Featured
-
-
Article |
 Single-cell multimodal imaging uncovers energy conversion pathways in biohybrids
Single-cell multimodal imaging uncovers energy conversion pathways in biohybrids
Understanding interfacial and cellular electron transport is essential for guiding efficiency optimization in microbe–semiconductor biohybrids for energy conversion. A multimodal imaging platform that combines optical imaging and photocurrent mapping can now interrogate such electron-transport pathways at the single-cell level, uncovering different roles of hydrogenases and a microbe’s large electron-uptake capacity.
- Bing Fu
- , Xianwen Mao
- & Peng Chen
-
Article |
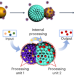 Emulsion-oriented assembly for Janus double-spherical mesoporous nanoparticles as biological logic gates
Emulsion-oriented assembly for Janus double-spherical mesoporous nanoparticles as biological logic gates
Large biomolecules cannot be loaded into conventional Janus nanoparticles with small mesopores, preventing the establishment of efficient logic-gate systems in single Janus nanoparticles. Now, an emulsion-oriented assembly approach has been shown to fabricate Janus double-spherical nanoparticles with dual-tunable mesopores, enabling the design of various single-particle-level logic systems.
- Tiancong Zhao
- , Liang Chen
- & Dongyuan Zhao
-
Research Briefing |
 Nanomachines built from multiple components can have functional advantages
Nanomachines built from multiple components can have functional advantages
Nanomachines are central to life and are becoming an important part of self-regulated nanotechnologies. Inspired by natural self-assembled nanosystems, it has been shown that artificial nanosystems can evolve and adopt regulatory functions upon fragmentation of their structures into multiple components that reassemble to form the same nanostructure.
-
Article |
 Nanoparticle stereochemistry-dependent endocytic processing improves in vivo mRNA delivery
Nanoparticle stereochemistry-dependent endocytic processing improves in vivo mRNA delivery
Stereochemistry can affect the reactivity and transport properties of small molecules; however, it is unclear whether the stereochemistry of components in a lipid nanoparticle influences its activity in vivo. Now, it has been shown that lipid nanoparticles made with a stereopure component can increase delivery of mRNA. A biological mechanism driving the effect is also proposed.
- Marine Z. C. Hatit
- , Curtis N. Dobrowolski
- & James E. Dahlman
-
Article |
 Protein nanopore reveals the renin–angiotensin system crosstalk with single-amino-acid resolution
Protein nanopore reveals the renin–angiotensin system crosstalk with single-amino-acid resolution
A nanopore framework has been developed to reveal the crosstalk effect on the renin–angiotensin system. By reading the single-amino-acid differences in angiotensin peptides with high accuracy and high efficiency, the selective inhibition of angiotensin-converting enzyme by angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 was revealed. This activity was shown to be suppressed by the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2.
- Jie Jiang
- , Meng-Yin Li
- & Yi-Tao Long
-
Article
| Open Access Adaptive insertion of a hydrophobic anchor into a poly(ethylene glycol) host for programmable surface functionalization
Adaptive insertion of a hydrophobic anchor into a poly(ethylene glycol) host for programmable surface functionalization
Modulation of surface properties and functions can be achieved through covalent and non-covalent molecular binding, but the lack of responsiveness and requirement for specific binding groups makes spatiotemporal control challenging. Now, it has been shown that adaptive insertion of a hydrophobic anchor into a poly(ethylene glycol) host is an effective non-covalent binding strategy for programmable surface functionalization.
- Shaohua Zhang
- , Wei Li
- & Daniela A. Wilson
-
Article |
 A soil-inspired dynamically responsive chemical system for microbial modulation
A soil-inspired dynamically responsive chemical system for microbial modulation
Creating hierarchical synthetic materials that can modulate microbial communities remains a great challenge due to the complex interactions between microbiota and their colonized environments. Now, a soil-inspired chemical system that responds to chemical, optical and mechanical stimuli has been developed. The soil-inspired chemical system can enhance microbial cultures and biofuel production, enrich gut bacterial diversity and alleviate ulcerative colitis symptoms.
