Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Altering the spectroscopy, electronic structure, and bonding of organometallic curium(III) upon coordination of 4,4′−bipyridine
Altering the spectroscopy, electronic structure, and bonding of organometallic curium(III) upon coordination of 4,4′−bipyridine
Despite the distinct electronic properties of the wide variety Cm3+ compounds that have been prepared to date, no singlecrystal structural characterization of a complex containing a Cm−C bond has been reported. Here the authors report the synthesis of a Cm complex bearing trimethylsilylcyclopentadienyl and 4,4’-bipyridine ligands with a low energy emission and identify the 4,4’-bipyridine ligand as the primary quenching agent.
- Brian N. Long
- , María J. Beltrán-Leíva
- & Thomas E. Albrecht-Schönzart
-
Article
| Open Access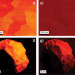 Deconvoluting Cr states in Cr-doped UO2 nuclear fuels via bulk and single crystal spectroscopic studies
Deconvoluting Cr states in Cr-doped UO2 nuclear fuels via bulk and single crystal spectroscopic studies
Additive based UO2 nuclear fuels, which incorporate small amounts of metal oxides such as chromia (Cr2O3), are an important class of accident tolerant fuels. Here authors determine the structural-redox mechanism for Cr lattice incorporation into UO2 nuclear fuels.
- Gabriel L. Murphy
- , Robert Gericke
- & Nina Huittinen
-
Article
| Open Access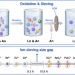 Ion sieving in graphene oxide membrane enables efficient actinides/lanthanides separation
Ion sieving in graphene oxide membrane enables efficient actinides/lanthanides separation
Separation of actinides from lanthanides is very important for the safe management of nuclear waste, however still challenging due to the chemical complexity of the f-elements. Here, authors report an efficient strategy with graphene oxide membranes for ion sieving of high valent actinyl ions and spherical lanthanide ions.
- Zhipeng Wang
- , Liqin Huang
- & Chao Xu
-
Article
| Open Access A charged diatomic triple-bonded U≡N species trapped in C82 fullerene cages
A charged diatomic triple-bonded U≡N species trapped in C82 fullerene cages
Diatomic actinide molecules are ideal models for studying rare multiple-bond motifs. Here, the authors report host-guest structures of metastable charged U≡N diatoms confined in fullerene cages and stabilized by coordinative electron transfer.
- Qingyu Meng
- , Laura Abella
- & Ning Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Highly selective cesium(I) capture under acidic conditions by a layered sulfide
Highly selective cesium(I) capture under acidic conditions by a layered sulfide
The removal of radiocesium from acidic solutions is challenging. Here, the authors report the rapid and highly selective capture of cesium(I) from strongly acidic solutions by a robust layered metal sulfide.
- Jun-Hao Tang
- , Jian-Ce Jin
- & Xiao-Ying Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Cyclopentadienyl coordination induces unexpected ionic Am−N bonding in an americium bipyridyl complex
Cyclopentadienyl coordination induces unexpected ionic Am−N bonding in an americium bipyridyl complex
The coordination environment has a great impact on the electronic structure, bonding and properties of metal complexes. Here the authors report a dinuclear organometallic americium complex that displays unexpectedly ionic Am−N bonding, but enhanced covalency in the Am−C bonds compared to its neodymium analogue.
- Brian N. Long
- , María J. Beltrán-Leiva
- & Thomas E. Albrecht-Schönzart
-
Article
| Open Access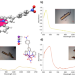 Creation of an unexpected plane of enhanced covalency in cerium(III) and berkelium(III) terpyridyl complexes
Creation of an unexpected plane of enhanced covalency in cerium(III) and berkelium(III) terpyridyl complexes
Studying how the ligand design influences the bonding of f-block complexes is crucial to control their properties. Here, the authors report the preparation of Bk(III) and Ce(III) complexes featuring a terpyridyl ligand; structural, spectroscopic, electrochemical, and theoretical analysis reveal that the ligand induces unusual bonding by creating a plane of enhanced bond covalency.
- Alyssa N. Gaiser
- , Cristian Celis-Barros
- & Thomas E. Albrecht-Schönzart
-
Article
| Open Access In-situ anodic precipitation process for highly efficient separation of aluminum alloys
In-situ anodic precipitation process for highly efficient separation of aluminum alloys
Traditional electrorefining process is limited by deposition potential of the metal itself. Here, the authors explore an in-situ anodic precipitation process based on different solubility of target metal chlorides that can efficiently separate components of aluminum alloys.
- Yu-Ke Zhong
- , Ya-Lan Liu
- & Wei-Qun Shi
-
Article
| Open Access Visible colorimetric dosimetry of UV and ionizing radiations by a dual-module photochromic nanocluster
Visible colorimetric dosimetry of UV and ionizing radiations by a dual-module photochromic nanocluster
Radiation dosimeters that measure ionizing radiations over a broad range and allow for direct readout are desirable. Here, the authors present a dual-mode photochromic thorium-based metal-organic nanocluster that enables direct visible colorimetric dosimetry of UV, β-ray, and γ-ray radiation.
