Featured
-
-
Article |
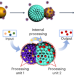 Emulsion-oriented assembly for Janus double-spherical mesoporous nanoparticles as biological logic gates
Emulsion-oriented assembly for Janus double-spherical mesoporous nanoparticles as biological logic gates
Large biomolecules cannot be loaded into conventional Janus nanoparticles with small mesopores, preventing the establishment of efficient logic-gate systems in single Janus nanoparticles. Now, an emulsion-oriented assembly approach has been shown to fabricate Janus double-spherical nanoparticles with dual-tunable mesopores, enabling the design of various single-particle-level logic systems.
- Tiancong Zhao
- , Liang Chen
- & Dongyuan Zhao
-
Article |
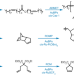 Plasmonic visible–near infrared photothermal activation of olefin metathesis enabling photoresponsive materials
Plasmonic visible–near infrared photothermal activation of olefin metathesis enabling photoresponsive materials
Current strategies for photoinduced olefin metathesis lack wavelength tunability. Now, plasmonic nanoparticles have been used to activate latent ruthenium catalysts, enabling light-induced olefin metathesis in the infrared range with several advantages when compared with conventional heating. Implementing this approach in ring-opening metathesis polymerization resulted in photoresponsive polymer–nanoparticle composites with enhanced mechanical properties.
- Nir Lemcoff
- , Noy B. Nechmad
- & Yossi Weizmann
-
Article |
 Supercrystal engineering of atomically precise gold nanoparticles promoted by surface dynamics
Supercrystal engineering of atomically precise gold nanoparticles promoted by surface dynamics
Gold nanoparticles typically exhibit hard-sphere-like assembly behaviour, but now the size, morphology and symmetry of crystals of Au25 nanoparticles have been tuned. The presence of excess tetraethylammonium cations has been shown to promote the one-dimensional assembly of the nanoparticles, which in turn form rod-like crystals, by stabilizing dynamically detached ligands from adjacent particles into interparticle linkers through CH⋯π and ion-pairing interactions.
- Qiaofeng Yao
- , Lingmei Liu
- & Jianping Xie
-
Article |
 Spin-crossover nanoparticles anchored on MoS2 layers for heterostructures with tunable strain driven by thermal or light-induced spin switching
Spin-crossover nanoparticles anchored on MoS2 layers for heterostructures with tunable strain driven by thermal or light-induced spin switching
Spin-crossover nanoparticles have been covalently grafted onto a semiconducting MoS2 layer to form a self-strainable heterostructure. Under light or thermal stimulus, the nanoparticles switch between their high- and low-spin states, in which they have different volumes. This generates a reversible strain over the MoS2 layer and, in turn, alters the electrical and optical properties of the heterostructure.
- Ramón Torres-Cavanillas
- , Marc Morant-Giner
- & Eugenio Coronado
-
News & Views |
 Ionic glue
Ionic glue
Charged nanoparticles can behave as large ions or as small colloids. Their interaction with multivalent ions has now been shown to reflect this dichotomy, providing new paths to large, self-assembled nanoparticle superstructures.
- Tobias Kraus
-
Article |
 Electrostatic co-assembly of nanoparticles with oppositely charged small molecules into static and dynamic superstructures
Electrostatic co-assembly of nanoparticles with oppositely charged small molecules into static and dynamic superstructures
Coulombic interactions can be used to assemble charged nanoparticles into higher-order structures, but this process typically requires similarly sized oppositely charged partners. Now, small anions or cations with as few as three charges have been shown to induce attractive interactions between oppositely charged nanoparticles in water, guiding the assembly of colloidal crystals.
- Tong Bian
- , Andrea Gardin
- & Rafal Klajn
-
News & Views |
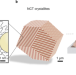 Colloidal metallurgy
Colloidal metallurgy
Colloidal self-assembly requires carefully balanced particle interactions that are often incompatible with the mechanical disturbances associated with macroscopic-scale manufacturing. Now, a practical bottom-up route has enabled the production of bulk solid materials with nanoscale components.