- Yiliang Lin
- , Xiang Gao
- & Bozhi Tian
-
Article |
 Nanopore microscope identifies RNA isoforms with structural colours
Nanopore microscope identifies RNA isoforms with structural colours
A method has been developed to identify RNA transcript isoforms at the single-molecule level using solid-state nanopore microscopy. In this method, target RNA is refolded into RNA identifiers with designed sets of complementary DNA strands. Each reshaped molecule carries a unique sequence of structural (pseudo)colours that enables identification and quantification using solid-state nanopore microscopy.
- Filip Bošković
- & Ulrich Felix Keyser
-
In Your Element |
 Ionic liquids charge ahead
Ionic liquids charge ahead
Choline 2-hexenoate is an ionic compound that is a liquid at room temperature, and is just one of a class of compounds that have huge potential in biomedical research and clinical applications, explains Eden E. L. Tanner.
- Eden E. L. Tanner
-
Article |
 Parallel transmission in a synthetic nerve
Parallel transmission in a synthetic nerve
Soft bioelectronic devices have exciting potential applications in robotics, computing and medicine, but they are typically restricted by the requirement for tethers or stiff electrodes. Now, a synthetic nerve has been developed that is bioinspired, wireless and powered by light. By patterning functionalized lipid membrane compartments, information was directionally conveyed using electrochemical signals.
- Charlotte E. G. Hoskin
- , Vanessa Restrepo Schild
- & Hagan Bayley
-
Article |
 Bottom-up fabrication of a proteasome–nanopore that unravels and processes single proteins
Bottom-up fabrication of a proteasome–nanopore that unravels and processes single proteins
An integrated multiprotein nanopore has been fabricated using components from all three domains of life. This molecular machine opens the door to two approaches in single-molecule protein analysis, in which selected substrate proteins are unfolded, fed to into the proteasomal chamber and then processed either as fragmented peptides or intact polypeptides.
- Shengli Zhang
- , Gang Huang
- & Giovanni Maglia
-
Article |
 Integrating programmable DNAzymes with electrical readout for rapid and culture-free bacterial detection using a handheld platform
Integrating programmable DNAzymes with electrical readout for rapid and culture-free bacterial detection using a handheld platform
Methods to detect and identify bacteria typically rely on enrichment steps such as bacterial culture and nucleic acid amplification. Now, an assay for detecting bacteria based on a two-channel electrical chip that combines electroactive DNAzymes with an electrochemical readout, has been developed. This assay enables reagentless and culture-free detection of bacteria in clinical samples.
- Richa Pandey
- , Dingran Chang
- & Leyla Soleymani
-
Article |
 RNA origami design tools enable cotranscriptional folding of kilobase-sized nanoscaffolds
RNA origami design tools enable cotranscriptional folding of kilobase-sized nanoscaffolds
RNA origami can be used for the modular design of RNA nanoscaffolds but can be challenging to design. Newly developed computer-aided design software has now been shown to improve the folding yield of kilobase-sized RNA origami. These structures fold from a single strand during transcription by an RNA polymerase, and are able to position small molecules and protein components with nanoscale precision.
- Cody Geary
- , Guido Grossi
- & Ebbe S. Andersen
-
News & Views |
 Signal transduction with a swing
Signal transduction with a swing
The continuous monitoring of proteins is a current challenge in medical diagnostics. A new electrochemical approach aiming to address this has been described. The method uses antibodies as a recognition element to achieve the real-time measurement of proteins in saliva in the mouth.
- Kevin J. Cash
- & Kevin W. Plaxco
-
News & Views |
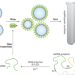 Wrap to sort
Wrap to sort
Modelling the structure and behaviour of vesicles in cells requires liposomes with precise sizes, but producing liposomes with a narrow size distribution is challenging. An approach has now been developed to accurately size-sort liposomes in a scalable way by coating them with customized structures based on DNA nanotechnology.
- Silvia Hernández-Ainsa
-
Article |
 A programmable polymer library that enables the construction of stimuli-responsive nanocarriers containing logic gates
A programmable polymer library that enables the construction of stimuli-responsive nanocarriers containing logic gates
A programmable polymer library that responds to external and internal stimuli has been developed and used to fabricate a series of nanocarriers for drug release. The carriers respond to disease biomarkers, triggering self-immolative motifs and leading to the site-specific release of therapeutics both in vitro and in vivo.
