 as an autophagy receptor required for paternal organelle clearance in Caenorhabditis elegans, and this process is dependent on ALLO-1 phosphorylation by the TBK1 family kinase IKKE-1.
- Miyuki Sato
- , Katsuya Sato
- & Ken Sato
-
News & Views |
 Capturing endosomal vesicles at the Golgi
Capturing endosomal vesicles at the Golgi
Membrane trafficking specificity between distinct compartments ensures that cargo proteins and lipids are delivered to their target organelle. However, accurate recognition of cargo carriers by tethering factors on target membranes is poorly understood. TBC1D23 is now identified as an adaptor that links endosome-derived vesicles with golgins at the trans-Golgi.
- J. Christopher Fromme
- & Mary Munson
-
Letter |
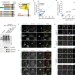 TBC1D23 is a bridging factor for endosomal vesicle capture by golgins at the trans-Golgi
TBC1D23 is a bridging factor for endosomal vesicle capture by golgins at the trans-Golgi
Shin et al. identify TBC1D23 as an adaptor that interacts both with golgins and endosomal WASH and is required for the delivery of endosome-derived vesicles to the trans-Golgi.
- John J. H. Shin
- , Alison K. Gillingham
- & Sean Munro
-
News & Views |
 Myofibrils put the squeeze on nuclei
Myofibrils put the squeeze on nuclei
During muscle development, nuclei travel from the centre of the myofibre to the periphery, a process defective in certain diseases. A new study reveals that this movement is due to centripetal forces imposed on nuclei by the crosslinking and contraction of myofibrils.
- Jonathan N. Rosen
- & Mary K. Baylies
-
Article |
 Myofibril contraction and crosslinking drive nuclear movement to the periphery of skeletal muscle
Myofibril contraction and crosslinking drive nuclear movement to the periphery of skeletal muscle
Roman et al. demonstrate that crosslinking and contraction of myofibrils mediate the movement of nuclei to the periphery of myofibres, and describe a role for Arp2/3 in organizing desmin.
- William Roman
- , João P. Martins
- & Edgar R. Gomes
-
Article |
 Lactate dehydrogenase activity drives hair follicle stem cell activation
Lactate dehydrogenase activity drives hair follicle stem cell activation
Flores et al. show that hair follicle stem cells rely on the production of lactate via the LDHA enzyme to become activated. Inducing Ldha through Mpc1 inhibition or Myc activation successfully reactivates the hair cycle in quiescent follicles.
- Aimee Flores
- , John Schell
- & William E. Lowry
-
Review Article |
 Organelle biogenesis in the endoplasmic reticulum
Organelle biogenesis in the endoplasmic reticulum
In this Review, Prinz and co-authors discuss the role of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) in the de novo generation of peroxisomes, lipid droplets and omegasomes, and how this requires subdomains with specific protein and lipid compositions.
- Amit S. Joshi
- , Hong Zhang
- & William A. Prinz
-
News & Views |
 OPA1 and cardiolipin team up for mitochondrial fusion
OPA1 and cardiolipin team up for mitochondrial fusion
Fusion between the inner membranes of two mitochondria requires the GTPase optic atrophy 1 (OPA1), but the molecular mechanism is poorly understood. A study now shows that fusion of two liposomes can be performed by OPA1 tethered to just one liposome, through an interaction with the phospholipid cardiolipin on the opposing liposome.
- Raymond Liu
- & David C. Chan
-
Letter |
 Molecular basis of selective mitochondrial fusion by heterotypic action between OPA1 and cardiolipin
Molecular basis of selective mitochondrial fusion by heterotypic action between OPA1 and cardiolipin
Ban et al. show that optic atrophy 1 (OPA1) and cardiolipin mediate mitochondrial fusion. In contrast, a homotypic trans-OPA1 interaction independent of cardiolipin mediates membrane tethering to form mitochondrial cristae.
