Featured
-
-
Article |
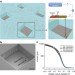 Probing single- to multi-cell level charge transport in Geobacter sulfurreducens DL-1
Probing single- to multi-cell level charge transport in Geobacter sulfurreducens DL-1
Microbial fuels cells present a way of generating electricity using the natural metabolism of microorganisms. Here the authors carry out single-cell current measurements ofGeobacter sulfurreducensDL-1 to determine the upper limits of microbial fuel cell performance.
- Xiaocheng Jiang
- , Jinsong Hu
- & Justin C. Biffinger
-
Article |
 Surface tension and contact with soft elastic solids
Surface tension and contact with soft elastic solids
Solid contacts on a microscopic level are widely described by a classical contact mechanics theory. Here Styleet al.show that this theory breaks down when a small particle adheres to a soft surface where a fluid-like behaviour is observed because of the predominant role played by surface tension.
- Robert W. Style
- , Callen Hyland
- & Eric R. Dufresne
-
Article |
 Functionalization of the living diatom Thalassiosira weissflogii with thiol moieties
Functionalization of the living diatom Thalassiosira weissflogii with thiol moieties
Biomineralization processes have inspired the design of synthetic silica structures in vitro. Here, the authors use a living diatom to fabricate organo-silica constructs and are able to incorporate thiol moieties into the diatom frustule without the loss of nano-scale architectural features.
- Yvonne Lang
- , Francisco del Monte
- & Abhay Pandit
-
Article |
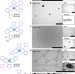 Nanorings and rods interconnected by self-assembly mimicking an artificial network of neurons
Nanorings and rods interconnected by self-assembly mimicking an artificial network of neurons
Molecularly interconnected networks are the building blocks for molecular circuits in nanoelectronic devices, but a mass production with tunable properties is difficult. Escárcega–Bobadilla et al.develop an approach to form interconnected self-assembled nano-rings, which resemble a network of neurons.
- Martha V. Escárcega-Bobadilla
- , Gustavo A. Zelada-Guillén
- & Arjan W. Kleij
-
Article
| Open Access Confinement of pyridinium hemicyanine dye within an anionic metal-organic framework for two-photon-pumped lasing
Confinement of pyridinium hemicyanine dye within an anionic metal-organic framework for two-photon-pumped lasing
Two-photon-pumped dye lasers are useful for applications such as biological imaging; however, loss processes reduce their efficiency. Here, metal-organic frameworks, into which the laser dye is incorporated, demonstrate enhanced laser operation because losses such as dye aggregation-caused quenching are reduced.
- Jiancan Yu
- , Yuanjing Cui
- & Guodong Qian
-
Article |
 Highly confined ions store charge more efficiently in supercapacitors
Highly confined ions store charge more efficiently in supercapacitors
Nanopores of porous electrodes have key roles in enhancing supercapacitor performance, but little is known at the atomic level. Merlet et al. perform molecular dynamics simulations and report the effects of confinement of electrolyte ions inside the pores on charge storage efficiency.
- C. Merlet
- , C. Péan
- & M. Salanne
-
Article |
 Synthesis and physical properties of a ball-like three-dimensional π-conjugated molecule
Synthesis and physical properties of a ball-like three-dimensional π-conjugated molecule
Curved π-conjugated compounds, such as the fullerenes, have a variety of practical uses in addition to being structurally striking. Here, the authors demonstrate metal-mediated assembly and subsequent reductive elimination as an elegant synthetic route to a fully conjugated ball-like molecule.
- Eiichi Kayahara
- , Takahiro Iwamoto
- & Shigeru Yamago
-
Article
| Open Access Green chemistry and nanofabrication in a levitated Leidenfrost drop
Green chemistry and nanofabrication in a levitated Leidenfrost drop
Droplets of water on very hot surfaces form levitating droplets, according to the Leidenfrost effect. Here, the authors show that green chemistry can be performed in these charged droplets, demonstrated by the synthesis of a range of nanoparticles, nanoscale coatings and porous metallic materials.
- Ramzy Abdelaziz
- , Duygu Disci-Zayed
- & Mady Elbahri
-
Article
| Open Access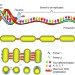 Attomolar DNA detection with chiral nanorod assemblies
Attomolar DNA detection with chiral nanorod assemblies
Nanoscale plasmonic assemblies are known to display exceptionally strong chiral optical activity. Here, the authors assemble gold nanorods into DNA-bridged chiral systems, and demonstrate their high efficiency for DNA detection at very low concentrations.