- Penghui Zhang
- , Di Gao
- & Weihong Tan
-
News & Views |
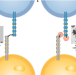 Plastic antibodies for cancer therapy?
Plastic antibodies for cancer therapy?
Monoclonal antibodies have shown tremendous success in cancer treatment; however, humanization for clinical applications is expensive and not straightforward. Now, molecularly imprinted polymer nanogels have been developed that can block cell-surface proteins and disrupt tumour spheroids.
- Alessandra Maria Bossi
-
News & Views |
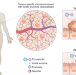 Unique enzymatic repertoire reveals the tumour
Unique enzymatic repertoire reveals the tumour
The tumour microenvironment has a specific enzymatic fingerprint, which provides opportunities for cancer therapy. Now, two studies show how this unique chemical environment can be used to produce reporter molecules or nanoclusters within the tumour that can subsequently be identified in urine or breath, enabling cancer detection and monitoring.
- Alexander N. Zelikin
-
Article |
 Designer DNA architecture offers precise and multivalent spatial pattern-recognition for viral sensing and inhibition
Designer DNA architecture offers precise and multivalent spatial pattern-recognition for viral sensing and inhibition
DNA is capable of self-assembling into a wide range of user-defined structures and so can be used as a scaffold to arrange binding motifs with nanometre precision. Now, DNA has been used to accurately display aptamers that fit the repeated epitope pattern of a dengue viral antigen to produce a nanostructure that can be a potent viral inhibitor or a fluorescent sensor.
- Paul S. Kwon
- , Shaokang Ren
- & Xing Wang
-
News & Views |
 Super-resolution writing
Super-resolution writing
The in situ, nanoscale positioning of a single molecule below the diffraction limit remains a challenge for chemists. Now, two approaches show how this can be accomplished through a combination of super-resolution microscopy and photo-inducible crosslinking chemistry.
- Limin Xiang
- & Ke Xu
-
Article |
 Supercharging enables organized assembly of synthetic biomolecules
Supercharging enables organized assembly of synthetic biomolecules
Symmetrical protein oligomers perform key structural and catalytic functions in nature, but engineering such oligomers synthetically is challenging. Now, oppositely supercharged synthetic variants of normally monomeric proteins have been shown to assemble via specific, introduced electrostatic contacts into symmetrical, highly well-defined oligomers.
- Anna J. Simon
- , Yi Zhou
- & Andrew D. Ellington
-
News & Views |
 Talking across the membrane
Talking across the membrane
One goal of synthetic biologists is to develop artificial systems to help study biological processes. Now, cell communication and differentiation have been demonstrated using spatiotemporal patterns created in artificial multicellular compartments.
- Yi Li
- & Rebecca Schulman
-
News & Views |
 Scissoring genes with light
Scissoring genes with light
Enzymes can perform various biological functions because of their delicately and precisely organized structures. Now, simple inorganic nanoparticles with a rationally designed recognition capability can mimic restriction enzymes and selectively cut specific DNA sequences.
- Aleksandar P. Ivanov
- & Joshua B. Edel
-
News & Views |
 Optimizing orthogonality
Optimizing orthogonality
A new pyrrolysyl-tRNA synthetase/PyltRNA (PylRS/PyltRNA) pair that is mutually orthogonal to existing PylRS/PyltRNA pairs has now been discovered and optimized. This system could enable the site-specific incorporation of a greater number of distinct non-canonical amino acids into a protein.
- William S. C. Ngai
- & Peng R. Chen
-
Article |
 A molecular multi-gene classifier for disease diagnostics
A molecular multi-gene classifier for disease diagnostics
Gene expression profiling remains cost-prohibitive and challenging to implement in a clinical setting. Now, a molecular computation strategy for classifying complex gene expression signatures has been developed. Classification occurs through a series of molecular interactions between RNA inputs and engineered DNA probes designed to implement a relevant linear classification model.