- Tadato Ban
- , Takaya Ishihara
- & Naotada Ishihara
-
News & Views |
 Mitochondria link metabolism and epigenetics in haematopoiesis
Mitochondria link metabolism and epigenetics in haematopoiesis
Due to their varied metabolic and signalling roles, mitochondria are important in mediating cell behaviour. By altering mitochondrial function, two studies now identify metabolite-induced epigenetic changes that have profound effects on haematopoietic stem cell fate and function.
- John C. Schell
- & Jared Rutter
-
Article |
 Regulation of mitochondrial biogenesis in erythropoiesis by mTORC1-mediated protein translation
Regulation of mitochondrial biogenesis in erythropoiesis by mTORC1-mediated protein translation
Two papers by Liu et al. and Ansó et al. study the post-transcriptional regulation of mitochondrial factors in erythropoiesis and the role of RISP-mediated mitochondrial respiration in fetal and adult HSC function via metabolites and epigenetic changes.
- Xin Liu
- , Yuannyu Zhang
- & Jian Xu
-
Letter |
 Microbial metabolites regulate host lipid metabolism through NR5A–Hedgehog signalling
Microbial metabolites regulate host lipid metabolism through NR5A–Hedgehog signalling
Lin and Wang show that methionine deprivation reprogrammes bacterial metabolism to regulate host mitochondrial dynamics and lipid metabolism in Caenorhabditis elegans through nuclear receptor and Hedgehog signalling.
- Chih-Chun Janet Lin
- & Meng C. Wang
-
News & Views |
 PARL paves the way to apoptosis
PARL paves the way to apoptosis
Although the mitochondrial inner membrane rhomboid peptidase PARL is known to participate in critical signalling cascades, its role in apoptosis has remained unclear. PARL is now shown to process the mitochondrial pro-apoptotic protein Smac (also known as DIABLO) for its subsequent release into the cytosol where it antagonizes XIAP-mediated caspase inhibition to promote apoptosis.
- Naotada Ishihara
- & Katsuyoshi Mihara
-
Article |
 Endocytic proteins are partitioned at the edge of the clathrin lattice in mammalian cells
Endocytic proteins are partitioned at the edge of the clathrin lattice in mammalian cells
Using large-scale, super-resolution microscopy, Sochacki et al. define the spatial organization of 19 proteins within clathrin-coated pits during distinct stages of clathrin-mediated endocytosis.
- Kem A. Sochacki
- , Andrea M. Dickey
- & Justin W. Taraska
-
Article |
 The TDH–GCN5L1–Fbxo15–KBP axis limits mitochondrial biogenesis in mouse embryonic stem cells
The TDH–GCN5L1–Fbxo15–KBP axis limits mitochondrial biogenesis in mouse embryonic stem cells
Donato et al. show that Fbxo15 targets acetylated KBP for degradation to limit mitochondrial expansion, whereas KBP accumulation promotes mitochondrial biogenesis in a Kif1Bα-dependent manner.
- Valerio Donato
- , Massimo Bonora
- & Michele Pagano
-
Letter |
 Endoplasmic-reticulum-mediated microtubule alignment governs cytoplasmic streaming
Endoplasmic-reticulum-mediated microtubule alignment governs cytoplasmic streaming
Through imaging and theoretical modelling, Kimura et al. discover that endoplasmic reticulum flow determines microtubule alignment to promote cytoplasmic streaming of yolk granules in Caenorhabditis elegans zygotes.
- Kenji Kimura
- , Alexandre Mamane
- & Akatsuki Kimura
-
Article |
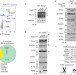 PARL mediates Smac proteolytic maturation in mitochondria to promote apoptosis
PARL mediates Smac proteolytic maturation in mitochondria to promote apoptosis
Saita et al. show that PARL cleaves Smac (also known as DIABLO) to generate an IAP-binding motif required for its apoptotic activity, identifying PARL-mediated Smac processing as a pro-apoptotic mitochondrial pathway.