- Wei Ma
- , Hua Kuang
- & Nicholas A. Kotov
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular switches from benzene derivatives adsorbed on metal surfaces
Molecular switches from benzene derivatives adsorbed on metal surfaces
Short-lived precursors typically occur before molecules chemisorb on surfaces. Liu et al. predict that for benzene derivatives on metal surfaces, the precursors can be long-lived and the transition to chemisorption states can be reversible, which may be useful in molecular switch applications.
- Wei Liu
- , Sergey N. Filimonov
- & Alexandre Tkatchenko
-
Article
| Open Access Localized cell stimulation by nitric oxide using a photoactive porous coordination polymer platform
Localized cell stimulation by nitric oxide using a photoactive porous coordination polymer platform
Localized cell stimulation is useful in the analysis of biological signalling networks. Here the authors develop a photosensitive porous framework to achieve spatiotemporally controlled cellular delivery of the gaseous biomolecule nitric oxide, using it to regulate intracellular calcium levels.
- Stéphane Diring
- , Dan Ohtan Wang
- & Shuhei Furukawa
-
Article |
 Chitosan confinement enhances hydrogen photogeneration from a mimic of the diiron subsite of [FeFe]-hydrogenase
Chitosan confinement enhances hydrogen photogeneration from a mimic of the diiron subsite of [FeFe]-hydrogenase
Naturally occurring hydrogenase enzymes are capable of efficient hydrogen production but low stability and high cost limits their industrial use. Here, the authors show that chitosan encapsulation improves the catalytic efficiency of a mimic of the diiron subsite of the H-cluster of [FeFe]-hydrogenase.
- Jing-Xin Jian
- , Qiang Liu
- & Li-Zhu Wu
-
Article |
 Capsule-controlled selectivity of a rhodium hydroformylation catalyst
Capsule-controlled selectivity of a rhodium hydroformylation catalyst
The selectivity and activity of enzymes is largely attributed to the well-defined cavities around their active sites, defined by the secondary coordination sphere. Here, the authors show that similar strategies may be applied to tune the selectivity of synthetic rhodium hydroformylation catalysts.
- Vladica Bocokić
- , Ayfer Kalkan
- & Joost N. H. Reek
-
Article |
 A solid–solid phase transition in carbon dioxide at high pressures and intermediate temperatures
A solid–solid phase transition in carbon dioxide at high pressures and intermediate temperatures
It is desirable for scientists to be able to predict the structures, spectra and phase diagrams of molecular crystals using ab initio computation. Li et al. demonstrate such an approach, which is able to determine the phase behaviour of solid carbon dioxide at a range of pressures and temperatures.
- Jinjin Li
- , Olaseni Sode
- & So Hirata
-
Article |
 Harvesting singlet fission for solar energy conversion via triplet energy transfer
Harvesting singlet fission for solar energy conversion via triplet energy transfer
The efficiency of organic solar cells may be increased by the incorporation of materials capable of singlet fission. Here, Tritsch and colleagues identify strategies to enhance the extraction of multiple excitons from the desirable singlet fission process.
- John R. Tritsch
- , Wai-Lun Chan
- & X-Y. Zhu
-
Article |
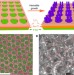 Plasmon-induced photonic and energy-transfer enhancement of solar water splitting by a hematite nanorod array
Plasmon-induced photonic and energy-transfer enhancement of solar water splitting by a hematite nanorod array
Plasmonic nanostructures may enhance solar energy collection. Here, the authors exploit both plasmon-induced resonant energy transfer and surface plasmon polaritons in a hematite–gold nano-array, leading to a tenfold increase in the photocurrent at a bias of 0.23 V in a photoelectrochemical cell.
- Jiangtian Li
- , Scott K. Cushing
- & Nianqiang Wu
-
Article |
 Hydrodefluorination of carbon–fluorine bonds by the synergistic action of a ruthenium–palladium catalyst
Hydrodefluorination of carbon–fluorine bonds by the synergistic action of a ruthenium–palladium catalyst
Selective hydrodefluoridization is important as an industrial reaction and in the disposal of chlorofluorocarbons. Here, the authors prepare a heterodimetallic ruthenium–palladium complex, which is active in the hydrodefluorination of aromatic and aliphatic molecules under mild reaction conditions.