- Randolph Lopez
- , Ruofan Wang
- & Georg Seelig
-
Article |
 Single-cell mRNA cytometry via sequence-specific nanoparticle clustering and trapping
Single-cell mRNA cytometry via sequence-specific nanoparticle clustering and trapping
Cell-to-cell variation in gene expression creates a need for techniques that characterize expression at the level of individual cells. Now, a technique for characterizing mRNA expression has been developed. The technique uses the intracellular self-assembly of magnetic nanoparticles to quantitate RNA levels at the single-cell level.
- Mahmoud Labib
- , Reza M. Mohamadi
- & Shana O. Kelley
-
Review Article |
 Engineering nucleic acid structures for programmable molecular circuitry and intracellular biocomputation
Engineering nucleic acid structures for programmable molecular circuitry and intracellular biocomputation
DNA nanotechnology provides a versatile toolbox for engineering synthetic circuits in living cells. This Review discusses how nanostructures made from nucleic acids can enable biocomputation and also be readily interfaced with a variety of intracellular and in vivo components to facilitate synthetic biology applications.
- Jiang Li
- , Alexander A. Green
- & Chunhai Fan
-
News & Views |
 Silver-wired DNA
Silver-wired DNA
DNA double helical structures are supramolecular assemblies that are typically held together by classical Watson–Crick pairing. Now, nucleotide chelation of silver ions supports an extended silver–DNA hybrid duplex featuring an uninterrupted silver array.
- Pascal Auffinger
- & Eric Ennifar
-
Article |
 A metallo-DNA nanowire with uninterrupted one-dimensional silver array
A metallo-DNA nanowire with uninterrupted one-dimensional silver array
A metallo–DNA hybrid nanowire composed only of silver-mediated base pairs has been prepared and its crystal structure resolved by X-ray diffraction. The nanowire, which is 2 nm wide and whose length reaches the μm to mm scale, holds silver ions into uninterrupted one-dimensional arrays along the DNA helical axis.
- Jiro Kondo
- , Yoshinari Tada
- & Yoshiyuki Tanaka
-
Article |
 Placing and shaping liposomes with reconfigurable DNA nanocages
Placing and shaping liposomes with reconfigurable DNA nanocages
Controlling liposome shape, arrangement and dynamics is important for biophysical studies and synthetic biology applications. Now, using a family of reconfigurable DNA nanocages as templates, spherical, tubular, toroidal and helical liposomes with predefined geometry have been produced. DNA-guided membrane fusion and bending is also demonstrated.
- Zhao Zhang
- , Yang Yang
- & Chenxiang Lin
-
News & Views |
 Precision in 3D
Precision in 3D
Biomimetic molecules that can be easily tailored offer numerous opportunities. Now, boron-based clusters have been shown to be excellent biomimetics. The ease with which the cluster surfaces can be modified stands to change how chemists might go about preparing materials for imaging, drug delivery and other applications.
- Marek B. Majewski
- , Ashlee J. Howarth
- & Omar K. Farha
-
Article |
 A monodisperse transmembrane α-helical peptide barrel
A monodisperse transmembrane α-helical peptide barrel
The assembly of transmembrane barrels formed from short synthetic peptides has not been previously demonstrated. Now, a transmembrane pore has been fabricated via the self-assembly of peptides. The 35-amino-acid α-helical peptides are based on the C-terminal D4 domain of the Escherichia coli polysaccharide transporter Wza.
- Kozhinjampara R. Mahendran
- , Ai Niitsu
- & Hagan Bayley
-
Article |
 High-resolution mapping of bifurcations in nonlinear biochemical circuits
High-resolution mapping of bifurcations in nonlinear biochemical circuits
Dynamic nonlinear biochemical circuits are functionally rich; however, this nonlinear nature also makes programming them delicate and painstaking. Now a droplet microfluidic platform reveals precisely the bifurcations of two canonical systems: a bistable switch and a predator–prey oscillator, exposing optimal regions and mechanistic insights that inform the design of these systems.
