Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Single-shot stereo-polarimetric compressed ultrafast photography for light-speed observation of high-dimensional optical transients with picosecond resolution
Single-shot stereo-polarimetric compressed ultrafast photography for light-speed observation of high-dimensional optical transients with picosecond resolution
Existing high-dimensional optical imaging techniques that record space and polarization cannot detect the photon’s time of arrival due to the limited speeds of electronic sensors. Here, the authors develop a single-shot ultrafast imaging modality to record light-speed high-dimensional events with picosecond resolution.
- Jinyang Liang
- , Peng Wang
- & Lihong V. Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Computational optical imaging with a photonic lantern
Computational optical imaging with a photonic lantern
Here, the authors demonstrate a route to high resolution microendoscopy using a multicore fibre with a photonic lantern. They show that distinct multimode patterns of light can be projected from the output of the lantern by individually exciting the single-mode MCF cores, whose patterns are highly stable to fibre movement.
- Debaditya Choudhury
- , Duncan K. McNicholl
- & Robert R. Thomson
-
Article
| Open Access Polariton condensation and surface enhanced Raman in spherical ZnO microcrystals
Polariton condensation and surface enhanced Raman in spherical ZnO microcrystals
Polariton dynamics are usually studied in high quality cavities in semiconductor hetero structures. Here, the authors demonstrate polariton dynamics and surface polariton field enhanced Raman responses in micro-spherical ZnO.
- Victor V. Volkov
- , Daniel J. Oliver
- & Carole C. Perry
-
Article
| Open Access Porous carbon nanowire array for surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy
Porous carbon nanowire array for surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy
SERS can be unreliable for biomedical use. The authors demonstrate a metal-free nanostructure composed of porous carbon nanowires in an array as a SERS substrate. It offers 106 signal enhancement due to strong broadband charge-transfer resonance and substrate-to-substrate, spot-to-spot and time-to-time consistency in the SERS spectrum.
- Nan Chen
- , Ting-Hui Xiao
- & Keisuke Goda
-
Article
| Open Access Visualization of ferroaxial domains in an order-disorder type ferroaxial crystal
Visualization of ferroaxial domains in an order-disorder type ferroaxial crystal
The presence of ferroaxial domain states is recently experimentally demonstrated by a nonlinear optical technique, which lacks high spatial resolution to visualize ferroaxial domains. Here, the authors visualize spatial distributions of ferroaxial domains in NiTiO3 showing an order-disorder type ferroaxial transition.
- T. Hayashida
- , Y. Uemura
- & T. Kimura
-
Article
| Open Access Polariton-driven phonon laser
Polariton-driven phonon laser
Efficient generation of phonons is an important ingredient for a prospective electrically-driven phonon laser for coherent control of quantum systems. Here, the authors report on laser-like phonon emission in a hybrid semiconductor microcavity that optomechanically couples BEC polaritons with phonons.
- D. L. Chafatinos
- , A. S. Kuznetsov
- & A. Fainstein
-
Article
| Open Access Three-dimensional imaging through scattering media based on confocal diffuse tomography
Three-dimensional imaging through scattering media based on confocal diffuse tomography
Techniques for imaging through scattering media are generally invasive, operate at microscopic scales or require a priori information. Here, the authors overcome these limitations by introducing confocal diffuse tomography, which captures the 3D shape of objects hidden behind scattering media.
- David B. Lindell
- & Gordon Wetzstein
-
Article
| Open Access Single-molecule photoreaction quantitation through intraparticle-surface energy transfer (i-SET) spectroscopy
Single-molecule photoreaction quantitation through intraparticle-surface energy transfer (i-SET) spectroscopy
Single-molecule sensing is very challenging due to weak emitted signals and environmental interference. Here the authors design a method (i-SET) for single molecule sensing with core-shell upconverting nanoparticles, which relies on signal enhancement by the activator-rich probes to quantify fluorophores attached to a single nanoparticle.
- Jian Zhou
- , Changyu Li
- & Renren Deng
-
Article
| Open Access Photo-acoustic dual-frequency comb spectroscopy
Photo-acoustic dual-frequency comb spectroscopy
Here, the authors show that the resolution and speed limitations in broadband photo-acoustic spectroscopy can be overcome by combining dual-comb spectroscopy with photo-acoustic detection. This enables broadband detection and allows for rapid and sensitive multi-species molecular analysis across all wavelengths of light.