- Sara Sabater
- , Jose A. Mata
- & Eduardo Peris
-
Article |
 Macromolecular semi-rigid nanocavities for cooperative recognition of specific large molecular shapes
Macromolecular semi-rigid nanocavities for cooperative recognition of specific large molecular shapes
Large molecular shape-consistent host molecules are required for molecular recognition applications and the development of artificial enzymes. Here, the authors synthesize semi-rigid dendritic molecules with cavities capable of tunable discrimination between a range of large guest molecules.
- Takane Imaoka
- , Yuki Kawana
- & Kimihisa Yamamoto
-
Article |
 An electrostatic model for the determination of magnetic anisotropy in dysprosium complexes
An electrostatic model for the determination of magnetic anisotropy in dysprosium complexes
Understanding the anisotropic electronic structure of lanthanide complexes is useful for a range of advanced applications. Here, the authors present a simple electrostatic method, capable of predicting the magnetic anisotropy of low-symmetry mononuclear and polynuclear dysprosium(III) complexes.
- Nicholas F. Chilton
- , David Collison
- & Alessandro Soncini
-
Article |
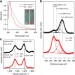 Revealing the ultrafast process behind the photoreduction of graphene oxide
Revealing the ultrafast process behind the photoreduction of graphene oxide
Photoreduction is a promising method for the synthesis of reduced graphene oxide, but the dynamics of the process are unclear. Here, the authors explore the process via a pump–probe technique, revealing its ultrafast nature and the involvement of solvated electrons produced by irradiation of the solvent.
- Régis Y. N. Gengler
- , Daniel S. Badali
- & R. J. Dwayne Miller
-
Article |
 Cobalt phosphate-modified barium-doped tantalum nitride nanorod photoanode with 1.5% solar energy conversion efficiency
Cobalt phosphate-modified barium-doped tantalum nitride nanorod photoanode with 1.5% solar energy conversion efficiency
The search for efficient photoanodes for water oxidation is ongoing. Here, the authors investigate the effect of barium doping on a tantalum nitride nanostructured photoanode, and report a solar energy conversion efficiency of 1.5% in the presence of a cobalt phosphate co-catalyst.
- Yanbo Li
- , Li Zhang
- & Kazunari Domen
-
Article |
 Model studies of force-dependent kinetics of multi-barrier reactions
Model studies of force-dependent kinetics of multi-barrier reactions
In chemical reactions, inner barriers, which precede the rate-determining transition state, are kinetically invisible but mechanistically significant. On an example of reduction of macrocyclic disulphides, the authors quantify these inner barriers by studying the reaction rate as a function of applied force.
- Yancong Tian
- , Timothy J. Kucharski
- & Roman Boulatov
-
Article |
 Mn(II) deposition on anodes and its effects on capacity fade in spinel lithium manganate–carbon systems
Mn(II) deposition on anodes and its effects on capacity fade in spinel lithium manganate–carbon systems
Lithium manganate is an important cathode material for lithium-ion batteries; however, its capacity-fading mechanism is unclear. Zhan et al. identify the oxidation state of manganese deposited on the anode, which leads to an irreversible rising in anode resistance and consequently a shortened battery life.
- Chun Zhan
- , Jun Lu
- & Khalil Amine
-
Article |
 Rapid and quantitative one-pot synthesis of sequence-controlled polymers by radical polymerization
Rapid and quantitative one-pot synthesis of sequence-controlled polymers by radical polymerization
Sequence control of multiblock copolymers is a difficult task for polymer chemistry. Here the authors report a simple radical method that allows the synthesis of well-defined block copolymers with a wide range of functional groups, including a 20-unit multiblock copolymer.
- Guillaume Gody
- , Thomas Maschmeyer
- & Sébastien Perrier
-
Article |
 Direct visualization of a guest-triggered crystal deformation based on a flexible ultramicroporous framework
Direct visualization of a guest-triggered crystal deformation based on a flexible ultramicroporous framework
Host–guest materials open up the possibility of tuning physical properties based on the addition of appropriate guests. Here, a flexible, porous coordination polymer is reported, in which the addition of guest molecules significantly alters the thermal expansion properties as well as deforming the crystal lattice.