- Theodore Hueckel
- & Stefano Sacanna
-
Article |
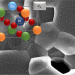 Platinum incorporation into titanate perovskites to deliver emergent active and stable platinum nanoparticles
Platinum incorporation into titanate perovskites to deliver emergent active and stable platinum nanoparticles
Nanoparticulate platinum is a highly active catalyst, but it is scarce, expensive and not always sufficiently durable. Now, barium platinate has been used as a vehicle to preserve platinum as an oxide during the solid-state synthesis of a Pt-doped titanate perovskite; this enables the production of a structure with active and stable Pt nanoparticles on the perovskite surface that catalyses CO oxidation.
- Maadhav Kothari
- , Yukwon Jeon
- & John T. S. Irvine
-
Article |
 Mechanochemical bond scission for the activation of drugs
Mechanochemical bond scission for the activation of drugs
Stimuli-responsive control of drug activation can mitigate issues caused by poor drug selectivity. Now, it has been shown that mechanical force—induced by ultrasound—can be used to activate drugs in three different systems. This approach has enabled the activation of antibiotics or a cytotoxic anticancer agent from synthetic polymers, polyaptamers and nanoparticle assemblies.
- Shuaidong Huo
- , Pengkun Zhao
- & Andreas Herrmann
-
Article |
 A programmable polymer library that enables the construction of stimuli-responsive nanocarriers containing logic gates
A programmable polymer library that enables the construction of stimuli-responsive nanocarriers containing logic gates
A programmable polymer library that responds to external and internal stimuli has been developed and used to fabricate a series of nanocarriers for drug release. The carriers respond to disease biomarkers, triggering self-immolative motifs and leading to the site-specific release of therapeutics both in vitro and in vivo.
- Penghui Zhang
- , Di Gao
- & Weihong Tan
-
Article |
 Achieving spin-triplet exciton transfer between silicon and molecular acceptors for photon upconversion
Achieving spin-triplet exciton transfer between silicon and molecular acceptors for photon upconversion
Quantum dots functionalized with energy-accepting dyes hold promise for converting low-energy photons into higher-energy visible light for bioimaging, catalysis and solar energy harvesting. Now, it has been shown that non-toxic silicon quantum dots can be used in these systems; the transfer of spin-triplet excitons to molecules at their surface has been observed.
- Pan Xia
- , Emily K. Raulerson
- & Sean T. Roberts
-
News & Views |
 Scissoring genes with light
Scissoring genes with light
Enzymes can perform various biological functions because of their delicately and precisely organized structures. Now, simple inorganic nanoparticles with a rationally designed recognition capability can mimic restriction enzymes and selectively cut specific DNA sequences.
- Aleksandar P. Ivanov
- & Joshua B. Edel
-
News & Views |
 Communicating catalysts
Communicating catalysts
The beauty and activity of enzymes inspire chemists to tailor new and better non-biological catalysts. Now, a study reveals that the active sites within heterogeneous catalysts actively cooperate in a fashion phenomenologically similar to, but mechanistically distinct, from enzymes.
- Bert M. Weckhuysen
-
Article |
 Harvesting multiple electron–hole pairs generated through plasmonic excitation of Au nanoparticles
Harvesting multiple electron–hole pairs generated through plasmonic excitation of Au nanoparticles
Multi-electron redox reactions are kinetically sluggish; however, plasmonic nanoparticles have shown promise as multi-electron reduction catalysts. Now, the principles that govern the harvesting of multiple electron–hole pairs from plasmonically excited gold nanoparticle photocatalysts are elucidated, providing a general foundation for the plasmonic catalysis of challenging multi-electron, multi-proton chemistry, such as N2 fixation and CO2 reduction.
- Youngsoo Kim
- , Jeremy G. Smith
- & Prashant K. Jain
-
Article |
 Single-cell mRNA cytometry via sequence-specific nanoparticle clustering and trapping
Single-cell mRNA cytometry via sequence-specific nanoparticle clustering and trapping
Cell-to-cell variation in gene expression creates a need for techniques that characterize expression at the level of individual cells. Now, a technique for characterizing mRNA expression has been developed. The technique uses the intracellular self-assembly of magnetic nanoparticles to quantitate RNA levels at the single-cell level.