- Shotaro Saita
- , Hendrik Nolte
- & Thomas Langer
-
News & Views |
 Remodelling germ cells by intercellular cannibalism
Remodelling germ cells by intercellular cannibalism
Work from the early 1980s reported strange lobes protruding from Caenorhabditis elegans germ cell precursors. However, the fate and potential significance of these lobes remained unexplored for decades. Now, neighbouring endodermal cells are shown to sever and digest these lobes, in an unexpected process of 'intercellular cannibalism', which could play an important part in regulating primordial germ cells.
- Jennifer K. Heppert
- & Bob Goldstein
-
Article |
 Developmentally programmed germ cell remodelling by endodermal cell cannibalism
Developmentally programmed germ cell remodelling by endodermal cell cannibalism
Caenorhabditis elegans primordial germ cells (PGCs) transiently extend large lobes, which are found to be actively removed and digested by endodermal cells to alter PGC content in a process dependent on actin and dynamin.
- Yusuff Abdu
- , Chelsea Maniscalco
- & Jeremy Nance
-
News & Views |
 On keeping the right ER size
On keeping the right ER size
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is the largest membrane-bound organelle in cells, and its size needs to be carefully controlled. Downsizing the ER by autophagy is now shown to involve Sec62, a protein that also helps to build up the organelle. This link suggests a molecular switch for ER size control.
- Sebastian Schuck
-
Article |
 Translocon component Sec62 acts in endoplasmic reticulum turnover during stress recovery
Translocon component Sec62 acts in endoplasmic reticulum turnover during stress recovery
Fumagalli et al. show that Sec62 delivers ER components to the autolysosome for clearance by acting as a receptor for autophagy protein LC3-II. This identifies Sec62 as a critical factor for selective ER turnover.
- Fiorenza Fumagalli
- , Julia Noack
- & Maurizio Molinari
-
News & Views |
 Turn up the lysosome
Turn up the lysosome
Lysosomes are digestive organelles of the endocytic and autophagic pathways. Increasing lysosome enzyme activities could help to clear pathological cellular waste. A recent study shows that lysosomal digestive functions can be promoted in isolated cells and mice by pharmacologically stimulating the autophagy- and lysosome-regulating transcription factors TFEB and ZKSCAN3 through previously unrecognized mTORC1-independent pathways acting via PKC.
- Paul Saftig
- & Albert Haas
-
Article |
 Protein kinase C controls lysosome biogenesis independently of mTORC1
Protein kinase C controls lysosome biogenesis independently of mTORC1
Using a chemical screening approach, Yang and colleagues identify PKC as a regulator of lysosome biogenesis, which controls the subcellular localization of TFEB and ZKSCAN3 through parallel signalling pathways and independently of mTORC1.
- Yang Li
- , Meng Xu
- & Chonglin Yang
-
Article |
 Autophagosome–lysosome fusion triggers a lysosomal response mediated by TLR9 and controlled by OCRL
Autophagosome–lysosome fusion triggers a lysosomal response mediated by TLR9 and controlled by OCRL
De Leo et al. identify a lysosomal response to autophagic cargo during lysosome–autophagosome fusion that involves TLR9 activation and OCRL recruitment, and leads to a regulated local increase in PtdIns(4,5)P2, which is necessary for a normal autophagic flux.
- Maria Giovanna De Leo
- , Leopoldo Staiano
- & Maria Antonietta De Matteis
-
Article |
 Staccato/Unc-13-4 controls secretory lysosome-mediated lumen fusion during epithelial tube anastomosis
Staccato/Unc-13-4 controls secretory lysosome-mediated lumen fusion during epithelial tube anastomosis
Luschnig and colleagues present a model in which Staccato, in combination with Rab39, mediates the control of apical membrane fusion by interacting with components of the SNARE machinery in the formation of anastomoses in the tracheal tube.
- Sara Caviglia
- , Marko Brankatschk
- & Stefan Luschnig
-
Article |
 Peroxin-dependent targeting of a lipid-droplet-destined membrane protein to ER subdomains
Peroxin-dependent targeting of a lipid-droplet-destined membrane protein to ER subdomains
Kopito and Schrul show that the peroxisome proteins PEX19 and PEX3 mediate the correct insertion of the lipid droplet protein UBXD8 into ER subdomains.