- Hao-Long Zhou
- , Rui-Biao Lin
- & Xiao-Ming Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Super liquid-repellent gas membranes for carbon dioxide capture and heart–lung machines
Super liquid-repellent gas membranes for carbon dioxide capture and heart–lung machines
Membranes allowing transfer of a gas between a liquid and gas layer have applications in areas such as blood oxygenation and carbon dioxide capture. Here, a super liquid repellent membrane is fabricated, allowing high gas transfer and also avoiding wetting and clogging of the membrane pores.
- Maxime Paven
- , Periklis Papadopoulos
- & Hans-Jürgen Butt
-
Article |
 Stable platinum nanoparticles on specific MgAl2O4 spinel facets at high temperatures in oxidizing atmospheres
Stable platinum nanoparticles on specific MgAl2O4 spinel facets at high temperatures in oxidizing atmospheres
Supported platinum nanoparticles are highly active catalysts, but often gradually degrade under standard reaction conditions. Here, a well-defined spinel material is used as a support, resulting in a catalyst capable of maintaining performance even after severe thermal aging in oxidizing atmospheres.
- Wei-Zhen Li
- , Libor Kovarik
- & Charles H. F. Peden
-
Article |
 Ordered macroporous platinum electrode and enhanced mass transfer in fuel cells using inverse opal structure
Ordered macroporous platinum electrode and enhanced mass transfer in fuel cells using inverse opal structure
Inverse opal structures are desirable for fuel cell electrodes, but application of such structures in polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells is yet to be realised. Kimet al.report fabrication of a platinum catalyst layer with an inverse opal structure, and show improved fuel cell performance.
- Ok-Hee Kim
- , Yong-Hun Cho
- & Yung-Eun Sung
-
Article |
 Cadmium iodide-mediated allenylation of terminal alkynes with ketones
Cadmium iodide-mediated allenylation of terminal alkynes with ketones
The allenylation of terminal alkynes is a convenient route to allenes from simple starting materials, though previously limited to formaldehyde and aldehyde substrates. Here a method enabling the use of ketones is reported, giving easy access to trisubstituted allenes.
- Xinjun Tang
- , Can Zhu
- & Shengming Ma
-
Article |
 Double perovskites as a family of highly active catalysts for oxygen evolution in alkaline solution
Double perovskites as a family of highly active catalysts for oxygen evolution in alkaline solution
New catalysts for the oxygen evolution reaction in basic solution are important for energy storage applications. Here, the authors report the high activity and stability of double perovskites in this role, and their performance is attributed to the proximity of the oxygenp-band to the Fermi level.
- Alexis Grimaud
- , Kevin J. May
- & Yang Shao-Horn
-
Article |
 Unidirectional suppression of hydrogen oxidation on oxidized platinum clusters
Unidirectional suppression of hydrogen oxidation on oxidized platinum clusters
Platinum is a widely studied catalyst for the reduction of protons to hydrogen in water splitting, but it also catalyses the competing hydrogen oxidation back-reaction, thus limiting efficiency. Here, the authors show that the back-reaction can be limited by tuning the platinum oxidation state.
- Yu Hang Li
- , Jun Xing
- & Hua Gui Yang
-
Article |
 Evidence of two distinct local structures of water from ambient to supercooled conditions
Evidence of two distinct local structures of water from ambient to supercooled conditions
Liquid water shows anomalous behaviour, which is expected to be related with critical phenomena below its melting temperature. Taschinet al.experimentally identify two intermolecular vibrational modes that provide evidence for the coexistence of high-density and low-density water forms.
- A. Taschin
- , P. Bartolini
- & R. Torre
-
Article |
 Directing reaction pathways by catalyst active-site selection using self-assembled monolayers
Directing reaction pathways by catalyst active-site selection using self-assembled monolayers
Control of active sites of heterogeneous catalysts can lead to enhanced product selectivity. Here, the authors use self-assembled alkanethiolate monolayers with varying surface densities to tune the selectivity of hydrogenation and hydrodeoxygenation of furfural on supported palladium catalysts.
- Simon H. Pang
- , Carolyn A. Schoenbaum
- & J. Will Medlin
-
Article |
 Two-dimensional vanadyl phosphate ultrathin nanosheets for high energy density and flexible pseudocapacitors
Two-dimensional vanadyl phosphate ultrathin nanosheets for high energy density and flexible pseudocapacitors
Graphene-like materials with pseudocapacitive characteristics are desirable for flexible solid-state pseudocapacitors. Here Wu et al. report such a graphene analogue, vanadyl phosphate ultrathin nanosheets, which exhibits excellent pseudocapacitive properties, leading to a high energy density.