- Mahmoud Labib
- , Reza M. Mohamadi
- & Shana O. Kelley
-
Article |
 Cooperative communication within and between single nanocatalysts
Cooperative communication within and between single nanocatalysts
Nanocatalysts can undergo various dynamic phenomena that affect their activity, such as restructuring and spillover. Now, using spatially and temporally resolved imaging of individual catalytic reactions, cooperative communication between different sites within single palladium- and gold-based nanocatalysts, and between different nanocatalysts, has been observed during three distinct catalytic reactions.
- Ningmu Zou
- , Xiaochun Zhou
- & Peng Chen
-
Article |
 Direct observation of sequential oxidations of a titania-bound molecular proxy catalyst generated through illumination of molecular sensitizers
Direct observation of sequential oxidations of a titania-bound molecular proxy catalyst generated through illumination of molecular sensitizers
Photosynthesis uses sunlight to oxidize or reduce reaction centres multiple times and prepare them for multiple-electron-transfer reactions. Now, it has been shown that a molecular proxy for a multiple-electron-transfer electrocatalyst can be oxidized twice by dye molecules when both are anchored to a mesoporous TiO2 thin film and excited with low-intensity visible light.
- Hsiang-Yun Chen
- & Shane Ardo
-
News & Views |
 Precision in 3D
Precision in 3D
Biomimetic molecules that can be easily tailored offer numerous opportunities. Now, boron-based clusters have been shown to be excellent biomimetics. The ease with which the cluster surfaces can be modified stands to change how chemists might go about preparing materials for imaging, drug delivery and other applications.
- Marek B. Majewski
- , Ashlee J. Howarth
- & Omar K. Farha
-
Article |
 Scalable and uniform 1D nanoparticles by synchronous polymerization, crystallization and self-assembly
Scalable and uniform 1D nanoparticles by synchronous polymerization, crystallization and self-assembly
A scalable, one-pot, solution-based protocol for the controlled synthesis of uniform non-spherical block copolymer micelles is a desirable but challenging target. Now, a polymerization-induced crystallization-driven self-assembly process has been developed that offers facile access to 1D and platelet micelle morphologies and to near monodisperse cylinders of controlled length.
- Charlotte E. Boott
- , Jessica Gwyther
- & Ian Manners
-
Article |
 Atomically precise organomimetic cluster nanomolecules assembled via perfluoroaryl-thiol SNAr chemistry
Atomically precise organomimetic cluster nanomolecules assembled via perfluoroaryl-thiol SNAr chemistry
The operational simplicity of modifying the surfaces of thiol-capped gold nanoparticles has been a hallmark of their success in materials chemistry, despite having limited control over the surface composition. Now, SNAr chemistry on activated perfluoroaromatics has been shown to mimic this simplicity and allow for the synthesis of atomically precise nanomolecules.
- Elaine A. Qian
- , Alex I. Wixtrom
- & Alexander M. Spokoyny
-
Article |
 Self-assembly of nanoparticles into biomimetic capsid-like nanoshells
Self-assembly of nanoparticles into biomimetic capsid-like nanoshells
Biomolecular nanoscale compartments are ubiquitous in living systems. Although their formation is fairly straightforward, the same cannot be said of their inorganic counterparts. In this study, uniform nanoshells are observed self-assembling from stabilizer-free inorganic nanoparticles in water, under ambient conditions, and without the need for spherical tiling. This enables further study of inorganic prebiotic systems and compartmentalized biomimetic catalysis.
- Ming Yang
- , Henry Chan
- & Nicholas A. Kotov
-
-
Article |
 Multistep nucleation of nanocrystals in aqueous solution
Multistep nucleation of nanocrystals in aqueous solution
Crystals grow from nuclei. In systems where nuclei are nanometre-sized and form quickly, it is difficult to determine the mechanism of their formation. Now, through in situ TEM, the demixing of a supersaturated aqueous gold solution into metastable gold-poor and gold-rich liquid phases is observed, the latter yielding stable clusters that become nuclei for nanocrystal growth.