- Bianca Schrul
- & Ron R. Kopito
-
Article |
 A molecular mechanism to regulate lysosome motility for lysosome positioning and tubulation
A molecular mechanism to regulate lysosome motility for lysosome positioning and tubulation
Following autophagy induction, lysosomes move to the perinuclear region. Xu and colleagues delineate a pathway involving PtdIns(3,5)P2-mediated activation of the TRPML1 channel and the Ca2+ sensor ALG-2 in this process.
- Xinran Li
- , Nicholas Rydzewski
- & Haoxing Xu
-
News & Views |
 STIMATE reveals a STIM1 transitional state
STIMATE reveals a STIM1 transitional state
Decreases in endoplasmic reticulum calcium content are sensed by resident STIM proteins, which can activate plasma membrane Orai channels to facilitate Ca2+ entry. The role of STIMATE, a previously unknown component of the store-operated calcium entry complex, has now been identified and defined.
- Robert Hooper
- & Jonathan Soboloff
-
Letter |
 Proteomic mapping of ER–PM junctions identifies STIMATE as a regulator of Ca2+ influx
Proteomic mapping of ER–PM junctions identifies STIMATE as a regulator of Ca2+ influx
Through a proteomic analysis of ER–PM junctions, Zhou and colleagues and Wang and colleagues discover that the transmembrane protein STIMATE is a positive regulator of STIM localization and function, thereby stimulating Ca2+ influx.
- Ji Jing
- , Lian He
- & Yubin Zhou
-
Article |
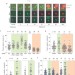 AMPK and PFKFB3 mediate glycolysis and survival in response to mitophagy during mitotic arrest
AMPK and PFKFB3 mediate glycolysis and survival in response to mitophagy during mitotic arrest
Malumbres and colleagues reveal that mitotic arrest is accompanied by reduced mitochondrial mass and oxidative respiration resulting in activation of AMPK and induction of glycolysis to promote cell survival.
- Elena Doménech
- , Carolina Maestre
- & Marcos Malumbres
-
Article |
 A nuclear role for the respiratory enzyme CLK-1 in regulating mitochondrial stress responses and longevity
A nuclear role for the respiratory enzyme CLK-1 in regulating mitochondrial stress responses and longevity
Whitmarsh and colleagues identify a nuclear form of the mitochondrial enzyme, CLK-1 in C. elegans and COQ7 in human cells, respectively, that senses reactive oxygen species and regulates gene expression.
- Richard M. Monaghan
- , Robert G. Barnes
- & Alan J. Whitmarsh
-
Letter |
 ATP synthase promotes germ cell differentiation independent of oxidative phosphorylation
ATP synthase promotes germ cell differentiation independent of oxidative phosphorylation
Lehmann and colleagues describe a role for the ATP synthase in Drosophila germline stem cell differentiation that is independent of ATP synthesis, and involves the maturation of mitochondrial cristae.
- Felipe K. Teixeira
- , Carlos G. Sanchez
- & Ruth Lehmann
-
Article |
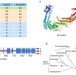 EARP is a multisubunit tethering complex involved in endocytic recycling
EARP is a multisubunit tethering complex involved in endocytic recycling
Bonifacino and colleagues identify a four-protein complex, called the endosome-associated recycling protein (EARP) complex, that associates with Rab4-positive endosomes and promotes recycling-endosome tethering and fusion.
- Christina Schindler
- , Yu Chen
- & Juan S. Bonifacino
-
Article |
 Active diffusion positions the nucleus in mouse oocytes
Active diffusion positions the nucleus in mouse oocytes
By live imaging of mouse oocytes, Verlhac and colleagues demonstrate that actin-coated vesicles together with myosin Vb participate in centring of the nucleus by creating a gradient of cytoplasmic forces.