- Changzheng Wu
- , Xiuli Lu
- & Yi Xie
-
Article |
 Carbon precipitation from heavy hydrocarbon fluid in deep planetary interiors
Carbon precipitation from heavy hydrocarbon fluid in deep planetary interiors
Methane is a major constituent of planetary interiors, yet phase relations in the C–H system are poorly understood. This work documents the chemical reactivity of the C–H system over a wide range of temperatures and pressures, and sheds light on the chemical composition of Earth and icy giants.
- Sergey S. Lobanov
- , Pei-Nan Chen
- & Alexander F. Goncharov
-
Article |
 Diameter-dependent ion transport through the interior of isolated single-walled carbon nanotubes
Diameter-dependent ion transport through the interior of isolated single-walled carbon nanotubes
Calculations suggest that ion transport through nanochannels is significantly modified as the diameter approaches molecular dimensions. Choi et al.introduce a single-nanotube platform to demonstrate this effect and find a maximum ion transport rate at a diameter of approximately 1.6 nm.
- Wonjoon Choi
- , Zachary W. Ulissi
- & Michael S. Strano
-
Article |
 Macroscopic scattering of cracks initiated at single impurity atoms
Macroscopic scattering of cracks initiated at single impurity atoms
The mechanical properties of brittle materials are largely determined by how cracks propagate through them. Contrary to expectations, Kermodeet al.show that a crack propagating below a critical speed through a silicon crystal can be scattered by a single isolated boron impurity.
- J.R. Kermode
- , L. Ben-Bashat
- & A. De Vita
-
Article
| Open Access A protective layer approach to solvatochromic sensors
A protective layer approach to solvatochromic sensors
Colorimetric differentiation of solvents is difficult as many solvatochromic molecules exhibit broad overlaps in their absorption and emission bands. Here, the authors present a ‘turn-on’ type sensor in which the colorimetric sensor responds only when its protective layer is disrupted by a specific solvent.
- Jung Lee
- , Hyun Taek Chang
- & Jong-Man Kim
-
Article
| Open Access A platform for designing hyperpolarized magnetic resonance chemical probes
A platform for designing hyperpolarized magnetic resonance chemical probes
Hyperpolarization of chemical nuclei is known to greatly increase sensitivity to characterization by magnetic resonance imaging. Here a new platform that allows for the design of a number of hyperpolarized probes for chemical sensing applications is demonstrated.
- Hiroshi Nonaka
- , Ryunosuke Hata
- & Shinsuke Sando
-
Article |
 DNA-directed self-assembly of shape-controlled hydrogels
DNA-directed self-assembly of shape-controlled hydrogels
The development of a series of orthogonal binding interactions to direct the controlled self-assembly of mesoscale objects is desirable. Here, the authors use DNA as a sequence-specific glue to assemble hydrogel cuboids into a diverse series of structures in the micro- to millimeter length scale.
- Hao Qi
- , Majid Ghodousi
- & Ali Khademhosseini
-
Article |
 All-thiol-stabilized Ag44 and Au12Ag32 nanoparticles with single-crystal structures
All-thiol-stabilized Ag44 and Au12Ag32 nanoparticles with single-crystal structures
Noble metal nanoparticles are used for applications in optics, catalysis, sensing and others. Here the authors study the crystal structures of silver and gold-silver intermetallic nanoparticles stabilized by thiol ligand layers, helping to understand the relationship between their structure and properties.
- Huayan Yang
- , Yu Wang
- & Nanfeng Zheng
-
Article |
 Twin-induced one-dimensional homojunctions yield high quantum efficiency for solar hydrogen generation
Twin-induced one-dimensional homojunctions yield high quantum efficiency for solar hydrogen generation
Efficient charge separation is of crucial importance for enhanced performance of photocatalysts. Here the authors demonstrate efficient charge separation by twin induced one-dimensional homojunctions, which have a high efficiency for solar hydrogen evolution without the need for additional dopants.
- Maochang Liu
- , Dengwei Jing
- & Liejin Guo
-
Article |
 A copper-phyllosilicate core-sheath nanoreactor for carbon–oxygen hydrogenolysis reactions
A copper-phyllosilicate core-sheath nanoreactor for carbon–oxygen hydrogenolysis reactions
Nanoscale copper catalysts are useful for the selective hydrogenation of carbon–oxygen bonds, although they may be deactivated under harsh conditions. Here the authors report the enhanced activity and stability of core-sheath copper-phyllosilicate nanoreactors due to electronic and morphological effects.