- N. Duane Loh
- , Soumyo Sen
- & Utkur Mirsaidov
-
Article |
 Observation of trapped-hole diffusion on the surfaces of CdS nanorods
Observation of trapped-hole diffusion on the surfaces of CdS nanorods
Photoexcited holes in CdS nanocrystals rapidly trap to the surface and although they are integral to nanocrystal photophysics and photochemistry, their dynamics have remained elusive. Time-resolved spectroscopy and theoretical modelling have now revealed that trapped holes in CdS nanorods are mobile and undergo a random walk on the nanocrystal surface.
- James K. Utterback
- , Amanda N. Grennell
- & Gordana Dukovic
-
Article |
 Self-organized architectures from assorted DNA-framed nanoparticles
Self-organized architectures from assorted DNA-framed nanoparticles
A broadly applicable strategy that can control the self-assembly of nanoparticles into a predefined structure has been reported. Integrating nanoparticles with DNA constructs creates individual modules that can be assembled into complex planar architectures. The approach combines nanoparticles with the selectivity and directionality of bonds provided by DNA.
- Wenyan Liu
- , Jonathan Halverson
- & Oleg Gang
-
Article |
 Transfer of molecular recognition information from DNA nanostructures to gold nanoparticles
Transfer of molecular recognition information from DNA nanostructures to gold nanoparticles
DNA nanostructures are typically used as molecular scaffolds. Now, it has been shown that they can also act as reusable templates for ‘molecular printing’ of DNA strands onto gold nanoparticles. The products inherit the recognition elements of the parent template: number, orientation and sequence asymmetry of DNA strands. This converts isotropic nanoparticles into complex building blocks.
- Thomas G. W. Edwardson
- , Kai Lin Lau
- & Hanadi F. Sleiman
-
Article |
 Efficient green methanol synthesis from glycerol
Efficient green methanol synthesis from glycerol
Impure glycerol is obtained as a significant by-product of biodiesel production. Now it is shown that this crude glycerol can be reacted with water over very simple basic or redox oxide catalysts to produce methanol in high yields, together with other useful chemicals, in a one-step low pressure process.
- Muhammad H. Haider
- , Nicholas F. Dummer
- & Graham J. Hutchings
-
Article |
 Light-controlled self-assembly of non-photoresponsive nanoparticles
Light-controlled self-assembly of non-photoresponsive nanoparticles
Controlling the self-assembly of nanoparticles using light has been demonstrated in many systems where the particle surfaces are functionalized with photoswitchable ligands. Now, it has been shown that the light-controlled self-assembly of non-photoresponsive nanoparticles can be achieved in a quantitative and reversible fashion by placing them in a photoresponsive medium.
- Pintu K. Kundu
- , Dipak Samanta
- & Rafal Klajn
-
-
-
News & Views |
 Rise of the nanobots
Rise of the nanobots
Bioorthogonal catalysis provides new ways of mediating artificial transformations in living environs. Now, researchers have developed a nanodevice whose catalytic activity can be regulated by host–guest chemistry.
- Asier Unciti-Broceta
-
Article |
 Supramolecular regulation of bioorthogonal catalysis in cells using nanoparticle-embedded transition metal catalysts
Supramolecular regulation of bioorthogonal catalysis in cells using nanoparticle-embedded transition metal catalysts
Regulation of bioorthogonal catalysis in living systems is challenging because of the complex intracellular environment. Now, the activity of protein-sized bioorthogonal nanozymes has been regulated by binding a supramolecular cucurbit[7]uril ‘gate-keeper’ onto the monolayer surface. This arrangement enables the controlled activation of profluorophores and prodrugs inside living cells for imaging and therapeutic applications.