- Thibault Wildi
- , Thibault Voumard
- & Tobias Herr
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic spatiotemporal beams that combine two independent and controllable orbital-angular-momenta using multiple optical-frequency-comb lines
Dynamic spatiotemporal beams that combine two independent and controllable orbital-angular-momenta using multiple optical-frequency-comb lines
Orbital angular momentum takes several forms in structured light beams. Here, the authors demonstrate control of dynamic spatiotemporal beams combining two forms of orbital angular momenta, by coherently adding frequency comb lines.
- Zhe Zhao
- , Hao Song
- & Alan E. Willner
-
Article
| Open Access Subwavelength pixelated CMOS color sensors based on anti-Hermitian metasurface
Subwavelength pixelated CMOS color sensors based on anti-Hermitian metasurface
Pixel size in imaging and displays is limited by fundamental constraints that compromise performance at wavelength scales. Here the authors present subwavelength color pixel sensors based on anti-Hermitian metasurfaces relying on structural color for increased performance.
- Joseph S. T. Smalley
- , Xuexin Ren
- & Xiang Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access A neurovascular high-frequency optical coherence tomography system enables in situ cerebrovascular volumetric microscopy
A neurovascular high-frequency optical coherence tomography system enables in situ cerebrovascular volumetric microscopy
High resolution intravascular imaging in the brain is limited by the high tortuosity of the vasculature. Here the authors present a fiber optic imaging technology using high-frequency optical coherence tomography (HF-OCT) to provide volumetric high resolution images in the highly tortuous cerebral vasculature.
- Giovanni J. Ughi
- , Miklos G. Marosfoi
- & Ajit S. Puri
-
Article
| Open Access Observation of topological transport quantization by dissipation in fast Thouless pumps
Observation of topological transport quantization by dissipation in fast Thouless pumps
Topological quantized transport has been limited to slow varying potentials. Here, the authors report that a topological band structure and associated quantized transport can be restored by non-Hermitian Floquet engineering at a driving frequency as large as the system’s band gap.
- Zlata Fedorova
- , Haixin Qiu
- & Johann Kroha
-
Article
| Open Access Mitochondrial dynamics quantitatively revealed by STED nanoscopy with an enhanced squaraine variant probe
Mitochondrial dynamics quantitatively revealed by STED nanoscopy with an enhanced squaraine variant probe
Live cell imaging of mitochondrial cristae is challenged by the unsuitability of current fluorescent probes and high phototoxicity. Here the authors develop a squarine variant probe (MitoESq-635) that is capable of longitudinal imaging of cristae with STED with minimal phototoxicity.
- Xusan Yang
- , Zhigang Yang
- & Peng Xi
-
Article
| Open Access Synucleinopathy alters nanoscale organization and diffusion in the brain extracellular space through hyaluronan remodeling
Synucleinopathy alters nanoscale organization and diffusion in the brain extracellular space through hyaluronan remodeling
The nanoscale organisation of the brain extracellular space can be studied in vivo. Here, the authors investigate how it changes in response to α-synuclein pathology, and identify interactions between microglia and the extracellular matrix.
- Federico N. Soria
- , Chiara Paviolo
- & Erwan Bezard
-
Article
| Open Access Subsurface chemical nanoidentification by nano-FTIR spectroscopy
Subsurface chemical nanoidentification by nano-FTIR spectroscopy
Nano-FTIR spectroscopy allows chemical characterization of composite surfaces, but its capability in subsurface analysis is not much explored. The authors show that spectra from thin surface layers differ from those of subsurface layers of the same organic material, and establish a method for distinguishing them in experiments.
- Lars Mester
- , Alexander A. Govyadinov
- & Rainer Hillenbrand
-
Article
| Open Access Reconstruction of evolving nanostructures in ultrathin films with X-ray waveguide fluorescence holography
Reconstruction of evolving nanostructures in ultrathin films with X-ray waveguide fluorescence holography
The authors introduce X-ray waveguide fluorescence holography based on the waveguiding properties of thin films. Combined with model-independent reconstruction algorithms, they show that the method can be used for real-time nanostructure kinetic studies.