- Hairong Yue
- , Yujun Zhao
- & Jinlong Gong
-
Article |
 The first total synthesis of the cyclodepsipeptide pipecolidepsin A
The first total synthesis of the cyclodepsipeptide pipecolidepsin A
Pipecolidepsin A—commonly isolated from a marine sponge—is a promising anticancer agent but is challenging to synthesise in the lab. Here the authors describe the first total synthesis of this cyclodepsipeptide using a versatile strategy applicable to other similar compounds.
- Marta Pelay-Gimeno
- , Yésica García-Ramos
- & Fernando Albericio
-
Article
| Open Access Activation and splitting of carbon dioxide on the surface of an inorganic electride material
Activation and splitting of carbon dioxide on the surface of an inorganic electride material
Effective activation and spitting of carbon dioxide are important steps in its conversion to valuable chemicals. Here the authors report an inorganic electride material with a high concentration of near-surface electrons that is capable of adsorbing and decomposing carbon dioxide.
- Yoshitake Toda
- , Hiroyuki Hirayama
- & Hideo Hosono
-
Article |
 Trinuclear zinc complexes for biologically relevant μ3-oxoanion binding and carbon dioxide fixation
Trinuclear zinc complexes for biologically relevant μ3-oxoanion binding and carbon dioxide fixation
Molecular models of the biologically relevant oxoanion-bridged trinuclear zinc cluster found in numerous enzymatic active sites are desirable. Cao et al. report the synthesis of a trinuclear zinc scaffold, pre-organized to capture oxoanions, and its ability to catalytically convert CO2to carbonates in solution.
- Xiao Liu
- , Pingwu Du
- & Rui Cao
-
Article |
 Nitrogen-doped carbon nanomaterials as non-metal electrocatalysts for water oxidation
Nitrogen-doped carbon nanomaterials as non-metal electrocatalysts for water oxidation
Efficient and economical water splitting is desirable for energy conversion, but it is limited by high overpotential and the need for noble metals. Zhao et al. report that nitrogen-doped graphite materials function as a promising electrocatalyst, with efficiency comparable to that of benchmark metal oxides.
- Yong Zhao
- , Ryuhei Nakamura
- & Kazuhito Hashimoto
-
Article |
 A zero-strain layered metal oxide as the negative electrode for long-life sodium-ion batteries
A zero-strain layered metal oxide as the negative electrode for long-life sodium-ion batteries
Anode materials in sodium-ion batteries can undergo significant volume change upon sodium insertion and extraction, leading to deteriorated cycling performance. Wang et al. report a layered metal oxide anode with zero-strain characteristics, which may lead to extended battery cycle life.
- Yuesheng Wang
- , Xiqian Yu
- & Xuejie Huang
-
Article |
 Reductive assembly of cyclobutadienyl and diphosphacyclobutadienyl rings at uranium
Reductive assembly of cyclobutadienyl and diphosphacyclobutadienyl rings at uranium
Despite their prevalence in the d-block, f-block cyclobutadienyl complexes are hitherto unknown. Here, the authors report the syntheses of inverted sandwich cyclobutadienyl dianion uranium(IV) complexes and show computational analysis that suggests the bonding is predominantly electrostatic.
- Dipti Patel
- , Jonathan McMaster
- & Stephen T. Liddle
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Analytical chemistry
- Biochemistry
- Biosynthesis
- Catalysis
- Chemical biology
- Chemical education
- Chemical engineering
- Chemical safety
- Cheminformatics
- Chemistry publishing
- Communicating chemistry
- Coordination chemistry
- Electrochemistry
- Energy
- Environmental chemistry
- Green chemistry
- History of chemistry
- Inorganic chemistry
- Materials chemistry
- Medicinal chemistry
- Nuclear chemistry
- Organic chemistry
- Chemical origin of life
- Photochemistry
- Physical chemistry
- Polymer chemistry
- Process chemistry
- Supramolecular chemistry
- Surface chemistry
- Chemical synthesis
- Theoretical chemistry

 Efficient and tunable white-light emission of metal–organic frameworks by iridium-complex encapsulation
Efficient and tunable white-light emission of metal–organic frameworks by iridium-complex encapsulation