- Maria Almonacid
- , Wylie W. Ahmed
- & Marie-Hélène Verlhac
-
Review Article |
 Tipping the metabolic scales towards increased longevity in mammals
Tipping the metabolic scales towards increased longevity in mammals
Riera and Dillin review how longevity is affected by metabolic changes and mitochondrial function.
- Celine E. Riera
- & Andrew Dillin
-
Article |
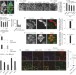 Lysosomal calcium signalling regulates autophagy through calcineurin and TFEB
Lysosomal calcium signalling regulates autophagy through calcineurin and TFEB
Medina, Ballabio and colleagues report that calcium release from the lysosome stimulates calcineurin, which dephosphorylates and activates TFEB. These findings reveal a central role for calcium signalling in autophagy and lysosome homeostasis.
- Diego L. Medina
- , Simone Di Paola
- & Andrea Ballabio
-
Letter |
 Directional Notch trafficking in Sara endosomes during asymmetric cell division in the spinal cord
Directional Notch trafficking in Sara endosomes during asymmetric cell division in the spinal cord
Castanon, González-Gaitán and colleagues report that Sara endosomes can regulate asymmetric cell division by unequally positioning endocytosed Notch ligand in one daughter cell.
- Sabine Kressmann
- , Claudia Campos
- & Marcos González-Gaitán
-
Article |
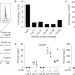 USP30 and parkin homeostatically regulate atypical ubiquitin chains on mitochondria
USP30 and parkin homeostatically regulate atypical ubiquitin chains on mitochondria
Cunningham et al. characterize the ubiquitin chain linkages regulated by the opposing activities of the E3 ligase parkin and the deubiquitylation enzyme USP30 on mitochondria.
- Christian N. Cunningham
- , Joshua M. Baughman
- & Jacob E. Corn
-
News & Views |
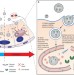 Milk makes lysosomes lethal
Milk makes lysosomes lethal
Stat3 has been shown to regulate lysosome membrane permeabilization and cell death in vivo during post-lactation mammary gland involution. It is now revealed that Stat3 induces lysosome membrane permeabilization by causing phagocytosis of milk fat globules, which destabilize the lysosome membrane leading to leakage of cathepsin proteases.
- Shefali Krishna
- & Michael Overholtzer
-
Letter |
 FHOD1 interaction with nesprin-2G mediates TAN line formation and nuclear movement
FHOD1 interaction with nesprin-2G mediates TAN line formation and nuclear movement
Gundersen and colleagues report that the FHOD1 formin is involved in nuclear positioning, by physically linking nesprin-2G, a protein of the outer nuclear membrane, to actin cables, to allow the formation of the transmembrane actin-associated nuclear (TAN) lines that are needed to move the nucleus.
- Stefan Kutscheidt
- , Ruijun Zhu
- & Gregg G. Gundersen
-
-
News & Views |
 Selective autophagy goes exclusive
Selective autophagy goes exclusive
Using in vitro reconstitution systems, three studies shed light on the interactions of Atg8 family proteins with cargo receptors and components of the basal autophagy machinery. The results have important mechanistic implications for selective macroautophagy, scaffold formation and spatio-temporal organization of the lipidation process during autophagosome formation.
- Terje Johansen
- & Trond Lamark
-
Article |
 Cargo binding to Atg19 unmasks additional Atg8 binding sites to mediate membrane–cargo apposition during selective autophagy
Cargo binding to Atg19 unmasks additional Atg8 binding sites to mediate membrane–cargo apposition during selective autophagy
The Cvt pathway in yeast operates constitutively, but the mechanism by which non-cargo material is excluded from the vacuole is incompletely defined. Martens and colleagues show that cargo binding to the cargo receptor Atg19 exposes further Atg8 binding sites on the receptor, which draws the isolation membrane around the autophagic cargo and prevents inclusion of non-cargo material in autophagosomes.
- Justyna Sawa-Makarska
- , Christine Abert
- & Sascha Martens
-