- Zhang Jiang
- , Joseph W. Strzalka
- & Jin Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Phonon-exciton Interactions in WSe2 under a quantizing magnetic field
Phonon-exciton Interactions in WSe2 under a quantizing magnetic field
An out-of-plane magnetic field is expected to strongly modify exciton-phonon interactions in atomically thin transitional metal dichalcogenides. Here, the authors show that the phonon-exciton interaction in monolayer WSe2 lifts the inter-Landau-level transition selection rules for dark trions.
- Zhipeng Li
- , Tianmeng Wang
- & Su-Fei Shi
-
Article
| Open Access Spectral cross-cumulants for multicolor super-resolved SOFI imaging
Spectral cross-cumulants for multicolor super-resolved SOFI imaging
Here, the authors generalize cumulant analysis by extending it into the spectral domain to allow multicolour super-resolution optical fluctuation imaging. The simultaneous acquisition of two spectral channels followed by spectral cross-cumulant analysis and unmixing allows denser spectral and spatial sampling of the super-resolved image.
- K. S. Grußmayer
- , S. Geissbuehler
- & T. Lasser
-
Article
| Open Access A library of ab initio Raman spectra for automated identification of 2D materials
A library of ab initio Raman spectra for automated identification of 2D materials
The authors develop a first-principles workflow for calculating Raman spectra of 733 monolayers from the computational 2D materials database. After benchmarking results against experimental data for 15 monolayers, an automatic procedure for identifying a material from its Raman spectrum is proposed.
- Alireza Taghizadeh
- , Ulrik Leffers
- & Kristian S. Thygesen
-
Article
| Open Access Pushing the boundaries of optoacoustic microscopy by total impulse response characterization
Pushing the boundaries of optoacoustic microscopy by total impulse response characterization
Characterizing the total impulse response (TIR) of photoacoustic microscopes has been challenging due to difficulties distributing appropriate point sources. Here, the authors present a method for 3D generation of spatially-distributed optoacoustic point sources and show that subsequent TIR correction results in improved image quality.
- Markus Seeger
- , Dominik Soliman
- & Vasilis Ntziachristos
-
Article
| Open Access Visualizable detection of nanoscale objects using anti-symmetric excitation and non-resonance amplification
Visualizable detection of nanoscale objects using anti-symmetric excitation and non-resonance amplification
The authors introduce the concept of electromagnetic canyons and non-resonance amplification for optical detection of nanoscale objects. They demonstrate that a pair of nanowire sensors enable detection of 25-nm radii objects with a standard widefield microscope.
- Jinlong Zhu
- , Aditi Udupa
- & Lynford L. Goddard
-
Article
| Open Access Buoyant particulate strategy for few-to-single particle-based plasmonic enhanced nanosensors
Buoyant particulate strategy for few-to-single particle-based plasmonic enhanced nanosensors
Plasmonic-enhanced nanosensors are limited in practical applications, as it remains challenging to detect molecules at low concentrations. Here, the authors introduce a buoyant particulate strategy in order to enrich analytes in the plasmonic hot spots.
- Dongjie Zhang
- , Leqin Peng
- & Jixiang Fang
-
Article
| Open Access Near-field transmission matrix microscopy for mapping high-order eigenmodes of subwavelength nanostructures
Near-field transmission matrix microscopy for mapping high-order eigenmodes of subwavelength nanostructures
Nanoscale integrated photonic devices have complicated combinations of optical eigenmodes. Here, the authors develop a far- to near-field transmission matrix microscopy that enables measuring higher-order modes of nanostructures beyond the capabilities of conventional near-field microscopy.
- Eunsung Seo
- , Young-Ho Jin
- & Wonshik Choi
-
Article
| Open Access Unique hole-accepting carbon-dots promoting selective carbon dioxide reduction nearly 100% to methanol by pure water
Unique hole-accepting carbon-dots promoting selective carbon dioxide reduction nearly 100% to methanol by pure water
Solar-driven CO2 reduction by abundant water to alcohols is hindered by the sluggish water oxidation reaction. Here, the authors demonstrate that the microwave-synthesized carbon-dots possess unique hole-accepting nature, allowing stoichiometric oxygen and methanol production from water and CO2 with nearly 100% selectivity to methanol.