- A. J. Genot
- , A. Baccouche
- & Y. Rondelez
-
Article |
 Self-assembling biomolecular catalysts for hydrogen production
Self-assembling biomolecular catalysts for hydrogen production
The encapsulation and stabilization of an oxygen tolerant [NiFe]-hydrogenase, sequestered within the bacteriophage P22 capsid, has now been achieved through a directed self-assembly process. Probing the catalytic activity and infrared spectroscopic signatures of the bio-inspired assembly shows that the capsid provides stability and protection to the hydrogenase cargo.
- Paul C. Jordan
- , Dustin P. Patterson
- & Trevor Douglas
-
Article |
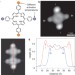 Controlling on-surface polymerization by hierarchical and substrate-directed growth
Controlling on-surface polymerization by hierarchical and substrate-directed growth
The bottom-up construction of covalently linked molecular architectures on surfaces has recently been demonstrated, but only rather simple structures can be obtained in such one-step connection processes. A sequential approach has now been used to induce the selective connection of molecules with a programmed reactivity, enabling network formation with high selectivity.
- L. Lafferentz
- , V. Eberhardt
- & L. Grill
-
Article |
 A total-synthesis framework for the construction of high-order colloidal hybrid nanoparticles
A total-synthesis framework for the construction of high-order colloidal hybrid nanoparticles
Colloidal hybrid nanoparticles represent an emerging class of multifunctional artificial molecules. However, unlike actual molecules, their complexity is limited by the lack of a mechanism-driven design framework. Here, nanoparticle analogues of chemoselectivity, regiospecificity, molecular substituent effects, and coupling reactions are used to predictably synthesize hybrid nanoparticle trimers, tetramers, and oligomers.
- Matthew R. Buck
- , James F. Bondi
- & Raymond E. Schaak
-
Article |
 Facile removal of stabilizer-ligands from supported gold nanoparticles
Facile removal of stabilizer-ligands from supported gold nanoparticles
Small nanoparticles with controlled morphologies can be prepared for catalysis applications by colloidal methods using stabilizing ligands. A solvent-extraction method has now been described that removes the ligands without affecting the morphology of the nanoparticles, or their catalytic activity over a range of reactions.
- Jose A. Lopez-Sanchez
- , Nikolaos Dimitratos
- & Graham J. Hutchings
-
Article |
 The effect of gold loading and particle size on photocatalytic hydrogen production from ethanol over Au/TiO2 nanoparticles
The effect of gold loading and particle size on photocatalytic hydrogen production from ethanol over Au/TiO2 nanoparticles
The photocatalytic production of hydrogen from renewables such as ethanol and water could be a key means of future fuel production. There are few, if any, catalysts available for such a reaction, and our understanding of photocatalytic reactions generally remains poor. It is now demonstrated that gold–titania nanoparticles are effective catalysts for producing hydrogen from ethanol, and the rate is independent of gold particle size.
- M. Murdoch
- , G. I. N. Waterhouse
- & H. Idriss
-
Article |
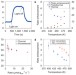 Visible-light-enhanced catalytic oxidation reactions on plasmonic silver nanostructures
Visible-light-enhanced catalytic oxidation reactions on plasmonic silver nanostructures
High operating temperatures in heterogeneous catalytic processes compromise energy efficiency, catalyst lifetime and product selectivity. Plasmonic silver nanoparticles are shown to couple thermal energy and a low-intensity photon flux to drive commercially important oxidation reactions at lower temperatures than conventional thermal processes.
- Phillip Christopher
- , Hongliang Xin
- & Suljo Linic
-
Article |
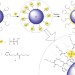 Core@shell bimetallic nanoparticle synthesis via anion coordination
Core@shell bimetallic nanoparticle synthesis via anion coordination
Bimetallic core@shell nanoparticles often have properties that are different from those of single-metal or alloy nanoparticles. Here, a route to such nanoparticles that binds the second metal to the core surface prior to reduction is described. The unique catalytic properties of the nanoparticles are demonstrated in the selective production of chloroaniline.
- Christopher J. Serpell
- , James Cookson
- & Paul D. Beer
-
News & Views |
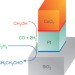 Where the action is
Where the action is
Heterogeneous catalyst systems comprising metals supported on oxides are widespread. Evidence now suggests that it is the interfacial regions that are most catalytically active, and this has been exploited to create a tandem nanocatalyst system.