- Gulen Yesilbag Tonga
- , Youngdo Jeong
- & Vincent M. Rotello
-
-
-
Article |
 Genetically encoded reporters for hyperpolarized xenon magnetic resonance imaging
Genetically encoded reporters for hyperpolarized xenon magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging of gene expression has been limited by the low molecular sensitivity of conventional 1H-MRI. To overcome this limitation, the first genetically encoded reporters for hyperpolarized xenon MRI have been developed. These expressible reporters, based on gas-filled protein nanostructures from buoyant microorganisms, are detectable at picomolar concentrations.
- Mikhail G. Shapiro
- , R. Matthew Ramirez
- & Vikram S. Bajaj
-
Article |
 Time-resolved observations of water oxidation intermediates on a cobalt oxide nanoparticle catalyst
Time-resolved observations of water oxidation intermediates on a cobalt oxide nanoparticle catalyst
The conversion of water to oxygen is an essential process for both natural and artificial photosynthesis. Important intermediates in the stepwise mechanism of water oxidation on the surface of cobalt oxide have now been spectroscopically identified, providing key insights for the development of higher-efficiency catalysts made from Earth-abundant materials.
- Miao Zhang
- , Moreno de Respinis
- & Heinz Frei
-
Article |
 Building an appropriate active-site motif into a hydrogen-evolution catalyst with thiomolybdate [Mo3S13]2− clusters
Building an appropriate active-site motif into a hydrogen-evolution catalyst with thiomolybdate [Mo3S13]2− clusters
Non-noble-metal-based MoS2 nanostructures are hydrogen evolution catalysts whose active sites are known to be located at the edges. Supported thiomolybdate [Mo3S13]2− nanoclusters have now been prepared that exhibit a structural motif similar to that of MoS2 edges. The nanoclusters, synthesized by a scalable route, demonstrate a high turnover frequency.
- Jakob Kibsgaard
- , Thomas F. Jaramillo
- & Flemming Besenbacher
-
News & Views |
 Phase transition singled out
Phase transition singled out
Four-dimensional electron microscopy has been applied to the detailed characterization of metal–organic-framework nanoparticles undergoing an electronic transition. The transition characteristics of a single particle were found to differ from those of an ensemble, and also to vary from one nanoparticle to the next.
- Nigel D. Browning
-
Article |
 Single-nanoparticle phase transitions visualized by four-dimensional electron microscopy
Single-nanoparticle phase transitions visualized by four-dimensional electron microscopy
Introducing a small aperture in a 4D electron microscope has enabled researchers to visualize the phase transition of a single metal–organic framework particle with excellent spatio-temporal resolution. The spin-crossover dynamics of one nanoparticle are found to be distinct from those observed for an ensemble of heterogeneous nanoparticles.
- Renske M. van der Veen
- , Oh-Hoon Kwon
- & Ahmed H. Zewail
-
Article |
 Uranium and manganese assembled in a wheel-shaped nanoscale single-molecule magnet with high spin-reversal barrier
Uranium and manganese assembled in a wheel-shaped nanoscale single-molecule magnet with high spin-reversal barrier
A {U12Mn6} wheel-shaped cluster that has been assembled through cation–cation interactions exhibits single-molecule-magnet behaviour. Single-molecule magnets are promising for magnetic storage devices at the nanoscale, and the observation of magnetic bistability with an open hysteresis loop and high relaxation barrier in this 5f–3d complex suggests that uranium-based compounds could be useful components.
- Victor Mougel
- , Lucile Chatelain
- & Marinella Mazzanti
-
Article |
 Control of selectivity in heterogeneous catalysis by tuning nanoparticle properties and reactor residence time
Control of selectivity in heterogeneous catalysis by tuning nanoparticle properties and reactor residence time
Heterogeneous catalysts are generally more readily recycled than homogeneous catalysts, but the latter are more easily modified to tune reactivity and selectivity. Here, the dendrimer coating of gold nanoparticle catalysts is shown to be a surrogate for the ligands of homogeneous catalysts. Tuning of product distribution and reaction selectivity is possible when these catalysts are employed in a fixed-bed flow reactor.