- Yiou Wang
- , Xu Liu
- & Junwang Tang
-
Article
| Open Access Real-time terahertz imaging with a single-pixel detector
Real-time terahertz imaging with a single-pixel detector
Terahertz imaging is promising in many applications, but still relies on complex equipment. Here, the authors develop a simplified solution that enables terahertz real-time imaging using a single-pixel detector and rapid reconstruction methods.
- Rayko Ivanov Stantchev
- , Xiao Yu
- & Emma Pickwell-MacPherson
-
Comment
| Open Access Prospects and fundamental limits in exceptional point-based sensing
Prospects and fundamental limits in exceptional point-based sensing
Exotic degeneracies in open quantum systems, so-called exceptional points, show rich physics and promise new applications, such as sensors with greatly enhanced response. Recent research on laser gyroscopes has uncovered limits of such sensors due to excess quantum noise.
- Jan Wiersig
-
Article
| Open Access Ballistic supercavitating nanoparticles driven by single Gaussian beam optical pushing and pulling forces
Ballistic supercavitating nanoparticles driven by single Gaussian beam optical pushing and pulling forces
Control of small particles in fluid can have a range of applications. The authors explore a phenomenon that allows an extremely low friction environment around a nanoparticle, demonstrating high-speed nanoparticles driven by optical forces in both directions of an optical beam.
- Eungkyu Lee
- , Dezhao Huang
- & Tengfei Luo
-
Article
| Open Access A self-operating broadband spectrometer on a droplet
A self-operating broadband spectrometer on a droplet
Compact spectrometers can be useful in many applications and many sophisticated architectures have been proposed. In this work, the authors show that with an evaporating droplet on a fiber tip, spectrometry can be robustly and accurately performed with a simple and passive microfluidic system.
- P. Malara
- , A. Giorgini
- & G. Gagliardi
-
Article
| Open Access Imaging radiation dose in breast radiotherapy by X-ray CT calibration of Cherenkov light
Imaging radiation dose in breast radiotherapy by X-ray CT calibration of Cherenkov light
Imaging Cherenkov emission during radiotherapy can provide information on the delivered radiation dose, but is attenuated by optical properties of the tissue. Here the authors derive a correction factor applicable to breast X-ray radiotherapy in human subjects to improve the correlation between Cherenkov emission intensity and dose.
- R. L. Hachadorian
- , P. Bruza
- & L. A. Jarvis
-
Article
| Open Access Single-shot ultrafast imaging attaining 70 trillion frames per second
Single-shot ultrafast imaging attaining 70 trillion frames per second
Ultrafast imaging has been limited by the speed of electronic sensors. Here, the authors demonstrate single-shot compressed ultrafast spectral photography, which combines spectral encoding, pulse splitting, temporal shearing, and compressed sensing in order to achieve real-time imaging at 70 trillion frames per second.
- Peng Wang
- , Jinyang Liang
- & Lihong V. Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Spectro-temporal encoded multiphoton microscopy and fluorescence lifetime imaging at kilohertz frame-rates
Spectro-temporal encoded multiphoton microscopy and fluorescence lifetime imaging at kilohertz frame-rates
Two-photon microscopy has been limited by low acquisition rates due to mechanical scanners. Here, the authors employ pulse-modulated, rapidly wavelength-swept lasers and inertia-free beam steering through angular dispersion in order to achieve non-linear microscopy with kilohertz frame rates.
- Sebastian Karpf
- , Carson T. Riche
- & Bahram Jalali
-
Article
| Open Access Optoplasmonic characterisation of reversible disulfide interactions at single thiol sites in the attomolar regime
Optoplasmonic characterisation of reversible disulfide interactions at single thiol sites in the attomolar regime
Visualising single-molecule reactions, to understand their mechanisms, is a challenging task. Here, the authors investigate disulfide exchange reactions with thiolates immobilised on a gold nanoparticle through a label-free optoplasmonic sensor, and detect individual disulfide interactions in solution
- Serge Vincent
- , Sivaraman Subramanian
- & Frank Vollmer
-
Article
| Open Access Real-time non-contact cellular imaging and angiography of human cornea and limbus with common-path full-field/SD OCT
Real-time non-contact cellular imaging and angiography of human cornea and limbus with common-path full-field/SD OCT
Currently a cell-resolution map of the human cornea can only be obtained in the clinic with a confocal microscope in contact with the eye. Here the authors develop a full-field/spectral-domain OCT microscope (FF/SD OCT) to enable cell-level detail of the entire ocular surface, as well as blood flow and tear dynamics.