- Peter C. Stair
-
Article |
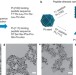 Platinum nanocrystals selectively shaped using facet-specific peptide sequences
Platinum nanocrystals selectively shaped using facet-specific peptide sequences
Crystal growth in nature is controlled by biomolecules to produce precisely engineered crystal shapes. Now, facet-specific peptide sequences that have been rationally selected through a biomimetic evolution process are used as regulating agents for predictable synthesis of platinum nanocrystals with selectively exposed crystal surfaces.
- Chin-Yi Chiu
- , Yujing Li
- & Yu Huang
-
Article |
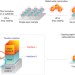 Nanocrystal bilayer for tandem catalysis
Nanocrystal bilayer for tandem catalysis
The development of high-performance ‘smart’ catalysts will rely on the rational design of nanoscale metal–metal oxide interfaces. A tandem catalyst that has both CeO2-Pt and Pt-SiO2 interfaces is now reported, and is capable of catalysing sequential reactions to convert methanol into ethylene.
- Yusuke Yamada
- , Chia-Kuang Tsung
- & Peidong Yang
-
Article |
 Biodegradable nanostructures with selective lysis of microbial membranes
Biodegradable nanostructures with selective lysis of microbial membranes
Macromolecules with antimicrobial properties are promising materials for combating multi-drug-resistant microbes. Now, it has been shown that amphiphilic cationic polycarbonates that are biodegradable can self-assemble into micellar nanoparticles that can kill gram-positive bacteria, MRSA and fungi efficiently, even at low concentrations. Moreover, no significant toxicity is observed during in vivo studies in mice.
- Fredrik Nederberg
- , Ying Zhang
- & Yi-Yan Yang
-
Article |
 Palladium-mediated intracellular chemistry
Palladium-mediated intracellular chemistry
Palladium nanoparticles trapped within polystyrene beads can enter cells and mediate a variety of Pd0-catalysed reactions, including allylcarbamate cleavage and Suzuki–Miyaura cross-coupling. The methodology presented provides the basis for the customization of heterogeneous unnatural catalysts as tools for carrying out artificial chemistries within cells.
- Rahimi M. Yusop
- , Asier Unciti-Broceta
- & Mark Bradley
-
Article |
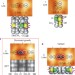 Surface-mediated chain reaction through dissociative attachment
Surface-mediated chain reaction through dissociative attachment
Chain-reactions could provide an alternative method for surface patterning. Now the chain reaction of CH3Cl molecules on a silicon surface has been observed to create lines that are made up of alternating CH3 groups and Cl atoms. The reactions are propagated through surface-mediated charge-transfer and have been studied using microscopy and ab initio theory.
- Tingbin Lim
- , John C. Polanyi
- & Wei Ji
-
News & Views |
 Diversity for self-assembly
Diversity for self-assembly
Self-assembly typically occurs through reversible interactions that slowly arrange building blocks into the most thermodynamically favoured structure. The involvement of enzymatic catalysis in the process has now enabled the rapid construction of a variety of low-defect architectures.
- Ehud Gazit
-
News & Views |
 Detection by failure
Detection by failure
Testing for enzymes is important for diagnosing various medical conditions but can be problematic because of the complexity of physiological media such as blood. Now, a method of detecting phospholipases has been developed that neatly couples their concentration with the aggregation of gold nanoparticles.
- Nicholas A. Melosh
-
Article |
 Synergistic self-assembly of RNA and DNA molecules
Synergistic self-assembly of RNA and DNA molecules
DNA has been used as a building block to make a wide variety of molecular architectures, but it remains difficult to make functional structures from this particular construction material. Now, a strategy for the assembly of hybrid RNA–DNA nanostructures has been described, which offers the possibility of combining the programmability of DNA with the rich functionality of RNA.
- Seung Hyeon Ko
- , Min Su
- & Chengde Mao

 Nanopore DNA sequencing technologies and their applications towards single-molecule proteomics
Nanopore DNA sequencing technologies and their applications towards single-molecule proteomics