- Huangjie Lu
- , Jian Xie
- & Jian Lin
-
Article
| Open Access 99TcO4− removal from legacy defense nuclear waste by an alkaline-stable 2D cationic metal organic framework
99TcO4− removal from legacy defense nuclear waste by an alkaline-stable 2D cationic metal organic framework
Separation of 99TcO4− from nuclear waste at the Savannah River Site is hampered by the extreme conditions. Here, the authors propose a solution by developing an alkaline-resistant metal organic framework material featuring unique recognition sites for selective incorporation of 99TcO4− anions.
- Nannan Shen
- , Zaixing Yang
- & Shuao Wang
-
Article
| Open Access A general 11C-labeling approach enabled by fluoride-mediated desilylation of organosilanes
A general 11C-labeling approach enabled by fluoride-mediated desilylation of organosilanes
Convenient and fast methods to introduce 11C into organic molecules are of great help for molecular imaging studies. Here, the authors developed an efficient incorporation of [11C]CO2 and [11C]CH3I into molecules via a fluoride-mediated desilylation process.
- Wenchao Qu
- , Bao Hu
- & Julie Urgiles
-
Article
| Open Access A 3,2-Hydroxypyridinone-based Decorporation Agent that Removes Uranium from Bones In Vivo
A 3,2-Hydroxypyridinone-based Decorporation Agent that Removes Uranium from Bones In Vivo
In vivo decorporation of U(VI) from bones is an unsolved challenge because of the formation of stable uranium phosphate complexes. Here, the authors develop a hydroxypyridonone-based ligand with strong uranium complexation and low cytotoxicity. They find this ligand effectively removes uranium from kidney and bones in mice, and is suitable for oral administration.
- Xiaomei Wang
- , Xing Dai
- & Shuao Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Ultra-selective ligand-driven separation of strategic actinides
Ultra-selective ligand-driven separation of strategic actinides
Radionuclides are of great importance for fields such as nuclear medicine and waste recycling, but their efficient purification remains a challenge. Here the authors show that an octadentate hydroxypyridinone chelator enables efficient and robust separation processes for isotopes of Ac, Pu, and Bk.
- Gauthier J.-P. Deblonde
- , Abel Ricano
- & Rebecca J. Abergel
-
Article
| Open Access Emergence of the structure-directing role of f-orbital overlap-driven covalency
Emergence of the structure-directing role of f-orbital overlap-driven covalency
In actinide chemistry, a longstanding bonding model describes metal-ligand binding using 6d-orbitals, with the 5f-orbitals remaining non-bonding. Here the authors explore the inverse-trans-influence — a case where the model breaks down — finding that the f-orbitals play a crucial role in dictating a trans-ligand-directed geometry.
- Erli Lu
- , Saira Sajjad
- & Stephen T. Liddle
-
Article
| Open Access Ion association with tetra-n-alkylammonium cations stabilizes higher-oxidation-state neptunium dioxocations
Ion association with tetra-n-alkylammonium cations stabilizes higher-oxidation-state neptunium dioxocations
The electrochemical behaviour of redox-active metal cations foremost depends on the metal centre’s inner-sphere coordination environment. Here the authors show that electrolyte cations unexpectedly stabilize higher-oxidation-state neptunium dioxocations in water through extended-coordination sphere interactions.
- Shanna L. Estes
- , Baofu Qiao
- & Geng Bang Jin
-
Article
| Open Access A diuranium carbide cluster stabilized inside a C80 fullerene cage
A diuranium carbide cluster stabilized inside a C80 fullerene cage
While metal–carbon double bonds are common in transition metal chemistry and catalysis, unsupported uranium–carbon double bonds remain highly challenging to prepare. Here, the authors stabilize and characterize a U=C=U cluster containing unusually short, unsupported double bonds inside an Ih(7)-C80 fullerene cage.
- Xingxing Zhang
- , Wanlu Li
- & Ning Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Synthesis and preliminary PET imaging of 11C and 18F isotopologues of the ROS1/ALK inhibitor lorlatinib
Synthesis and preliminary PET imaging of 11C and 18F isotopologues of the ROS1/ALK inhibitor lorlatinib
Lorlatinib—a ROS1/ALK inhibitor—is currently undergoing clinical trials for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancers. Here the authors develop synthetic routes to11C- and 18F-labelled lorlatinib, with subsequent PET imaging showing good blood brain barrier permeability in non-human primates.
- Thomas Lee Collier
- , Marc D. Normandin
- & Neil Vasdev
-
Article
| Open Access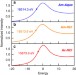 Spectroscopic and computational investigation of actinium coordination chemistry
Spectroscopic and computational investigation of actinium coordination chemistry
Actinium-225 is a promising isotope for α-therapy but progress in developing its chemistry is hindered by its high radioactivity and short supply. Here, the authors characterize actinium coordination in HCl solutions using X-ray absorption spectroscopy and molecular dynamics density functional theory.
- Maryline G. Ferrier
- , Enrique R. Batista
- & Justin J. Wilson

 Accessing five oxidation states of uranium in a retained ligand framework
Accessing five oxidation states of uranium in a retained ligand framework