- Elad Gross
- , Jack Hung-Chang Liu
- & Gabor A. Somorjai
-
-
News & Views |
 Autonomous propulsion
Autonomous propulsion
Polymer vesicles have been constructed that entrap platinum nanoparticles in their outer surface. These serve to break down a fuel of hydrogen peroxide, generating water and oxygen and in turn inducing a propulsive effect.
- Jonathan Howse
-
Article |
 Topological insulator nanostructures for near-infrared transparent flexible electrodes
Topological insulator nanostructures for near-infrared transparent flexible electrodes
Transparent conductive electrodes are widely used in modern optoelectronic devices, but they are rarely transparent in the near-infrared, limiting their use. Nanostructured bismuth selenide, a topological insulator, is now shown to be a flexible near-infrared transparent electrode.
- Hailin Peng
- , Wenhui Dang
- & Zhongfan Liu
-
Article |
 Autonomous movement of platinum-loaded stomatocytes
Autonomous movement of platinum-loaded stomatocytes
A supramolecular system has been assembled that moves autonomously in the presence of a molecular fuel. Platinum nanoparticles entrapped in a polymer stomatocyte — a bowl-shaped polymer vesicle — catalyse the decomposition of the molecular fuel, hydrogen peroxide. The resulting generation of water and oxygen induces a directional movement of the stomatocyte.
- Daniela A. Wilson
- , Roeland J. M. Nolte
- & Jan C. M. van Hest
-
Article |
 Imparting functionality to a metal–organic framework material by controlled nanoparticle encapsulation
Imparting functionality to a metal–organic framework material by controlled nanoparticle encapsulation
Surfactant-capped nanoparticles of various sizes, shapes and compositions have been completely enshrouded within a metal–organic framework in a controlled, well-dispersed manner. The resulting hybrid materials exhibit active properties — catalytic, magnetic and optical — arising from the nanoparticles as well as sieving and orientation effects originating from the porous framework.
- Guang Lu
- , Shaozhou Li
- & Fengwei Huo
-
Article |
 A total-synthesis framework for the construction of high-order colloidal hybrid nanoparticles
A total-synthesis framework for the construction of high-order colloidal hybrid nanoparticles
Colloidal hybrid nanoparticles represent an emerging class of multifunctional artificial molecules. However, unlike actual molecules, their complexity is limited by the lack of a mechanism-driven design framework. Here, nanoparticle analogues of chemoselectivity, regiospecificity, molecular substituent effects, and coupling reactions are used to predictably synthesize hybrid nanoparticle trimers, tetramers, and oligomers.
- Matthew R. Buck
- , James F. Bondi
- & Raymond E. Schaak
-
Article |
 Facile removal of stabilizer-ligands from supported gold nanoparticles
Facile removal of stabilizer-ligands from supported gold nanoparticles
Small nanoparticles with controlled morphologies can be prepared for catalysis applications by colloidal methods using stabilizing ligands. A solvent-extraction method has now been described that removes the ligands without affecting the morphology of the nanoparticles, or their catalytic activity over a range of reactions.
- Jose A. Lopez-Sanchez
- , Nikolaos Dimitratos
- & Graham J. Hutchings
-
Article |
 The effect of gold loading and particle size on photocatalytic hydrogen production from ethanol over Au/TiO2 nanoparticles
The effect of gold loading and particle size on photocatalytic hydrogen production from ethanol over Au/TiO2 nanoparticles
The photocatalytic production of hydrogen from renewables such as ethanol and water could be a key means of future fuel production. There are few, if any, catalysts available for such a reaction, and our understanding of photocatalytic reactions generally remains poor. It is now demonstrated that gold–titania nanoparticles are effective catalysts for producing hydrogen from ethanol, and the rate is independent of gold particle size.
- M. Murdoch
- , G. I. N. Waterhouse
- & H. Idriss

 Entropy compartmentalization stabilizes open host–guest colloidal clathrates
Entropy compartmentalization stabilizes open host–guest colloidal clathrates Two sides to every particle
Two sides to every particle Tales from the cryptates
Tales from the cryptates A right tangle
A right tangle An interfering delivery
An interfering delivery Gold rush
Gold rush Microfluidics for microcapsules
Microfluidics for microcapsules