- Viacheslav Mazlin
- , Peng Xiao
- & A. Claude Boccara
-
Article
| Open Access The optical conductivity of few-layer black phosphorus by infrared spectroscopy
The optical conductivity of few-layer black phosphorus by infrared spectroscopy
For many two-dimensional semiconductors, such as MoS2, the exciton absorption increases with thickness. Here, the authors show that, in black phosphorus, less material absorbs more light due to exciton resonances.
- Guowei Zhang
- , Shenyang Huang
- & Hugen Yan
-
Article
| Open Access Optogenetic restoration of retinal ganglion cell activity in the living primate
Optogenetic restoration of retinal ganglion cell activity in the living primate
Non-human primate models are important for the development of high quality vision restoration therapies for blindness. Here, the authors demonstrate restoration of light responses in foveal retinal ganglion cells of the living macaque following optogenetic gene therapy.
- Juliette E. McGregor
- , Tyler Godat
- & William H. Merigan
-
Article
| Open Access Rapid time-resolved Circular Polarization Luminescence (CPL) emission spectroscopy
Rapid time-resolved Circular Polarization Luminescence (CPL) emission spectroscopy
Circular polarization luminescence (CPL) spectroscopy is a tool to study chiroptical systems, but the measurement process is generally very slow. The authors introduce a CPL technique with much faster acquisition, demonstrating meaningful time-dependent measurements and enabling new applications.
- Lewis E. MacKenzie
- , Lars-Olof Pålsson
- & Robert Pal
-
Article
| Open Access Phasor field diffraction based reconstruction for fast non-line-of-sight imaging systems
Phasor field diffraction based reconstruction for fast non-line-of-sight imaging systems
Current implementations of non-line-of-sight imaging use reconstruction algorithms that are difficult to implement fast enough for real-time application using light efficient equipment. The authors present an algorithm for non-line-of-sight imaging that is low complexity and allows fast and efficient reconstruction on a standard computer.
- Xiaochun Liu
- , Sebastian Bauer
- & Andreas Velten
-
Article
| Open Access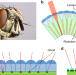 Plasmonic ommatidia for lensless compound-eye vision
Plasmonic ommatidia for lensless compound-eye vision
The compound eyes of arthropods provide a visual advantage by seeing a wide range of angles all at once, but cameras that mimic them are usually curved and bulky. Here, the authors develop a flat, plasmonic image sensor array that enables high-quality wide-angle vision without lenses or curvature.
- Leonard C. Kogos
- , Yunzhe Li
- & Roberto Paiella
-
Article
| Open Access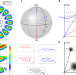 Petermann-factor sensitivity limit near an exceptional point in a Brillouin ring laser gyroscope
Petermann-factor sensitivity limit near an exceptional point in a Brillouin ring laser gyroscope
Operating a laser gyroscope near an exceptional point has been shown to enhance its responsivity. However, here the authors demonstrate in theory and experiment that the enhanced responsivity is exactly compensated by increased noise that is inherent to this system near the exceptional point.
- Heming Wang
- , Yu-Hung Lai
- & Kerry Vahala
-
Article
| Open Access Imaging grain microstructure in a model ceramic energy material with optically generated coherent acoustic phonons
Imaging grain microstructure in a model ceramic energy material with optically generated coherent acoustic phonons
Optically generated acoustic phonons have enabled depth resolved microstructure characterization. Here, the authors extend this method to obtain information on the orientation of individual crystallites by studying influence of probe beam polarization on detected signal amplitude.
- Yuzhou Wang
- , David H. Hurley
- & Marat Khafizov
-
Article
| Open Access A flexible topo-optical sensing technology with ultra-high contrast
A flexible topo-optical sensing technology with ultra-high contrast
Flexible materials with mechano-responsive luminescence has gained interest for their potential in sensing devices. Here, the authors demonstrate targeted folding under high compressive strains, which, together with the oxygen quenching of fluorophores, forms the basis for topo-optical sensing.
- Cong Wang
- , Ding Wang
- & Ben Bin Xu
-
Article
| Open Access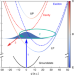 Polaritonic molecular clock for all-optical ultrafast imaging of wavepacket dynamics without probe pulses
Polaritonic molecular clock for all-optical ultrafast imaging of wavepacket dynamics without probe pulses
Pump-probe method is commonly used for studying ultrafast molecular dynamics. Here, the authors discuss alternative approach of using time-dependent ultrafast light emission from excited molecules coupled to a plasmonic nanocavity instead of using probe pulse.
- R. E. F. Silva
- , Javier del Pino
- & Johannes Feist
-
Article
| Open Access Plasmonic nanostar photocathodes for optically-controlled directional currents
Plasmonic nanostar photocathodes for optically-controlled directional currents
Photocurrent control in nanoscale systems offers opportunities for nanoelectronic devices and ultrafast imaging applications. Here, the authors show by means of angle-resolved two-dimensional velocity mapping that angular photoemission distributions can be controlled by varying the polarization and frequency of the laser.
- Jacob Pettine
- , Priscilla Choo
- & David J. Nesbitt
-
Article
| Open Access Thermodynamics of continuous non-Markovian feedback control
Thermodynamics of continuous non-Markovian feedback control
The second law of thermodynamics cannot be straightforwardly applied to systems with non-Markovian feedback control, and previous extensions to cover that regime have not been tested experimentally. Here, the authors bridge this gap using an optically levitated microsphere in a feedback-cooling system.
- Maxime Debiossac
- , David Grass
- & Nikolai Kiesel
-
Article
| Open Access Megahertz-rate shock-wave distortion cancellation via phase conjugate digital in-line holography
Megahertz-rate shock-wave distortion cancellation via phase conjugate digital in-line holography
Shock-waves in explosive, supersonic or ionizing environments impart phase distortions to holographic imaging. Here, the authors report an ultra-high-speed phase conjugate digital in-line holography technique where a laser passes through the shock-wave and is reflected back through the phase distortion, thus correcting phase delays.
- Yi Chen Mazumdar
- , Michael E. Smyser
- & Daniel R. Guildenbecher
-
Article
| Open Access Unveiling the radiative local density of optical states of a plasmonic nanocavity by STM
Unveiling the radiative local density of optical states of a plasmonic nanocavity by STM
Disentangling the radiative and non-radiative plasmon mode contributions to the total photonic density of states is a challenge. Here, the authors report a procedure to eliminate the electronic-structure factors from scanning tunnelling microscope luminescence spectra to isolate the radiative component.
- Alberto Martín-Jiménez
- , Antonio I. Fernández-Domínguez
- & Roberto Otero
-
Article
| Open Access Noise-tolerant single photon sensitive three-dimensional imager
Noise-tolerant single photon sensitive three-dimensional imager
Imagers capable of reconstructing three-dimensional scenes in the presence of strong background noise are desirable for many remote sensing and imaging applications. Here, the authors report an imager operating in photon-starved and noise-polluted environments through quantum parametric mode sorting.
- Patrick Rehain
- , Yong Meng Sua
- & Yu-Ping Huang
-
Article
| Open Access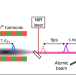 Tracking attosecond electronic coherences using phase-manipulated extreme ultraviolet pulses
Tracking attosecond electronic coherences using phase-manipulated extreme ultraviolet pulses
Light pulses with controllable parameters are desired for studying the fundamental properties of matter. Here the authors generate and use phase-manipulated and highly time-stable XUV pulse pairs to probe the coherent evolution and dephasing of XUV electronic coherences in helium and argon.
- Andreas Wituschek
- , Lukas Bruder
- & Frank Stienkemeier

 High resolution spectral metrology leveraging topologically enhanced optical activity in fibers
High resolution spectral metrology leveraging topologically enhanced optical activity in fibers